Executive Summary
This report provides an analysis of Toyota Motor Corporation, which specializes in the design, manufacturer, and assembling of vehicles. The report covers the company’s general overview including the internal and external environments, as well as a summary of Toyota’s operations and strategic plan. The internal and external aspects were explored through VRIO framework and PESTEL analysis.
According to this report, it was evident that Toyota is a global leader in the automotive industry in terms of quality and low-cost products. Additionally, the report indicates that Toyota has the potential to grow than its present state if it maximizes the opportunities availed by the external factors.
Based on the five forces of industry analyzed, it was evident that Toyota has remained to be a very strong company within the automotive industry. The fact that Toyota has been successful in spite of the various challenges that have affected the industry is an indication that the company has strong business strategies effective in withstanding negative forces. Nevertheless, for the company to remain at the top of the industry, continuous use of technology is needed for the purpose of gaining the necessary competitive advantage over other players in the global automotive industry.
Company Overview
Introduction
Toyota Motor Corporation was started in 1937 in Japan and specializes in designing, manufacturing, assembling, and selling commercial vehicles, minivans, passenger cars, as well as parts and accessories that are related to car manufacture, design, and assembling. The company has a wide market all over the world, with some of the major customers of Toyota Motor Corporation coming from Asia, Europe, North America, and Japan.
The recent brands available for this corporation include Hino, Daihatsu, Lexus, and Toyota. The products released to the market by Toyota Motor Corporation are of high quality; a factor that has immensely contributed to the creation of a large market share for this company (Toyota Motor Corporation, 2015). As such, Toyota is considered a leader in terms of auto manufacturing (Takami, 2014). For example, its yearly revenue in March 2013 amounted to 213 billion US dollars, with an employee capacity of more than 333,400.
Business Model
Toyota Motor Corporation has been highly successful in the domestic market and international markets. Research and analysis into the success of this corporation indicated that there are a number of business strategies that Toyota adopts in its business model to ensure that its activities are geared towards creation, delivery, and capture of value in cultural, social and economic contexts (Toyota Motor Corporation, 2015; Barabba, 2007).
A large percentage of Toyota’s success is attributable to the fact that the company relies on the combination of several strategies. Merchant (2014) asserted that the generic strategy of Toyota Motor Corporation outlines the overall approaches that the corporation adopts in the competition for the global market given that there are numerous other car manufacturers and sellers from different parts of the world.
The other strategy, the intensive growth strategy, is used in highlighting the approaches which the corporation should adopt to maintain continuous growth in domestic and international markets. A review of the level of innovation present at Toyota provides clear evidence that the company has vibrant and intensive growth strategies. The management ensures that all the strategies are implemented simultaneously for the purpose of ensuring that the company grows while making a substantial impact in both domestic and international markets.
Generic Strategies
In its generic strategy, Toyota combines a broad differentiation strategy with the cost leadership generic strategy in order to achieve its set goals for global markets (Barabba, 2007). For example, by adopting the cost leadership strategy, the company is able to sell at reduced costs since its operational costs are also minimized (Toyota Motor Corporation, 2015). This way, the company is able to beat its competitors both domestically and internationally.
The aspect of a broad differentiation strategy, on the other hand, is a key factor in Toyota’s success as it involves the development of unique business and products for the purpose of ensuring that the company gains a competitive advantage in all its markets (Merchant, 2014). As such, by combining these two generic strategies, it becomes possible for Toyota to gain a considerable global market share.
Based on the generic strategy of Toyota, one of the strategic goals of the company is the maximization of the cost of production in order to attain cost leadership (Toyota Motor Corporation, 2015). Such a goal is achieved by adopting a production methodology referred to as “just-in-time (JIT)” or the “Toyota Production System” (Takami, 2014). According to Merchant (2014), the efficiency of the Toyota Production System method and the attainment of the strategic goal of reduction in the cost of production are based on the minimization of the number of raw materials that go into waste, reduced cost of inventory, as well as the response time. By adopting innovative methods of production and approaches to business, Toyota is able to avail attractive and unique products to its market segments, thereby fulfilling its generic strategy.
Intensive Growth Strategies
As pointed out earlier, the incentive growth strategies of Toyota are aimed at ensuring that the company grows both in domestic and international capacities (Gargasas & Mugiene, 2012). As such, these strategies are based on the development of quality products, market development, and penetration. Market penetration forms one of the company’s major intensive growth strategies as it encourages the growth of the company by ensuring that existing customers are retained, as well as creating links for new ones in the current markets for Toyota.
