Strategic Human Resource Management
Strategic human resource management (SHRM) is a tactical method for the management of an organization’s human resource function in line with organizational goals and objectives. SHRM enhances these functions by linking the traditional human resource practices to business strategy and the realization of organizational goals to enable the organization to achieve a competitive advantage. In the business field, strategy refers to the leadership provided by the management of an organization, which is geared towards steering the organization in a particular direction to achieve particular goals and objectives. In strategic human resource management, the main goal is to acquire a competitive advantage.
Importance of SHRM in Organisations
According to Wei (2006), properly designed and executed SHRM can facilitate the achievement of organizational goals. Set goals require the dedication of all the organization’s employees. The human resource department of the organization must identify the business sectors that require human resource expertise. SHRM, therefore, helps organizations to achieve their long-term and short-term objectives. Strategic Human Resource Management is essential in ensuring that the company acquires a competitive advantage by effectively utilizing the potential of its human resource. It contributes to reinforcing and overseeing the successful implementation of the organization’s business strategies.
Due to the increasingly competitive nature of the globalized business environment, organizations need to integrate their human resource functions with their business strategies to acquire a sustainable competitive advantage in the market. Strategic human resource management helps in the realization of organizational goals through its application of performance measurement approaches to assess the contribution of each employee to the organization.
Also, SHRM helps by improving the relationship between the human resources function and line managers. This relationship is important since it expands the role of line managers and gives them more authority and responsibility for employees who work under them. In this respect, SHRM enhances the management process. According to Sisson and Storey (2000), the benefits of line management include their ability to identify issues in human resource management that would not have been detected by the top management of the organization and the motivation of employees due to direct contact with management. Line management also ensures that routine problems can be dealt with in a speedy way to allow time for important organizational activities.
SHRM also helps in the attraction and retention of the most qualified workforce that can enable the organization to achieve its goals (Becker & Huselid 2006). Moreover, the strategic human resource function facilitates the organization’s growth by ensuring the retention and proper management of the acquired talent. A motivated workforce is significant to organizational development.
SHRM also assists in the creation of an organization’s vision and interlinked values which essentially create a good working environment for the attainment of the organization’s objectives (Fitz-enz 2000). SHRM provides employees with authority in their responsibilities and affords them the flexibility that can motivate innovation. Such flexibility and responsibility can improve an organization’s productivity.
The resource-based method of achieving competitive advantage emphasizes a link between the internal resources of the organization, its profit margins, and the ability to maintain competitiveness through the process of forming an objective-aligned strategy (Nick 2010). This requires that organizations are mobile, unique, and difficult to duplicate and steady. The human resource function is very essential in adopting this resource-based approach to competitive advantage.
Strategic human resource management is useful in effective talent management. Strategic human resource management expands the skill base of the organization’s employees to enable them to acquire the necessary skills which are useful in the organization’s strategic growth (Armstrong 2008). Constant learning and skill development is important due to the changing nature of business environments and information technology. With this knowledge-based economy, it is the skills and abilities of employees to leverage the power of these technological inventions, rather than the intrinsic capacities of the inventions. The capacity of the human resource function of an organization, therefore, can determine its ability to acquire mileage in the business environment.
The Contribution of SHRM to the Achievement of an Organisation’s Objectives
At Merton Campaign Society, the organization seeks to create an environment where people are safe by encouraging active participation in community affairs. The strategic human resource function of Merton Campaign Society is geared towards the transformation of the local community into a safe place for all residents. SHRM urges the organization’s employees to identify with and contribute towards the realization of organizational values and objectives. It develops an environment of trust and a sense of unity among the employees of Merton Campaign Society.
Also, the SHRM at Merton Campaign Society has created a performance culture that inspires productivity, growth, and customer service. The organization applies strategic human resource management to improve the relationship between employees and encourage cooperation between managers and company employees. According to Rudiger (2005), creating a supportive work culture facilitates the creativity, team spirit, and innovativeness of employees inspired by a feeling of partnership with the organization. To motivate employees, Merton Campaign Society has a reward management scheme where employees who demonstrate exemplary performance are identified and rewarded accordingly. This helps in encouraging employee commitment to company objectives and discretionary behavior (Bamberger & Meshoulam 2000).
