Companies have employed various strategies in trying to capture a significant percentage of their market share. Some of the multinationals have come up with ideal strategies that have helped them maintain their positions at the top of the market. One crucial element to consider is that although globalisation gave rise to the ease of movement from one part of the world to the other, it also encouraged localisation and support of locally made products. Initially, the large corporations enjoyed the benefits of globalisation as it meant that their market changed from regional to global. Today, however, they are challenged more by local competition as opposed to other international brands. This challenge has been resolved in two main ways. The first is through acquisition and absorption of these local competitors to reduce the pressure in the market. The second, and most encouraged, is through market intermediaries. These parties act as the local connector between the target market and the international brand. Several companies have used this approach to ensure successful entry into new markets. The intermediaries offer the foreign brands an opportunity to localise their product such that the target market believes that the product enhances the status of the community while at the same time allowing them to get the quality goods and services they deserve.
This assignment focuses on the Coca Cola brand. This brand is one of the largest in the world and has a strong presence in all the continents. One crucial element to note about Coca Cola is that it has such a strong brand and the numerous products it offers can be easily linked to the parent brand by the consumers. The company has over 20 different products they offer with a further approximately 10 brand variations. For example, the firm produces Coke, Fanta, Sprite and area specific soft drinks such as Krest (India) and Stony (Africa). On the other hand, brand variations in Coke have led to the creation of products such as Coke Zero and Diet Coke. Additionally, Fanta has Fanta Orange, Fanta Passion and Fanta Pineapple. The brand variations go further and also comprise of different sizes that are offered at different prices. Therefore, it goes without saying that the brand is extensive. For the purpose of this assignment, the Coke Zero product will be evaluated in relation to its penetration into the Nigerian market. The specific market has been selected as the company’s market share has been diminishing over the years due to both international and local competition. Kant and Aantjes (2018) confirm that the company recorded profits in all but its Nigerian market in the year 2018, which dropped by 4.3%. This is surprising considering the fact that the company has been recording an increase in sales in all of its Third World markets.
Critically, the stated market is one of the largest economies in the continent of Africa. Therefore, one can assume that the target population is able to afford the various sizes of the product on a regular basis. One of the factors that have to be determined when penetrating this new market is the price of the item. If it is expensive for a significant percentage of the target market, then the company will be unable to capture a significant percentage of the market share. However, pricing is complicated as products that are sold as premiums yet have a low price will also fail in the open market. The selected product, Coke Zero, is sold as a premium. However, the price is also controlled by the competitor rates. Therefore, this also has to be factored in to get the best rate for the selected brand. This essay provides a brief background of Coca Cola as a foundation for the discussion on the implementation of several strategies in an attempt to capture a significant size of the market for Coke Zero. The paper also provides a PESTLE and SWOT as part of the macroenvironment analysis of the company. A microenvironment analysis is also presented alongside pricing strategies and market penetration approaches.
Company History
The selected company, Coca Cola, was established in 1892 and is headquartered in Atlanta, Georgia. The company is known for its manufacture of beverages such as soft drinks, bottled water, and several syrups. The corporation is considered one of the largest in the world with a net income of approximately USD 6 billion. Interestingly, the company was formed in an attempt to get a drink that would help the public treat constant headaches (Griffiths & Vernotica, 2016). The original Coca-Cola product was, therefore, placed in drug stores and pharmaceutical shops as a medicinal beverage. The company registered extremely low sales in the first few years of operation due to this, and the fact that many people did not believe the beverage would work. The brand changed ownership in 1889 when the original owner, John Stith Pemberton, sold the formula to a business man, Asa G. Candler, who marketed the brand as a family beverage. The company has been able to hold its large market share through several strategies such as product differentiation, strategic marketing and advertising, and acquisition of competitors. Currently, the enterprise’s total equity and assets have reduced due to several modern challenges such as the desire for healthy dieting options among its target audience and climate change. The company has, over the years, been accused of leaving a large carbon footprint due to its massive production schedule.
Mission Statement
Coca Cola’s mission statement reads “To refresh the world… To inspire moments of optimism and happiness… To create value and make a difference.” (Coca Cola, 2020). The company strives to achieve this mission statement in all its processes, not just in their direct interaction with the target audience. Important to note, Coca Cola has also been closely linked with several corporate social responsibility activities that target environmental protection. These are also closely tied to the corporation’s mission statement.
The Marketing Environment- Environmental Scanning
The term microenvironment refers the immediate surroundings of a business. There are numerous factors that influence and shape this atmosphere. It is important to note that whereas some can be resolved internally, a significant number cannot. Despite this, companies are able to mitigate and adjust their internal processes in order to control their microenvironment. This section will look into the impact of Coca Cola’s suppliers, marketing intermediaries and competitors in an attempt to understand the company’s market position.
Suppliers
As mentioned earlier, Coca Cola has been in operation for approximately 128 years. During this period, the management has changed their suppliers accordingly. However, as Kant et al. (2018) explain, their supply chain processes have remained similarly unchanged for the last 40 years. The lack of adoption of modern supply chain methodologies has its advantages and disadvantages. As an advantage, it means that the company has mastered their systems. The same systems that are used in the US are also used in Nigeria. This has allowed the quality of products in Nigeria to be at par with that of other countries where the brand also operates. Kee and Yazdanifard (2015) explain that corporations such as Coca Cola rely heavily on the effectiveness and predictability of their production across all their regional hubs. The old but tested approach, therefore, offers a reliable option without introducing change. This is a case of “if it is not broken, then it should not be fixed”.
On the other hand, a weakness of this approach is that there are numerous methodologies that have been invented that have revolutionized the concept of supply chain management. In turn, they have made engagement with suppliers that much streamlined. McKelvey (2016) explains that the company uses one of the most traditional approaches compared to its competitors. The Khare (2017) adds that the company recently appreciated the need to upgrade their systems in an attempt to better manage their suppliers and contracted a consultant to help them integrate the same. It is crucial to note that the company is now able to better manage costs that were initially being wasted through their traditional supply chain management system. Whereas Coca Cola was not able to control what their competitors used, they were able to upgrade their systems in order to be at par with other companies in the sector.
