Introduction
This CFO report is going to focus on the renowned Colgate- Palmolive Company. It is one of the world’s largest cosmetics and toiletries companies which are serving various consumer goods for more than consumers of 200 nations with 36600 employees. The company has been founded in 1806 under the governance of State of Delaware, 1923. Its major goal is to offer well and enjoyable goods to the target markets. Colgate’s major international brands involve the integrated core functioning of oral, personal, home and nutrition of pets.
Its vital product lines are composed of bar soap, liquid soap, toothpaste, toothbrush, home cleaners, deodorants, detergents for dishwashing etc. It is being the market leader in various item categories of the popular personal care, liquid hand wash, soft shower gels, and spring soaps segment. Such criteria of product line introduced Palmolive as a global leader in the market. Outside of home country, those product lines also involve Palmolive conditioner and shampoo for which it is the recognized top brand in Latin America and Europe. The company has highly effectual investment in research and development and in this purpose the company has incurred about $253.1 million in 2008. Colgate-Palmolive Company (2008) expressed that it normally uses direct distribution network with some sort of brokers and distributors engagement.
Major packaged and raw materials supplies come from outsider corporations. Facing an intense global competition, basic trademarks involve Palmolive, Colgate, Softsoap, Elmex, Axion, Tom’s of Maine etc. Recently, it is running with greater success through a strong financial performance in the last financial year with. For example, the company has increased sales volume more than 4% involving each of the functional units in total growth, merely duel profit, income and EPS (Earning Per Share) and obviously the rate of dividend.
Corporate governance readiness
DiPiazza, S and Eccles, R., (2009) reported that in 2002, as a consequence of the serious fall down of Enron and WorldCom, the U.S. government has engaged its effort to recover public confidence by enacting Sarbanes-Oxley Act 2002 and now companies are bound to follow this act for external and internal control of the company. Besely, S., & Brigham, E. F. (2007) argued that generally, corporate governance focuses the relationships among shareholders for shaping and controlling the strategic route and performance of the corporation.
In this focus, Colgate occupies a running obligation which is being shared by the Board of Directors, general employees and the appointed management team. It must involve the basic business tactics, product criteria, international brand image, employee development programs and the top corporate standards. All of those motives are being carried and implemented upon this team of governing bodies. Some integral features of this corporate governance system are as below-
- Board of directors: – According to the board, a director ought to have flexible relationship with the entity along with the top management. It generally reflects the director’s capability for making unbiased decisions and adjustment with unique standards on such rules. The board is composed of external individual directors from 1989 – 2007 periods, exception Reuben Mark as Chairman and CEO. Today, Mr. Cook is the president and CEO who has been selected as Chairman. Following the explanation of this Board, the company valuates corporate skills, learning and community service areas, global experience, educational requirements, proper ethical behavior and variety. The board’s independence has been extended by a continuous practice of the executive session rather than the CEO. A president director guides these meetings who perform according to the required guidelines of governance committee. All of individual directors have 1 year session as president one based on the specific scheduling. Cahill, Conway, Hancock, Johnson, Kogan, Sadove, Lewis are some of the directors of the board [Colgate-Palmolive Company (2008)].
- Priority sector and leadership: – The entire strategic techniques are handled under the board’s supervision. Revising strategic roadmap and accumulation the summary of per year of crucial areas for execution are two of the major tasks. Additionally, it occupies vast introduction in sequential planning and HR development concentrated mostly on series of CEO. Discussion on capable successors to top personnel, historical evaluation, skills and proper growth tasks are also performed by this.
- Nature of communication: – The directors have regular and straight communication with the management team from the internal and external part of the formal boardroom. Top management continuously with the directors in the meeting session. Informally, they join in open discussion on different legal tasks. In the formal meetings, directors are asked to make questions along with possible solutions to senior executives. This sort of wide communication has been enrolled by the smaller corporate board that emphasizes on frankness and active participation.
- Direction of policies: – Colgate-Palmolive Company (2008) stated that the “Guidelines on Significant Corporate Governance Issues” as developed in 1996, are revised to judge standards. Lawful charters identify responsibilities of the Board and thus lead their operation. Also, Colgate’s conducting codes and basic business guidelines are supported by the Board for promoting the top ethical functionality in all forms of transactions and commitments. During the last year, Code of Conduct has been refined and spread over the global workforces.
- Integration of financial reports: – The board has a high commitment relating to quality, reliability and clarity of the company’s financial statements. Such commitment is replicated in long- term techniques and proceedings regarding in-house audit committee for the supervision monetary regulations over the world. Individual auditors having a board authorization as well as an Audit Group for such supervision.
- Better governance: – The global Colgate HR is entrusted for delivering caring, regular development and integrated team effort and value- added services. Such tasks also consider open networking, group work and individual responsibility. Continuous effort for sharpening better governance is helpful for fresh organizational culture along with broader objectives.
