Executive Summary
ExxonMobil Singapore, being a part of the largest global oil exploration and refining company occupies a predominant position in the industry in the South East Asian region. The company’s market position is strategically important in the light of the growing demand for oil from the regional countries such as China and India. At the same time there is growing competition from other global regional players of the industry. The company’s policy on the development of alternative energy sources has been subjected to severe criticism. With this background this report makes an analysis of the strategic choices and their implementation of ExxonMobil. Though the focus is on ExxonMobil Singapore- the downstream unit, the issues involved are considered including the upstream, downstream and chemical business of the global entity.
Introduction
With the growing demand for oil, large oil companies focus their efforts in economizing their production by employing new and improved technological advancements in exploration and refining and distribution. Since the development of alternative energy sources appears to be a distant dream, in the medium term the companies have to strategically align their efforts to be competitive and maximize the returns for the stockholders. On a long-term perspective the companies invest huge sums of money in research leading to alternative fuel sources. This paper analyses the relative position of ExxonMobil Singapore. The strategic analysis of ExxonMobil may take the following form.
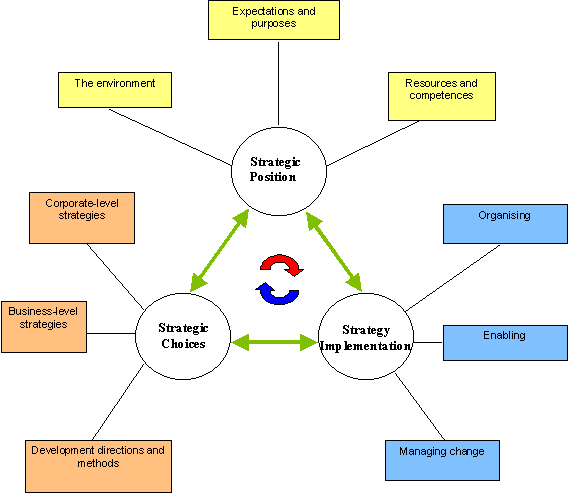
Background: Current Position Analysis
- ExxonMobil is one of the most successful and efficient petroleum and petrochemical companies in the world.
- The company has an investment of US $ 6.5 billion which is the largest any foreign company has made in Singapore.
- Singapore being the Asia Pacific hub for the downstream in petroleum products and chemical businesses, the company has a large market presence in the region.
- The company operates a 605,000 barrel-per-day refinery which is the largest one at the global level.
- Singapore Refinery operates as a fully integrated facility with company owned Singapore Chemical Plant (SCP). ExxonMobil has the largest manufacturing facility in Asian region with the combination of both Singapore Refinery and Singapore Chemical Plant.
- The products of the company include Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG) for household use. The company operates the largest network of service stations with the brand name of ‘Esso’. Industrial, aviation and marine fuels and lubricants are some of the other products which are being dealt with by the company (ExxonMobil, 2009).
- Presently the company operates and sells its products in more than 200 countries and regions across the world.
- ExxonMobil is one of the largest international oil and gas companies which have listed its shares for public trading on a global basis.
- The company with its associates in the region offers a wide range of petroleum products and lubricants under the brand name of ‘ExxonMobil’, ‘Mobil’, and ‘Esso’.
Environmental Analysis and Commentary
- The company’s external environment can be analyzed using the models of PEST analysis and Porter’s Five Forces analysis (Porter, 1980). The objective of the analysis is to identify the current and evolving issues in the marketplace in which the company is operating.
- There are Political/legal, Economic, Socio-demographic, and Technical and environmental issues that affect the performance of the company in the given market. The PEST analysis deals with these issues.
- Five Forces model helps in analyzing an industry to determine the level of competitiveness and attractiveness of the industry (MBATutorials, 2009).
- The initiatives of the Singapore government to maintain the country as a clean and green city is the primary political factor affecting the industry. The Clean Energy Program Office (CEPO) focuses on the regulation of clean energy in the country.
- Increased oil consumption in Singapore is one of the positive economic factors affecting the petroleum industry in Singapore. On the fillip side the new refineries in India, Malaysia and Thailand catering to the Asian market may affect the growth of ExxonMobil. Strong base in Singapore for petroleum refining strengthens the growth prospects. Frequent change in global oil price is yet another important economic factor affecting the industry.