According to Gargasas and Mugiene (2012), the company fulfills the market penetration strategy by ensuring that all its products are designed for different market segments. This is evident in the company’s recent products released to the market. By fulfilling the market penetration growth strategy, the company is in a position to achieve its cost leadership goal creating an opportunity to make maximum sales thereby making profits despite the adoption of the strategy of low selling prices.
Secondly, the company works towards product development as an intensive growth strategy. The purpose of the product development approach is to ensure that there are more customers for Toyota products (Gargasas & Mugiene, 2012). Innovation is used as the key method through which quality products are developed for the purpose of attracting new customers to Toyota. For instance, one of Toyota’s products, the Toyota Prius is environmentally-conscious and hence is appropriate for customers that care about the environment (Toyota Motor Corporation, 2015; Jenn, Azevedo, & Michalek, 2016).
Evidently, the product development growth strategy is very important in the growth of Toyota Corporation in that it provides background for broad differentiation through the use of innovative products as evident in the case of Toyota Prius.
On the other hand, the company works towards market development, which serves as a strategy to support the company’s global presence given that it is already established in many parts of the world. As such the market development approach ensures that Toyota continues to grow in areas where it has already set base (Barabba, 2007). The growth strategy of Toyota includes entry into new markets or even making its products available in areas that are completely new. Nevertheless, the company has grown tremendously such that it has a presence in numerous global markets. Through the adoption of the market development approach, Toyota is in a position to grow since the strategy is instrumental in the realization of the cost leadership goal.
From the following analysis, it is evident that Toyota has a very effective business model, which aims at ensuring maximum sales volume at a reduced cost of production. As such, the business strategies adopted by Toyota have been very instrumental in the success of the company. The KAIZEN strategy that is used to imply continual improvement has been very important in the quality of Toyota products (Toyota Motor Corporation, 2015).
This strategy is based on the cross-functional approach and involves gradually improving and managing business activities to ensure efficiency in terms of competitiveness, productivity, and quality parameters. The product development strategy of Toyota targets quality products and this goal is achieved through the use of innovative strategies. As such, the company invests in hard work, creativity, and research (Lavanya, 2012).
The company is considered to be a global leader in research as well as in the development of automobile technologies. It ensures that its activities and products are highly sustainable. For example, vehicles have been considered to be notorious contributors to global warming due to the emission of greenhouse gases. Toyota overcomes the problem of environmental pollution by ensuring that its products have a reduced effect on the environment (Jenn, Azevedo, & Michalek, 2016).
Evidently, Toyota has developed a number of car brands that are environmentally-conscious such as the Toyota Prius and other electric vehicles (Toyota Motor Corporation, 2015). In the design of vehicles that have less harmful emissions, Toyota adopts various strategies. For example, the company develops hybrid systems that are based on the manufacture of clean technology cars through the combination of different energy sources.
Mission
Toyota has a tendency of using different mission statements in different markets. This is attributed to the fact that different regions of the world have different business environments. As such, the company adjusts according to the business environment that it finds itself in. In spite of this, considering the manufacturing and sales business within the automobile industry, the mission statement of Toyota Corporation is based on its strategic actions within the technological arena. As such, the company’s statement is “We deliver outstanding automotive products and services to our customers, and enrich our community, partners, and environment.”
Nevertheless, Toyota has an expanded mission statement that focuses on the provision of a world-class safety to customers’ lives, optimizing infrastructure and energy to local communities, putting high priority in matters associated with safety and the promotion of product development in the hope of complete elimination of traffic casualties; delivering cars which stimulate as well as inspire and meet the needs of the customers; addressing the educational needs of its employees based on the “Genchi-genbutsu” philosophy; contributing towards technological development alongside improved expertise; contributing towards the development of the local communities and the general economy of the country where it operates through investment in research and development.
Vision
The vision statement of Toyota Motor Corporation is based on the company’s needs to ensure the achievement of its long term goals within the automobile industry. The vision statement of Toyota Motor Corporation is highlighted below:
“Toyota will lead the way to the future of mobility, enriching lives around the world with the safest and most responsible ways of moving people. Through our commitment to quality, constant innovation, and respect for the planet, we aim to exceed expectations and be rewarded with a smile. We will meet our challenging goals by engaging the talent and passion of people, who believe there is always a better way.”