Marketing Intermediaries
As stated earlier, Coca Cola has invested in acquisitions. Whereas some of the acquisitions were bought to resolve competition, others were purchased to add to the growing portfolio of the company. Since the company has numerous brands, it has different teams that work on the individual brands. The division of the departments into their respective brands allows for a better management of the substantive portfolio. There are two things that have to be considered in the discussion of the corporation’s market intermediaries.
The first is the firm’s efforts that have contributed to establishment of intermediaries. For example, the company has further created independent websites for a significant number of their products. These websites are managed by intermediaries (Kee & Yazdanifard, 2015) whose sole purpose is to ensure the sale of the products while highlighting the company’s mission and vision. The special websites are a resource to retailers who sell the specific products as they can acquire more information about the goods for their consumers. Additionally, they get training tips on the same website on better management of their stock (Kee & Yazdanifard, 2015). The sites also announce any new products that may interest the retailers who are selling the specified item.
The second is that the intermediaries support regional trade that enhances the company’s reach. An example can be given to explain this notion further. Dana and Oldfield (2018) reveal that in many regions, the Coca Cola company has also helped establish area bottlers who serve as part of their marketing intermediaries. In Nigeria, they have the Nigerian Bottlers Company, which not only produce the different bottles for the Coca Cola products but also help share the company’s vision and mission. Additionally, the Nigerian Bottlers Company offers more exposure to the Coca Cola brand on a local level. The premise suggests that the company (Coca Cola) has taken advantage of their need for marketing intermediaries to also penetrate these new markets.
Competitors
There are two main things that have to be considered when discussing the impact of competitors on a brand. First, one has to consider how competitors affect the internal processes a firm subscribes to at all times. Secondly, one also has to consider how the competition affects the industry as a whole. Arguably, understanding one’s competitors helps shape processes in an attempt to be better than the other corporations in the same field. In Nigeria, Coca Cola has had the same main competitors for decades, namely Pepsi Nigeria and Bigi Cola. One way the two companies have affected Coca Cola’s internal processes is through, as stated, forcing the latter to adopt modern supply chain management processes for purposes of efficiency. It is critical to note that such methodologies reduce the amount of operating costs. This trickles down to lower prices of the product that is released into the market. It is arguable that the competitors had more efficient supply chain management systems that gave them a competitive edge over Coca Cola, thereby, forcing the latter to also adopt these modern technologies. Currently, Coca Cola and Pepsi have near similar product sizes as well as prices.
Secondly, competitors help shape the industry through innovation and creation of newer ways of consumer engagement. Apart from processes, competitors also encourage innovation in an attempt to either retain or capture a larger percentage of the market. For instance, competitive advantage realized by Coca Cola will also encourage Pepsi to come up with a new way of doing things in order to curb the added competition. Noticeably, such competition not only helps the industry grow but also ensures that the target audience receives excellent quality of service/product at the same time. An example can be given to explain this concept further. Currently, Coca Cola has several non-sugary beverages that support healthy dieting. The same has been incorporated in the other competitors such as Pepsi as well in order to manage the competition.
Macroenvironment
One way of analysing Coca Cola’s macroenvironment is through the PESTLE analysis. This approach looks into the political, economic, socio-cultural, technological, legal, and environmental factors that affect the company.
Political factors
As mentioned, the multinational company operates in numerous countries around the globe. Therefore, one has to consider that each of the countries/regions, have unique political factors that can have an impact on the company’s bottom line. One major political aspect in Nigeria that has to be considered is security or peace and conflict. Intra-country and intercountry wars can affect production and profitability in general. The country has suffered from numerous internal attacks from guerrilla groups such as Boko Haram that declare conflict based on exaggerated religious beliefs. Such conflicts make the economy unstable and also limit production. Further, such activities will not only affect the company’s ability to produce their goods but also the publics need for the same. On the same note, corruption is also a vital element to consider when discussing the political environment. Nigeria is among the most corrupt countries in the planet. Khare (2017) explains that countries that have high rates of corruption also have high rates of production. This affects the company’s operating costs, thus, also influence the cost of the end product.
Economic factors
Several elements such as the population’s ease of accessibility to disposal funds, inflation rates, and economic cycle have to be considered when discussing the economic elements that affect Coca Cola. This is because they all regulate the aggregate demand for the company’s products. If there is no demand, then the company will also not get any sales. The first matter that the firm has to consider is the type of economic system that is in place in their target country. Khare (2017) argues that there are numerous economic cycles namely mixed, market, traditional, and command. Nigeria can be defined as a middle income economy. It is also a mixed economy that is supported by numerous elements, but primarily, manufacturing. The type of economy affects the labour rates and other significant operating costs. Looking at Nigeria’s economy, it is arguable that labour and production costs can be relatively high. Khare (2017) explains that this is one of the crucial reasons many companies prefer to manufacture their products in China as they economic cycle allows for more affordable labour.
Socio-cultural factors
Due to the fact that the company specializes in beverages, one can argue that it offers a leisure product. Therefore, the corporation has to consider whether the target market in Nigeria can afford the product. The ease of access to disposal funds is critical to determine whether the company will be successful or otherwise. One common culture practiced by Nigerians is that women tend to shop more than men. Additionally, families buy shopping as gifts for friends and other relatives. This information is critical as it can affect the way Coca Cola shapes its advertisements to suit this culture. Khare (2017) explains that the attitude towards, for instance, health options will affect the company’s success. Currently, there are countries whose population is keener on the healthy diet option. Therefore, for Coca Cola to record profits in these markets, the management has to push for their healthy beverages as opposed to their traditional ones.
Technological factors
One has to consider two main things that affect Coca Cola in regards to technological factors. These are the firm’s competitor’s advancements and the sector’s technological developments. Khare (2017) argues that it is vital for any company to be knowledgeable on its competitor’s technological prowess. Such information is critical as it also determines the competitive edge among the affected companies. Secondly, the company will be affected by the sector’s ability to incorporate new technology. It is common to find that the manufacturing industry develops faster compared to the individual sectors within this larger industry. For instance, manufacturers of cement might have new technology that beverage factories have not yet implemented. It is critical that Coca Cola understand the new technologies that influence the industry as a whole and attempt to use them at their advantage.
