Introduction
Unilever is one of the topmost multinational corporations operating in more than one hundred seventy countries with its wide variety of products. Currently, it has approximately 163000 employees where top management consists of twenty nations of different countries who are serving the growth of the company (Unilever, 2009). Unilever plans to double the size of the company in near future, which requires a pool of talented executives to succeed in the plan. This is paper examines the gradual HR policies, functions, and strategies that contribute to the acceleration of the company. Unilever is a global company and its focus is on the development of a uniform HR strategy, which serves in all the operations of the company.
From a global perspective, the multinational company has to choose the geocentric approach to do business worldwide. However, the company needs to concentrate on local responsiveness as well. Unilever currently plans to strengthen its brands and developed a new product in the market, which required a substantial amount of investment in R&D projects and the company tries to gather and retain the top researcher in this sector. On the other hand, to do business successfully in various regions it gives importance to building a team through diversity and they recruit and build their top management team with members of different regions. Unilever provides competitive salaries and other benefits to the top executives to retain them in the company. However, Unilever has to face some competition in employee retention in some regions like China, UK, and India, etc were other top multinationals try to attain high-profile executives. The environmental pressure is also high for the companies because the culture is different in the different region such as in China, the management is
centralized but in UK, it is very different. To response to the change, Unilever uses hard approach in China and other regions like India, UAE and in other Arab countries. Unilever tries to expand its market further and to do so it plans to expand its current market as well enter into the new market. To do this effort better, Unilever invested more money to cover investment for R&D and new product development with improved feature and quality of the current product.
Corporate Strategies of Unilever
According to the Annual report of 2009, Unilever is a global organization and its corporate strategies mainly focus on the global business development. The main strategies of the company are as following:
- Growth Strategy: Unilever focus on the growth in the market through its existing product line and this growth address both the developed countries as well as the developing countries. Unilever has a long product portfolio with strong brand and positioning in most of the region of the globe, which enables the company to meet the future growth.
- Brand and innovation: Unilever always works to establishing new brands and continue the popularity of the current brands in the existing and new market. This was happening only because of its long and strong brand portfolio with high quality product and strong marketing endeavor. The innovation of the company stresses on using latest technology to create well-improved way to innovate, which enables the company to enter into most of its market at good pace.
- Market position: Unilever continuously enhance its category and concentration on its customer through increase penetration in the market, consumption and motivate customer to buy supreme products
- Continuous improvement: Unilever tries to ensure continuous improvement in three areas, which includes flexibility in supply chain to response to the changing needs of customers, increase the capabilities and economies of scale, and finally, higher return on the investment in advertising and promotional activities.
- HRM strategy: The human resource strategies of Unilever focus on building a team of employee, which will fit with the future growth of the company. The company tries to leverage the growth with the required members available to lead the growth through skill and competence. To sustain the growth Unilever change its organizational structure, modify its recruiting strategies, review employee retention approach, change organizational culture and provides intense training to build the capabilities to contribute to the growth.
- Unilever currently focus on selecting employees from different culture with age, gender, race, and region to create a diverse team who will serve the customer across the national boundaries crate a link between the company and customers of different categories (Evanes, et al, 2007). It also tries to support its employee the washing ambiguity of their role and the vision of the company.
Recruitment and selection process of Unilever
Unilever currently works on developing a uniform recruitment and selection strategy for all of the operation located in various regions and to do this it develops a system called Talent Management Solutions. This program is developing for the current employees for choosing the leader form the current working team (Mclaren Solutions, 2009). It has also a good history of selecting fresh graduate from different business schools (Jackson, 2009). In case of fresh graduate selection, it follows some logical manners which are as follows:
- Application form: The first step of selection process is filling application form by the prospective candidate. The application form designs in a way that helps to assess presence of the primary requirement in a candidate. It is very important in a sense that it clearly dictates the potentials of the candidates in leadership and growth prospect in the company (Unilever, 2008).
- Test: After the primary assessment through the application at this stage, the candidates need sit for some test which includes the aptitudes test and psychometric test. These two types of test designed to prove the validity of the information in the application and measure the mental strength of the candidates which is vital to get success in Unilever’s global work environment.
- Interview: It is a primary interview which includes the orientation of the company to the candidates as well as company oriented with the candidates. A wide variety of issues are involving in this interview which may be the question about the candidate’s personal information as well as their educational information.
