Executive Summary
McDonald’s is one of the successful global organizations. Ray Kroc established it in 1955. Currently, it has more than 35,000 retail stores that serve beyond 70 million customers every day. The company expands globally through the franchise business model. By 2013, McDonald’s reported a net revenue of more than 30 billion dollars.
McDonald’s vision, goals, and mission are aligned with the company’s plan-to-win corporate strategy. The strategy centers on the creation of an exceptional experience for customers who prefer McDonald’s foods and services. It rests on five pillars, namely price, promotion, place, products, and people.
This paper focuses on people as an important aspect of McDonald’s overall strategy of improving its customer experience. Management of people falls in the realm of the human resource department in any organization. At McDonald’s, human resource strategies focus on recruitment, selection, training, and development, and retaining employees.
The paper explores the role that is played by HR professionals in the formulation of a human resource plan by focusing on McDonald’s human resource strategies. Apart from presenting a brief overview of the company under analysis, it also discusses the steps that are necessary during the formulation of a human resource plan.
Introduction
McDonald’s constitutes one of the largest fast-food retailers not only in the US but also in other parts of the world, such as Australia. It has more than 35,000 retail stores around the globe, although new stores continue to be established. According to Greco and Michman, statistical findings indicate that McDonald’s opens a store after four to five hours (1). As Greco and Michman confirm, the company’s strategic trademark, as shown below, has played a key role in attracting clients from around the world.

The presence of McDonald’s is experienced in about 119 countries. In Australia, the company has more than 730 stores. In China, it has an excess of 800 stores that are currently functional. McDonald’s employees are in excess of 400,000 people who serve about 70 million clients around the world on a daily basis. In 2005, the company reported revenue of about 21billion US dollars. In 2013, its revenue base exceeded 30billion US dollars. McDonald’s company expands through the establishment of franchises.
In foreign nations, it re-engineers its products to meet local people’s needs. Indeed, more than 80 percent of its stores across the globe are owned and operated through the franchise model. Suppliers and franchises are collectively termed as the McDonald’s system. By leveraging this system, the organization develops the capability to identify and/or implement ideas that address the needs and preferences of its customers.
The business model also facilitates the delivery of consistent and locally satisfying restaurant experiences to all customers. In this sense, it enables the organization to constitute an integral element of the communities it serves. As the paper reveals, the company’s HR section has played a key role in placing the business in its current competitive position.
Company’s Vision, Mission, and Goals
Mission, vision, and goals define the dreams of an organization. McDonald’s mission is to become the most preferred customer eating and drinking base. McDonald’s main goals entail serving good food to people in a friendly and funny environment. It seeks to become socially responsible while giving optimal returns to its shareholders.
As suggested in the mission of the company, these goals imply that the company seeks to build its success on its people who comprise the surrounding communities, suppliers, owners, and customers. Therefore, it is not by coincidence that the company invests incredibly in building positive customer relationships. The development of effective human resource capability is also valued since the goals and mission can only be archived through employees.
McDonald’s vision provides its outlook. According to McDonald’s, its vision is to be “the world’s best quick-service restaurant experience by being the best means for providing outstanding quality, service, cleanliness, and value, so that it makes every customer in every restaurant smile” (2). This statement is compelling and powerful enough to constitute an inspirational view of the organizational desired future status.
Forces that are changing the Firm’s Operational Environment
McDonald’s company has been in operation in the USA. It opened its first store in Illinois in 1955. After five years, its founder Ray Kroc purchased exclusive privileges for McDonald’s brand name. By the end of 1958, the company had sold about 100 million hamburgers. In the same year, the company opened a new location in England. It also opened a new outlet in Florida. Later, in 1959, it opened a new outlet in Hawaii. During the 1960s and 1980s, the company’s operations expanded immensely in the USA and Europe.
It opened its first store in 1971 in Yagoona in Sydney, Australia. Amid the extensive growth into virtually all parts of the world, McDonald’s introduced new product lines in the 1980s, including the famous McChicken and McNuggets. In the 1990s, more franchises were opened across 119 nations where a Canadian franchise owner invented McFurry in 1997.
In 2002, the company posted a loss of $344million over a period of one business quarter. Consequently, it closed its operation in some nations such as Bolivia and 175 underperforming outlets elsewhere across the globe.