Ecological Factors
Coca Cola has been accused of enhancing environmental degradation through the massive production of plastics that are used to package their products. This, coupled with the extensive production of their products, has ensured the firm’s carbon footprint has been red flagged by environmentalists. The debate has been enhanced by the fact that multinationals have been accused of penetrating African countries in an attempt to hide their overall carbon footprint. Khare (2017) adds that waste management and recycling are also a big concern for multinationals such as Coca Cola. These companies have been accused of dumping their waste in Third World countries in Africa, such as Nigeria, and Asia (Khare, 2017). The corporation has developed a comprehensive statement on their activities that safeguard the environment to curb the challenges faced in this light. The company has also used both traditional and digital communication platforms to encourage their target audience to properly dispose of their packaging after use. Additionally, the enterprise’s marketing department has been keen on corporate social responsibility activities that help protect the environment.
Legal factors
One key legal consideration is intellectual property law. One advantage that the company has is its special formula that is considered a trade secret. Arguably, as Khare (2017) observes, there is no one law that offers global intellectual property protection. Therefore, the company has to seek this cover in all the regions where they want to operate. The trade secret can also be protected under intellectual property to through unfair competition laws. Other legal regulations that might affect the company include employment laws, health and safety regulations, and data protection rules (Khare, 2017). Critically, legislation goes hand-in-hand with political goodwill. Thus, the company has to be able to foresee the political turmoil that the target market will face in order to also manage the legal repercussions of the same.
SWOT Analysis
Strengths
One strength of the Coca Cola company is that it has a strong brand within Nigeria. This is interesting due to the fact that the company has a plethora of products under its parent brand. Kee and Yazdanifard (2015) explain that the company has used strategic marketing and advertising components to ensure a strong brand globally. One of the factors that has to be considered is the time of entry into the market. Since Coca Cola entered the market before its international competitors, it became a house-hold name early as well. The strong attachment the company enjoys has also boosted its brand equity, which can also be highlighted as a strength.
A third advantage of the firm is its large market share. Nigeria has approximately 200 million citizens and as mentioned, is Africa’s largest economy. Despite the constant and strong competition, the company still holds the top spot in the market. This position can be attributed to strategic placements, advertising, marketing, and also customer engagement. As stated, the company has also acquired various firms and uses market intermediaries for market penetration. All these can be highlighted as advantages especially when compared to the company’s competitors. On the same note, Coca Cola has a large distribution system that ensures their products are also available in rural settings. Indeed, the intermediaries offer great opportunities here as the locals in the rural settings have a feel that the products made are also for their own benefit. Arguably, to the people in these rural settings, the impact of having such a brand associated with them is not only prestigious but it also provides work for their children.
Weaknesses
There are two main weaknesses that can be associated with the selected corporation. The first is that its main ingredient is water, and this resource is getting scarce. The loss of water can be attributed to climate change and drastic environmental degradation that has been observed in the last decade. This is especially the case in the selected country or market. Khare (2017) explains that Coca Cola has started to invest heavily in water related projects to not only help communities that need the water but also make up for their own use of the same product. For instance, the company has helped communities in arid and semi-arid areas dig boreholes for easier access to the resource. This makes up for the large tons used in the more productive parts of the country.
A second weakness the company faces is product diversification. The firm has been keen on producing various non-beverage drinks but has not diversified out of the beverage sector. Khare (2017) explains that companies have to ensure they are in different industries in order to grow beyond their comfort zone. Competitors in the field have expanded their portfolio to also include snacks that complement their drinks. The fact that Coca Cola has not broadened its reach in this manner means that they are losing out on the competitive edge that other competitors are experiencing, and secondly, that they are also losing out on a significant percentage of the market.
Opportunities
The weaknesses mentioned offer the company numerous opportunities that they can explore. First, the company has a chance to diversify and offer snacks or food biting that go well with their individual beverages. This will not only ensure a balance in terms of the competitive advantage but also raise their profits. Additionally, this is not an offer provided by the competitors in Nigeria. It can be assumed that the snacks segment of the firm will ride on the already established and strong brand name of the beverages.
A second opportunity to be explored is the new markets cropping up within Nigeria. Arguably, markets including health enthusiasts, energy drink fans and even natural juice lovers can be incorporated into the larger Coca Cola brand plan. This is further enhanced by the fact that the First World nations, where the brand is also enhanced, have become more concerned with their diets due to an increase in lifestyle diseases. Arguably, Coca Cola has penetrated the markets in Third World countries significantly. However, the company can still take advantage of these regions to expand their products database.
Additionally, there is an opportunity in the modern supply chain management options that the company can explore. These solutions can help the firm lower its operating cost, increase its productivity, and establish stronger connections with all stakeholders. Further, due to the corporation’s interest in ensuring accessibility to water, there is still untapped potential in the packaging of water. The company has a few water products but can expand this portfolio to also include other forms of larger water storage options. For example, numerous companies use water dispensers and this area has not been exploited by any major beverage company.
Threats
A critical threat to the productivity of the firm is the issue of climate change. Environmental degradation affects the company in two ways. The first is the fact that it ensures the scarcity of the raw materials used. As mentioned previously, water is the main ingredient of all Coca Cola products (Clarke, 2017). Climate change and global warming have made it that much harder for people to access this basic need for consumption. Thereby, the firm’s operating costs have increased due to this scarcity. The additional fact that solutions to resolve the fast depletion of water are yet to make an impact make the situation worse.
On the same note, the same issue of climate presents a problem to the corporation due to their choice of packaging. As explained earlier, Coca Cola uses plastic bottles as its primary packaging. This has been described as highly inappropriate considering the fact that plastics are identified to be the worst form of environment pollutant (Khare, 2017). Their negative impact on air, land, and aqua is equally devastating and companies have been encouraged to seek alternatives to such packaging. It is also important to note that the fact that the enterprise’s target market is seeking alternative and healthier options is a threat. The company has tried to resolve this through production of beverages that have zero sugar. However, it can be argued that the firm will have to invest significantly in the marketing of these products for the target market to trust the brand in regards to offering healthy beverages.