Goals
Toyota Motor Corporation has several goals that guide its operations in various parts of the world. For example, the company aims and ensuring the achievement of corporate citizenship by ensuring that it contributes to something that is worthwhile in areas where it operates. As such, Toyota has always been working to ensure that it makes an impact on community involvement, cars, and jobs (Fleming, 2013).
However, the primary goal of Toyota Motor Corporation is the improvement of the efficiency of fuels as well as designs especially for all types of vehicles that are available to the customers in numerous parts of the world (Barabba, 2007). This is based on their new strategy of cutting about 30% of their production cost by adopting shared parts in the production process. Basically, Toyota Corporation aims at ensuring the cars available in the market have a high impact on the demand of customers since they ought to match the quality needed by the customers worldwide.
Values
The success of Toyota Motor Corporation in different parts of the world is largely attributable to its core values. The company thrives in four values which include respect for all people, continuous improvement and innovation, international focus, and customer-first initiative. The company’s value of continuous improvement and innovation ensures that the Toyota stays focused on its operations aimed at the provision of innovative products to its customers.
Such a value is very important in the success of the company since it sets a base for the company’s goal of product differentiation and continual growth. Secondly, the company has an international focus. Domestic markets cannot be enough in ensuring cost leadership, competitive advantage, and a large market share (Toyota Motor Corporation, 2015). As such, the company is always adopting new strategies to help it succeed in the international markets. Thirdly, ensuring respect for others is a strategy that is used by Toyota to gain respect and loyalty from competitors and consumers. The last value of Toyota is ensuring that all priorities are given to the customer.
This value is very important in the design and creation of products targeted at customers’ needs and satisfaction (Lavanya, 2012). For example, the creation of the electric cars and the hybrid ones was aimed at ensuring that the demand for cars that have low fuel and low impact on the environment among its customers is met (Fleming, 2013). The combination of the four core values plays a significant role in the achievement of the goals and objectives of Toyota Corporation in different parts of the world.
Summary of Operations
Operations of Toyota based on external environments
Over recent years, the automotive industry of the world has experienced numerous external challenges that have affected the sales volume of many automotive manufacturers in the world (Stewart & Raman, 2007). Nevertheless, Toyota Corporation has always been ahead of its competitors in terms of strategies and quality products. For example, in 2009 the automotive industry suffered from low sales volume due to increased prices of fuels.
At this period, most of the automakers shifted their focus to the production of cars that were fuel-efficient and most preferred by the customers. Such a condition affected the sales volume of Toyota greatly (Toyota Motor Corporation, 2015). However, the company engaged in research and development alongside product development to produce cars that matched the economic conditions of that period. By 2013, the company witnessed considerable growth in revenue.
Secondly, the increased concerns on the environment have had adverse effects on the profit margins of Toyota in the past, based on the increased demand among customers for vehicles that are environmentally-friendly and highly sustainable. Nowadays, Toyota is known for the production of its electric car and hybrid cars that have dealt away with the problem of high fuel consumption and the emission of harmful gases into the environment (Lavanya, 2012). In addition, Toyota improved its products such that its cars no longer make a lot of noise whenever opening and locking the doors.
Activities within various functional areas of Toyota Motor Corporation
Toyota Motor Corporation has been actively involved in strategies that are aimed at increasing is the percentage share of the global market. Some of the activities that the company has engaged in to achieve this objective include research and development, market and product promotion, as well as working towards reduced cost of production (Lavanya, 2012). For example, the increase in the demand for environmentally friendly cars forced Toyota to engage in more research and development and product development to design vehicles that met such needs such as the Toyota Prius and other electric cars (Toyota Motor Corporation, 2015).
Secondly, Toyota has been working towards cost leadership and competitive advantage within the automotive industry. To achieve this objective, the company adopted the Toyota Production System to ensure the production of differentiated products that are hard to be imitated. On the other hand, its engagement in market penetration and product development has been very instrumental in gaining a considerable global market share making it possible to sell at reduced prices.
Financial Performance
Toyota has had financial ups and downs due to changes in external and internal factors. For example, Toyota experienced high revenue growth between 2007 and 2008, whereby the gross profit margin was estimated at 19.7% during this period. However, the financial crisis of 2009 affected the sales volumes of Toyota which saw a drop in revenue from 2008 to 2010 (Toyota Motor Corporation, 2015). Between 2010 and 2011, there was a slight growth in the company’s revenue which can be attributed to the recovery of the sector from the financial crisis of the previous years. Since then, Toyota has been experiencing steady growth in its revenue. Such a situation is attributed to its investment in research and development, market penetration, product development, and the attainment of competitive advantage.