Merton Campaign Society implements a vertical integration system. With this system, the organization’s policies and practices, including human resource practices, are aligned according to the company’s strategic goals and objectives (Randall & Jackson 2007). The company believes that only by building its human resource function and supporting the continued training and sharpening of employee skill base can it properly prepare for any changes in the business environment. The training and retraining of employees at Merton Campaign Society are intended to facilitate the long-term business growth of the organization.
Merton Campaign Society implements an internal fit approach to strategic human resource management. In this approach, the company develops a range of related and interlinked human resource policies and practices. It adopts a set of best human resource management practices that are best tailored for organizational success. In the Organisation’s human resource practice, the synergy of the functions is perceived as key to the success of the internal fit model. Strategic human resource management enables the human resource managers at Merton Campaign Society to design their human resource policies and practices in a way that the combined contribution of such efforts exceeds the sum of the individual contributions of the practices and policies.
Human Resource Planning
Human resource planning is a strategic and methodical approach of people management in a way that encourages employee motivation and contributes towards the achievement of company objectives. A human resource plan is a document that outlines the programs that are required in the short and long-term future of the organization. The main objective of the human resource plan is to assist the human resource department in the achievement of the mission and targets set in line with organizational objectives through a systematic strategy.
A five-tier methodology can be implemented to establish the present and future resource demands of an organization. The methodology includes the determination of business objectives, performing environmental analysis of internal and external factors, a gap evaluation, measuring progress, as well as evaluating and reporting on progress (Hall 2002).
Factors that Underpin Human Resource Planning
The ability of the human resource plan to achieve the intended objectives relies significantly on the commitment of the top management and line managers to the idea that the employees are the most important factor in realizing the objectives of the company. A non-committal attitude of the organization’s management can only serve to derail the creation and adoption of the human resource plan. This is especially true since the top managers usually influence financial decisions in the company and budgetary allocation to the various organizational departments. Another important factor to consider when creating a human resource plan is the link between the human resource programs of the organization and the missions and objectives of the organization. A good and strategic plan must be aligned to the overall organizational objectives for an organization to achieve a competitive advantage. Moreover, line managers should also be encouraged to own the human resource planning process as it is likely to influence the productivity of their departments.
The development of a successful human resource plan demands a shift in the way employees are managed. The human resource department should shift from managing people to the achievement of human resource goals through people. It rests upon the understanding of the organization’s objectives, mission, values, and human resource challenges. In developing a business plan that factors-in these organizational requirements, the human resource department assists the company to prioritize its human resource practices and programs in line with the business priorities.
Various internal and external business factors affect the formulation and application of human resource plans. Once an organization has established its objectives, it is important to perform a workforce analysis to determine the future needs of the organization. Workforce planning helps organizations to successfully carry out reforms, expansions, downsizes, or restructures strategically by ensuring the required number of employees is available for successful business operations. Like business and financial plans, a human resource plan is an essential tool in the achievement of organizational goals.
Some of the internal factors that an organization needs to consider include organizational strategy, organizational culture, and the location of the organization (Beardwell & Claydon 2007). Merton Campaign Society, for instance, aligns its human resource plans according to its business location around London since a bulk of its employees come from and resides in the city. The location of the organization is likely to determine the availability and quality of talent. If the organization is located in a city, for instance, there is likely to be a variety of talent and it is finding qualified personnel is likely to be easy. A business located in a suburban setting, on the other hand, is likely to face challenges in acquiring competitive talent. Therefore, the strategic planning of an organization, including plans for retraining and remuneration, must consider the location of the business.
Other internal factors to consider include the business environment (such as business decline, growth, or change), the changing nature of employee roles, and the innovative capacity and flexibility of current employees. Employee flexibility refers to the ability of existing employees to take on new roles and to adapt to organizational changes. Retraining may be required to enable employees to take on new roles.
The external factors that influence human resource planning include government regulations, economic conditions, technological advancements, and workforce demographics (Torrington et al. 2009). Economic trends influence the pool of talent available for employment as well as the ability of the organization to acquire new employees. For instance, a bad economy may force the company to downsize. The organization needs to understand the global and local economic trends to prepare for changes in the job market.
According to Sims (2002), human resource planning is also influenced by technological trends. New technologies can lead to downsizing, especially if the technological invention reduces the workload. Though such innovations can lead to reduced costs of production, they eventually affect human resource management since employees must be trained on how to use technological gadgets and applications.