Target Market, Market Size, Segmentation Strategy, and Market Opportunities, Product Characteristics
This section of the paper will focus on one product of Coca Cola. It is crucial to reiterate that the company has over 10 products (with variations) in the Nigerian market. Specifically, the rest of the paper will concentrate on one item, which is Coke Zero.
Target Market
The target market refers to the group of people a product is primarily made for and is, therefore, expected to also purchase the item. The Nigeria population is the target market selected for the product. Arguably, firms cannot sell their products to everyone. It is highly unlikely that everyone in a selected region will be interested in the Coke Zero product. Therefore, and more specifically, the product will focus on female sample population that is between the ages of 16 and 48 in the Nigerian market.
Demographic characteristics
The main reason why Coke Zero was introduced into the Nigerian market was to cater for people who loved the taste and quality of the original product but were concern about the health hazard it also carried. Arguably, the first demographic characteristic of the target audience for the drink is that they are middle aged. Abere et al. (2016) reveal that this is the age when a significant number of the population start to think about healthy living. A second characteristic of the selected target population in Nigeria is that they are mainly women. Abere et al. (2016) argue that the product was designed to be consumed by the male gender. However, as time progressed, the company realised that women took the drink more than men. This decision was informed by two things. The first is market research that showed that the company’s main audience was women for all its products (Abere et al., 2016). The second is that they were the most concerned with healthy eating when they became middle aged (Abere et al., 2016). It is critical to mention that men were also considered when creating the drink but more focus was put on the female consumer.
Another characteristic of the target market (Nigerian sample population) is that they are mainly working class. It was critical for the company to get this demographic as it then informed some of the marketing and advertising decisions that were made for the item. For example, since a significant percentage of the target population was working, the packaging of Coke Zero was made lighter with other smaller, thus, more portable, options. The advertising around the item specifically focused on the fact that it could be substituted for a healthy yet light drink at the office or during a short lunch break. The working factor also allowed the company to come up with the right pricing for the product. Despite using less raw materials compared to the original version (no sugar) the company placed the price at a slightly higher rate. This was meant to entice the target group that they were paying for premium quality raw materials that would support their desire for healthy dieting.
Psychographic characteristics
A significant percentage of the traditional consumer population was targeted in regards to psychological needs such as happiness during family gatherings. It is due to this approach that the company invested heavily in advertising around Christmas. The approach for Coke Zero in the Nigerian market is, however, different due to the difference in terms of needs for the target audience. One major psychographic characteristic is that the population has a significant desire to either lose weight or lower bad cholesterol. McKelvey (2016) explains that there are numerous advertisements that sugar is not only bad for general healthy but also leads to the accumulation of bad cholesterol. This then leads to lifestyle conditions such as high blood pressure and diabetes, which are made worse by obesity. The issue of weight loss and its link to sugar has further been enhanced by professionals in the medical field who have warned people to stop taking fizzy drinks – such as the products manufactured by Coca Cola.
Still on the psychographic characteristics of the target population, it is arguable that they believe they have certain values that they have to uphold. This is especially in regards to the manufacturing process of the product. As explained earlier Coca Cola has been accused of significantly contributing to earth’s carbon footprint due to both its manufacturing process and packaging. The target group of Coke Zero is not only knowledgeable on the impact of climate change but also desire to help lower earth’s carbon footprint by monitoring the things they use that would ideally contribute to the same. This realisation led to the creation of Coke Zero, which takes less manufacturing effort, therefore, ensures lower pollution. The firm took advantage of this and used it as a marketing and advertising theme to ensure it attracted the right audience as well.
Benefits sought
There are several benefits sought through the product. It is critical to divide the issue of advantages to both the enterprise and the usual Nigerian customer. First, a benefit for the company is that it uses less raw materials, therefore, has a lower operating cost. This is important as it affects (in this case significantly improves) the corporation’s bottom line. Since the company does not have to use artificial sweeteners, it saves money compared to the original product. A second benefit sought for the company is the quality of the product. Initially, the Nigerian population believed that the “caffeine minus sugar” formula used in the creation of Coke Zero would not result in a tasty beverage. It is critical to note that the product also uses caffeine as one of the main ingredients (Clarke, 2017). The challenge for the firm was to ensure same quality and great taste despite the removal of the ingredient that actually brought on the desired taste.
On the other hand, one of the benefits sought by the Nigerian community is the ability to support a healthy lifestyle. Kee and Yazdanifard (2015) explain that the US and other developed countries have been identified to carry a large disease burden linked to lifestyle conditions such as diabetes and hypertension. As mentioned, this has been made worse by obesity. It is important to point out that a majority of these conditions are brought on, and can, therefore, be managed, by diet. A significant percentage of the population, therefore, has become concerned about the things they eat and drink. This, coupled with the fact that nutritionists have argued that fizzy soft drinks do not have any nutritional value, has created a target group that seeks quality and tasty beverages that support healthy living.
Usage rate
The table below shows usage rate based on age. Importantly, this data shows people who drank the product and not those who bought it.