In 2003, McDonald’s embarked on healthier meals. In the same year, Technomic market research showed a drop in the company’s market share to stand at 15.2%, where it reported a $126million loss during the fourth quarter. In 2006, it announced its intention to include nutritional information on all its food packaging whilst narrowing its focus on healthier foods such as salads, fresh foods, and chicken. It also reduced its emphasis on hamburgers. In 2008, the company introduced McSkillet burrito.
From 2010 to 2014, the company mainly focused on introducing more healthy foods such as the Maple Oatmeal in 2010 and the Asian salad in 2011. The graph below shows how this strategy worked out for the company to secure close to the top position in terms of client restaurant preferences, as McDonald’s reveals (2).
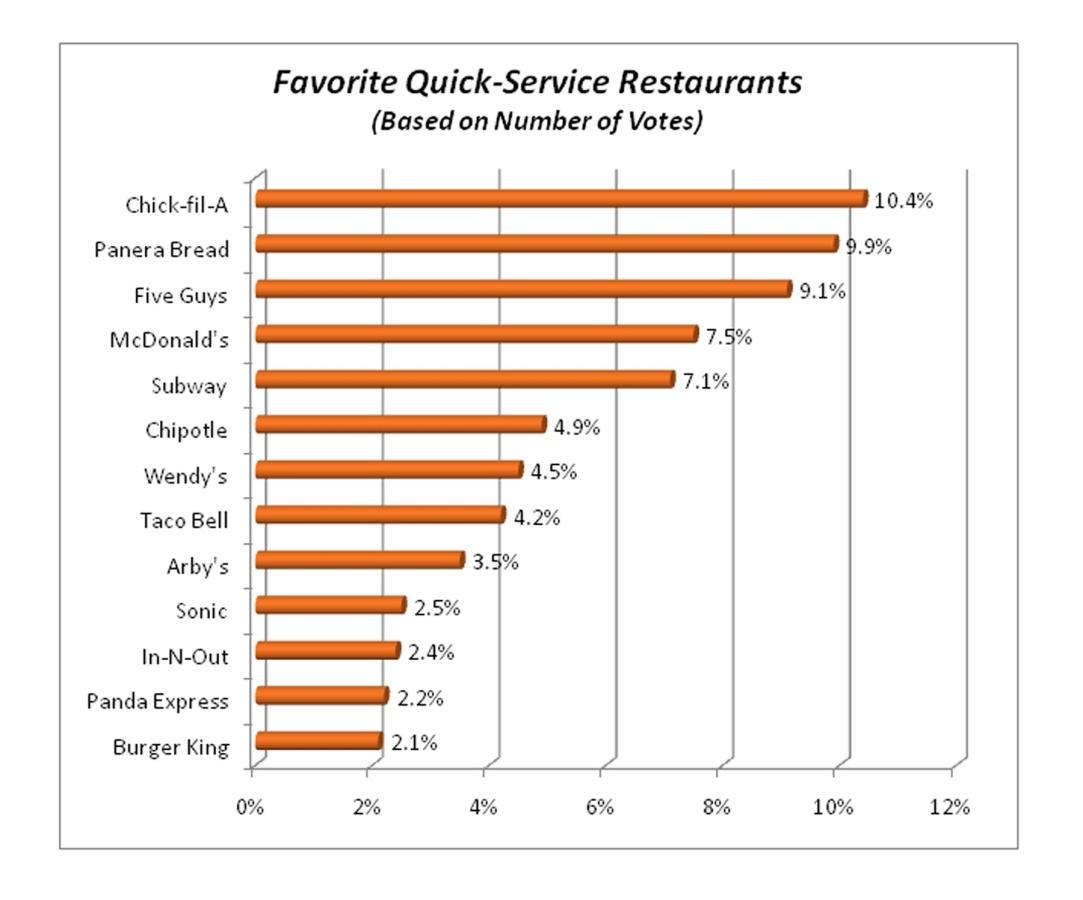
In 2013, McDonald’s introduced online ordering in Sydney (2). In 2014, it made trials for custom burgers. The trials mainly focused on buns, cheese, and sausages, among others. These product lines were launched in Sydney.
Amid McDonald’s continuous growth since its establishment in 1955, it has encountered various forces in its operational environment. The forces have helped in shaping the organization’s operational strategies.