- Frequent development programs: – Annual report (2008) published that it is the responsibility of the board for annual evaluation of its financial performance in terms of the important criteria. Such criteria involve monetary supervision, continuous planning, and compensation of top personnel, corporate governance, conformity, strategic orientation and ethical issues. Personal evaluation is also required besides the Board Charters. By harmonizing this two fold assessments, an independent director examination system has also been developed within the board. Here, peer assessment process is run upon in few years by them. Such reaction is potential for recognizing the strong and effective criteria through a mutual coordination.
- Controlling process: – Corporate management lies in the observation of the governing bodies, essentially supervised by the CEO and CFO for conducting an effectiveness analysis regarding Colgate’s disclosure monitoring procedures. Result of such evaluation has been proved in SEA effectiveness.
- Internal control on financial result: – Management bears the responsibility to make an internal control. It is also governed by the previously mentioned bodies to ensure its accuracy with US accounting principles. It follows COSO for “internal control- integrated framework”. Its assigned professional public accounting company named as PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP makes audit to analyze the financial statements.
- Altering of internal control: – No scope has given to make any change to that control in financial reports.
- Other factors: – Other important rules and principles of corporate governance have clearly been identified in Section 16(a) – Exchange Act through a reference of Proxy Acts in the yearly meeting of 2009. Some of the most important aspects are
- Code of Ethics: Any sort of new amendment regarding this code is quickly being adjusted to the corporate web site. However, the company does not accept any waiver to the standard rule. But for an emergency when it offers waiver to any top executive, it certainly puts that information in the web site by following the rules of SEC.
- Compensation of executives: The executive compensation plan is set upon by Proxy statements in the year 2009.
- Advantageous factors for the owners, management team and equivalent stockholders affairs: It considers a lot of issues, like: –
- Required information of security ownership for certain beneficial parties are positioned by Proxy statement.
- The stated equity compensation schedule for the year 2008, 31st December can be shown as-
- Relationships, contacts and independence of directors.
- Rules regarding the accountant charges and services.
- Receiving loans from Bank of America, BNP Paribas, Citibank N.A, HSBC, Northern Trust Company etc.
Recommendation to Sarbanes-Oxley Act
While Colgate’s governing body has complied with the Sarbanes- Oxley Act, 2002, the purpose would be to make an improvement in the interior control processes of Colgate-Palmolive. Sec.gov, (2009) stated that the intended advantages derived from this Act could be experienced by the stakeholders. So, it is essential for Colgate to cope with various related aspects of the Act, especially section 404, such as
- The company must utilize informal decision for documentation and examine its management for coping with individual functionality, vulnerability and techniques.
- Management of Colgate should involve Form- K as an estimation of ICFR (Internal Control over Financial Reporting) in its yearly financial reporting.
- The outsider auditor should offer 2 options for each audit of the firm regarding an individual process and a general mechanism.
- Management must conduct an assessment of “material weaknesses” regarding the internal controlling plan.
- Section 302 is another effective way for ensuring more control. It requires that it is not essential for having ICFR over other monetary statements, insider decision issue or obtaining discharge substitute statements.
- The ICFR technique should be extended to procurement, management of inventory, production, sales and IT which would not be in the criteria of CFO.
- Management should examine each quarter of the report regularly. If it is not fully possible, it should perform partial functionality.