An Assessment of Human Resource Requirements at Merton Campaign Society
Marchington and Wilkinson argue that successful recruitment needs to be consistent with the objectives and vision of the organization (2008). Identification of present and future human resource needs of the Merton Campaign Society can be conducted using gap analysis. After assessing the human resource requirements of Merton Campaign Society, it is evident that most employees do not have the necessary recreational and volunteer skills needed to grow the company.
It is possible to predict the future human resource needs of the Merton Campaign Society using the methodology of forecasting labor demands. The bottom-up managerial judgment technique shows that managers are likely to need additional employees.
As a company grows and spreads its presence, its human resource needs are likely to expand. Merton Campaign Society needs to identify capable and caring employees who can assist the company in reaching its objective of ensuring security for residents. From the gap analysis, the areas of Merton Campaign Society that need additional attention include training, recruitment, and reward programs. Once the gap analysis has been conducted, the information collected forms the basis for the creation of strategies that are likely to attract and retain quality talent to Merton Campaign Society.
A Three-Year Human Resource Plan for Merton Campaign Society
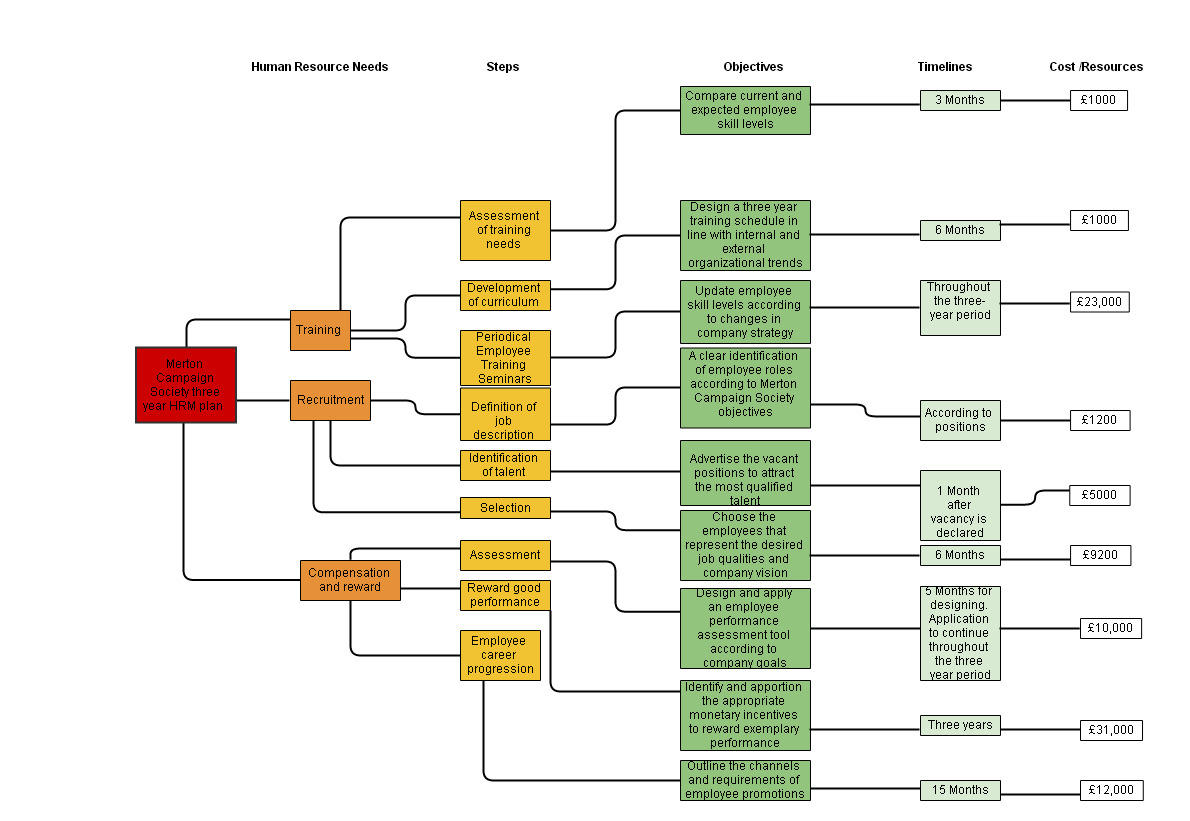
The human resource management plan outlined above covers key areas that require attention in the growth of the Merton Campaign Society. Using SMART analysis, the objectives of the HRM plan have been set in a way that they are realistic and sustainable. However, the plan could have been supported by key indications about the available funds for human resource activities and the mechanisms used in prioritizing human resource projects. Also, an outline of how the timelines would be achieved would have helped in clarifying the plan. Moreover, short term plans ought to have been distinguished from long term plans.