Strategic Plan
External Analysis
Toyota Motor Corporation operates in the automobile industry. This industry has faced tremendous numerous challenges over the past few years. For example, the prices of fuels have skyrocketed which has adversely affected the volume of sales for most car manufacturers, Toyota included. In addition, there have been a lot of concerns on the impact of car manufacturers’ activities in the whole world on the environment, an effect that has led to the shift of the preferences of consumers to small cars that are efficient in terms of fuel consumption (Lavanya, 2012).
The increased car prices led to the maximization of the portfolios of small cars in comparison to the fuel-guzzling trucks. In spite of this, there were some of the automakers that did not move with the tide of shifting their focus to small cars and hybrid models with the expectation that the price would rise in the future.
In 2009, the revenue of the automobile industry decreased to 15.4%, but in 2013 the revenue grew by 2.1% due to pent-up demands (Toyota Motor Corporation, 2015). In the years that followed, there were high expectations that the revenue from the automobile industry would increase after the recovery efforts. The revenue from the automotive industry is likely to increase in the coming years by about 2.5%. Evidently, the automotive industry suffers from numerous challenges affecting car dealers.
Nevertheless, there are also a number of opportunities (Barabba, 2007). For example, the rise in the prices of fuels has negatively affected the productivity of most automakers all over the world. This is attributed to the fact that the customers were scared away from buying new cars due to the high fuel costs. This section provides an in-depth analysis of the industry environment by examining Porter’s five industry forces and the broader socio-economic environment (PESTEL analysis).
Porter’s Five Forces of Toyota
The external factors in the automotive industry have a significant effect on competitiveness and overall productivity. This can be attributed to the fact that the external factors exert a lot of pressure on the activities of Toyota influencing the company’s strategic direction and approaches. The five industry forces are discussed below.
The threat of new entrants
The automobile industry has numerous barriers such that it is not easy for new players to join the industry. For example, the business of manufacturing, assembling, and selling cars requires a lot of capital to start and operate. This is a limitation for players that are limited in terms of capital and resources. Channels of distribution are also a factor of consideration in the entrance to the automotive industry since for any given company to avail its products to the customers, there must be effective channels of distribution, which are at times hard to find and maintain. In addition, the recent automobile brands in the entire world are faced with challenges of economies scale (Lavanya, 2012).
This is attributed to the fact that the industry comprises extensive economies of scale that can only be enjoyed by the established automobile makers (Toyota Motor Corporation, 2015). For this reason, the new entrants in this industry are required to use a lot of resources to match the available players. However, such a situation is very appropriate for the case of Toyota Motor Corporation in ensuring that it remains at the top of the automotive industry of the world. According to Stewart and Raman (2007), Toyota is very large and has a wide scope of operations in the global arena.
As such, the company has a lot of advantages in terms of large economies of scale, since such advantages are very important in the company’s growth and product development. The large economies of scale are very instrumental in Toyota’s reach for customers, reduction of the prices for its products, as well as in ensuring that the company remained competitive. The threat of new entrants in the automobile industry is reduced by various regulatory barriers in numerous global market segments. Additionally, eth retaliation expected from existing automakers in the industry as well as the significance of product differentiation has a role in the reduction of new entrants’ threat.
The threat of entry to the automobile industry is affected by a number of elements. Some of these factors include product differentiation, capital requirements, costs switching among customers, barriers related to regulation and legal aspects of the business, the degree of reaction expected among the existing players in the industry, economies of scale, as well as the time of entry (Barabba, 2007). If the regulation and legal aspects and capital requirements are high, it is more likely that the threat of new entrants into the market will be low and vice versa. Similarly, a high degree of retaliation from the existing players and large economies of scale will lead to a low threat of entry. The barriers to new entrants are high making it possible for Toyota to enjoy a large market share.
Suppliers’ Bargaining Power
In the automobile industry, the suppliers’ bargaining power is considered to have little significance. Such a situation is associated with the fact that suppliers of various manufacturing accessories are very many implying that decision of one does not affect the manufacturing process. The factors that influence the bargaining power of suppliers include the number of suppliers in the market, the suppliers’ size, the different products availed into the market by various suppliers, the difference in the services and products’ uniqueness, costs switching, forward integration, the role of volume to suppliers, cost of products supplied, as well as the capacity of players to substitute suppliers of various services and products into the market.