- Determination of spreadsheet for supervision through an introduction of transitional database for initial control issue.
Financial Statement and Policy Analysis of Colgate- Palmolive
Financial Statement Analysis
For proper financial statement analysis, first it is important to know the amount of Balance Sheet, Income Statement, and Cash Flow Statement. The combinations of these financial statements are considered as Consolidated Financial Statements. From the Annual Report (2000 to 2008) of Colgate-Palmolive Company, the consolidated financial statements are found and combined below for further analysis of the report. (Colgate-Palmolive Company, 2008)
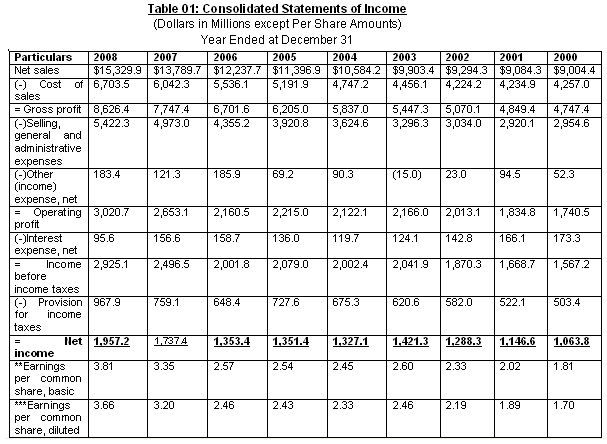
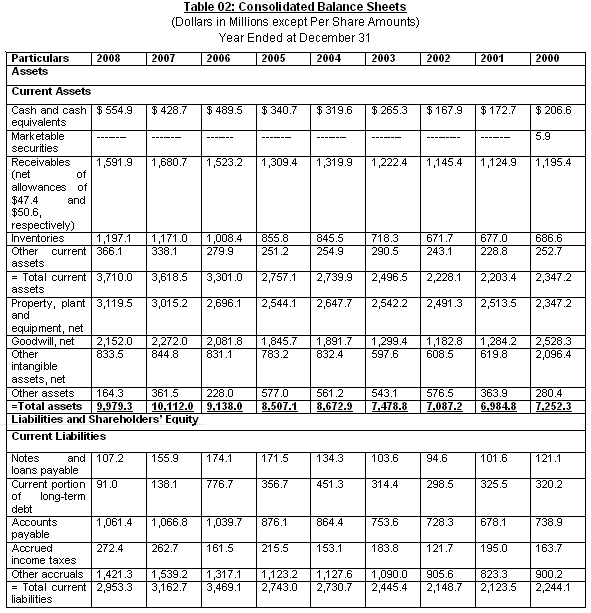
Common Size Analysis
OCFO, (2009) added that the common size analysis is used to analyze the financial statements of Colgate- Palmolive Company, with the previous period’s or with the entity of one another of financial statements. It is mainly focus on the measurement of size of standard financial statements with trends over time. For Colgate–Palmolive Company, the common size analysis is done for financial statements of Balance Sheet and Income Statement. There are mainly two ways to analyze common size financial statements:
Horizontal Analysis
When the common size analysis is measured within two periods (must be immediate periods to one another) known as Horizontal Common Size Analysis. For Colgate- Palmolive Company, the period of 2008 and 2007 has been taken as the basis of latest statements. The way of calculating the Horizontal Analysis is shown below:
Horizontal Analysis= (Current Period’s Entity- Previous Period’s Entity) * 100/ Previous Period’s Entity
For Example, Horizontal Analysis of Net Sales= (Amount of 2008-Amount of 2007) *100/Amount of 2007 = ($15,329.9- $13,789.7) *100/$13,789.7 = 11.17%
By horizontal analysis of each entity of Income Statement and Balance Sheet, the balance of entity between two periods is measured. After the analysis, the warning would be identified according to Schilit, H (2002), in Financial Shenanigans.
Vertical Analysis
When the common size analysis is measured with the item of interest with the reference item, is considered as vertical analysis. For Colgate- Palmolive Company, the vertical common size analysis is done for recent two periods, 2008 and 2007, taken from the Annual Report of the company. The way of calculating Vertical Analysis is shown below:
Horizontal Analysis= Item of Interest * 100/Reference Item
(Reference Item: For Income Statement= Net Sales For Balance Sheet = Total Assets)
For Example, Vertical Analysis of Net Income (From Table 4, 2008)= Net Income *100/ Net Sale s= $1,957.2 *100/ $15,329.9 = 12.77%
By Vertical Analysis, each interested entity or item is measured according to the total amount of reference item, to measure the portion of interested item comparing with the total assets or total sales portion of Colgate- Palmolive Company. Schilit, H. (2002) pointed out some warnings those are analyzed below the table.
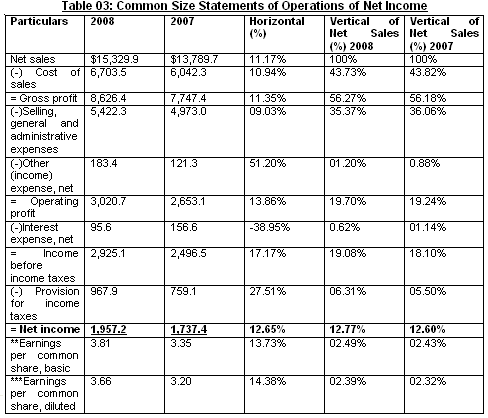
Warning Sign found Using Vertical Analysis
From Income Statement of Colgate- Palmolive it has been demonstrated that the Selling, general and administrative expenses has increased with Net Sales and increased Income Taxes. Colgate- Palmolive’s Inventory represents larger portion, total current assets or amount of Liquid portion is higher in hand when there is excess expenditure for property, plant and equipment and loosing value of Goodwill.
Trend Analysis
Trend analysis is another method of Financial Statement Analysis, to represent the collected information in a pattern or trend. In a trend, the historical data are used to predict the future outcome and to overcome uncertain events.
The trend analysis of Financial Statements of Colgate- Palmolive Company is given below:
Trend Analysis of Income Statement
Income statement is represented with the help of Net Income of Colgate- Palmolive Company. The trend of Net Income is shown below:
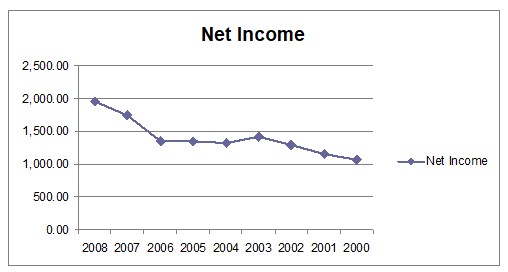
From the trend analysis of Net Income of period of 2008 to 2000, it is seen that, the net income of Colgate- Palmolive Company is increased every period. The increase was started in large scale from year 2006. So, it can be estimated that, in 2009, the scale of Net Income will be increased more.