Human Resource Management Policies
The Purpose of Human Resource Management Policies in Organisations
Human resource policies refer to a set of formal regulations and guidelines formulated by human resource departments to govern the hiring, assessment, training, remuneration, and dismissal of employees. Human resource policies should form part of any organization seeking to achieve a competitive advantage. The human resource policies are designed to assist in the management of the human resource function of the organization and to protect employees from manipulation and unethical practices by managers. These policies and practices must comply with existing labor laws and regulations. Human resource management policies also cover equality and equity, benefits, working hours and leaves, employee discipline, intellectual property, and drug use.
One of the benefits of clearly formulated and communicated HR policies is the capacity such policies have to encourage consistency. Such consistency can be achieved in the way messages are drafted and transmitted throughout the tiers of the organization as well as in the management of employees. For instance, different employees from different departments of the organization who are consistently late can receive consistent punishment according to the company policy regarding lateness irrespective of the departments concerned. This is likely to prevent complaints of biased treatment as management protocols are clearly outlined in the policy. The Civil Rights Act of 1964 (Title VII) outlines the treatment of employees and how organizations should design their HRM policies to achieve consistent treatment of employees.
Most human resource management policies are concerned with training, recruitment, teamwork, and organizational culture. For instance, policies that view employees as assets are likely to encourage increased expenditure in the training and remuneration of employees to encourage performance. Viewing employees as assets in the short-term is likely to improve the company’s performance in the long-term.
In an organizational setting, human resource policies contribute to establishing organizational structure and culture. If certain policies such as those governing safety in the workplace, performance assessment and appraisal, employee discipline, and working hours were to be eliminated, most work settings of organizations would be completely chaotic. In this respect, HR policies govern the relationships among employees as well as interactions between employees and managers.
Human resource policies function as a tool for the supervision of employees. In a large company like the Merton Campaign Society, the human resource general manager may not always be on hand to handle all employee disputes, employee questions, and issues of employee discipline. A formulated human resource policy enables supervisors to understand issues relating to employee welfare and discipline. It offers authority to the supervisor while enabling the supervisor to maintain fairness.
Human resource policies are created to oversee employee welfare and ensure fairness (David 2004). These policies ensure equal opportunities for employment as well as equal treatment in the workplace. Human resource policies, therefore, protect employees from exploitation and unwarranted discrimination.
Also, HRM policies aid in performance management and maintenance of best HR practices (Boxall & Purcell 2003). These policies are significant during the analysis of business performance and human resource activities. Besides enhancing the adoption of best practices, HRM policies facilitate consistency and efficiency. This is important in Human resource management since inconsistency can cause worker discontent and conflict in the workplace. HRM policies not only assist in the formulation of strategic goals but also assist in the definition and redefinition of an organization’s strategic direction.
The Impact of Regulatory Requirements on Human Resource Policies in an Organisation
Many legal provisions govern the relationships between employers and employees and the work environment. The Employment Act of 2008, for instance, describes the essential terms of labor for employees in the private and public sectors. The act applies to all forms of employment apart from the military and the police, who, due to the sensitive nature of their job descriptions, are covered under the Armed Forces Act of 2008 and the Police Act. The Employment Act prohibits forced employment as well as the employment of minors. By setting the age for employment, the Employment Act ensures that the human resource policies of organizations on employment are drafted and implemented taking into consideration the age of targeted employees. Also, the Employment Act forbids discrimination in the workplace and discusses working hours. Organizations can design their anti-discrimination policies in line with the Act. This not only informs the policies on anti-discrimination but also reduces the chances of lawsuits based on charges of biased treatment and discriminatory behavior.
Other forms of legislation that cover human resource policies include the Employment Relations Act of 2004 and the Employment Rights Act of 1996, which discuss the relationships between employees and employee rights and responsibilities. The Employment Relations Act of 2004 deals with trade unions as well as the rights and responsibilities of the members of these trade unions. It also covers issues related to minimum wages of employees and the joining of trade unions. This Act is particularly significant during the formulation of an organization’s strategy as it covers issues of employee rights relationship between employers and trade unions. The policy of an organization regarding the unionization of its employees must consider the provisions of the Employment Relations Act of 2004.
