Abstract
This paper will discuss the internal and external environment of Apple, for example, various models assist in the analysis, including PEST factors, Ansoff matrix, Porter’s five forces, strength, weakness, opportunities, and threats. In conclusion, this strategic plan will scrutinise the iPod’s contribution to recover the company from turmoil and it will provide few recommendation for future prospect.
Introduction
Apple Computer is one of the most common names in the global PC industry. Back in 1997, Apple had gone through five years turmoil and Dell had recommended that it should shut down and give the money back to the shareholders but CEO Steve Jobs had made several dramatic steps since returning to apple and in 2006, after considering the stock price, Jobs stated that Apple is worth more than Dell Computer.
The purpose of this case study is to identify Jobs role to solve long-standing problems and to find out potential entry opportunities and strategies of Apple Inc. This paper will consider internal and external environment of Apple such as various models assist in the analysis, including PEST factors, Porter’s five forces, SWOT analysis, Ansoff matrix.
Finally, this strategic plan will scrutinise the iPod’s contribution to recover the company from turmoil and it will provide few recommendation for future prospect.
Background of Apple Inc
Apple Inc has established in 1976 by Steve Jobs and Steve Wonzniak who built a computer circuit board that they named the Apple I and in 1978, the company launched the Apple II to bring an easy-to-use computer to every one. According to the annual report 2009, now this company designs personal computers, manufacture mobile phones, and develops handy digital music and video systems, offer own software products like Mac OS X and markets these products including in-house and outsourced software and networking solution products. The company has a global presence on online retail and wholesale including third party warehousing and value-added resellers for own product and third party items like printers, speakers, i-Pod and i-phone and so on. The target customers of the company are governmental agencies, educational institutes, SMB (Small And Mid-Sized Business) enterprises, as well as individual customers.
PEST analysis
Political Factors: To reduce intellectual property claims, the US government had passed several rules, which would affect to implement its policy and besides these laws, trading policies, pressure groups, political trends, and shareholders’ demand have impact on its business.
Economical Factors: from 1992 to 1997, this company has suffered serious financial crisis and Steve Jobs saved the company from liquidity
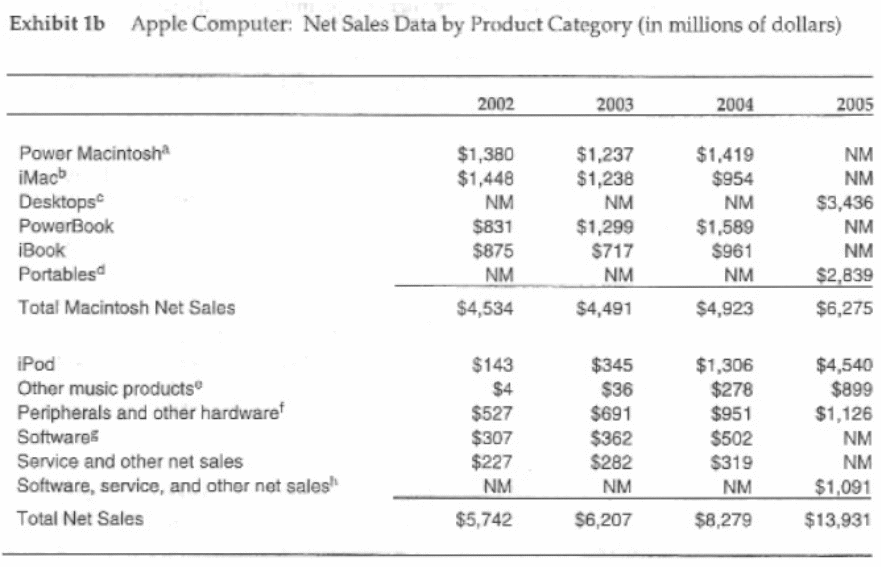
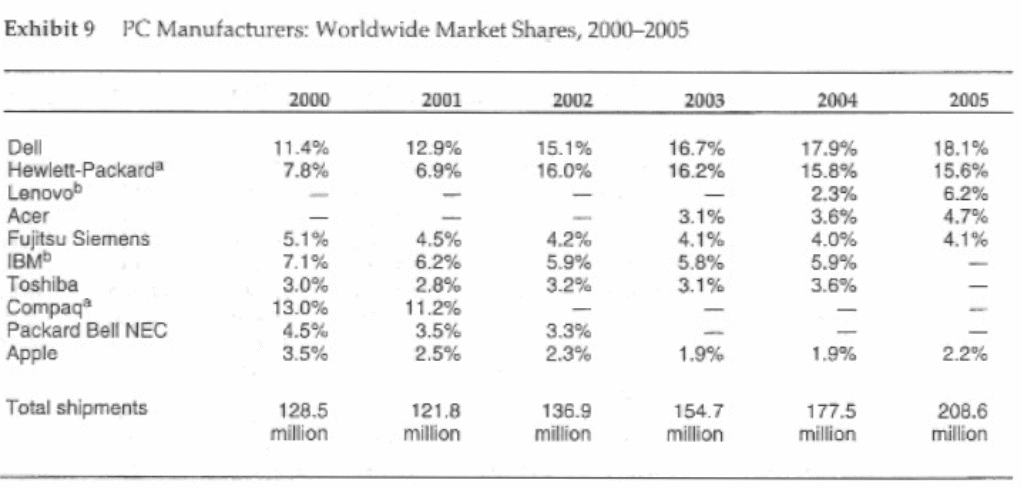
The following table demonstrates the net sales data of Apple by product category (in million of dollars) and from this figure it can say that Desktops, portables, iPod, Peripherals and other hardware, software, service were profitable business product for this company.