McDonald’s has experienced a myriad of changes in its operational environment, especially by noting that there has been an increasing emphasis on the need for changing people’s eating behaviors to avoid the danger of health risks that are associated with eating unhealthy foods. In fact, health specialists classify foods that contain high calories such as fast foods, which form the McDonald’s menus as unhealthy.
Micro-environmental forces constitute an important element that shapes McDonald’s success strategies. These forces comprise internal factors that are so close to the company to the extent that they affect organizational growth strategies directly. For McDonald’s, some of these factors include customers, shareholders, employees, and the media. According to Gerry, Kevan, and Whittington, an excellent advertisement plan plays a central role in aiding an organization’s strategy to succeed (3).
Media attention on an organization’s operations may result in building the success of organizational strategies or even destroying them. For McDonald’s, the company aims to achieve three fundamental aims by harnessing the media platform. It seeks to create customer awareness of its products, make them have a positive feeling about the products, and/or make them remember the offered products.
Customers constitute subtle micro-environmental factors that influence McDonald’s based on their likes, choices, and even the reason why they buy. On the other hand, McDonald’s has a large number of employees who constitute young and old people from multicultural populations. These people have different needs and cultural affiliations, which McDonald’s has to harness to yield success. Lastly, shareholders form the class of people who contribute the capital for running the company. In return, McDonald’s has to give returns on investments. Therefore, the adopted strategies need to guarantee an increment of the company’s profitability so that shareholders can reap maximally from their investments. The company has an obligation to ensure that it harnesses all forces that affect its microenvironment for its operations to remain smooth and consistent with the long-term and short-term goals.
Another important force that is shaping McDonald’s is competition. This force includes rivalry among fast-food outlets, potential for new market entrants, pressure from substitutes, and supplier and buyer bargaining influence. McDonald’s experiences rivalry due to its many food alternatives for its customers, price wars, availability of many substitutes, promotional incentives, and differentiation of products.
Many organizations that compete with McDonald’s strive to acquire a larger market share through increased product offerings as a way of responding to consumers’ needs. They also offer diverse menus. However, amid this rivalry, McDonald’s also responds to the competitive forces by developing new products and/or improving its customer experience. Unfortunately, most of the organizations in the fast-food industry have relatively equal direct and indirect resources for enhancing their growth.
Human Resource Approaches and their role in HR planning strategies at McDonald’s
Strategic Plan
Global McDonald’s operations are developed and aligned with its plan-to-win operational strategy. This strategy mainly oscillates around the need to provide an exceptional customer experience.
The plan-to-win strategy focuses on products, people, place, price, and promotion (5Ps). With the combination of these 5Ps, the company believes that it can achieve its mission of continuous improvement of customer experience. The company’s human resource strategy constitutes human resource preparation, selection, education, performance, remuneration, and staff maintenance.
In its strategic plan of using employees as its primary source of ensuring customer satisfaction by improving their experiences, McDonald’s has developed an effective employment planning strategy. The company endeavors to make the right employment plans by ensuring that it deploys the right people in terms of their number and expertise.
This plan helps in ensuring that it does not fall short of employees who are needed to deliver not only the company’s products and services but also its values to customers. Without adequate people who can avail of services at the highest possible speed, the organization recognizes that it may fail to push enough products to the market. Customers may consider eating in the firm’s competitor restaurants, which have low waiting times.
In the process of securing the best people to drive McDonald’s success, selection constitutes an important element of the organization’s human resource strategy. In all regions where McDonald’s operates, it has access to a large pool of labor supply. However, it is keen to choose people who can be profitable. Although it selects skilled employees to drive its profitability agenda, it recruits unskilled people.
Nevertheless, it commits organizational resources in their training and development to ensure that they adequately understand the firm’s objective, goals, and mission.
This plan ensures that the organization’s objectives, mission, and goals influence all their work and decisions. The idea of recruiting unskilled employees is driven by the recognition of the fact that the selection may not comprise the only effective way of obtaining the most effective employees, as Leopold and Harris observe (4). Some skills may not be available in the labor supply.
Training ensures awareness of the organization’s values to the new hires. It also guarantees skill development to the existing workers. McDonald’s human resource strategy also focuses on educating employees to ensure that they bring new skills to the organization. It also ensures the improvement of employee performance, together with increasing their awareness of the economic, operational environment for them to take part in the formulation of successful strategies.