- Selection Board: Selection board refers to the committee of selection that formed with members of the top management team of the company. In this stage the candidates need to do some exercise like case study, presentation or project work both individual and together with the other candidates in group. It is the last and most important part of the selection of the candidates and based on this performance, selection committee would finally select the candidate for employment (Unilever, 2008).
Employee Retention Strategy
Unilever has a strong remuneration and benefit plans to retain its key executives. The basic salary of the executives reviewed annually with company’s internal structure and the outside salaries paid by other company. The top executives receive annual incentives for filling target and contributed to the business growth which is approximately 200% of his or her basic salary. There are also long term incentives plan for the executives which includes awarding the employee with the share of the company. The top executives enjoy the pension facilities after the retirement from the job and they also enjoy the other benefit enjoyed by the employee of Unilever. Beside this, the top executives have the opportunity to serve as a non-executive director of the other company (Remuneration policy 2008).
Environmental Change
PESTLE analysis
Political Factors: Political factors include the policies regarding the labor and employment in the country and the political stability, tax regulation etc. of a country. In case of Unilever, when they do business in China, they have to face more restriction than in UK. This is because the government of China imposes different restrictions, inherited from its sate controlled socialist economy and the operation of MNCs regulated strictly in context of national interest.
Economic Factors: Economic factors mainly influence HR policies of Unilever through the compensation and benefit policy of the company. The compensation policies varies across the countries as the economic condition like inflation rate, level of income an expenditure are not same in all the countries. As an example, the salary structure of Unilever in Pakistan and Unilever in UK are not same because of economic differences. Whereas in UK the economic condition is stable, in Pakistan the economic condition changed frequently.
Social Factors: Social factors of HRM include the consciousness of health, age distribution, career attitudes etc. When Unilever doing business in various countries in the world, always need to concern about the social difference among the various nation. In case of UK, the employees are more health conscious and attitude towards the job or career is different so that the company needs to give substantial attention on employee retention. On the other hand, in Japan the employees like to work under single employer for lifetime more loyal to the employer. As a result, the company needs to give less focus on retention.
Technological Factors: The technology is changing rapidly and company like Unilever quickly adopts new technologies to remain competitive in the market. However, not all countries are equally technologically advance as the people. Unilever invests a substantial amount of money in R & D activities and to do this, the required specialists are not available in the less advance countries. When Unilever tries to diversify its work team, the unavailability of competence person in third world country creates problem for the countries. Suppose, in Japan and China the technologic advancement is very high and Unilever gets the required person for R&D and other operation whereas in south Asian region, the technology and skills of people are not match to the company’s requirement.
Legal Factors: Legal factors include the labor law, employment law, trade union policy etc. of a country. When Unilever operates in UK, they do not face restriction regarding the employee selection but in case of Hindustan Unilever, the government made regulation to select the host country nation for foreign operation. The minimum wages, labor hour, vacation etc are substantially different in various countries.
Environmental factors: Environmental factors closely related to the corporate sustainability and corporate social responsibilities of the company. Unilever is very much aware of the nature and uses natural ingredients in their product. Company recruits local employees in the foreign operation to understand the local environmental protection need and corporate social responsibilities of the locality.
Competition in Staff Retention
Unilever face a strong completion in China with its industry rival Procter & Gamble where P&G has a reputation in employee retention, the rate of turnover of Unilever in China is very high (Goel, & Mehta, 2004). The reason behind that situation is the employees selected from local partner who are not dedicated and a wide variety of product creates chaotic situation for the company. Another reason behind this situation is that in China currently a lot of local and multinational manufacture establish their operation where the employee get much opportunity to do job. In India, Unilever face the same situation where most of the global company set their operation and try to attract the potential candidate. Nevertheless, country like South Africa, Unilever awarded as top employer and successfully able to retain the potential candidates and attracts more employees (Samuel & Chipunza, 2009). In Indonesia, the company creates opportunity for the prospective employees to join the team and contribute to the growth initiative (Clay, 2009).
Current Position of Unilever– Strength & Weakness
Unilever’s strength in HR
- Unilever has well-managed professionals who are enable to cope with the growth of the company.
- Unilever composed its workforce from the diverse community so that the team can interact with any kind of culture around the globe. This diversity includes members from the different race, gender, religion, ethnicity, region etc.
- Unilever follows an integrated and uniform strategy in recruitment, selection and other HR function over all of its operation.
- The training and learning method of Unilever designed in a way so that members of the workforce get the proper knowledge and expertise, which contribute to the overall growth of the company.