Social Factors: Apple has invested and will continue to invest in programs to improve reseller sales and to do this it should require efficient employees so it motivated employees, changed lifestyle, and culture by removing all discrimination between male and female.
Technological Factors: According to annual report 2006, Apple Computer has focused on the use of technology in education because effective integration of technology brings higher levels of achievement, in addition, it offers hardware, software products and solutions for clients in the IT and scientific markets.
Porter Five Forces Analysis
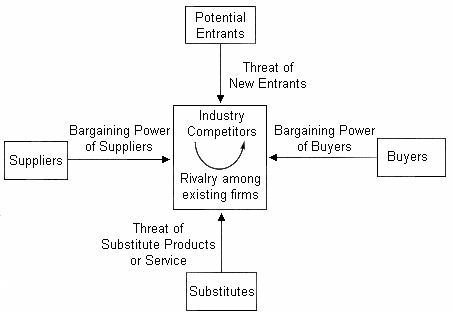
Competitive Rivalry: There exists huge range of competitors those offer similar products, such as -Packard, IBM, Gateway, Acer, Sony, Fujitsu-Slemens, Legend, Sun-Micro-systems, Enterasys, Nortel etc but the relationship is not always rivalry.
Threat of Substitute: threat of substitute in the industry is very high as this is an era of technology, where competing firms in the industry try to introduce new upgrade products.
Threat of New Entrants: Threat of new entreat is very low For Apple Inc, as it should require advance technology, experience, and huge investment to capture market.
Bargaining Power of Suppliers: Apple needs subsequently qualifies, additional suppliers as Bargaining power of suppliers is high because Apple collects its raw materials from single or limited sources, which subjects Apple to important supply and pricing risks.
Bargaining Power of Buyers: bargaining power of buyer is moderate because competitors offer similar products with advance technology so Apple’s customers become IBM’s customer if it offer low price with high quality service.
Strategic Analysis of Apple Inc
Four major strategies of Apple Computer Inc are:
- Apple’s strategy also includes increasing its distribution network to successfully reach more of its targeted consumers;
- Apple desires to support the community for the advance of third-party products;
- Constant investment in R & D is critical to the growth and improvement of innovative products as well as technologies.
- Apple’s business strategy leverages its unique capability to design & develop its own operating system.
Boykin et al (2008) argued to recommend Apple Inc that to lead new campaign into the professional market with its hot selling i-pod to generate a new source of huge revenue with an offering of lower price but higher revenue with the aim to gain large market share. This would facilitate Apple to bit the competitors with a grater advantage in long run. I-pod also has a wider market in corporate level and apple has thus recommended to driving serious events to attract the corporate clients for i-pod. It also suggested that i-Pod needed to have more research and development to introduce more facilities such as PowerPoint presentation and PDF views for the next generation product development.
Competitive Advantage
Apple (2009) argued that the company has the opportunity to enjoy competitive advantage by contribution of its superior innovation as well as amalgamation of the complete solution together with the some hardware and software. The product list those are capable to facilitate competitive advantage are as PCs, i-Phone, i-Tunes and i-Pod and some software. The distribution network of Apple Inc. is enough strong to generate competitive advantages for the company. Moreover the company have enough resource and ready to devote to face any challenge of competitors by providing the product and service at a very lower price even at a lose to break the pacts and join collaboration of competitors which ultimately provide a high degree of competitive advantage for Apple Inc.
SWOT Analysis of Apple Inc
Strength
- Strongest market stability as well as brand awareness;
- Apple Inc participates in several highly competitive markets, and it is broadly renowned as a leading innovator in the PC, mobile sectors, and customer electronics markets;
- It has skilled, experienced, talented, and dynamic directors and employees to manage the company and to provide product advice, service and training;
- It had more than 34,300 full-time permanent workers and an extra 2,500 full-time temporary workers and contractors, who enjoyed equal rights.