McDonald’s human resource strategy emphasizes on employee performance evaluation. Evaluating employee performance in terms of their ability to meet customer expectations and/or shape their experience helps to develop change at the appropriate time. This plan guarantees that the organization does not lose its loyal customers to the competitors. Through remuneration, reward systems, and promotions, McDonald’s human resource strategy ensures staff retention.
Role of the Human Resource in the Strategic Plan Formulation
Health organizations have raised campaigns against foods that have high calories. Such campaigns have resulted in the need for fiber-rich foods. For this purpose, creativity and innovation are necessary for the effort to come up with new products that meet the emerging customer need. This effort is directly congruent with the efforts of human resource in any organization.
HR professionals focus on developing strategic plans that ensure continuous employee development to enhance creativity, novelty, and productivity. In the effort to ensure that McDonald’s remains profitable through the innovation of new products and modes of service delivery, HR professionals can help in ensuring the recruitment of highly creative people or in training and development of the existing employees to increase their expertise levels.
McDonald’s focuses on various mechanisms of ensuring that it provides healthy foods in its menus. According to McDonald’s, the pie chart below shows how the company’s move to introduce healthy foods attracted many clients from its competitor restaurants (2).
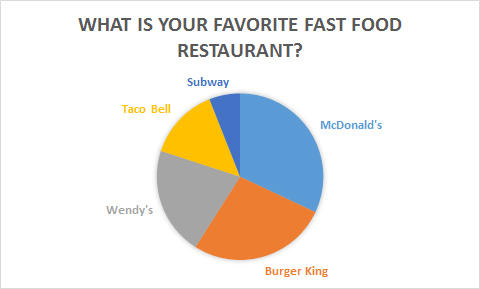
It reflects such changes in its marketing plans. Such a change of pattern in the marketing planning of the company is important to ensure that the company continues to be a global market leader for fast foods.
A particular strategy that the company should reflect in its changing marketing strategies is to incorporate fruit salad in its menus. However, marketing only becomes appropriate during the product promotional process. People must develop and produce such products. Formulation of human resource strategies can support or result in the failure of this process.
Upon identification of the role that people play in the maintenance of an organization’s competitive advantage, McDonald’s considers investment in its human resources, one of its core values. McDonald’s offers work opportunities to its employees, nurtures their talent, develops them, and rewards their achievement. The company believes in the creation of effective work teams that are composed of people from diverse backgrounds.
The company gets experienced workers who can work in an environment that promotes respect and a high level of party engagement to foster collective organizational success. Amid this emphasis, workers have criticized the company concerning employee exploitation through low wages and maintenance of highly hierarchical and bureaucratic organizational structures. Such an organizational structure hinders innovation and creativity as opposed to the company’s strategy of using employees to create and improve its products.
By recognizing this plan, human resource professionals can take part in the formulation of strategies that ensure alteration of organizational culture and structure by convincing organizational management that some practices are inconsistent with an organization’s mission and vision.
Benefits of well-thought-out HR Plan
A well thought out HR plan forms the foundation for resolving any problems that may influence all employees at McDonald’s. In all organizations, customers interact directly with employees. Customers channel their complaints about an organization through the employees. This claim implies that the implementation of a well-thought human resource plan facilitates the attainment of competitive advantage. Every organization experiences problems due to changes in the work environment.
For instance, McDonald’s experiences challenge while developing people to acquire requisite skills to enable them to meet the emerging changes. Revels and Morris assert, “Rapid change requires a skilled and knowledgeable workforce with employees who are adaptive, flexible, and focused on the future.” (5).
The Human resource management arm of an organization has the responsibility of developing an organization’s labor force to enhance its productivity through training and development. This goal can only be achieved upon the formulation of a well-thought human resource plan.
McDonald’s evaluates the performance of its employees using the appropriate changes in their management to ensure that they remain committed to improving the customer experience within the organization. Performance is a function of employee productivity. For organizations that seek to build their success in the short-term and in the end, the human resource arm is organized in such a manner that it permits all employees to develop skills and knowledge.
Highly skilled employees can deliver optimally the expected outcomes of various tasks that are allocated to them both within the shortest time possible and at the set quality standards. While this situation depends on the effectiveness of the training and development process, motivation is a necessary functional responsibility of the human resource.
Effective motivation, training and development, and remuneration plans are only possible to develop when HR professionals are incorporated in the formulation of well thought out human resource strategies.