The impact of the suppliers is very important in the formation of supplier and manufacturer relationships. Where the bargaining power of the suppliers is very strong, it is more likely that the suppliers can influence the prices of the raw materials in the market (Stewart & Raman, 2007). The implication is that the prices are higher the amount of profit that the manufacturers get is also affected. A higher cost of raw materials translates to the high cost of production and hence, high prices on the finished products. However, where the suppliers have lower bargaining power, they tend to sell their raw materials at a lower price with the implication that the cost of production of the manufacturers is low and hence, low prices on products.
The ability of the suppliers to switch costs with respect to various auto manufacturers is determined by the type of suppliers available in the industry as well as the nature of the product that the supplier is selling. For example, Toyota Motor Corporation relies on a lean manufacturing strategy alongside the just-in-time approach of eth supply chain management. For this reason, the company’s source of raw materials for the production process is always near the point of manufacture.
Such a strategy is a bit disadvantageous in the case of Toyota due to the fact that suppliers that are close to the manufacturing units tend to have high bargaining power in comparison to those that are located far away from the manufacturing units. As such, the overall production cost of Toyota is adversely affected by the bargaining power of the suppliers especially whenever it is higher. In spite of this, since there are numerous suppliers in the automotive industry, the bargaining power of the suppliers becomes insignificant.
Rivalry among existing firms
The level of competition in any industry is very important as it helps in the determination of the profitability of the concerned industry and subsequent market. An industry that is highly competitive has a higher chance of the companies operating in it having challenges in maintaining as well as increasing their level of market share. The extent of rivalry among firms operating in a given market depends on a number of factors.
Some of the determinants such rivalry include the rate at which the concerned industry is growing, the number of competing firms in the industry as well as how they balance with one another, competitors’ diversity, how the rival products and services are different from one another, the quality of products and services offered by the competing firms, costs switching, existing barriers and excess capacity, brand equity, the expenses incurred in advertising, and the level of transparency in the industry.
In the automotive industry, Toyota faces competition from several other firms such as the Honda Motor, BMW Group, Daimler, Volkswagen, General Motors, SAIC Motor, Hyundai, Nissan, and Ford Motor Company among others (Lavanya, 2012). Despite the fact that Toyota is a leader when compared with the other competing firms in terms of sales, there are other companies that have great market share in international markets.
For example, a review of the market share of Toyota in comparison to other motor vehicle dealers in the US market shows that General Motors has a large market share than Toyota. The figure below represents the percentage market share of a number of key players in the auto market of the US. According to the pie chart, it can be seen that General Motors has the highest market share of 18.5% ahead of Ford Motor Company and Toyota, which have a market share of 15.2% and 14.0% respectively.
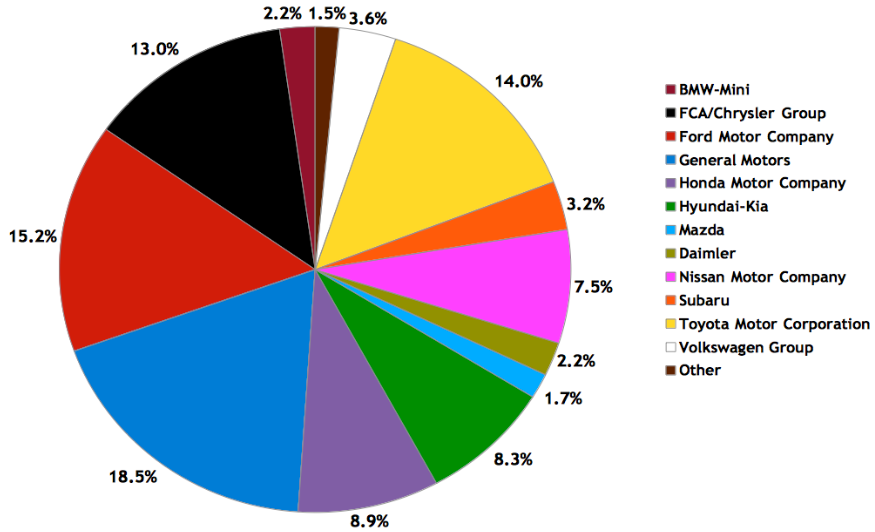
The automotive industry features an aggressive rivalry among the firms that are only in operation within the industry. This is attributed to the fact that the industry comprises firms that have varying sizes and competing for the same market share. Due to the aggressiveness of the rivalry between the existing firms, the threat of acquisition by a competitor is very high. In addition, the industry is very large and at the same time matures, with each brand having loyal customers.