- The demand for oil in the region is in the order of 24.1 million barrels per day. This is almost 30% of the total world’s demand and the demand is continuously increasing due to expanding population in China and India. This implies that there would be a pressure on the refinery feedstock shortages in the region and consequent rise in fuel prices in the Western economies. However there may not be any change in the demand pattern because of the diversity in the economies of Southeast Asian region (Lynch, 2008).
- The socio-demographic factors as they have changed in the larger economies of China and India have considerable impact on the demand for petroleum products which will have a positive impact on ExxonMobil’s future outlook in terms of sales growth.
- The building up of Jurong Island as the hub of petrochemical refineries with ultra modern facilities for waste treatment, warehousing, fire fighting, roads and drain infrastructure has provided the necessary technical excellence for ExxonMobil to house its major refineries in Singapore (Pillai, 2005).
- The development of logistics, utilities, and engineering and finance industries in Singapore as key supporting industries for the petrochemical industry has helped ExxonMobil and other players for sustaining their growth in the industry.
- Porter’s Five Forces – Threat of New Entrants – Low – barriers include high capital investment, economies of scale, wider network of distribution channels, environmental regulations and higher fixed costs in downstream and chemical products – entry of new players is difficult.
- Business Rivalry – High – large number of competitors and the commodity-based nature of products make the rivalry high.
- Supplier Power – High – suppliers are oil mining and extraction firms who control a major proportion of the world supply of oil and hence influence the price. Since Exxon buys oil in the open market, the suppliers have more power.
- Buyer Power – Low – both industries and individuals constitute the customers for Exxon. Industrial downstream buyer power is low because ExxonMobil is in a position to control the downstream supply and price. Individual buyer power is low because of huge demand for the products.
- Threat of Substitute Products – Low – the substitutes are nuclear power, hydroelectric, biomass, thermal, solar, photovoltaic and wind power. Environmental considerations restrict the proliferation of nuclear and hydroelectric power. Technological and cost considerations limit the use of thermal, solar and photovoltaic power sources. Biomass could be a potential threat; but demand volumes cannot be met either by biomass or wind power.
- Industry is attractive because the threat of new entrants is low, buyer power is low and the threat of substitute products is low. Supplier power is high; but this does not affect the attractiveness as large suppliers also represent large buyers (Miller, 2008).
Organization Analysis
This section presents the internal capabilities and core competencies of ExxonMobil.
- The largest volume in the world in terms of refining capacity, unique business mix, investment discipline, integration of chemical and petroleum downstream activities, world-class operating proprietary technology and product applications are some of the core competencies that contribute to the success of ExxonMobil (ExxonMobil.com, 2004).
- Capability to capture fullest benefits of integration across the different operations of the company and consistently delivering best-in-class performance are the internal capabilities that ExxonMobil possesses (ICIS.com, 2009).
- According to Rex Tillerson Chairman and President of ExxonMobil “To be successful requires a disciplined approach which looks through the petroleum and petrochemical business cycles to focus on the long-term viability of each project. We continue to identify and progress a diverse portfolio of world-class profitable investment opportunities, with over 60 major projects currently in development”. (ICIS.com, 2009)
- The company has entered into a long-term agreement with US based Symyx Technologies Inc for the development and application of High Throughput Experimentation (HTE) as a part of Exxon’s innovative strategy. The tools and techniques developed through this association will enable Exxon to generate and accelerate the commercialization of newer technological applications. This has widened the intellectual property portfolio of ExxonMobil (BusinessWire, 2003).
- The internal strengths of the company are depicted in the following figure.
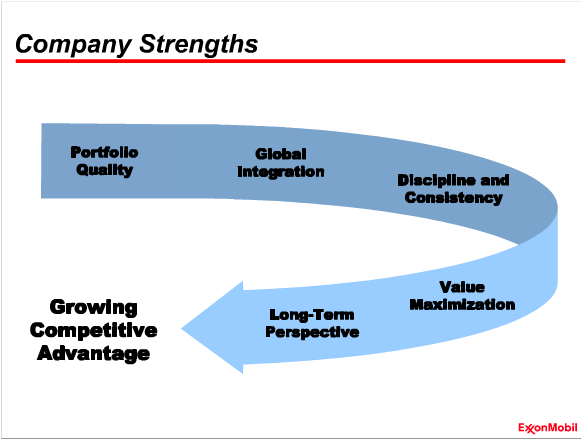
- A continued long-term commitment to research determining research priorities by business requirements enables Exxon to strengthen its market position among the competitors. This is complemented by the superior scale of the refineries of Exxon which proves to be a distinct competitive advantage for the company.