Trend Analysis of Balance Sheet
The Balance Sheet of Colgate- Palmolive Company is represented with the help of total assets, total liabilities and total shareholders’ equity, which is shown below:
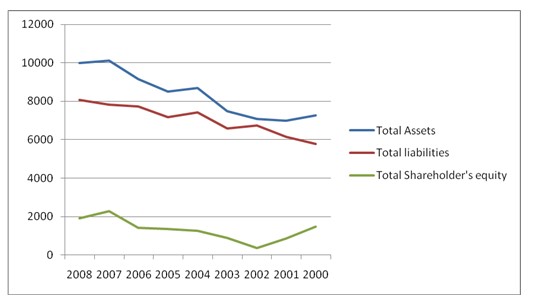
The total assets, liabilities and shareholders’ equity are increased from 2000 to 2008 with a high rate. The shareholders’ equity is increased in current time, but also high in 2000. So, assets and liabilities are increased, but considering previous situation, the improvement of shareholders’ equity is not equitable in current period.
Trend Analysis of Cash Flow Statement
The analysis of cash flow statement of Colgate- Palmolive Company is shown with the help of Cash and Cash Equivalents at the end of period 2000 to 2008, which is:
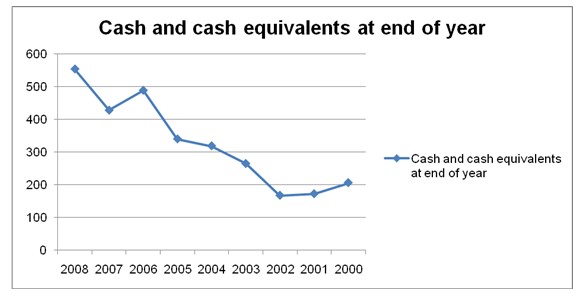
From the figure, it is identified that, the cash and cash equivalents items are more in hand in every year. But the portion is increased more and more with every period, which is not good for Colgate- Palmolive Company. Because, as the company has more liquid portion in hand, the chance to utilize the liquid in investment is decreased.
Hidden Information about Financial Statements and Notes to Public
There are no hidden items in the financial statement in the Annual Report of Colgate- Palmolive Company in the Consolidated Financial Statements. There are some items which should be included in the notes but not presented in the Colgate annual report 2008. So considering those items as hidden here some items are discussed briefly:
Investments
There are two types of investments which should include in the notes with their market value. These are investments in corporate stocks and investments in marketable bonds. Management determines the estimated value of some marketable investments like real estate and private equity investments. So, this item is an important one which should include.
Organization and its purpose
The organization’s full structural appearance is important. The mission vision and goals must be included in this section.
General idea about the business
What is the mainstream business and what are the sections of this business is also an important note, which should be included. Here the characteristics of the business operations and the consequences of the business should also be discussed.
Foreign currency
Any foreign currency hold by the entity must be a crucial factor as a tax purpose. So, clear identification of the amount of having foreign currency should be presented in the note.
Promotional costs
The amount spent for the advertising and promotional purpose is also important. To indicate the marketing expense, it should be included in the note.
Accounting standards
For their transparency and financial condition, which accounting standards are being used by the company is an important indication. The changes in the accounting standard should also be included along with the presence of the present accounting standards.
Business combination
Any acquisition or merge with other company is a crucial item. So, it must be making clear that whether any acquisition or merge has occurred or not.
Risk association
It is important for the investor’s to learn about the risk associated with the business to invest. So, clear picture of risks associated with the business is necessary.
Research and Development
As a business entity Colgate has to do many research and development activities which costs a lot. So, in the notification area the research and development programs and activities and associated costs should be clearly mentioned in the note.
Risks associated with the business
Clear identification of risks is necessary to ensure the potential investments about investing with the company. So, it is also an important item.
Risk assessment
USA Today (2008) stated that the Colgate- Palmolive Company is generally facing major corporate risks from its worldwide international functioning. Other associated risk factors are assessed as following
As the company earns about 75% of its net sales from outside of the home country, for assessing total risks, geographic variety takes a very important role. Here, such factor is also effective in minimizing risk in a single or whole operating area of the world. It indicates that the entity is in the criteria of complete global risks, but not restricted in that concern. However, some other integral visions in this regard as below-
- Fluctuation in rate of exchange. It can deduct the home country currency value of profit from global markets or raise human or supply expenses in that zones.
- Colgate is facing devaluation problem in Venezuela for excessive controls in exchange and other restrictions.
- Vulnerable macroeconomic conditions, political and economic instability in international markets.
- Improper legal interventions in different zones.
- Problems of foreign ownership, expropriation and patriotism.
- Impact of local and overseas regulations for negative tax impact, burden of trade limitation and government invasion policies.
