This report presents the discussion of the situation which emerged in the company InteCom in 1982. This work is aimed at developing action plan for this enterprise. The paper includes SWOT analysis and Porter’s Model of Five Forces. The examination proceeds to the development of the key developmental strategies which comprise product development, organizational changes and marketing policies, branding and advertising. Furthermore, this report contains approximate time-scales for the implementation of this program.
Introduction
The main purpose of this report is to develop an action plan for the company InteCom. The paper is mostly based on the case study report prepared by Ghemawat who gives overview of the situation in communication industry in early eighties and gives overview of InteComs history, products, infrastructure, and marketing (1986). The discussion will be based only the data available in this case study. This company commenced it operation in 1979. In 1982, this firm entered highly saturated market of PABX technologies with a new or even revolutionary product that could potentially become extremely popular among customers. However, at that moment, the firm had to face severe competition from such giants as AT&T, Rolm, Northern Telecom, Siemens and smaller manufactures. This report presents strategies that might have been used by the management in order to strengthen its position in this field.
Internal and external Environment
SWOT Analysis
At this stage, we need to analyze internal and external environment of the company. SWOT analysis is the most helpful tool in this purpose, as it enables to show strong and weak points of the organization as well as its opportunities and threats that may hypothetically arise.
Strengths
- Novelty of their product. The system IBX S/40 enabled to transmit both voice and data simultaneously. At that point, this product was a prototype of third generation of PBX (Private Branch Exchange). Furthermore, it could be adjusted to already-existing technologies.
- Good Reputation of the firm. InteCom had successfully completed several projects; one of them involved close partnership with Chicago University. Afterwards this enterprise won recognition at least in academic circles.
- Efficient human resource management.
According to the article, employees were quite satisfied with the position in InteCom because they had feasible prospects for promotion and could receive adequate monetary award for their work (Ghemawat, 1986). These factors might have been conducive to the growth and development of this enterprise..
Weaknesses
- Undeveloped infrastructure. The case study shows that the firm experienced significant difficulties in delivering their goods to the clients. In the future this could immensely influence the decisions of potential clients, who definitely wanted time-efficiency..
- Insufficient capital. Michael Bowen and his associates were strongly dependent on external investors, namely Exxon Enterprizes.
- Ineffective advertising. Despite the fact that, InteCom had produced a drastically new PABX system, the target audience were unaware of its existence. This brand was not known to potential clients
Opportunities
- Increasing demand for the third generation of PABX systems. In early eighties there emerged a necessity to incorporate both voice and data transmissions into a single entity.
- Keen interest of sponsors and investors. At that moment, large companies as well as average people understood that this area of research could be very profitable. Moreover, it became evident that InteCom could easily grow into the leading manufacturer of the third generation PABX systems.
- A vast variety of potential clients. Private Branch Exchange, which could convey both voice communications and data, might be used by governmental organizations, educational institutions, small or large companies, hospitals etc.
Threats
- Stiff competition. There were several well-known brands in the United States, for example, Northern Telecom, Western Electric, Rolm and Bell Operating Companies. All of them were had already demonstrated their effectiveness, while InteCom was a new- comer. Furthermore, we should not forget about local companies.
- Incompatibility of technologies. The installation of IBX S/40 required more sophisticated hardware, in particular, 32-bit processor that was rather expensive at lest in the dawn of computer era. Many clients could not afford to buy them (Ghemawat, 1986).
Porters’ Five Force Model
SWOT analysis may be supplemented by Porter’s Model of Five Forces or the factors that could shape the outcome of this venture.
- Threats of new entrants -The high growth prospects in a burgeoning PBX market might spawn a whole new generation of entrants, big and small. With lower pricing and higher servicing capabilities, they might have attracted more clients than InteCom. Moreover, they might have created similar communication systems and InteCom would no longer be a pioneer.
- Bargaining powers of suppliers – It is seen that the manufacturing and assembly aspect of PBX made by InteCom demanded close cooperation with vendors and robust supply management had to be enforced. Apart from that, this cost of production could be too high; hence the whole business could be unprofitable.
- Rivalry among existing competitors – As we have pointed in the SWOT analysis, the market was dominated by such companies as Western Electric, Rolm and Northern Telecom. Given the fact that they had stronger competitive advantages, InteCom had to excel itself in the quality of goods and products that they offered to the clients (Ghemawat, 1982).
- Bargaining powers of buyers – Private Branch Exchange IBX S/40 had be affordable for the clients. The major problem was that its installation entailed modernisation of the equipment, and this was rather expensive for many enterprises. This also imposed some restrictions and could hinder the growth of InteCom.
- Threats of products: The major peculiarity of the company’s innovation was the ability to render both voice and data. However, other firms could work out a less complicated solution but it might have been more practical than IBX S/40 and more applicable to the needs of potential clients.
On the whole, this analysis indicates that in the year of 1982 could make a significant breakthrough in the field of communication technology and win the palm of supremacy in the sphere of digital PBX. Nonetheless, success was dependent on their quality management, ability to attract buyers and relations with suppliers. At this stage, we need to map out the goals and tasks of InteCom.