- The company has “an ownership interest in 46 refineries in 26 countries and distillation capacity of 6.3 million barrels a day”. (ExxonMobil, 2009) The company’s “global supply organization coordinates and optimizes the supply of crude and feedstock to the refineries and the off-take of products. It also optimizes a global logistics system that includes ownership interest in crude oil and petroleum-product tankers, more than 25,000 miles of pipelines and some 300 major petroleum products terminals.” (ExxonMobil, 2009)
- ExxonMobil owns three powerful brands which cater to the demand for quality fuel to millions of customers through its 42,000 service stations situated across the world. The company is also serving 700 airports and 300 marine ports which mark the ability of the company to maneuver a successful global business. These brands are found in 118 countries.
- The company has implemented leading-edge technology which ensures the company has a competitive advantage and the ExxonMobil Research and Engineering Company further strengthens this competitive advantage to cover the global markets.
- ExxonMobil is supported by ExxonMobil Upstream Research Company for developing proprietary technology in the areas of exploration, development, production and gas commercialization.
- Competitive advantages to remain sustainable should meet the criteria of being unique, difficult to replicate, superior to competition, sustainable and applicable to multiple situations. The competitive advantages of ExxonMobil provided by its scale of operations, leading-edge technology, integrated resources and research and development initiatives cannot be replicated by any competitor, and are therefore superior to competition which makes them sustainable to ExxonMobil.
Gap Analysis and Strategic Alternatives
Gap analysis makes an assessment of the existing strategies of the company, and provides an understanding of any gap between the current strategies and required performance level. The analysis also discusses the strategic options available to get to the required performance levels.
- Through the statement on guiding principles, the company has stated its mission as “Exxon Mobil Corporation is committed to being the world’s premier petroleum and petrochemical company. To that end, we must continuously achieve superior financial and operating results while adhering to the highest standards of business conduct. These unwavering expectations provide the foundation for our commitments to those with whom we interact.” (ExxonMobil, 2009).
- Present strategy in terms of organizational structure with 10 core companies operating to cater individual business opportunities globally. This structure enables the company to determine the priorities on a worldwide basis and to transfer the technologies and best practices to units operating in different geographical locations. The company through its diverse workforce is able to capitalize on all available opportunities on a global basis. The procurement, information service and facilities for all the core companies are looked after by the ExxonMobil Global Services which functions as a centralized organization.
- Since the company financially performs in a sound manner with its well-designed organizational structure there does not appear any gap in the financial or other organizational performance areas. Therefore this report does not consider the financial implications on the strategic gap and opportunities. However there are still other areas where there appears to be a large gap which is discussed below.
- The business of ExxonMobil consists of upstream, downstream and chemical activities. The company participates in all major oil producing area in the world as a part of its upstream business. The company maintains large production base in several countries and the company’s current resource base is
- Since ExxonMobil Singapore is the downstream point of the whole organizational structure of ExxonMobil as a whole, it is strategically important that the upstream activities are maintained in its full capacity. This is the major area of gap where the company has to take care. The following points are to be noted in respect of this gap identified.
- Despite the strength acquired by the sheer volume and scale the company could maintain a flat production level up to the year 2004 (Banerjee, 2003). For instance the profits of the company increased by 38% the energy production fell by 1%. The company was also expected to replace 1.3 billion barrels of oil equivalents (Bryce, 2002). Therefore ExxonMobil has the tough task of taking care of the slipping reserve-replacement ratio as most of the oil reserves have been nationalized by the respective nations owning them.
- Even though the present Chairman and CEO could gain access to the fourth largest oil field of the world in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) and could end a five-year long deadlock on the development of large oil fields in Indonesia, there are still some grey areas where the company could advance its efforts for improving the resource base. For instance, the company, unwilling to submit the terms of the Venezuelan government in imposing higher taxes sold its rights to a Spanish company. This has affected the access to larger oil reserves by the company which will tell upon the performance of ExxonMobil Singapore which is dependent on larger oil resources of the company.
