Executive Summary
This work was created to overview and evaluate the current marketing environment surrounding one of the biggest media conglomerates in the world today – the Walt Disney Company. Having an unrivaled level of fame and influence, the company can be seen as a prime example of successful and fruitful entrepreneurship. With Disney’s name being known in almost every single country in the world, it can also be seen as one of the best discussion subjects on the topic of marketing in the digital age.
Despite the heavy reliance on traditional 2d cartoons and animation, the company has successfully shifted away from its roots, redefining the common understanding of Disney and continuing to offer value to people all around the globe, from young to old. In terms of current marketing challenges, however, the company has a few considerations to take into account. Conquering the emerging markets of countries such as China and India, for example, presents a significant problem. With the cultural and historic differences existing between various nations, Disney’s expansion into foreign markets has become more complex than before. In order to keep the high revenues and a good public image, the organization must adapt its approaches depending on the target market and its specificities.
Introduction
Company Overview
The Walt Disney Company is a multimedia entertainment corporation founded in the US and is regarded as one of the biggest and most influential conglomerates in the world. Named after its founder, Walt Disney, the organization has continuously grown and developed within the film and entertainment industry, expanding to a variety of other ventures with its growth in the modern age. Nowadays, the Disney company’s products and services reach people in more than 133 countries around the world. Additionally, the organization constantly expands further, acquiring other companies as a part of its multimedia network and reaching into more innovative industries.
Company Background
Disney has its humble roots in the US state of California, where two brothers, Walt, and Roy Disney, decided to found a cartoon company in 1923. Since its inception, the organization has quickly established its own unique brand in the cartoon industry, becoming a cultural behemoth of 20th-century entertainment. Becoming a de-facto leader of the entire American animation industry in the 90s, the Walt Disney Company has further delved into other entertainment spheres.
Disney’s Mission and Vision
As an entertainment industry giant, the main vision and mission of the company are to work for the people in many countries. As stated on the company website’s about section, “The mission of The Walt Disney Company is to entertain, inform and inspire people around the globe through the power of unparalleled storytelling, reflecting the iconic brands, creative minds, and innovative technologies that make ours the world’s premier entertainment company” (Disney – LEADERSHIP, history, corporate social responsibility 2020). The mission statement reflects Disney’s commitment to producing multimedia entertainment that appeals to a wide audience of people, from adults to children, and brings its own unique value to the world.
Marketing Challenges for Disney in the Digital World
In the modern business environment, there is a large variety of challenges that any successful company should overcome on a day-to-day basis. The constant creation of value and promotion, among the many social, economic, political, and environmental responsibilities, put corporations of today in a uniquely challenging spot. For the purposes of the overview, some of the major marketing challenges for Disney will be discussed.
Macro-Environment Analysis: Global PESTEL Analysis
As a major player in the international market, the Disney Company’s PESTEL analysis should be completed with a global perspective in mind. In regards to the political and legislative side of the discussion, Disney often finds itself in a favorable light, in a major part to using intellectual properties effectively and expanding into new markets with stable political structures. By often adapting stories that are a part of public copyright, the company avoids having to pay royalties in their adaptation of classic stories while also retaining their creative freedom. The appearance of new stable political environments and global cooperation between nations also helps Disney, as the company gains the ability to effectively establish its operation. Economically, the situation and circumstances surrounding the Walt Disney company are complicated.
On the one hand, the continuous expansion of mass media and the entertainment sphere is a big advantage to Disney, as movies, cartoons, and other productions represent a major part of their revenue. Additionally, the popularity of social media and the internet improves the potential for marketing, merchandise sales, and advertisement, further expanding the outreach of the brand. The development of new multimedia technology, as well as its adoption in developing countries, gives Disney a constantly improving potential avenue for growth. Alternatively, however, the US, as the home base and the main source of revenue for the conglomerate, presents particularly complicated circumstances (Stoll, 2021). With the emergence of the recent Covid-19 pandemic, as well as the general turbulence of the country’s economy, the Walt Disney company might be faced with difficulty in maintaining its revenues throughout recent years.