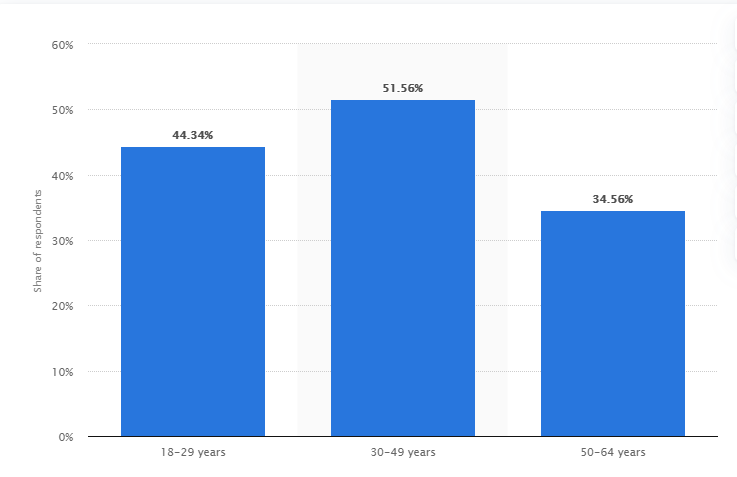
The table reveals that people aged 30 to 49 drank the product more than the rest of the target market. The second group, 18 to 29 year olds also used the product more due to the fact that they are also significantly cautious about how they look. The rate of usage is also significantly high in 50 to 64 year olds. This is an important statistic due to the fact that it makes the discussion on healthy living that more complicated. It can be assumed that people in that age group would ideally keep off fizzy beverages. However, they make up approximately 34% of the target population that consumes the product. This can be analysed in two ways. The first is that the marketing of the product was done exceptionally well that people in the said age group believe that the product will not affect their weight and general health even as they grow older. Secondly, it could mean that the said age group were the initial audiences targeted when the product was launched and have remained faithful to the brand.
The analysis of the product’s usage rate is crucial in evaluating the relevance of market research that is done prior to product launch. Khare (2017) reveals, however, that unlike the traditional coke, this specific product is not consumed frequently. The data collected and presented in Figure 1 features consumption at least once within 4 weeks (Kunst, 2020). The usage rate for Coke Zero is impressive as it confirms that the targeted population was the right one.
Geographic location
It is prudent to identify a specific location when determining the market position of a product. Towards this end, the selected location is Lagos, in Nigeria, Africa. There are two main characteristics that make this location ideal for the sale of the item. The first is the climate, which is mostly hot and humid. Khare (2017) explains that the brand Coca Cola is primarily associated with chilled non-alcoholic beverages. The company has strategically included the fact that their products are best served cold to increase sales in hotter areas where people tend to look for cold drinks more than in cooler regions. Lagos has the weather patterns of a hot coastal strip, therefore, more people will be attracted to drinks that taste good when cold. The weather patterns also ensure that the product is in demand through-out the year. This is important as it ensures the company records profits throughout the year.
The second element of the geographical location is the culture of the people. Khare (2017) explains that culture is largely influenced by both language and location. Therefore, people who live close to the sea will wear lighter clothes due to the heat, eat more seafood, and have cultural attachment to colours such as blue and green. On the other hand, people living in the highlights will pay more attention to heavier clothes, vegetables, and also be more inclined to appreciate brown and green as their cultural colours. The same concept can be applied in the beverage sector. As stated, people in humid regions will take more beverages. Additionally, due to the fact that they have many options, they will be keener on quality and price of the item.
Organizational size
Coke Zero is part of the larger Coca Cola company. Therefore, the parent organizational size will be considered in this section. The following table highlights the company chart.
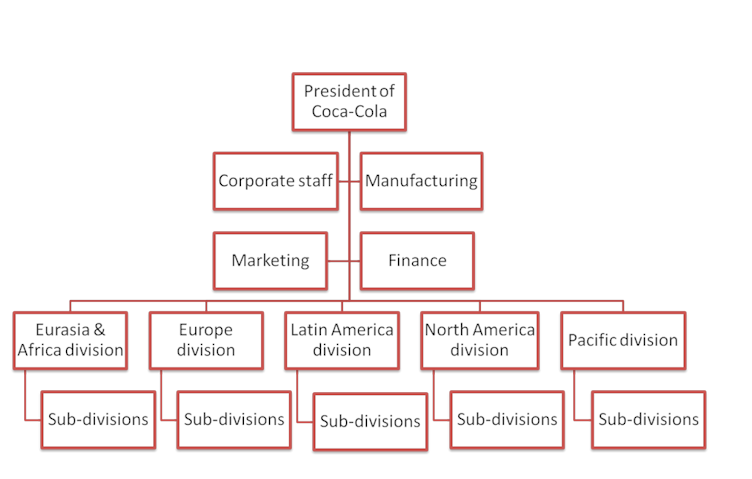
The organisational chart presented has been categorised in terms of regions and offices and not individual posts. Khare (2017) reveals that the whole Coca Cola company has employed a combined global workforce of approximately 86,000 individuals. This number is only for the parent company and its regional offices and has not included employees who are working in the stated market intermediaries such as the Coca Cola bottlers. The head of the group is the Coca Cola president who sits in the firm’s headquarters. This office also caters for the heads of manufacturing, marketing, finance and corporate staffing.
Further, the company has divided the globe into regions such as Latin America, North America, Eurasia and Africa, Pacific and Europe. It is arguable that the company has influence in all countries of the world using this parameter. However, closer examination shows there are countries that the firm is yet to penetrate, specifically in regards to the introduction of Coke Zero into all markets. Each of the stated regions has country offices that are further divided into departments. It is important to note that the company has a decentralised system of governance that encourages the individual country offices to make their own decisions as long as they align with the company objectives, mission and vision.
Product/ Service Characteristics
The product characteristics allow the consumers to differentiate between one item and the other. It is important to note that these elements are determined during the conception stage of the particular good. This section looks into the product Coke Zero in relation to its brand name and characteristics that makes it stand out from other Coca Cola products and their competitors as well.
Brand Name and Product/ Service Name
The selected product is Coke Zero, which is the first non-sugary non-alcoholic drink by Coca Cola. Arguably, the product is hinged on the larger Coca Cola brand under the service name Coke Zero Sugar. Khare (2017) explains that there is a direct correlation between the service, the brand and the product names. It is critical to note that Coke Zero has combined both the brand and the product features to give a label that can be easily noticed by the target population. Indeed, whereas the first part of the name (Coke) is derived from the primary brand (Coca Cola), the second part of the name (Zero) comes from the fact that the drink has zero sugar. One advantage of such naming according to Khare (2017) is the fact that it (the name) can be independently used to market and sales approaches. Towards this end, it makes it easier for the public to identify the item in the market. Additionally, the ease of name will prove useful in the selected region (Lagos) where the product will be marketed.