- Another gap exists in the area of development of alternative fuel than the traditional oil resources. With the global oil industry poised for dramatic information it is important that the company look for alternative ways of meeting the demand. This is essential despite the fact that ExxonMobil has a large oil resource base.
- While major competitors of ExxonMobil are investing more in cleaner alternative energy, the company considers it important to invest more in technology for better productivity on the petroleum products. Strategically there is a gap exists in this area which needs a closer look.
- ExxonMobil is of the view that renewable energy sources like solar and wind are non-viable businesses and therefore the company considers investing in these areas is not worth. The company understates the importance of the alternative fuels on the ground that it may take another 30 years or more for the world to switch to alternative energy sources.
- With the increased demand for oil and depleting supply sources investing in alternative fuel sources would prove to be a prudent business decision to sustain the market position of ExxonMobil. However there is an argument that, as the history of oil goes there can be no other substitute product for oil which could easily replace oil.
Strategic Options and Choice of Strategies
Gap analysis on the present strategies of ExxonMobil in the matter of development of alternative fuels would lead to consequences which are detrimental to the interest of the stakeholders. The company exposes itself to greater risks that it has to face in the event of changes in the governmental policies to reduce emissions.
- Damaged reputation is the major risk that Exxon is taking by not taking initiatives in the direction of developing alternative fuels. The company may also have to face several litigations in respect of climate-change related issues. Tobacco industry may as well serve as an example in this issue. The losses to the company on account of such litigation would be substantial, affecting the interest of the stakeholders to a large extent (Mansley, 2002).
- More than anything else the company is likely to miss out several business opportunities which would otherwise be available to the company, if it supports a mandatory framework to reduce greenhouse emissions. First the company has potential opportunities in cashing in on its huge cash reserves. Exxon has the potential to convert the company into a total energy business with a substantial market share (Odland, 2006).
ExxonMobil has the following strategic options to follow to ensure a sustained growth and market position. At the upstream level, the strategic choices include:
- Identifying and pursuing all attractive exploration activities
- Investing in projects that deliver superior returns
- Maximizing the profitability by increasing role of higher and improved technologies
- Higher investment in development of alternative fuel options
- Demonstrating a leadership position in low-carbon technologies
As per the 2004 Report of ExxonMobil on alternative energy sources the company has to cater the increasing demand for oil during the intervening period by increasing production (ExxonMobil, 2004). Till such time the alternative energy sources rise up to meeting the major demand fossil fuel would continue to have a predominant position. This calls for integrating the company’s resources more efficiently so that higher productivity can be achieved. The likely requirements are exhibited in the following figure.
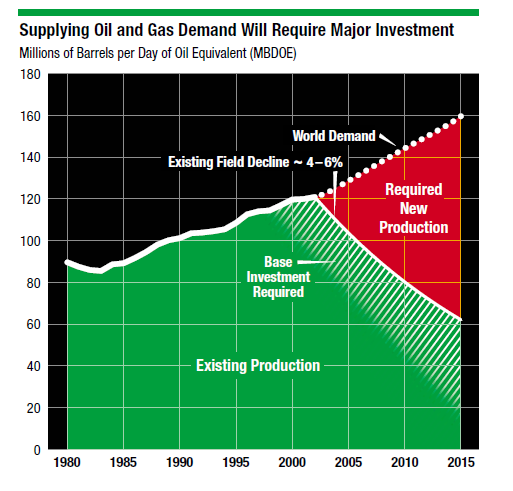
- Therefore strategically the company has to focus on integrating the oil resources by getting access to more oil fields and integrating them with the existing resources. It is imperative that the company continues to increase its investments in research and development on new technologies to sustain its present position in the area of petrochemical industry.
- However, the company can maintain its commitment to its shareholders as embedded in its mission statement by avoiding the substantial financial and competitive risk to which the shareholders are exposed because of the indifferent stance taken by ExxonMobil in the matter of protecting against climate change and its consequences (Logan & Grossman, 2006).
- The next strategic option for the company apart from integrating the present resources is to increase its investments
Implementation Plan
This section elaborates the actions required to be taken by ExxonMobil to put into practice the strategic choices discussed in the earlier section. Even though several steps have been taken by the company in the direction of executing the above strategic options, it is worth considering some of these for rapid progress.