Other Acts prohibit all forms of discrimination in the workplace, which include the Disability Discrimination Acts of 1995 and 2005 and the Sex Discrimination Act of 1997. The Sex Discrimination Act guides the formulation of company policies regarding gender, especially in the treatment of women in the workplace. The Sex Discrimination Act also covers gender balance in an organization’s workforce. The Equal Pay Act of 1970 covers policies about salaries and wages.
In the formulation of strategic human resource management policies, organizations are compelled to adhere to the legal requirements of the areas in which they operate (Shih & Chiang 2005). Besides local laws, there are also international labor laws that affect the formulation of human resource management policies. Observing these laws can help a company avoid the expenses associated with costly lawsuits and government penalties. In the event of a lawsuit generated from the observance of employment policies, a company whose policies are designed in line with existing legislation is likely to have the upper hand in court.
Organisational Structure & Culture and Human Resource Management
The Impact of Organisational Structure on the Management of Human Resources
A study by Gerhart and Fang (2005) indicates that management technique or the organizational structure of a company is the principal element in the quest for competitive advantage. The structure of the organization, including its complexity, concentration, and formality, significantly influences the management of the human resource function of the organization. The organizational structure can be perceived as the technique through which organizations apportion responsibility and distribute information within the company (Marchington & Wilkinson 2000).
The organizational structure of a company is determined by the existing rules that govern the relationships between managers and different categories of employees. Types of organizational structures include tall, flat, hierarchical, centralized, decentralized, functional, matrix, networked, and divisional structures. Tall structures are difficult to manage since they have many levels of employee classes. Hierarchical structures are relatively easier to manage since employees are ranked in levels and sub-levels.
Unlike a decentralized structure where decision-making authority is delegated to empowered company employees, centralized organizational structures prefer defined leadership and decision making roles headed by the company headquarters. Functional organizational structures, on the other hand, are easy to comprehend since the components of the organizations are well-defined. Since matrix organizational structure focuses on the development of teams of specialists from different parts of the organization, it resembles the network structure. All these types of organizational structure influence the management of the human resource function of organizations since roles, relationships, responsibilities, and information flow rely on the existing structure.
The right organizational culture creates the right working environment that facilitates the optimization of employee output. The chain of command not only influences the flow of information throughout the organization but also influences the degree of employee motivation. A motivated workforce is easy to manage. An inappropriate organizational structure, on the other hand, is a deterring bureaucracy and can deter the company from achieving its objectives.
The organizational structure of a company elucidates the duties and responsibilities and how they are assigned. Its effect in informing the interactions within the organization is pivotal to obtaining a competitive advantage. The organizational structure of a company is, therefore, essential to the success and practice of human resource management activities.
The Impact of Organisational Culture on HRM
According to Nick (2010), culture refers to the totality of the attitudes, beliefs, knowledge, and norms to which people in a certain community are socially conditioned. Through frequent contact with a certain culture, people acquire languages, behavioral patterns, beliefs, and values. Each organization possesses a set of unique shared values, traditions, and beliefs that are often visible in organizational policies and practices.
Organizational culture can, therefore, be defined as the unique deep-seated principles and values that define interactions and behaviors within organizations. Organizational culture includes a collection of shared meaning understood by members of the organization, which sets them apart from members of other organizations. Organizational culture is, therefore, more important for the overall success of the organization than structure and politics. Hofstede proposes certain cultural values that characterize organizational culture, including masculinity and femininity, individualism and collectivism, and the power of social hierarchy (Gerhart & Fang 2005). Other cultural theorists like Schein, Scholtz, and Handy also tried to explain the link between organizational culture and human resource management.
Organizational culture defines the formality of dressing within the company, the leadership styles adopted by managers, attitudes towards teamwork and risk, innovativeness, as well as employee commitment to quality and service delivery. All these aspects of organizational culture affect the way human resource functions are managed within the organization. The organizational culture and human resource management also have a symbiotic relationship with each one influencing the other.