- Unilever currently executes an outsourcing contract with Accenture a global management consultancy firm to provide all kind of HR service to the company. Certainly, it helps the company to recruit and select professionals with more diversity and growth potential.
- Unilever has an expert professional team for R&D, which continuously contributes on the development of new product in the market. It helps the company to increase its product, brand portfolio, and consequently expand the market.
- The marketing team is the core assets of Unilever, which contributes to growth of the company and it investment most resources in marketing its product.
Unilever’s weakness in HR
- Major weakness in Unilever’s HR polices are the uniform strategies because the culture and environment in different region are substantially different from one another. As a result sometime this strategy is not contributed to the growth of the company such as the management practice in china are more autocratic and centralize whereas in UK it is decentralize and power distance is low.
- Unilever make their human resource for the global perspectives whereas the local market does not get that much importance.
- Unilever’s HR strategy focuses on recruitment from the local area, which sometimes reduce the control of headquarter and in turn, the strategies are not properly implement in the local area.
Ansoff Matrix analysis from HR perspective
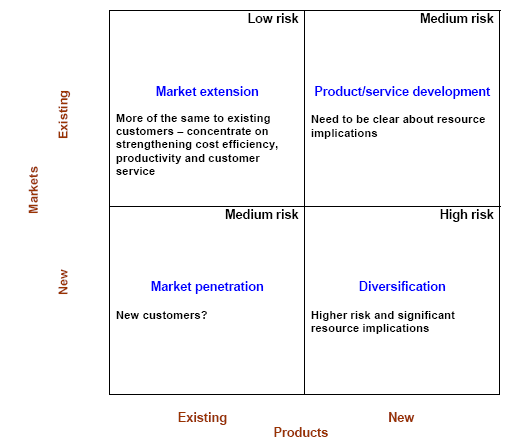
Market Extension
Unilever currently doing business in around one hundred countries in the world that means it required to extension of current market. To extend the current market and take share over other competitors company requires recruiting new employees and enhancing the expertise of the current workforce through extensive training on increasing productivity and efficiency. On the other hand, cost is a major concern, which demonstrates in Unilever’s decision to outsourcing the HR operation. As an example in China, employees required to concentrate on customer care where in UK advertisement is important, and HR strategy should created in that way.
Market Penetration:
Market penetration required to enter into the new market with current product line. When Unilever decided to enter into the new market the HR policies should tailored in a way so that it will match with the areas culture and environment. The HR manager should follow the polycentric approach in HR. When Unilever enter into the Chinese market, it recruits from local area so that the employee can understand the culture of the country and response to the local requirements (Wellins, et al, 2005).
Product Development
Unilever continuously work on developing new product for its existing market. To do so, it gathers the high professionals in R&D department to prompt its new product development. Unilever uses high professional training method, which enables its R&D members to develop new product in cost efficient manner.
Diversification
Unilever sometimes make efforts to enter into the new market with new product. The company creates more expert marketing teams to promote the new product whereas in the new market they build their HR strategies, which best suited with local market. Suppose in UK, when they promote new product, extensive promotional program like the advertisement and in store campaign taken by Unilever. However, in case of China, where the market is new, they use the employees who are familiar to the local culture approach to the local customer (Braeken, 2007).
Comment on the HR Strategy of Unilever
The HR strategies of Unilever are uniform and global in nature but it is not possible for the company to follow strictly these strategies in different countries due to the difference in cultural, society and the political view. However, there are two approaches, which will adopt by most of the multinational organization operating different countries.
Hard Approach of HRM
The hard approach of HRM, also known as Michigan School Model stresses on uses human resource to achieve the organizational strategy. Here, organization or management think people as a factor of production like the other factors and no special value treated to people as a human. The HRM approach directly derived from the corporate strategy and policy of the company and HR policies integrate with the corporate plan and policies of the organization. This approach is most common with the X theory of McGregor where he argues the basic nature of human are bad and they always try the avoid the work. Hence, tight control required to get the job done of the organization (Kidombo, 2000).
Unilever uses this approach in a country like China where the employee selection, reward, appraisal all are guiding by the overall objectives of the company and the compensation given to employees based on the individual performance of them. Unilever closely monitor the investment on the employee training and development to ensure it will best fitted with requirement to gain the overall objectives. This approach is suitable for China because most of the multination in there practices this as the corporate culture of China build on it. There the importance of HRM lies on the fact that it will helps the employees to increase their productivity to serve the organization. The existences of trade union and collective bargaining agents are not encouraged by the Government of China as it hampers to achieve the goals of the organization.