- Strategy implementation focuses on the translation of strategy into possible action scenarios. There are different parts of strategy implementation that need to be followed. These parts include: planning and allocation of the required resources, changes in the organization structure and design, managing strategic change.
- Managing strategic change is the critical aspect of implementing the strategic choice which needs operating different mechanisms concerned with organizational redesign, changing day to day routines and cultural spectrum of the organization and acting to overcome political and cultural barriers to changes.
- The objective of implementing the strategic choices is to maintain the leadership position in the core business of ExxonMobil. This necessitates being the most efficient competitor in every aspect of the business of the company. It also involves capturing a quality investment opportunities and at the same time maintaining a selective and disciplined approach.
- “Maintaining a high-quality portfolio of productive assets – Developing and employing the best technology – Ensuring safe, environmentally sound operations – Continually improving an already high-quality work force in a high-performance climate across the organization – Maintaining a strong financial position and ensuring that financial resources are employed wisely,” (Allbuisness.com, 2000) are some of the other objectives of an effective implementation of the strategic options.
- The strategic choice should enable ExxonMobil to meet its high investment standards and adherence to fundamental strategies should produce superior long-term returns. This calls for gaining access to major oil fields in different countries by a diligent negotiation with the governments for acquiring the access at economical costs.
- In order that the company is able to realize its long-term investment profile though business cycle, increasing the investments in technologies for improving the utilization of the existing resources to the maximum becomes an absolute necessity. This would involve development of better exploration and refining techniques. The implementation of strategic choices in this respect should enable the company to avoid inefficiencies associated with substantial changes in the year-to-year spending levels.
- The strong financial position which ExxonMobil enjoys consistently over many decades would enable increasing the efficiency in the transportation of oil and gas so that the cost can be economized. ExxonMobil should be able to pursue attractive projects and initiatives in this area, which the competitors would not be able to practice. The implementation of strategic choices will help the company the quality of its earning over time.
- The company should undertake tests on potential investments over a wide range of economic scenarios and adopt those projects which could promise resilient returns in the long-run in tune with the development of alternative energy sources. To accomplish this the company should consider increasing the investments in research on the development of alternative fuel technologies
Evaluation Plan
The current and future strategic choice of an organization may be evaluated by adopting several judgmental criteria such as critical success factors, desirability of the strategy, comparative or competitive advantage resulting from the implementation of such strategy, feasibility of the strategy in terms of functionality and profitability, appropriateness with respect to the time and purpose of implementation, knowledge and competence level prevailing in the organization, consistency in deriving the anticipated benefits from the strategy to be implemented and the ability of the organization in facilitating the change or innovation resulting from the implementation of the strategy.
- The identification, evaluation and selection of an adaptive strategy is a complex process in a progressive organization as in the case of a mature organization like ExxonMobil, the adoption and announcement of a strategic choice should take the company in a new direction. The strategy may relate to new market entry or one to counter the moves of the major competitors. It is important that the company evaluates the impact of the implementation of the strategic choices to ensure that the company could derive the anticipated benefits out of the strategy implementation.
- In any case, an evaluation of the strategic choices is an important step that the organization should follow after implementing a strategic option. Since the strategy change may always focus on one aspect of the strategy without considering how the strategy interacts with other strategic initiatives, the evaluation plan becomes all the more important.
- The following course of action may be followed for undertaking the evaluation of the implementation of the strategic choices.
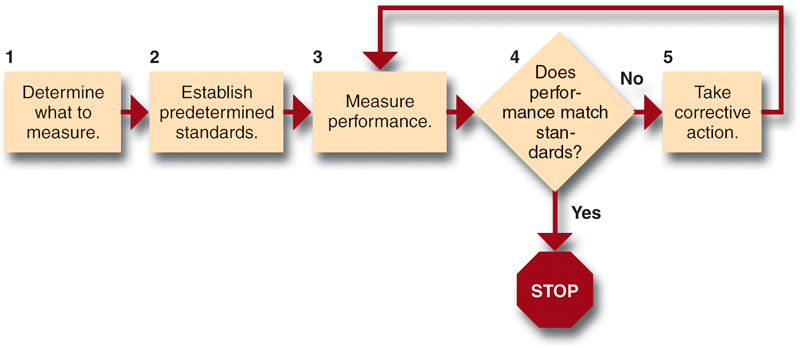
- Performance data and activity reports forms the information base for evaluation and these can be described as the control information.