Development Plan
- The key objective. The management of InteCom could formulate the major goal in the following way: to achieve a very good reputation as an innovative PBX manufacture and become a leading supplier of bundled peripheral products in the United States and overseas. The goal may seem to be slightly ambitious but insurmountable especially considering the potential of this enterprise.
- Tasks. The key actions that had to be taken by InteCom were two-dimensional: 1) to make the organization more mobile, cost-effective and time-efficient. 2) The second task was to gain competitive advantage over its rivals such as Bell Operating Companies, Western Electric, Rolm etc and attract potential purchasers of the product. The emphasis had to be placed on such aspects as organizational structure, product development, and marketing strategies: advertising, price, quality and search for would- be clients (Keillor, 2008).
- Product Development. The telecommunication system IBX S/40 had to be made user-friendly and compatible with available software. The constructors should consider specific needs of various organizations and companies. Perhaps, it might be prudent to create several versions of IBX S/40. Secondly, the company had to develop appropriate software for their device.
- Organizational Structure: the management needed to concentrate on the development of supply chain. They were to find the vendor that could satisfy the quality standards. The supplier had to be located in the proximity to InteCom so that there were no delays. Secondly, Michael Bowen had to find establish the delivery and tech support service that could easily address clients concerns (Crandall & Flamm, 1989).
- Marketing. First and foremost, it was necessary to conduct an advertising campaign so that their brand could position itself in the market. Advertising should have set stress on the novelty of their solution and on the quality of this telecommunication system (Laudon & Laudon 2009). Apart from that, marketing comprises search for people, who may be interested in this solution. Sales representatives of InteCom should visit governmental agencies, educational institutions and private companies that could use Private Branch Exchange combining voice and data communication (Schoder & Madeja, 2004).
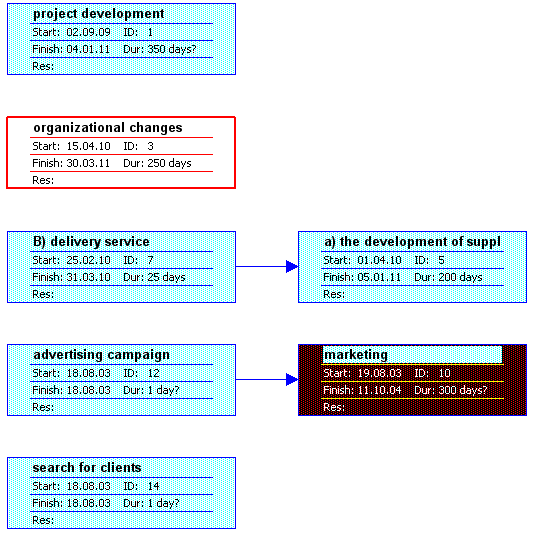
- Time-scales. The whole process can be subdivided into three phases: 1) construction stage which involves product development and organizational changes: 2) marketing (search for clients, advertising, branding) and 3) continues improvement of the company’s operations. This stages overlap with one another. Their chronological order may be presented in the PERT Chart (Please refer to the Appendix).
Competitors’ response
InteComs rivals could adopt several strategies to suppress the firm. First they might have reduced prices on their goods and services. Secondly, they could develop substitute products that could replace IBX S/40 (Keillor, 2008). Thirdly, they could create similar telecommunication systems that could be more serviceable. However, Intecom could achieve superiority if they had managed to carry out swift marketing campaign. Most importantly, they were bound to eliminate every possibility of information leakage.
Conclusions
Evaluation of the strategic plan can be done every week, monthly and even quarterly. The evaluation is only possible if there are clear benchmarked figures available for previous performance results. These results can be compared to the actual performance after the strategy implementation.
Reference List
Chen, IJ, and Popovich, K (2003) ‘Understanding customer relationship management (CRM): people, process and technology: abstract’, Business Process Management Journal, vol. 9, no. 5, pp. 672-688, Emerald.
Crandall, RW, and Flamm, K (1989), Changing the rules: technological change, international competition, and regulation in communications, Brookings Institution Press, Washington DC.
‘Directors’ briefing: cost control: who is involved?’ (2009), IOD.
Elmaleh, MS (2007) Do accounting rules discourage research & development?. Understand Accounting. Web.
Ghemawat. Pankaj. 1986. InteCom. HBS Case Services, Harvard Business School, Boston, USA.
Keillor, BD (2008) Marketing in the 21st Century: Interactive and Multi-Channel Marketing, Greenwood Publishing Group, Westport, CT.
LAN /WAN telephony solutions (1998) Telephony World.
Laudon, KC, and Laudon JP (2009) Management Information Systems: Managing the Digital Firm, Ed. 11, Pearson Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle River, New Jersey.
Schoder, D, and Madeja, N (2004) ‘Is Customer Relationship Management a Success Factor in Electronic Commerce?’, Journal of Electronic Commerce Research, Volume 5, No. 1, pp. 38-53, Hershey, PA.
Scullin, S, Allora, J, Lloyd, GO,and Fjermestad, J (2002) Electronic Customer Relationship Management: Benefits, Considerations, Pitfalls and Trends. Web.
Appendix