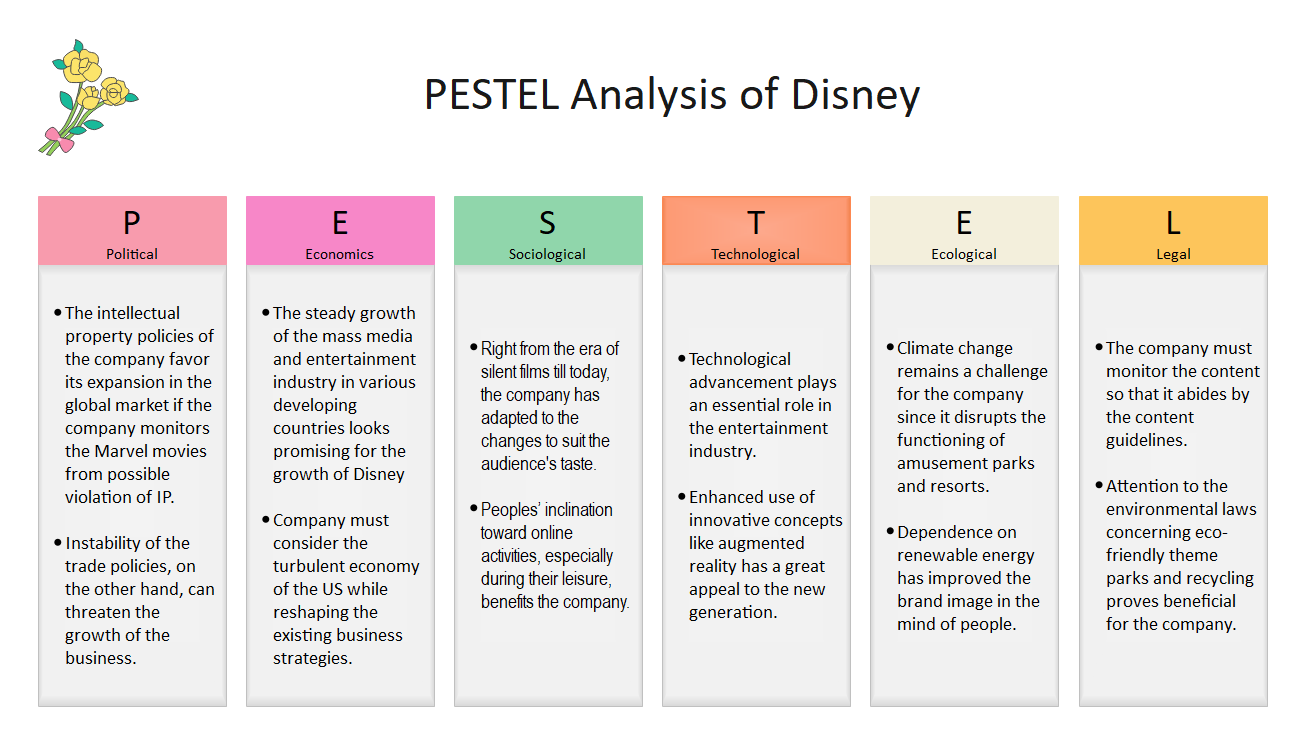
In terms of the sociological overview, the conglomerate has a most beneficial position, with both the people’s modern tendencies and the development of the company in the years since its foundation playing to its advantage. Throughout generations, the Walt Disney Company has managed to adapt, change, and improve based on the desires of the population and the trends of each subsequent age. The less-enduring ideas of the past were discarded, leaving only the ones that work and present the company with the most benefit. In addition, both the development of technology and the effects of the pandemic have driven people towards online spaces, which are currently dominated by Disney-owned services and intellectual properties.