- Controls may be behavior controls, output controls and input controls. Behavior controls determine how something can be accomplished through the introduction of policies, procedures, rules and system operating plans. Output controls encompass the things that need to be accomplished through strategy implementation. The focus of output controls is on the end result which can be attained through performance targets. Input controls represent measuring the adequacy of resources in the form of skills, abilities, values and motives.
- In the case of ExxonMobil ‘benchmarking’ can be used for evaluating the performance of the company on implementation of the strategic choices. Divisional and functional performance can be measured by establishing standard cost centers, revenue centers, expense and profit centers and investment centers.
- Benchmarking is a process undertaken continuously to measure products, services and practices against the toughest competitors or those companies which are recognized as the industry leaders. For ExxonMobil the company has always to gather information on the moves and actions of competitors and adopt suitable benchmarks for measuring its own performance in different areas where the company has implemented strategic choices.
- Performance criteria indicators such as the benchmarks and the elements associated with them may be expressed in quantitative physical terms such as unit quantities, frequency, and time, variation from the benchmark or the expected level of output quantity or service provision. The quantitative financial terms may include monetary value, revenue, cost efficiency, added-value, best-value, profitability and return on investment. For ExxonMobil these are the qualitative standards that may be suitable for deciding on the strategic choices in the case of development of new technologies in the existing core business functions.
- The qualitative terms may include degrees of relative acceptability, variation between the positive and negative customer attitudes, assessment of intangible service attributes, definitions of successful outcomes in terms of improved technological measures resulting in high-quality of refining. It is highly important that the performance evaluation criteria are clearly stated and easily understood and are capable of easy interpretation and unambiguous.
- For instance, in the matter of development of alternative energy sources, while the competitors are making large investments in research leading to the development of alternative sources of energy, ExxonMobil can draw its own benchmarks for the company’s initiatives in this direction. The following product and process innovation life cycle may help ExxonMobil to decide on the further investments in the technology relating to the development of alternative energy source.
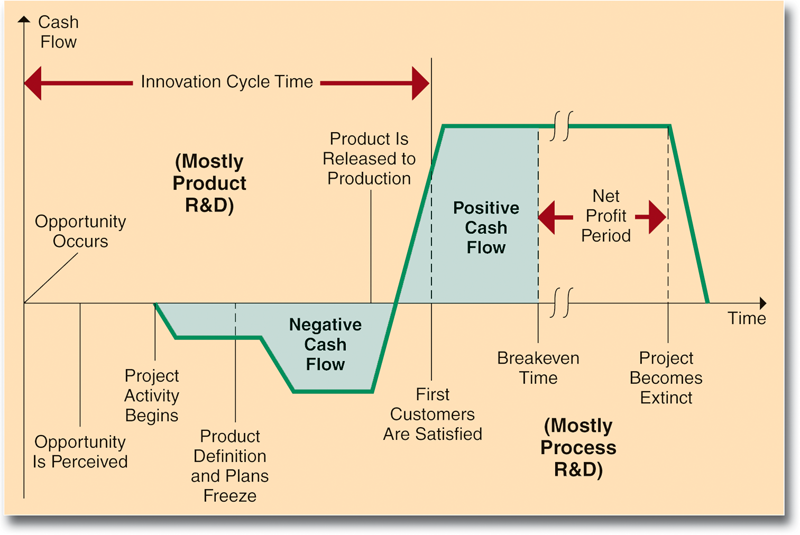
- In the matter of development of up to date technologies for the existing core business of oil exploration, revenging and distribution the company as an evaluation measure test is technological competence and its absorptive capacity. The company should decide on the categories of innovation based on the following strategic scope as evaluated from time to time so that the company can have an effective control in redefining its technological innovations and control further investments in this area.