All those can affect in the regular functionality, finance and cash flows for which it checks overseas currency contact by cost- control approach, raises sales prices and equivocates foreign reserve.
- The instability in international financial markets along with the monetary recession is another risk issue. For the tremendous downfall or bankruptcy of any financial partner, lower lending capabilities can be resulted. Inflexible market conditioning will also generate trade disorder with some vendors, contract producers and customers. Additionally, for recession, consumers could shift brand loyalty which will lead low sales and margin.
- Larger global competition could generate threats in terms of pricing, promotion, advertising and brand extension. Lack of appropriate prediction and adjusting the expenses of competition are alarming while Colgate’s trademark, patent and goodwill act as defender against those strong forces.
- As the items are placed in highly competitive international framework, trade attention and existence of mega- retailers and discounters are causing problems. For this, reliability on certain retailers generates low profit for the superior bargaining power of them, discounts and holding allowances. De- stocking of supply, limited shelf- space, delisting etc. are also problematic.
- Success dependency on current and new product along with expanding lines is being experienced by consumer and retailer acceptance insecurity in the competitive landscape. Those factors are also been affected by-
- Emerging and financing technological creativity.
- Maintenance of trademark and patent.
- Government acceptance and registration of restricted items.
- Acting with FDA (Food and Drug Administration) for consumer need and choice predictability.
- Raw items including tallow, soybeans and corns are becoming expensive. Energy factors, shipping and other associated costs are also negatively influencing the profitability in terms of higher prices or obtaining cost efficiencies in production or supply chain. Shift towards outsider vendors for ingredients and additional supports for cost and efficiency purpose has been yielded in the scenario of extreme dependence on them. As some new vendors are not as standard up to the legal and industry level, extra capitalization may increase cost.
- Proper protection of corporate goodwill with consumers and other business associates is very much complex in world wide distribution of the brand. For this, the company employs huge time and assets regarding business ethics, quality insurance, sustainability and protective policies. Basically, negative promotion, product misrepresentation and alteration can generate lower demand. Equivalently, periodic third party fake selling causes customer confusion in terms of poor quality, safety, and ultimate brand equity. All of those factors may have a negative appreciation over corporate goodwill with the requirement of reformulation.
- Significant problem exists in terms of vast local and foreign regulations in all the phases of production, packaging, maintaining, delivering, promotion and sales. Such as-
- Topic of US trade regulation as well as accepted by Food and Drug Administration (FDA), Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSF) and Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
- Regulation of US Trade Commission.
- Regulation of overseas nations of production and distribution.
- Intervention of authorities of competition.
All those issues may target Colgate for fining, harming, recalling of merchandise, criminal image etc. If a claim is proved as fake one, the adverse appreciation regarding the items would be harmful for the brand name. As a better response, the company has achieved all essential approvals although the excessive inflexibility is still threatening. For example, the use of triclosan in toothpaste, liquid hand wash and protex bar soap are being subject of the inspection of EC, FDA or other regulatory bodies.
- Since Colgate- Palmolive is involved in production, origination and materializing of goods on a global content, some initial risks accomplish those tasks. Some of them can be as bellow-
- Access to raw items.
- Uncertainty and other health and security factors.
- Ecological impact.
- Labor union consideration with strike and work disruption.
- Logistical interruption.
- Rebuilding or damage of major production spots.
- Ingredient, security and quality concern.
- Licensing as well as other restrictive objects.
- Natural accidents, terrorism, depression and other uncontrollable variables.
Since the organization has stability and backup plan for the basic production plots and supply of ingredients, tremendous collapsing in production for any of the above issue can distort regular supply and business flow. Simultaneously, if the present usable items or finished products are found to be faulty, a product recalling would become essential, the brand equity and appreciation would be reduced and it would misplace the projected market share.
- Finally, the corporate success factor is largely varied upon the sincere role playing of management and employment structure. Because of the firm’s inability for achieving and holding qualified, expert and capable human resources, negative impact on material feature can also be predicted. In this phase, appointment of incompetent CEO and top employees could also be financially threatening. Here, it must follow a structured, upgraded planning procedure for placing senior and other top executives.
For managing several risks, Colgate is effective in monitoring task by a through analysis of cash flows, sensitivity and company value. Here, market coverage is explained through a value- at- risk (VAR) and Earning- at- risk (EAR) model for calculating the highest possible loss in rate of interest, goods oriented monetary tools and foreign currency rate through an assumption of 95% confidence scale. All such variables are utilized for instability estimation and association with forthcoming rates. The calculated per day potential loss is immaterial for the 2007- 2008 functions while variation may occur between actual and estimated outcome. Growth in international monetary market would be responsible in this regard.
Shareholder value
Colgate- Palmolive Company is highly responsive in maximizing its intended shareholder value in the long and short- run. For this, the DPS (Dividend per Share) has been increased significantly from $1.40 to $1.56 recorded for 2007 and 2008 along with a positive performance in sales volume, operating profit, cash flow and quarterly dividend flow. Some of that value generating approaches is as following
- The renowned 2004 restructuring effort has improved the company’s competition capability. As a result, the international supply web, accumulated assets to emphasize sales and overall marketing performance has been improved. Because of the various profit maximization programs, overall corporate worth has been emerged which is contributing greatly to generate major shareholder monetary value.