Interestingly, there are markets where consumers do not pay much attention to the product name but focus more on the brand name. Therefore, a customer will only request for a Coke at their local store but not insist on it being the original, diet or zero. Khare (2017) explains that the Third World markets have been highlighted as having this unique approach to brands. Debatably, this could be due to the trust the consumer base has in the strong brand, in this case, Coca Cola as a whole. Alternatively, it could also mean that the market is not well penetrated by other competitors. There are numerous advantages and disadvantages that can be picked from this experience. An advantage is that the parent brand does not have to invest in segmented marketing as the population does not care. A disadvantage, however, is that the quality of the original product will be lost.
Features and benefits
Coke Zero is classified under the carbonated soft drinks and beverages sector. A critical feature of the product is that it has zero calories. This can be attributed to the fact that it also contains zero sugar or artificial sweeteners. This is the key feature for the product as it was created as an alternative to the original Coke. It is important to note that the product has the same raw materials and production process as the original product. This is unlike Diet Coke, which has completely different flavours. The premise is vital as it also informs the brand positioning. Traditionally, the company has associated the brand with men, when in fact, data shows that more women drink it. The target location will focus on women, towards this end. Therefore, the brand positioning in this region will shift from male to female oriented.
One benefit of the product is that it does not add artificial sugars into the body. This is important as the stated ingredients have been linked to weight gain and increase in bad cholesterol, which can lead to several lifestyle diseases. An additional benefit is that due to the fact that no sugar is added in the formula, the product also has significantly reduced the amount of caffeine used to ensure quality taste. Griffiths and Vernotica (2016) explain that the amount of caffeine that is in the original product has been linked to some form of addiction to the item. Indeed, there are people who get headaches if they do not drink the original Coke (Ellertson, 2016). The selected product has reduced chances of this same dependency happening. The product also has sodium and potassium which are nutrients that are used in the body for various functions.
Points of Differentiation
In order to establish the points of differentiation, one has to compare Coke Zero with other products. This will be done in two ways, first, by comparing the product with the original Coke, and one other item sold by the same brand. Secondly, is through a comparison with a competitor product. The main ingredient that makes Coke Zero different from the original Coke is the lack of sugar and artificial sugars. Therefore, there is some level of alteration in terms of taste. There are people who argue that the original Coke has a better taste that the selected product but this is mainly due to the artificial sugar added in the former.
The product can also be compared to Diet Coke, which is a product within the same brand (Coca Cola). One of the key point of difference between the two products is the use of sodium citrate and citric acid. Whereas Coke Zero uses the former, Diet Coke uses the latter. It is imperative to mention that Diet Coke does not have added sugars as well. However, the choice of the identified ingredient is based on the taste of the products. Notably, the two taste significantly different, with the latter tasting like a whole new product while the former tastes like the original Coke.
As mentioned, the product can also be compared with a competitor to also bring out its points of differentiation. The selected competitor product is Pepsi Max, which also has zero sugar. However, Pepsi Max has a different carbonation method that allows it to have smaller bubbles as compared to Coke Zero, which has larger bubbles. This point of differentiation also affects the products’ taste and helps their different consumers’ choice which brand they prefer.
Communication
As explained previously, initially (and also in other regions) the product is communicated as a male beverage. However, in the selected region, the product should be marketed differently, preferably, using the features, benefits and points of differentiation. Despite being a Third World country, the citizens in Nigeria are equally keen about their health as other citizens of the world. Khare (2017) explains that companies have to appreciate the fact that the internet has allowed extensive exposure all over the world. Therefore, if health enthusiasts in the US argue that carbonated and sugary soft drinks are bad for one’s health, then people from Nigeria will also get the same message through social media and other digital platforms. Therefore, the marketing and advertising of the product should focus on the fact that it is a healthier yet equally tasty drink that can be shared by the entire family.
It is also important that the product be communicated through both digital and traditional platforms. The selected region still values traditional media such as newspaper, TV and radio. Critically, the best way to communicate about the product is through spot ads in the radio as it has a wider reach compared to TV, newspaper and digital. Khare (2017) explains that marketing through social media cannot be overstated. This is due to the fact that a significant number of the target population can be found online. Additionally, the concept of e-commerce has grown (and is expected to grow even further). Indeed, Coca Cola does not participate in retail e-commerce. However, the firm’s market intermediaries are able to participate in the same. Largely, through digital communications, the company can keep track of the changing trends of their target population and use this to make appropriate ads that are distributed through the right channels.
Financial Considerations
There are numerous financial considerations that have to be discussed to allow for proper market penetration. For example, some elements that touch on the product itself include the product price and the marketing budget. On the other hand, financial implications realised during manufacturing also affects how a company will determine its products’ rates. This section analyses some of these implications in relation to the selected product, Coke Zero.
Price Strategy and Competitive Position
Price is one of the 4 main P’s of marketing. Khare (2017) explains that the right price is crucial in ensuring the success of a product that is being introduced into a new market. It is crucial that the management consider the manufacturing costs, marketing rates and also the economy of the target market before coming up with the right price of the product. Khare (2017) goes further to explain that many marketers believe that the cheaper the product the more profits it will record. However, it is important to note that whereas cheaper rates can attract clients, the company will have to move a significantly large percentage of product in order to get any profit. Employing such a pricing strategy will force the company to produce in mass in order to lower operating costs as well.
General pricing strategy
Despite the numerous approaches that a company can choose from, Coke Zero will focus on two main general pricing strategies. The first is profit maximization strategy while the second is market share pricing.
Profit maximisation strategy: As the name suggests, the profit maximisation strategy focuses on how a company can make the most profit from each individual product sold. Dhar et al. (2016) explain that when discussing this approach one also has to understand the revenue maximising approaches as well. The scholar explains that the latter focuses more on cost cutting to ensure that less money is used in the manufacturing and marketing processes while the former focuses on things like product variations and price premiums. Critically, revenue maximisation allows a company to produce large numbers of the product in order to lower the operating costs. For example, such an approach will reduce labour wages and also utility bills associated with manufacturing such as electricity and water as the number of days needed for production will be lower. Importantly, businesses that take this approach encourage employees to produce their goods both during the day and at night.