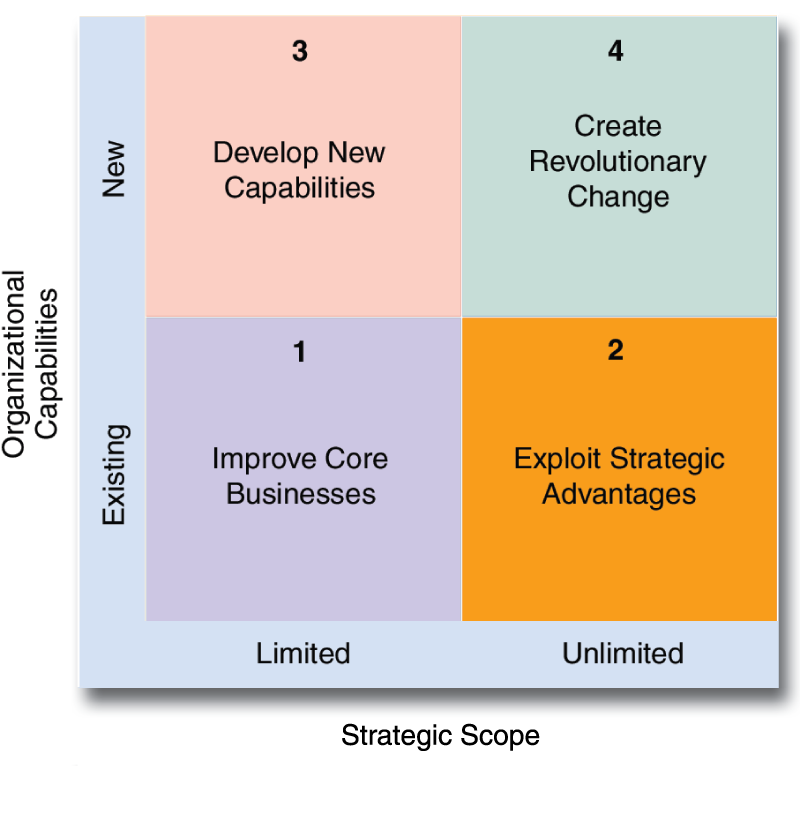
Although no specific plan can be suggested for evaluating the implementation of the strategic choices, the company can develop its own benchmarks for the acquisition of oil reserves and introducing other economies in production by comparing the industry standards. In the matter of involvement in the development of alternative energy sources, the company can form a consortium of like minded players of the industry to promote the research in this area.
Conclusion
In view of the continued increase in demand in the short run, it becomes imperative that ExxonMobil has to focus on sustaining its market position by improving on its oil reserves and employing improved techniques for economizing the production. The company should also undertake efforts to improve its market share on the gas-based energy provision. The company should involve more on the development of alternative energy sources, in line with the major competitors not only for thwarting the criticisms but also to contribute genuinely to the development of alternative energy sources to protect mankind from the adverse consequences of climate change. This would automatically prove to be a strategic move for the protection of the larger interests of the internal and external stakeholders of the company.
References
Allbuisness. 2000. ExxonMobil Strategic Planning – enhances long-term shareholder value. Web.
Banerjee, N., 2003. Market Place; For Exxon Mobil, Size Is a Strength And a Weakness. Web.
Bryce, R., 2002. Bush Is Wasting His Energy and Ours on Old Ideas. Web.
BusinessWire, 2003. ExxonMobil and Symyx Technologies Embark on Five Year High Throughput Experimentation Alliance. Web.
ExxonMobil. 2004. Capitalizing on Core Competencies. Web.
ExxonMobil, 2004. A Report on Energy Trends, Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Alternative Energy. Web.
ExxonMobil, 2009. Global Capabilties for 21st Century. Web.
ICIS. 2009. ExxonMobil | Strategy and Financial Highlights Information from ICIS. Web.
Logan, A. & Grossman, D., 2006. ExxonMobil’s Corporate Governance on Climate Change. Web.
Lynch, M., 2008. Exxon Mobil, Royal Dutch Shell, Singapore Refining dominate region’s exports. Web.
Mansley, M., 2002. Risking Shareholder Value: ExxonMobil and Climate Change. Web.
MBATutorials, 2009. Porter’s Five Forces Model. Web.
Miller, R.J., 2008. Why are Oil Companies so Profitable? Web.
Odland, S.K., 2006. Strategic Choices for Managing the Transition from Peak Oil to a Reduced Petroleum Economy. Web.
Pillai, J.S., 2005. Cluster Development: A Case of Singapore’s Petrochemical Industry. Web.
Porter, M., 1980. Competitive Strategy. New York: Free Press.