- Additionally, the company is ready enough to face external and internal challenging variables by monetary situation, strategic focus, long- run experiences, stronger customer integration, innovative approaches and leadership. All those variables take part in raising long- run shareholder value.
- Major strategic concern focuses on building closer relationship with prospects, consumers and customers, introduction of innovation throughout each phase of the operation, introduction of competence and value proposition and tactical leadership in operational criteria.
- For maximizing customer value as a common technique for enhancing sales. In terms of improving shareholder’s equity, Colgate makes geographic centered development strategy. Such as, in India, the company researches upon scientist’s view upon the health factor of this product. It is also being effective through a chemist educating program by a deep impact on 30% raise in using Colgate toothbrush. To have a quick reach to customers, Colgate is also using various IMC or Integrated Market Communication Tools involving “Feeding in Believing” campaign. Fulfilling customer demand through an introduction of soft soap and liquid hand soap, Palmolive liquid dishwasher etc. have been emerged with related health concern and beauty is also contributing higher sales margin.
- Partnership with dental expertise is one of the major catalysts for expanding global credibility and overall market share. In this regard, it has also established a customized web site for getting and patronizing professional support.
- Since the company poses a glorious past of a friendly and flexible relationship with the local retailers, mutual development is being achieved from such motto. So, to make this continuation, the company is performing shopper marketing programs. This program is highly being successful in USA. Other than that program, the combined business arrangement has been designed to progress distribution network for devoting more customer value and service. Since, the company’s major sales revenue comes from mini- local stores; selected workforces frequently submerge them in a shop for gathering a single day shopping experience.
- Innovation is playing as other progressive approaches for maintaining high growth rate of the company. Innovative approach does not only existing in product introduction but also each and every phase of operation. Colgate is also proving its innovative efficiency by brand leveraging via internet and mobile phones.
- For improving its supply chain management, now it is using software named as SAP. Change in management of production as well as position of plants, it is being very much successful in Brazil. This country based changing schedule is offering a high growth potential through a larger quantity of exportable earning. Being tuned with a motto of achieving the top point of effectiveness and efficiency, it has evolved a factory functionality and reliability program in 2008. Colgate Business Planning or CBP is another effort for the purpose of saving a huge amount of money which turns in more shareholder reserve. Cutting 24% costs in recruitment procedure in the same financial year is one of the important examples in this regard.
Performance Measures of Colgate- Palmolive Company
(All figures are in million dollars except per share amounts)
Liquidity Analysis Ratio
Liquidity ratio shows the relationship of Colgate- Palmolive Company’s cash and other current assets to its current liabilities.
Current Ratio
By this, the portion of current liabilities are covered by current assets are considered.
Current Ratio = Current Assets/ Current Liabilities
For 2008,
Current ratio= $3710/$2953.3 = 1.26 times
For 2007,
Current ratio= $3618.5/$3,162.7 = 1.14 times
Assumption: By these ratios, it is seen that, in 2008, the ratio is stand in 1.26 times and in 2007, it is 1.14 times. But with the standard of current ration, it would be 2 times. (Brigham, & Houseton, 2004)
Quick Ratio
This ratio is indicating the variation of current ratio, which is, how quick assets are covered current liabilities.
Quick Ratio = Quick Assets/ Current Liabilities
(Quick Assets = Current Assets – Inventories)
For 2008,
Quick Ratio = $554.9/$2953.3 = 0.188 times
For 2007,
Quick Ratio = $428.7/ $3,162.7 = 0.136 times
Assumption: The standard of quick ratio is 1 time. But in these two years’ quick ratio, no one is stand 1. (Brigham, & Houseton, 2004) So, the quick ratio is not appropriate.
Net Working Capital Ratio
The working capital or assets in hand of Colgate- Palmolive Company is measured comparing with total assets.
Net Working Capital = Current Assets – Current Liabilities
For 2008,
Net Working Capital = $3710 – $2953.3 = $756.7
For 2007,
Net Working Capital = $3618.5 – $3,162.7 = $455.8
Net Working Capital Ratio = Net Working Capital/ Total Assets
For 2008,
Net Working Capital Ratio= $756.7/ $9,979.3 = 0.076 times
For 2007,
Net Working Capital Ratio= $455.8/$10,112.0 = 0.045 times
Assumption: Here, Net working capital ratios of both years are under 0.50, but the standard is it. So, Colgate- Palmolive Company has to improve Net Working Capital Ratio.
Profitability Analysis Ratios
These ratios are showing the effect of liquidity, asset management, and debt management on operating results of Colgate- Palmolive Company.
Return on Assets (ROA)
Return on Assets provides an idea of overall return on investment earned by the company.