On the other hand, the profit maximisation method allows the management to explore the largest possible profit margin that the product can offer in the open market. Khare (2017) explains that the best way of determining this is through proper market research. The market research can ask the participants how much money they are willing to pay for a healthy, zero calorie, and zero sugar beverage to get the general pricing that the target population expects. This approach allows firms to also incorporate the element of premium prices. Arguably, products that are described as premium refer to both quality and status. Therefore, people who want to be associated with the product due to the social status attached to the same will be inclined to purchase. When such products are put on discount, or are priced poorly, the target audience will not purchase them as they will be perceived to be fake.
In the case of Coke Zero in Nigeria, the price should be slightly more than the original Coke. There are various factors that make this the viable option. First, is the fact that it is a premium product – associated with both status and class. An example can be given to explain this point further. Currently, the original Coke retails at ₦150 (USD 0.39) while Coke Zero goes for ₦85 (USD 0.22). The pricing already shows that the brand promise is not being considered as although the product is advertised as a premium, it is sold at a cheap price. Despite this, it is imperative that the company does not, however, make the price too high. This is due to the economic status of the target population. It is this reason that supports the argument that the product be priced at a slightly higher rate compared to the traditional Coke.
Market share pricing: The market share pricing relies fully on the brands performance in the market. Therefore, if the item is performing poorly, the pricing is adjusted to a more appropriate one and the vice versa if the product is performing well. There are several things the management has to consider in trying to determine whether this is an appropriate strategy for Coke Zero in Lagos. One is the fact that the approach encourages that the target population be undefined. Khare (2017) explains that this means that there is no demographics or other characteristics of the population that are used in the marketing of the product. The assumption is that the product is safe for consumption for people of all ages, thereby, anyone can purchase it. One advantage of the undefined market is that all marketing and advertising approaches will be generic. Additionally, the company does not lock out any potential group based on targeted marketing. One can argue that this approach is appropriate based on the fact that despite the product being created for men, it is largely consumed by women.
Secondly, despite the undefined market, the company still has to put the interests of the consumer first. Khare (2017) reveals that companies that just use the undefined market approach fail mainly due to the fact that they do not make their consumer their first priority. Arguably, it might prove difficult to combine the two approaches, and few companies have only successfully been able to achieve the same. One way this can be done is through market research that targets understanding the immediate needs of the whole population in regards to soft drinks. If the immediate concern is health, then premium pricing will still apply as people would rather pay more money to get a product that will not compromise their health.
Comparative pricing strategy
Apart from the general pricing strategies, a comparative approach can also be used to boost the product in the stated market. Khare (2017) defines the approach as the juxtaposing of two similar products with one having a different price compared to the other. The scholar explains that the strategy plays on psychology to ensure that clients buy the intended product. It is common to find identical items placed on the same shelf in the store yet they have different prices. For example, it is common to find the original Coke closer to Diet Coke, which is in turn closer to Coke Zero. The approach ensures that the consumer understands that there are alternative prices of the same brand (Coca Cola). Khare (2017) explains that many buyers use logic to purchase items they need. On the same note, however, a significant majority will rely on the psychological understanding to choose products based on prices. It is this premise that led to the wide adoption of 9 pricing where product prices have to end in a 9 in order to ensure impressive sales.
In particular, this careful methodology ensures that clients have a product that is of a low price, one that is of middle rates and the last one that is a premium. If the management wants Coke Zero to be the premium product between the three, then it would be imperative to make it the most expensive of the group. Therefore, the buyer will be able to clearly note that this particular product is a premium, therefore, offers better health options compared to the other two. On the other hand, the management can also make the item mid-priced. This means that it will be more expensive than the original Coke yet more affordable compared to Diet Coke. Khare (2017) reveals that many people will go for the middle priced product compared to the other two when the three are placed on the same shelf. This is due to the assumption that the buyer gets to save money but still get significantly good quality compared to the lower priced item.
Market Share
As mentioned earlier, market share refers to the percentage of the target population that is loyal to a brand. Companies are keen on ensuring they have captured the larger percentage of the market as it directly relates to better sales and profits. Khare (2017) notes that firms use various strategic approaches to acquire a significant market share. The first is through offering quality goods and services. Arguably, the quality of products is critical in attracting consumers. Secondly, the right price can also ensure a brand not only attracts but also retains consumers. As discussed earlier, there is no one method of determining the right price of a product. The management has to consider several factors that then determine the same.
Coca Cola currently enjoys control of the larger percentage of the Nigerian market. The term “larger” is used due to the fact that Pepsi, and other competitors also have shares in the same market. Further, different products within the larger Coca Cola brand have also divided the market. Arguably Coke Zero has one of the lowest controls in the market. The company already has an advantage in terms of the strong brand already in the market. However, to increase the market share of Coke Zero, several factors have to be implemented. The first is through innovation in regards to product placement, marketing and advertising. Khare (2017) explains that advertising and marketing should go hand-in-hand with what the target market likes. In Nigeria, this should focus on using the local dialect, using the local celebrities to promote the product and also the innovative advertising element.
Further, the brand can ensure market share through properly consumer engagement. Two things have to be considered when linking consumer engagement to market share. The first is the direct interaction between the brand and its target population. This can be easily achieved through digital engagements. One advantage of using the digital space for such interaction is that it is cost effective. The second thing that has to be considered is the interaction between market intermediaries and the target market. As explained previously, Coca Cola relies heavily on their market intermediaries, especially in their overseas markets such as Nigeria. These middlemen have to be trained on how the brand wants to engage with the public. This will ensure that the brand image is maintained both within the country and on a global scale.
Sales Forecast
Critically, many businesses have today been affected by the corona virus pandemic. Therefore, a viable forecast for the brand will show a decline in profits for the Coke Zero brand. This is due to the fact that a significant percentage of the target market have lost jobs and will not be able to purchase items described as leisure products as frequently as would have been expected. The impact of the pandemic can be felt all over the world, not just in Nigeria. It is prudent, therefore, to note that the assignment will take into consideration this impact in developing the sales forecast.