Soft Approach of HRM
Soft approach of HRM, which also known as the Harvard Model of HRM involved four issues to manage the human resources in the organization. Unilever uses this model in most of the country including headquarter (Gill, 1999). This soft approaches based on in the corporate strategies of Unilever and it mostly practiced in European region where the culture supported by this approach.
- Unilever delegates authorities and responsibilities to the employees voluntarily which comply with the interest and objectives of the company.
- Unilever always made effort on recruitment, selection, promotion, and creation of favorable work environment to the employee.
- Unilever decides on the issues of compensating the employees by means of salaries, bonus, and other faculties and creates rewarding employees on performing to achieve both internal and external growth.
- Unilever stresses on effective and efficient management for gathering workforce, information, and technologies in the organization.
Unlike the hard model, in soft model Unilever mangers role regarding the employees are enabler, empowerer and facilitators. As an enabler, a HR manager of Unilever creates organizational structure in way so that the member can achieve the goals and as a empowerer decentralize the decision making and finally, as a facilitators, helping and encouraging employees in their work.
The above-mentioned strategies are widely used in the modern multinationals in various regions but it is most useful in European context because the culture, society, and nature of people support this approach. However, it will be risky for operations where the culture is different like China. Therefore, Unilever uses this approach in only European region.
Recommendation
From the discussion of the overall HR strategies of Unilever, some areas need to change to get more success and implement the growth targets of the company. Some specific recommendation for Unilever has mentioned as follows:
- Unilever should tailor its HR strategies for different region to select more employees from the locality with high growth prospect. It should introduce high training facilities for the local employees for developing their skills;
- Unilever should introduce some expatriates in top management in local operation to prompt the growth and enhance the control of Headquarter over the local operation.
- The company should use more hard approaches in third world countries and other countries where the culture are more individualistic and power distance in high;
- The company should recruit more from third country nations for foreign operation.
- The recruitment and selection policies should be easier to attract the potential candidates for applying to the company;
- Unilever should attract more senior professional for their R&D projects to develop and innovate new product and brand.
- Unilever should expand its current market through employing more business development experts;
- Finally, it should select more dynamic person for its marketing team, which is very essential for developing new product, establishing the current and new brands.
Conclusion
Unilever’s current HR strategy develops in a way to serve best service considering the global demand and in order to do so they focus more on developing leaders from different area with diversity. However, diversity is important for managing operation in different areas of the world. Beside this, it stresses more on the uniform HR strategy for all the countries, which is not viable for all regions because the culture, social norms, and political situation are not same in all places, for example, employment terms and cultures in Japan is very different from US system. As a result, the company is not able to retain the prospective employee in China and India. The company tends to use soft approach more than the hard approach and the employees of the company are more participative in decision-making.
Reference
Braeken, F. (2007) Outpacing the market, Unilever China. Web.
Clay, J. (2009) Exploring the Links Between International Business and Proverty Reduction: Case Study of Unilever in Indonesia.Web.
Evanes, C. et al., (2007) Effective Recruitment Strategy and Practice, School of Business and social Science. Web.
Gill, C. (1999) Use of Hard and Soft Models of HRM to illustrate the gap between Rhetoric and Reality in Workforce Management. Web.
Goel, M. & Mehta, A. (2004) Case Study: Unilever and Procter & Gamble, Emerging Markets Club Newsletter. Web.
Jackson, B. (2009) History of Unilever Graduate Scheme. Web.
Kidombo H. J. (2000) The Moderating Effect of Human Resource Management Orientation on Business and HRM Strategic Responses to Environmental Change. Web.
McLaren Solutions. (2009) Talent Management Solution. Web.
Mikhail, G. V. (2004) Leadership Competencies for Unilever. Web.
Samuel, M. O. & Chipunza, C. (2009) Employee retention and turnover, Department of Industrial Psychology. Web.
Smith, I. (1994) Meeting Customer Needs. Web.
Unilever. (2008) Graduate recruitment process of Unilever. Web.
Unilever. (2008) Remuneration Policy of Unilever. Web.
Unilever. (2009) Annual Report 2009 of Unilever. Web.
Wellins, R. S. et al. (2005) Super Human Resources in China: Practices, Performances, And Opportunities among China’s Manufacturers. Web.