In spite of this, the cost of withdrawing from the industry can be enormous for any firm. For this reason, many firms run bankrupt while others stay in the industry forever. Toyota is able to succeed in such an industry due to its economies of scale and uniqueness of the products it sells and reduced prices at the market, thereby gaining a competitive advantage over its competitors.
Bargaining power of the customers
The extent of customers’ bargaining power has a close association with the degree of impact these buyers bring to the market. In a case whereby the buyer is strong, it is more likely that the capacity of reducing the prices of products or even increase the quality of the services and products offered in the market is very high. A number of factors influence the bargaining power of customers such as the switching of costs, differentiation of products, sensitivity of the prices of the offered services or products on the buyers, the ability of the buyers to switch to substitute products or services, as well as the concentration and size of buyers in comparison to the available suppliers.
In a case whereby the buyers are highly concentrated than the suppliers, it becomes possible for them to influence the prices of products and services implying that the final prices are very low (Stewart & Raman, 2007). The automobile industry has very many buyers since the industry is very large, implying that the bargaining power of the buyers is very strong. For this reason, the buyers within the auto industry have the ability to influence the prices of car products and services. This is attributed to the fact that the cost of switching from one manufacturer to the other is very low, with the implication that they are at will to choose the car brand that they want.
Effect of the availability of close substitutes
The availability of close substitutes in terms of services and products affect the prices at the market. In a case whereby the substitutes are available in the industry, the bargaining power of the firms in the industry is lowered. Often substitutes are considered to be products or services that are used directly or indirectly in the place of other products or services. Thus, if the prices of certain automobile products and services are increased, buyers can go for the substitutes provided they fulfill the same need.
The treat of substitution in the industry is depended on the availability of close or indirect substitutes, switching costs, the propensity of the buyers to substitute, the product differentiation perception, as well as the quality and performance of substitutes in comparison. However, in the case of Toyota and the automobile industry, the threat of substitutes is very weak due to the fact that substitutes in this industry can never provide the same extent of convenience to the consumers.
PESTEL Analysis
Political factors
The various changes in the political conditions in different parts in which Toyota operates have an immense effect on the operations, profitability, and productivity of the company. For example, Toyota enjoys a state of political stability in most of the areas where it operates, which implies that the company uses such a situation as an opportunity to grow in terms of productivity and profitability. Similarly, the company does not suffer from strict legal and regulatory requirements (Stewart & Raman, 2007). Instead, it enjoys free trade agreements as well as governmental support due to its initiative of eco-friendly products. As such, the political factor offers Toyota with opportunities to grow.
Economic factors
The organizational development of Toyota is influenced greatly by economic trends. Some of the economic factors that affect the productivity of Toyota include the availability of weaker Japanese Yen in comparison to the U.S. Dollar, which provides Toyota with cheap imports. Secondly, the economy of the United States has been experiencing a gradual growth, therefore presenting an opportunity for Toyota to grow alongside the economy of the U.S. Such growth is very important for Toyota since the U.S is considered to be number two in terms of market size after Japan. Additionally, many other developing countries are experiencing rapid growth, making it possible for Toyota to gain high revenue from these markets.
Sociocultural factors
Social factors in areas of operations have a considerable effect on Toyota Motor Corporation (Gillespie, 2007). There is a growing demand for hybrid and sustainable motor vehicles such as electronically-driven vehicles. As such, Toyota has been presented with the opportunity to meet the demand for hybrid cars in various regions in the world. Nevertheless, the widening wealth gap is a threat to the growth and productivity of Toyota due to the fact that the middle class has been declining over the past years. However, the company can capitalize on the increased demand for cars that are conscious of the environment in terms of reduced emission and low fuel consumption.
Technological factors
The introduction of technology in the automobile industry has had a lot of effects on the production methods used as well as brands available in the market (Gillespie, 2007). Given that Toyota is a technological business, changes in technology affect the level of profit made by Toyota. For example, recently the use of e-commerce and trends in mobile has risen among individuals. Nevertheless, such technological use has created for cybercrime and related evils.