Return on Assets (ROA) = Net Income/Total Assets
For 2008,
Return on Assets (ROA) = $1,957.2/ $9,979.3 = 0.1961 =19.61%
For 2007,
Return on Assets (ROA) = $1,737.4/ $10,112.0 = 0.171815= 17.18%
Assumption: As in these two years, ROA is greater, which indicates that, Colgate- Palmolive Company is using less debt considering assets more.
Return on Equity (ROE)
ROE is measured the rate of return on common shareholders’ investments to Colgate- Palmolive Company.
Return on Equity (ROE) = Net Income/ Stockholders’ Equity
For 2008,
Return on Equity (ROE) = $1,957.2/ $1,922.1 = 1.01826 = 101.83%
For 2007,
Return on Equity (ROE) = $1,737.4/$2,286.2 = 0.75995 =75.99%
Assumption: The Company is using less debt in these two years, but using net income to the common shareholders’ equity in these high ROE is not good for company.
Profit Margin
This ratio is indicated the net income per dollar of sales of Colgate- Palmolive Company.
Profit Margin = Net Income/Sales
For 2008,
Profit Margin = $1,957.2/$15,329.9 = 0.128 =12.8%
For 2007,
Profit Margin = $1,737.4/ $13,789.7 = 0.126 =12.6%
Assumption: The ratios of Profit Margin in these two years are almost same, which indicates the sales are average in every period.
Activity Analysis Ratios
These ratios are measuring the effectiveness of managing assets of the Company.
Assets Turnover Ratio
This ratio is measured the effectiveness of using assets to help generate sales of Company.
Average Total Assets = (Beginning Total Assets + Ending Total Assets) / 2
For 2008,
Average Total Assets= ($10,112.0 +$ 9,979.3) / 2 = $10,045.65
For 2007,
Average Total Assets= ($9,138.0 + $10,112.0) / 2 = $9625
Assets Turnover Ratio = Sales/ Average Total Assets
For 2008,
Assets Turnover Ratio = $15,329.9/ $10,045.65 = 1.53 times
For 2007,
Assets Turnover Ratio = $13,789.7/ $9625 = 1.43 times
Assumption: The effectiveness of asset turnover is decreasing every period, shown by measuring the ratios of 2008 and 2007.
Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio
This ratio helps to measure the effectiveness of account receivables in terms of sales.
Average Accounts Receivable = (Beginning Accounts Receivable + Ending Accounts Receivable) / 2
For 2008,
Average Accounts Receivable = ($1,680.7 + $1,591.9) / 2 = $1636.3
For 2007,
Average Accounts Receivable = ($1,591.9 + $1,523.2) / 2 = $1557.55
Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio = Sales/ Average Accounts Receivable
For 2008,
Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio = $15,329.9/ $1636.3 = 9.369 times
For 2007,
Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio = $13,789.7/ $1557.55 = 8.853 times
Assumption: In 2008 and 2007, accounts receivables are helped generating sales in effective times, more effective in recent period.
Inventory Turnover Ratio
By this ratio, the inventory is measured in terms of stocked or sold out, considering the times of the ratio.
Average Inventories = (Beginning Inventories + Ending Inventories) / 2
For 2008,
Average Inventories = ($1,171.0 + $1,197.1) / 2 = $1184.05
For 2007,
Average Inventories = ($1,008.4 + $1,197.1) / 2 = $1102.75
Inventory Turnover Ratio = Cost of Goods Sold /Average Inventories
For 2008,
Inventory Turnover Ratio = $6,703.5/ $1184.05= 5.66 times
For 2007,
Inventory Turnover Ratio = $6,042.3/ $1102.75 = 5.48 times
Assumption: By these ratios, it is estimated that, the goods are sold out or used over 6 times in these recent two years in terms of inventories in hand by Colgate- Palmolive Company.
Capital Structure Analysis Ratios
These ratios are indicating the capital management of shareholders in terms of liabilities and interests of the Company.
Debt to Equity Ratio
This ratio is indicating the portion of debt can be met up with the help of Shareholders’ equity of the Company.
Debt to Equity Ratio = Total Liabilities /Total Stockholders’ Equity
For 2008,
Debt to Equity Ratio = $8,057.2/$1,922.1 = 4.192 times
For 2007,
Debt to Equity Ratio = $7,825.8/ $2,286.2= 3.423 times
Assumption: To cover the liabilities with shareholders’ equity can be done easily by Colgate – Palmolive Company.
Interest Coverage Ratio
This ratio is helpful to measure the ability of Income to cover the interest expenses properly.
Income before Interest and Income Tax Expenses = Income before Income Taxes + Interest Expense
For 2008,
Income before Interest and Income Tax Expenses = $2,925.1+ $95.6 = $3020.7
For 2007,
Income before Interest and Income Tax Expenses = $2,496.5 + $156.6 = $2653.1
Interest Coverage Ratio = Income before Interest and Income Tax Expenses/ Interest Expense
For 2008,
Interest Coverage Ratio = $3020.7/ $95.6 = 31.597 times
For 2007,
Interest Coverage Ratio = $2653.1/ $156.6= 16.942 times
Assumption: Colgate- Palmolive Company has the efficient ability to maintain and cover the interest expenses according to Income of it in these two years.