- It had total 273 retail stores including 56 stores in international market;
- Apple distributes iPhone in more than 80 countries and intended to distribute all over the world;
- Its net sales is increasing dramatically, such as in 2009 its net sales is $ 36,537 million, where in 2006, its net sales was $ 19,315 million;
- by 2006, PCs were far easier to use due to technological invention;
- The audit process has maintained the standards of the PCAOB (Public Company Accounting Oversight Board) and the audit includes its performance plan, risk management system, external and internal control, fiscal condition and efficacy of the company to submit an effective report for its success.
Weakness
- The financial condition of resellers;
- Due to credit crash US has seriously lost its confidence and turned as a weak currency overseas trade that has reduced Apple’s export market share.
- In the US market, Companies such as product of Dell, Hewlett Packard, IBM, and Compaq had built strong sales that Apple would have to achieve in that area, for example reduced demand for the Apple’s hardware products.
Opportunities
- Though it raises prices on goods and services in outside of US market but the demand of its products is increasing;
- Joint venture, merger, and acquisitions with renowned companies give the opportunity to expand its business rapidly, for instance, Apple and IBM formed a joint venture, named Taligent, with the goal of creating a revolutionary new operating system.
- Apple has strong financial capability to expand their business outside of the US.
Threats
- Competitors are the main threat of this company, for example, its competitive position changed fundamentally in 1981, when IBM entered the PC market;
- Some positive steps of the competitors like joint venture, merger and acquisition may cause of huge lose;
- Escalating intellectual property claims;
- The prospect of Apple is in threat as its operating system depends on the performance of distributors, staffs and other retailers but for the global financial crisis many resellers operate on narrow operating margins;
Ansoff’s Matrix
Ansoff matrix is a tool, which assist to make an overview for the recognition of growth of the product by market penetration, market development, product development, or diversification (Manton 2008). Ansoff’s matrix can show as:
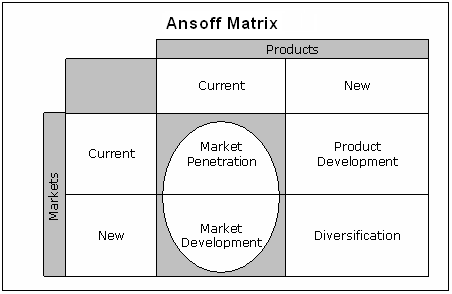
Market Penetration: Kotler & Keller (2006) argued that the business organisation applies this strategy try to increase sales volume in the existing market by inducing customers. They further added that to apply the strategy, the firm has to be aware about the success factors of the existing product and the existing market. Apple can follow this strategy as it has many current products in market and there are several related strategies such as exploiting irregular users to transfer them as regular users, attacking competitors’ consumers to turn them into Organisation’s consumers but here the exploitation of existing relationship with consumers is the best way to achieve the ultimate goal.
Market Development: Kotler & Keller (2006) mentioned that business organisation adopt this strategy to place its existing products in new market places or market segments. It may use this strategy as Apple always eager to expand its existing products in outside of US market but it is necessary to find out similar market.
Product Development: It is quite natural that Apple introduce new product in existing in the existing market to develop its business profit, for example, in 2006 Apple used product development strategy, and introduced iPod to recover the company from shut down situation.
Diversification: It is unusual that Apple would apply this diversification strategy, as new products in new market may increase risk though there are exploitable market opportunities for brand awareness and it has enough investment funds to exploit these opportunities.
Contribution of Steve Jobs to solve Apple’s long-standing problems
Yoffie & Slind (2007, p. 5) argued that to solve long-standing problems of Apple, Steve Jobs moved swiftly to shake things up, for example, in 1997, he announced that Microsoft had agreed to invest $150 million in Apple to develop core products such as Microsoft office and then he abruptly brought the Macintosh licensing program to the end. He planed that Apple spent $110 million to acquire the assets of the leading clone maker, Power computing, including its Mac OS license but his first real coup was the launch of iMac and in 1998, he stooped the production of Newton and portable PC for education as these were lose projects. Yoffie & Slind (2007, p. 5) argued that Jobs turned the company around, and then set it on a course of aggressive innovation but he did so largely through the force of his own strong leadership. Yoffie & Slind (2007, p. 5) further added that in the product development, in strategy, and in other key areas, Jobs remained at the centre of all decision making and they conclude that Apple would be able to sustain its innovative edge, if and when Jobs left the company, remained an open question.
What impact has the iPod had on Apple’s success?