In the case of Toyota, the company has the potential of improving its production by investing in e-commerce platforms or even exploiting third-party e-commerce service providers for the purpose of creating avenues to increase sales for the company. On the other hand, the company can make use of increased mobile technology in order to engage more customers. Nevertheless, the increased cases of cybercrime are a threat that Toyota Company ought to be prepared to deal with.
Environmental factors
There have been increased concerns over the harm that automobile manufacturers have on the environment, with respect to the greenhouse gas emissions from the cars. For this reason, it is advocated that environmentally-friendly products are preferred in the market. Toyota uses such a situation to offer products that adhere to the need to sustain the environment by reducing the percentage of harmful emissions in the environment. For this reason, Toyota has introduced electronic cars as well as higher fuel-efficient cars in order to take care of the environment (Stewart & Raman, 2007). Additionally, Toyota Motor Corporation can maximize the opportunity towards increasing its sustainability by ensuring efficiency in its business process.
Legal factors
Various countries have different legal and regulatory requirements. For this reason, Toyota ought to be careful when carrying out its operations since it has a presence in different markets which may have different legal systems from the ones the company is used to (Barraza, 2011). For example, there has been a global need to improve intellectual property, develop consumer and environmental laws to control certain practices.
The need to improve intellectual property has led to low concerns whenever it comes to intellectual property rights’ infringements. For this reason, the company ought to ensure that it grows with such changes. Secondly, the increasingly complex environmental laws act as an opportunity for Toyota to offer products that are highly-quality. On the other hand, there is a need for automotive products that can meet the desires of the customers.
Internal Analysis
Internal Resources and Capabilities
The primary capability in the case of Toyota is the production of high-quality automobile products at reduced charges; a move that ensures that customers remain satisfied. Such competence is based on the fact that Toyota adopts innovative production practices (Stewart & Raman, 2007). Over the past decades, the availability of high products from Toyota has greatly sparked the automobile industry. The production of products of high quality plays a significant role in the achievement of the company’s goal of cost leadership.
On the other hand, Toyota has a distinctive internal resource called the Toyota Production System. This method adopts the concept of lean manufacturing and involves the Six Sigma, Kaizen, and Just-in-Time innovative practices (Barraza, 2011). This distinctive competency of Toyota is very unique since it ensures product differentiation for Toyota, thereby ensuring that the company has a competitive advantage over its competitors.
VRIO framework Analysis
This section provides an in-depth internal analysis of Toyota Motor Corporation based on the company’s characteristics such as value, rare practices, inimitability, organization, and competitive implication. In the VRIO framework analysis, the aspect of ‘value’ is used to examine whether or not the available resources in the concerned company are likely to lead to improved effectiveness and efficiency. The ‘Rare’ aspect of VRIO looks at the value of the products, to find out whether or not they are atypical to those of competitors. The ‘imitability’ component examines the possibility of the product being imitated, while the ‘organization’ factor explores the level of organization of the concerned company and has the ability to exploit resources.
Valuable
Toyota Motor Corporation has numerous and useful resources that it uses to ensure efficiency as well as effectiveness in its operations. For this reason, it can be considered to be valuable in that its practices are aimed at reducing the cost of production for a chance to sell at reduced prices hence, attaining cost leadership and competitive advantage.
Rare
Toyota adopts a very unique business model that comprises of various innovative practices such as the Just-in-time approach. In spite of the fact that various companies in a verity of industries use just-in-time production, the methodology adopted by Toyota is quite rare.
Inimitable
There are quite a number of companies in the automobile industry that have tried copying the system used by Toyota to no avail. As such, Toyota has an inimitable system.
Organization
The model used by Toyota was adopted in the sixties. However, the company carries out analysis to perfect areas requiring attention as the years go by.
Competitive implication
Toyota has a competitive advantage that ensures that it gains and maintains a large market share in the global market.
Strategies and Strategic Recommendations
There is a high level of competition from other key players in the automotive industry such as General Motors and others. For this reason, Toyota Motor Corporation is required to put a lot of effort into ensuring that it remains at the top of the industry by ensuring high-quality products, reduced prices, and well as environmentally-friendly cars are available at all its different international markets.
According to the PESTEL analysis, it was evident that the company has numerous opportunities that it can utilize to ensure that it attains a competitive advantage against its competitors in different parts of the world as far as the automobile industry is concerned. As such, in order to remain successful in the market, the company ought to put a lot of effort into its product development to ensure that the products available in the market attract customers and that they are unique. Such an approach will ensure that Toyota achieves its product differentiation goals for a chance to remain competitively advantaged. For this objective to be achieved, the company needs to invest more in research and development as well as in more innovative production strategies.