The expansion of the brand into the computer sphere has guaranteed the prolonged relevance of the Disney brand, as well as its popularity and longevity in the public eye. As previously discussed with the social analysis, the advancement and the growing role of technology actively plays into the hand of the organization, allowing it to improve revenues and venture into new market segments. In terms of the company’s relation to ecology, it should be said that Disney is one of the more sustainable corporations in the market, showing the continued effort to minimize the impact of its operation on the world (Environmental sustainability 2021). In particular, its cruise ship industry and amusement parks employ sustainable energy, with the former being regarded as the most environmentally-friendly option currently in operation (Mănoiu & Crăciun, 2018).
Due to the effects a disregard for the environment has on an organization’s public image and customer retention, Disney invests a lot of resources into managing its climate trail. Legally, the company manages the operation of its numerous venues, including all the laws and regulations associated with the process. Copyright legislation, licensing, depictions of certain topics in media, and environmental regulations, are all abided by and overseen in order to be able to operate on a multinational scale.
Micro-environmental Analysis: Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
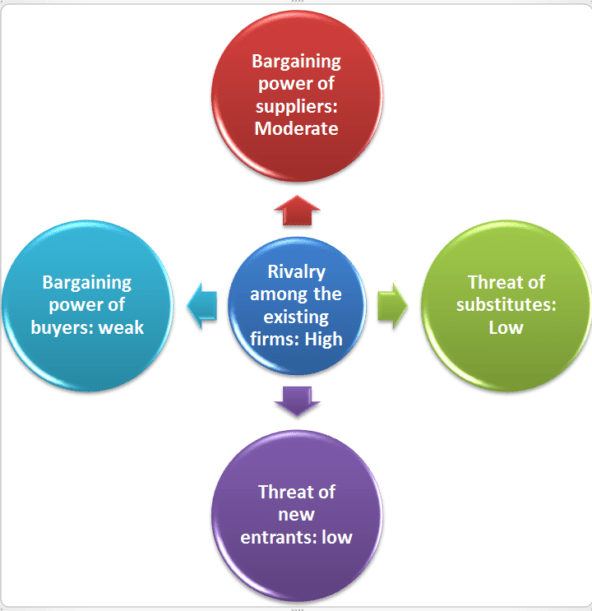
On a micro-environment level, the company’s current position is mixed. The first of the five considerations, rivalry among existing firms, is undoubtedly high. With the massive amount of directions and business ventures that Disney engages in, the company has found a number of professional rivals in almost any sphere of entertainment they penetrated. In the TV network and traditional multimedia field, such competitors as Comcast, Viacom, Warner Media, and AMC Networks (The world’s top broadcasting companies by market value as on 2021 2021).
Since the arrival of streaming services, the Disney Company has also had to face steep rivalry with such services as Netflix, Hulu, HBO+, and many others. With the gradual and continuous expansion of the company, the list of its potential rivals also expands, making operations more difficult for the Walt Disney Corporation.
The bargaining power of suppliers, on a related note, is much less prevalent. Due to the use of outsourcing as the primary method of production, the company manages to quickly and cheaply produce merchandise and goods. Comparatively, the amount of bargaining power and influence of any of the outsourcing sites is small, and no significant influence on the company at large from its suppliers has been made. In addition, there are reports of exploitation and other kinds of mistreatment at Disney factories, effectively making their level of impact on the company at an even lesser scale (China Labor Watch, 2010).
Similarly, the bargaining power of buyers and customers is severely limited, primarily due to the enormous size the company has grown to in recent decades. With the variety of revenue streams, business ventures, and millions in profits each month, the actual social and moral responsibility the organization bears can be disregarded. This tendency can be seen in the recent controversy over the filming of the live-action remake of the Disney classic cartoon Mulan. Disney’s choice of filming location has sparked outrage and controversy, which were not commented upon by the company itself and largely ignored by the public representatives of the Walt Disney Corporation.
This action shows that the organization can largely ignore and disregard the feedback from its customer base without suffering a major loss in support and revenue. One of the primary reasons for that is an extremely positive established reputation of the Walt Disney brand, as well as its popularity among its core demographics (Wasko, 2020). Largely due to the large selection of intellectual properties under its belt, as well as a prolonged brand history, the conglomerate has managed to amass a loyal following. The only potential avenue where people’s voices are regularly heard is environmental action, which often prompts organizations to enact positive change (Vote with your Wallet: Consumer power as Activism 2020).