A well thought out human resource plan reflects the need for incorporating effective performance management systems. Such systems reflect compensation and performance feedback models to help an organization to make decisions on whether the incentive programs that are designed to induce performance yield results. Any performance measurement process must possess a mechanism of providing feedback to the developed strategies.
Devinney and Yip reckon that performance is a reliable criterion that is deemed appropriate for the evaluation of various environments in which organizations operate (6). As an important aspect of a well thought out human resource strategy, the performance management system is beneficial since it provides a means of evaluating the outcome of human resource improvement strategies through a feedback loop.
Steps that McDonald’s follows while formulating its human resource strategies
Dessler, Cole, and Chhinzer provide a detailed plan on the steps that any successful business can adopt while developing its HR strategic plans (7). An effective human resource strategy is formulated by determining goals, scanning the environment, conducting workforce and gap analysis, and setting HR priorities to help in achieving departmental goals.
Monitoring, evaluation, and reporting on progress are also other crucial steps that have to be followed. Goals help in determining the requisite direction of an organization through human resources. They provide the basis for evaluating progress while utilizing people to drive organizational success. Human resource goals lie in the category of job-performance, executive-presentation, imitation, or individual-performance.
Human resource plans respond to the needs of the environment in which an organization operates. Thus, environmental scanning is incredibly important for the formulated plans to respond to any environmental changes. This stage involves systematic surveys that are aimed at identifying and helping in the interpretation of external threats and opportunities.
Workforce analysis involves determining the existing and future changes in the supply and need for people who have the required skills, knowledge, and competences. To formulate an effective strategy, HR needs to establish the differences between the demand and supply of people who have the required skills.
The HR executes various roles, which compete with one another within an organization. Therefore, it must prioritize its tasks in response to organizational needs. For example, McDonald’s determines whether to engage employees, train, and educate them or to focus on the overall management of HR strategies.
However, no guides have been established on what the organization should prioritize. It depends on the particular needs as determined by the strengths, weaknesses, and opportunities of its HR as determined in the environmental scanning phase.
Monitoring and evaluation ensure that the formulated plan remains in line with human resource needs. Monitoring means supervision of activities to enhance the correlation between the desired goals and the HR plan.
Evaluation determines the extent to which an implemented plan measures up to the formulated HR plan. In McDonald’s, monitoring and evaluation are done continuously. The company acknowledges the need for preparing progress reports, which avail data on the overall analysis process of its human resource plan.
Conclusions and Recommendations
The objective of the HR department is to handle issues that relate to employees. At McDonald’s, functional responsibilities include training and development, recruitment and selection, employee conflict resolution, deriving employee motivation strategies and job satisfaction programs, and taking active roles in the establishment of remuneration programs, among other issues. While developing any plan for its Human resource management, the organization involves its HR professionals.
McDonald’s benchmarking process elaborates on how the company manages its human resources right from strategy formulation. It is recommended for all organizations that seek to build their success around people to incorporate their HR in the formulation and subsequent implementation processes of all their organizational strategic plans.
Organizations need to develop well thought out human resource plans by determining goals, scanning their environments, conducting an analysis of their workforce, performing gap analysis, setting HR priorities, and monitoring, evaluating, and preparing progress reports. Hence, they can have the assurance of developing HR strategies that can result in positive working relationships between an organization, employees, customers, and other stakeholders.
References
- Greco J, Mitchman D. Retailing Triumphs and Blunders: Victims of Competition in the New Age of Marketing Management. New York, NY: Quorum Books; 1995.
- McDonald’s. Company Profile. Canberra: AIHW; 2015. Web.
- Gerry J, Kevan S, Whittington R. Exploring corporate strategy: text and cases. London: Prentice-Hall; 2005.
- Leopold, J, Harris L. The Strategic Managing of Human Resources. New York, NY: Prentice-Hall, 2009.
- Revels M, Morris M. Technology Impacts in Organizational Recruitment and Retention. Franklin Business and Law Journal. 2012; 3(1): 62-69.
- Devinney R, Yip J. Measuring business-unit level: Integrating administrative mechanisms with strategy. Academy of Management Journal. 2009; 31(4): 826-853.
- Dessler G, Cole N, Chhinzer N. Human Resources Management in Canada. Canada: Pearson Education Canada; 2013.