Secondly, the company is also needed to ensure that there is an improvement in its business operations as well as ensure that it has a heavy presence in numerous parts of the world. Such an approach for Toyota is an opportunity for the company to the opportunities presented by the external economic factors. Its large size ensures that the company can enjoy economies of scale. For this reason, the company should utilize available opportunities to gain substantial market share in various parts of the world for a chance to ensure that its products are used all over the world.
In spite of this, it is important for the company to be aware of the threats presented by various external factors such as the widening wealth gap and the increased cases of cybercrime. Investing in research and development alongside thorough product development will help the company to overcome the challenge associated with widened wealth gap. On the other hand, Toyota can overcome the problem of cybercrime through robust technological and innovative strategies.
To achieve cost leadership, Toyota ought to increase its investment in product development and market penetration. Through penetration into new markets, and the provision of quality products, the company will be in a position to sell at reduced prices and still make profits.
On the other hand, as pointed out earlier, product development is very important in the design and creation of products that mean the needs and demands of customers. For example, due to rising environmental concerns, Toyota should carry out more research to ensure the production of high quality and sustainable products. Such an approach will not only attract more customers but also contribute to the company’s objective of product differentiation and competitive advantage.
Conclusion
The analysis provided focused on the operations of Toyota Motor Corporation with respect to its business and corporate strategies of remaining competitive in a market full of many players. The analysis focused on the overview of the company, internal and external analysis with a special interest in the five industry forces, and the socio-economic environment. According to the discussion above, it suffices that Toyota Motor Corporation has superior products and charges low prices. In addition, the company has grown to a position of gaining a considerable market share in various regions of the world. Such achievements can be attributed to its generic and intensive growth strategies, which focus on actions that are suitable for the company to make a lot of impact growth-wise and in terms of delivery of the quality product to its customers.
According to the PESTEL and VRIO Framework analysis, it was evident that the operations of Toyota are aimed at increasing value for its operations, the creation of unique products, and the attainment of competitive edge.
In addition, the PESTEL analysis showed that there are numerous opportunities that the company can exploit such as the development of the market in most developing countries, the growth of U.S’s economy, the reduced valued of Japanese currency against the U.S dollar, reduced concerns over intellectual property laws, as well as the improvement of customer and environmental laws. For this reason, the company through its research and development and innovative strategies has a role to play by focusing on product development and market penetration to achieve the necessary level of competitive advantage and cost leadership within the automotive industry.
References
Barabba, V. (2007). The Toyota innovation model. Strategy & Leadership, 35(4).
Barraza, M. (2011). Standardisation without standardisation? A case study of Toyota Motor Corporation. IJPD, 15(4), 157.
Fleming, B. (2013). Electric Vehicle Collaboration-Toyota Motor Corporation and Tesla Motors. IEEE Vehicle Technology, 8(1), 4-9.
Gargasas, A., & Mugiene, I. (2012). Intensive growth strategy development trends in logistics services for agricultural organization providing companies. Management Theory and Studies for Rural Business and Infrastructure Development, 34(5), 47-53.
Gillespie, A. (2007). PESTEL analysis of the macro-environment. Foundations of Economics, Oxford University Press, USA.
Jenn, A., Azevedo, I., & Michalek, J. (2016). Alternative Fuel Vehicle Adoption Increases Fleet Gasoline Consumption and Greenhouse Gas Emissions under United States Corporate Average Fuel Economy Policy and Greenhouse Gas Emissions Standards. Environmental Science & Technology, 50(5), 2165-2174.
Lavanya, B. (2012). Corporate Environmental Responsibility with special reference to Toyota Motor Corporation. IOSR Journal Of Business And Management, 4(4), 8-15.
Merchant, H. (2014). Configurations of governance structure, generic strategy, and firm size. Global Strategy Journal, 4(4), 292-309.
Stewart, T., & Raman, A. (2007). Lessons from Toyota’s Long Drive. Harvard Business Review, 2(2), 18-25.
Takami, T. (2014). Production Engineering Strategies and Metalworking at Toyota Motor Corporation. Procedia Engineering, 81, 5-17.
Toyota Motor Corporation (2015). Toyota’s Strategy for Environmental technologies. Web.