Capital Market Analysis Ratios
These ratios are helping to analysis the market conditions of capital according to price of stock, book value of stock, dividend, and dividend payout by the Company.
Price Earnings (PE) Ratio
This ratio is helping to analyze the market price of shares considering with the earning per share of the Company.
Price Earnings (PE) Ratio = Market Price of Common Stock per Share/ Earnings per Share
For 2008,
Price Earnings (PE) Ratio = $68.54/ $3.9= 17.574 times
For 2007,
Price Earnings (PE) Ratio = $77.96/ $3.4= 22.929 times
Assumption: Price earning ratio is more in recent year, which indicates that, Colgate- Palmolive Company has the effective and higher market price of stocks to cover the earning per share.
Market to Book Ratio
This ratio is measured the book value of stock price considering the market price of stocks of the Company.
Book Value of Equity per Common Share = Book Value of Equity for Common Stock / Number of Common Shares
For 2008,
Book Value of Equity per Common Share = $732.9 / 501.4 = 1.50
For 2007,
Book Value of Equity per Common Share = $732.9 / 509.0 = 1.44
Market to Book Ratio = Market Price of Common Stock per Share/ Book Value of Equity per Common Share
For 2008,
Market to Book Ratio = $68.54/ $1.50 = 45.7 times
For 2007,
Market to Book Ratio = $77.96/ $1.44= 54.14 times
Assumption: The Company has the superior ability to cover the book value of stocks according to market price in the market.
Dividend Yield
This ratio is indicated the dividend of common shares according to market price of the Company.
Dividend Yield = Annual Dividends per Common Share/ Market Price of Common Stock per Share
For 2008,
Dividend Yield = $1.56/ $68.54 = 0.023 times
For 2007,
Dividend Yield = $1.40/ $77.96 = 0.018 times
Assumption: The annual dividends according to the market price of shares are not considered sufficient of Colgate- Palmolive Company.
Dividend Payout Ratio
The effectiveness of pay the dividend of shareholders with the help of Net Income is measured by this ratio.
Dividend Payout Ratio = Cash Dividends/ Net Income
For 2008,
Dividend Payout Ratio = $825.2/ $1,957.2 = 0.42 times
For 2007,
Dividend Payout Ratio = $749.6/ $1,737.4= 0.43 times
Assumption: In these two years, the dividend payout ratio is constant, but the portions of ratios are not effective to meet the dividend with Net Income.
Conclusion
In the ground of WorldCom and Enron fall down U.S. Congress has engaged its effort to recover public assurance by enacting obligatory compliance with Sarbanes-Oxley Act 2002 for all treaded companies. The board of Colgate-Palmolive has designed Guidelines for its global operation with compliance of Sarbanes-Oxley Act. Its Business Practices has provided proper resolution for the conflicts of Interest and Related Issues with fulfillment of SEC guidance for securities trading, environmental, occupational health & safety, policy statement of corporate governance.
Bibliography
Brigham, E. F., & Houseton, J. F. (2004). Fundamentals of Financial Management. 10th Edition, Thomson south-western, Singapore. Web.
Besely, S., & Brigham, E. F. (2007), Essentials of Managerial Finance, 13th edition, United States: Thomson South Western.
Colgate-Palmolive Company. (2008). Building on Global Strength: Colgate-Palmolive Company 2008 Annual Report.
DiPiazza, S and Eccles, R., (2009). Building Public Trust: The Future of Corporate Reporting. John Wiley & Sons.
Gokhale, J., (2009). Financial Crisis and Public Policy. Web.
Griffin, R. W. (2006). Management, 8th Edition, Houghton Mifflin Company, Boston New York, ISBN: 0-618-35459x.
Hitt, M. A., Ireland, R. D., Hoskisson, R. E. (2001). Strategic Management, 4th Edition, South-Western Thomson Learning, Singapore. Web.
Kirkpatrick, G., 2008. The Corporate Governance Lessons from the Financial Crisis. Web.
OCFO, (2009). Financial Policy and Training. Web.
OECD, 2009. Corporate Governance and the Financial Crisis: Key Findings and Main Messages. Web.
Schitlit, H. (2002). Financial Shenanigans, 2nd edition, McGraw Hill.
Sec.gov, (2009), Sarbanes-Oxley Act 2002. Web.
Skinner, S. J., Ivancevich, J. M. (2003). Business for the 21st Century, Homewood, Boston. Web.
Texas Instruments, (2008). Notes to Financial Statements. Web.
The Institute of Internal Auditors, (2008), Sarbanes-Oxley Section 404: A Guide for Management by Internal Controls Practitioners, 2nd Edition. Web.
USA Today, 2008, Collegiate Case Study. Web.
Virginia University, (1999), Notes To Financial Statements. Web.