Ana, (2005) pointed out that i-pod is a turning point and economic recovery route for Apple Inc. In October 2001, Apple has introduced this little portable digital media player and gained the customers satisfaction with a tremendous sells worldwide. I-pod also created a new class of Apple’s competitors including mobile phone manufacturers and marketers such as Sony, Nokia Samsung, and Google phone which placed i-pod in a market position as follows –
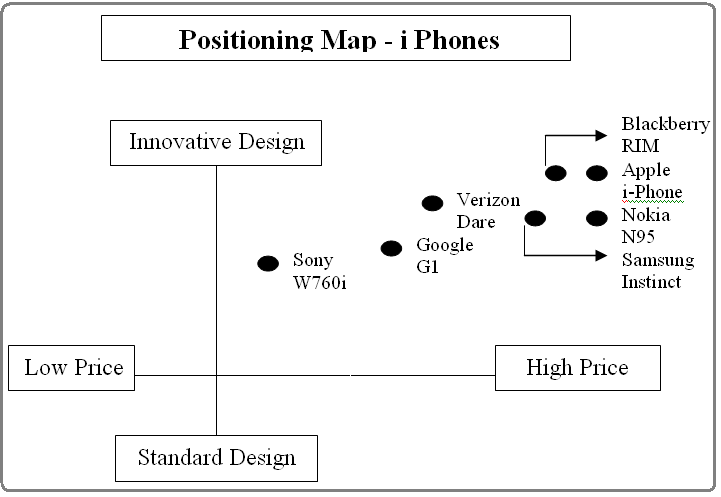
Now i-Pod has created enormous value for mobile phone users by offering software that are complicated to reproduce though the competitors are working to develop similar products, i-Pod has continued to its success is by positioning ahead of its competition and keep up on a unvarying flow of new features.
Zaky (2009) mentioned that, in 2006, Apple’s revenue from iPod grew at a rate of 75% while the aggregate revenue of Apple 38%. Within the fiscal year 2006 to 2007 but in 2007 to 2008 the aggregate revenue of Apple grew 75% where i-Pod indicates lower and in 2009 up to third quarter, i-Pod has only contributed 14.2% while i-phone has larger contribution.
Apple’s I-pod is affecting the sales of MP3 players by taking away 65% of MP3 market. Apple also involving its continuous efforts to adding new features with i-Pod primarily phone calls, e-mail as well as web browsing and i-Pod also evidenced to catching 29% of flash memory market with huge storage capacity. With in third quarter of 2009 i-Pod has recorder as a highest selling audio player, which has amounted 22 million units. This success of i-Pod has generated huge revenue for Apple and shown the path of recovering financial crisis.
Recommendation
- The previous data demonstrates that joint venture with competitors has enhanced its net sales, so it should follow this strategy in future;
- Many large company has collapsed due to global financial crisis and lack of following the rules and regulation of the government so it should more concentrate on its audit process for external and internal control of the company though its audit provides a reasonable basis for its opinion;
- To overcome the adversely affect the U.S. dollar value fall due to credit crash, Apple should consider to transact in the overseas market with a strong and stable currency like Euro;
- It requires the linking of all the monetary functions for having greater visibility as well as control on financing activities;
- Apple should continue to invest in programs to enhance reseller sales, together with staffing selected resellers’ stores with its workers and improving manufactured goods placement displays;
- It should increase its budget for promotion activities;
- It should come up with new ideas like a framework of making swift headway in other markets like networking, consumer electronics, storage etc;
- Annual report 2009 of Apple recommended that in order to remain competitive, it should increase the investment in R & D and marketing and advertising to uphold or develop its situation in the markets where it competes;
- By calculating business risk, Apple can identify the uncertainty inherent in the operations in the firm’s Return on investment capital, so it should perfectly measure the long & short-term risk factors, liabilities, trade credit, accrued liabilities, & receipts.
Conclusion
The out come of this strategic analysis depends on the implementation of the chosen strategies and it would measure with the gaining market share as well as increase in revenue generation. Under the present recessionary economy with the incredible pressure of competitors as well as other external forces if the sales volume indicate any enlargement that should prove the success of the implemented strategy. The issues identified in this present analysis would help encourage the rudiments of gaining a substantial competitive advantage and argue to exploit Apple’s internal strengths and weaknesses pedestal on environmental focus for further research and development.
Reference
Ana, S. (2005) Apple debuts budget computer and capitalizes on iPod success. High Beam Research. Web.
Apple Inc. (2009) Annual report 2009 of Apple Inc: Form 10-K. Web.
Apple Inc. (2006) Annual report 2006 of Apple Inc: Form 10-K. Web.
Boykin, R. Fiorini, A. Tanaka, L. & Webb, M. (2008) Apple Inc. Case Study# 1: iPhone. Web.
Kotler, P. & Keller, K. L. (2006) Marketing management. 12th ed. New Jersey: Pearson Prentice Hall.
Yoffie, D. & Slind, M. (2007) Apple Computer, 2006. Harvard Business School, HBS No. 9-706-496.
Zaky, A. 2009. iPod Sales Only 14.2% of Apple’s Q4 Total Revenue. Web.
Appendix