The revenue brought in by Coke Zero is expected to be better than any other Coca Cola product in the next two years. One of the reason this forecast is proposed is the pandemic. One can argue that a key lesson gained through the pandemic is the fact that lifestyle diseases put lives at risk more than ever. The World Health Organization has announced on several occasions that the corona virus is fatal for people who have underlying conditions such as diabetes and high blood pressure (Khare, 2017). People are now not only more concerned but also more aware of the need of proper and deliberate nutrition in ensuring healthy living. It can be assumed that the next two years will see an upsurge of people looking for healthier meal and beverage options. Therefore, ensuring the rise in demand of Coke Zero.
The sales forecast also reveals that the Coke Zero brand albeit performing better than other Coca Cola brands, will also be highly affected by the changing times. Therefore, the forecast will be lower than a forecast that was done by management two years ago. One of the reasons this is anticipated is the fact that more people will keep off soft drinks and prefer naturally made juices and water. Indeed, this provides another opportunity for Coca Cola to come up with great alternatives that can be introduced into the market. The decision will be informed by both the Covid-19 pandemic and the desire of the target market to be healthier.
Summary
In summary, Coca Cola is one of the strongest brands in the world today. The company is not only well known but has also been able to attract loyal consumers. The company has a wide range of beverages working under different names. Despite this, a significant number of these products can still be easily linked back to the mother brand by the ordinary consumer. Arguably, the company has invested fully in ensuring a positive brand image, valuable brand equity and excellent brand reception among the public. This is exceptional due to the fact that the original Coke was created as a medicinal beverage. Therefore, the company had an opportunity to rebrand long before the business community fully appreciated the power of branding. Despite the powerful brand image, the company has faced various challenges over the decades that have pushed it to rely on innovations as a way of maintaining their market share.
The paper puts the Coca Cola brand in context through the suggestion of better market penetration in Nigeria. Particularly, the paper has focused on one product, Coke Zero, and how it can be better sold in Lagos, Nigeria. One of the things one has to consider is the economic power of the target population (people in Lagos). It is arguable that the economy is active as Nigeria is one of the largest economies in the African continent. People have an easier access to disposal funds, thus, will be more likely to explore the Coke Zero product. It is important to note that the company already has significant market share in the region. Therefore, the selected item will be competing mainly against other products housed under the Coca Cola brand. Despite this, it is expected that the product will perform well due to the desire to consume products that support better healthy living. The item does not have any sugar or artificial sweeteners, thus, is also described as having zero calories.
Arguably, the product as a relatively positive sales forecast. One factor that has to be considered when discussing the item’s sales is the growing desire for healthier beverage options. This concern has been growing in the developed nations but the wave has also reached the Third World due to various reasons. One can argue that all the countries in the world are connected through technology and the internet. Therefore, information on the importance of healthy living that is shared in the US can be easily accessed in Lagos. This, coupled with the fact that the current corona virus pandemic has forced people to consider their general health, can be used to forecast a positive outlook for the brand. It is important to note that the company has to consider the consumer needs all through in order to also ensure this positive sales forecast. Already, the parent brand (Coca Cola) is known for simple yet effective consumer engagements and quality. This cannot be compromised in order to both protect the brand image and ensure profitability.
Additionally, the company can employ several strategies for improving the product’s performance in the stated market. The first is adopting the right pricing strategy. The product is sold as an alternative to the original Coke. Further, it is presented as a more valuable beverage compared to the competitor’s due to its superior ingredients. Due to this, it is advisable that the product be slightly more expensive than the original Coke. However, it should still be more affordable than other brands such as Diet Coke and Pepsi Max. Indeed, it is arguable that the company also has to provide various sizes of the same product in order to control the psychological nature of pricing. This will also ensure that no one in the target market is left out due to pricing concerns. The psychology of pricing has to be fully appreciated to ensure that the product is successful in the market. Indeed, the economy of the market also has to be put in consideration to ensure that the product targets the right people. Additionally, the company’s mission statement ties with the strategy as it ensures the target population is not only refreshed with healthier beverages, but also makes a difference in terms of the general wellbeing of the target audience.
References
Abere, A., Capps, O., Church, J., & Love, A. (2016). Mergers and market power: Estimating the effect on market power of the proposed acquisition by the Coca-Cola company of Cadbury Schweppes’ carbonated soft drinks in Canada. Contributions to Economic Analysis, 255, 233-290.
Clarke, T. (2017). Inside the bottle: Exposing the bottled water industry. Canadian Center for Policy.
Coca Cola. (2020). Purpose and vision. Web.
Dana, L. P., & Oldfield, B. M. (2018). Lublin Coca-Cola Bottlers Ltd. International Marketing Review, 16(4-5), 291-301.
Dhar, T., Chavas, J. P., Cotterill, R. W., & Gould, B. W. (2016). An econometric analysis of brand‐level strategic pricing between Coca‐Cola Company and PepsiCo. Journal of Economics & Management Strategy, 14(4), 905-931.
Ellertson, C. (2016). History and efficacy of emergency contraception: Beyond Coca-Cola. International Family Planning Perspectives, 52-56.
Griffiths, R. R., & Vernotica, E. M. (2016). Is caffeine a flavouring agent in cola soft drinks? Archives of Family Medicine, 9(8), 727.
Kant, G., Jacks, M., & Aantjes, C. (2018). Coca-Cola enterprises optimizes vehicle routes for efficient product delivery. Interfaces, 38(1), 40-50.
McKelvey, S. M. (2016). Coca-Cola vs. PepsiCo – A super battleground for the cola wars? Sport Marketing Quarterly, 15(2), 114.
Kee, A., & Yazdanifard, R. (2015). The review of content marketing as a new trend in marketing practices. International Journal of Management, Accounting and Economics, 2(9), 1055-1064
Khare, A. (2017). Guerrilla marketing – innovative and futuristic approach towards marketing. International Journal of Advanced Engineering, Management and Science, 3(5), 421-426.
Kunst, A. (2020). Share of Americans who drank Coca-Cola Zero in the past 4 weeks in 2018, by age. Statista. Web.