The principal role played by organizational culture in HRM is the definition of processes and provision of meaning to life within and around the organization. Culture affects key objectives, work techniques, and interpersonal communication within the organization. Different management styles such as autocracy, democracy, transactional, and laissez-faire rely on and impact organizational culture.
Other implications of culture on human resource management can be seen in conflict reduction due to consistency, coordination, and motivation of employees. Organizational culture also contributes towards the achievement of competitive advantage.
How to Monitor the Effectiveness of Human Resource Management
Merton Campaign Society conducts succession planning for its employees to ensure that the right skills are available for the right jobs. Also, training and development at Merton Campaign society are assessed through the evaluation of job-impact indicators. The profitability of the company is also evaluated using certain quantitative measures like the benefit-to-cost ratio.
A technique for monitoring HRM effectiveness is HR auditing where the value of a company’s human resource department is evaluated. The level at which employees are engaged with their employers can also indicate management effectiveness. Assessment of employee engagement can be conducted through periodic surveys. During these surveys at Merton Campaign Society, employees are encouraged to share their opinions on the management styles adopted by their managers. A good relationship between human resource managers and employees of Merton Campaign Society is important in ensuring employee productivity.
A workforce scorecard can also be used to assess the employee contribution to the organization. To benchmark and monitor HR effectiveness, many organizations successfully use human resource information systems. Benchmarking compares certain performance tools against the data collected using those tools by other companies.
Recommendations for Improvement of HRM at Merton Campaign Society
Though the Human resource function at Merton Campaign Society has registered considerable success in providing the labor required for company operations, some areas require improvement. The company can organize more value assessment surveys to evaluate the direct contribution of company employees. Also, external benchmarking can help the company to assess the progress made by other companies in the security industry. The human resource department of Merton Campaign Society should also consider introducing more training programs to update the skills and knowledge of its employees. This is likely to enable the company employees to keep up with the changes in the global business environment.
Reflective Statement
The main themes in this unit have enabled me to understand the changing nature of human resource requirements and the need to formulate strategic human resource policies and plans that are flexible. The knowledge obtained in this course will assist me in my role as a human resources manager to effectively oversee the definition of human resource needs of my organization as well as the effective management of my organization’s employees. At the beginning of the course, I did not fully comprehend the factors played by the business environment on human resource decisions. This unit has certainly been an eye-opener in that regard.
References
Armstrong, M 2008, Strategic human resource management: an action guide, Kogan Page, London.
Bamberger, P & Meshoulam, I 2000, Human resource strategy: formulation, implementation, and impact, Sage Publications, Beverly Hills.
Beardwell, J & Claydon, T 2007, Human resource management: a contemporary approach, FT/Prentice Hall, Harlow.
Becker, B & Huselid, M 2006, ‘Strategic human resources management: where do we go from here?’ Journal of Management, vol. 32. no. 6, pp. 898-925.
Boxall, P & Purcell, J 2003, Strategy and human resource management, Palgrave Macmillan, New York.
David, F 2004, Strategic management: concepts and cases, Prentice Hall, New Jersey.
Fitz-enz, J 2000, The ROI of human capital: measuring the economic value of employee performance, American Management Association, New York, NY.
Gerhart, B & Fang, M 2005, ‘National culture and human resource management: assumptions and evidence’, International Journal of Human Resource Management, vol. 6. no. 6, pp. 971-986.
Hall, R 2002, Organisations: structures, processes, and outcomes, Prentice Hall, New Jersey.
Marchington, M & Wilkinson, A 2000, Core personnel and development, Institute of Personnel and Development, London.
Marchington, M & Wilkinson, A 2008, Human resource management at work: people management and development, CIPD, London.
Nick, W 2010, An introduction to human resource management, Sage Publications Ltd, USA.
Shih, H & Chiang, H 2005, ‘Strategy alignment between HRM, KM, and corporate development’, International Journal of Manpower, vol. 26. no. 6, pp. 582-603.
Sims, R 2002, Organisational success through effective human resource management, Quortum Books, Westport, CT.
Sisson, K & Storey, J 2000, The realities of human resource management, Open University Press, Buckingham.
Torrington, D, Hall, L, Taylor, S, & Atkinson, C 2009, Fundamentals of human resource management: managing people at work, Pearson Education Harlow.
Wei, L 2006, ‘Strategic human resource management: determinants of fit’, Research and Practice in Human Resource Management, vol. 14. no. 2, pp. 49-60.