Thanks to the aforementioned factors, including brand image and a long-established history, both the threat of new entrants and the threat of substitutes are low. Most companies in the entertainment industry do not possess the same outreach and influence that Disney has, putting them at a significant disadvantage (Whitten, 2019). The process of acquiring other brands and intellectual properties, including such famous examples as Marvel and Star Wars, additionally makes it difficult for any other company to replace Disney (Beattie, 2021). In the process of its cultural expansion, the brand creates a monopoly on entertainment and denies potential new competition the same access to audience or platform.
Disruptive & Sustaining Innovations
As one of the biggest players on the market, the Disney Company has managed to both find a comfortable, sustainable innovation structure and periodically use more disruptive tactics to its advantage. With a reliable and constant movie release schedule, the company has the ability to collect revenue at a planned rate, supporting its outward development and further growth (Goodman, 2021). The operation of Disney amusement parks and the constant merchandising of Disney properties further sustain this notion, giving the corporation marginally more finances to use (Richter, 2021).
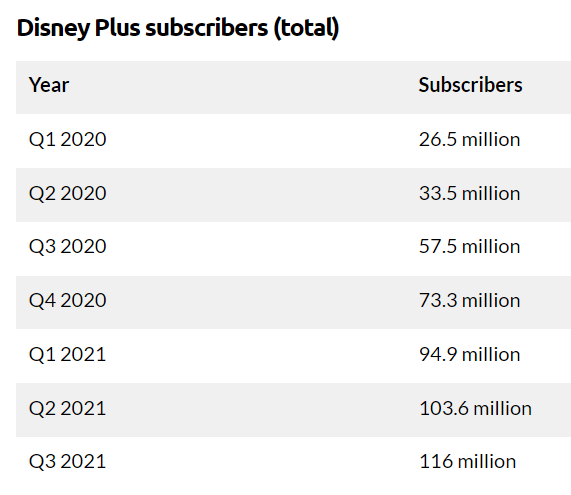
In lieu of the corporation’s stable position in the market and good financial leverage, it also has the ability to take risks and experiment with its approaches (Hornor et al., 2017). The move toward online streaming services, especially, can be seen as a positive and radical change in direction for the Walt Disney Brand. With the popularization of Disney+, and the effects of the recent Coronavirus pandemic, the organization has been able to reap increasingly large profits year after year. Within the last two years, especially, a dramatic rise in subscriptions can be seen.
The Global Paradox, The World is Flat
The World is Flat theory presupposes that any business and competitor have an equal chance for success, in all accounts except labor. In the entertainment industry, this effectively means that many organizations and companies present a challenge to the Disney Company. In the case of Walt Disney, then, the challenge can be resolved by buying out the competition and establishing a complete monopoly on the movie and entertainment. Similarly, with the acquisition of Fox and Pixar, Disney can work to expand its labor force and increase its chances of success by decreasing the amount of competition faced.
The Long Tail
In terms of the main business model offered by the corporation, the long tail approach can be identified as the major contributor to corporate success (Anderson & Andersson, 2007). The Long Tail solution to revenue is effectively utilized throughout the entertainment industry and adopted by other major players on the market. For Disney, this approach means investing and advertising a large number of products, services, intellectual services, goods, subscriptions, and other types of deals to their customer base (VanDeBrake, 2020).
Instead of overwhelming the potential buyers with the biggest possible amount of one property or item, the business spreads its efforts out, increasing the public appeal and producing only the necessary amount of goods or services. Additionally, the company has mastered the process of creating demand for its products through the creation of artificial scarcity (Ledger, 2021). By purposely limiting the access to goods and services produced by Disney, and other companies owned by Disney, the business drives up the market demand for its wares while also narrowing the customer choice.
Evaluation and Recommendations
Current Marketing Strategy Evaluation
Evaluation by Sales & Market Share of the Company
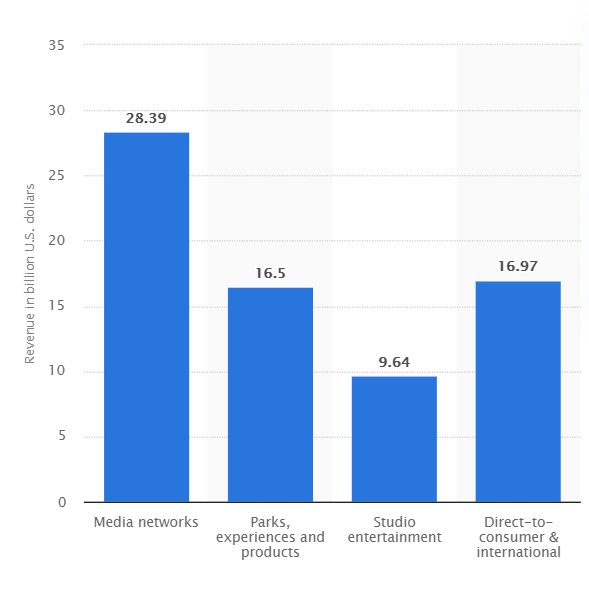
It is difficult to estimate and understand the full impact the Disney Company has on the market, primarily due to the cheer scope and influence it has in a variety of entertainment sectors. Taking into consideration two of the company’s most profitable and notable avenues, the box office market and the online streaming market, it can be seen that both present the Walt Disney Conglomerate as a major contender (Ness, 2020).
For the movie industry, Disney is undoubtedly the force that sets future trends and moves the goalposts for revenue, as its share in the industry after the recent merger with Fox is even bigger than before. In 2019 alone, the company has managed to hold almost half the global film industry revenue (Whitten, 2019). More than 16% of the whole box office market is occupied by Disney, with Warner, Sony, Universal Pictures, and others following suit. Similarly, the company has managed to gain a stable footing in the streaming segment despite its late arrival and fierce competition. While Netflix remains the biggest force in this segment, as of 2020, the company is occupying second place in terms of subscriptions.
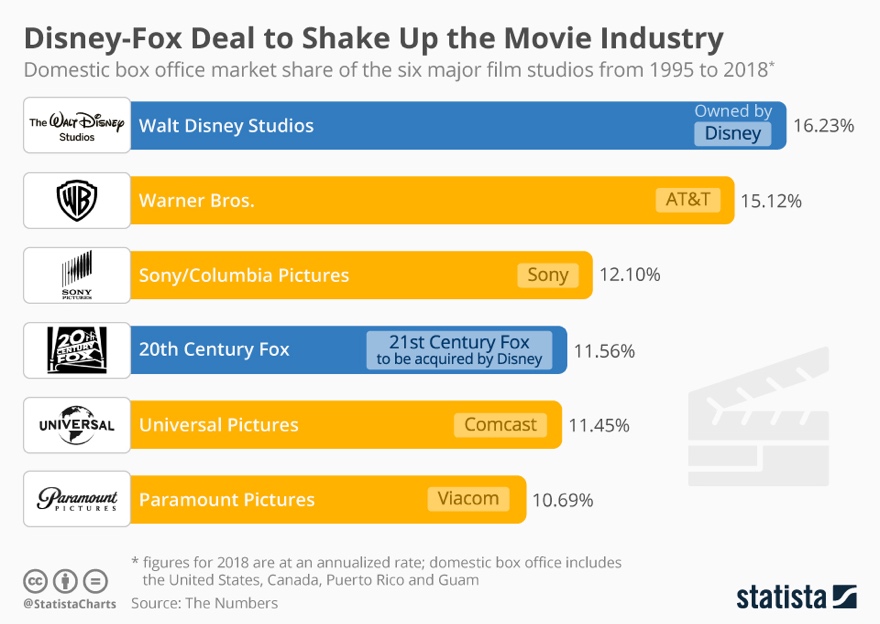
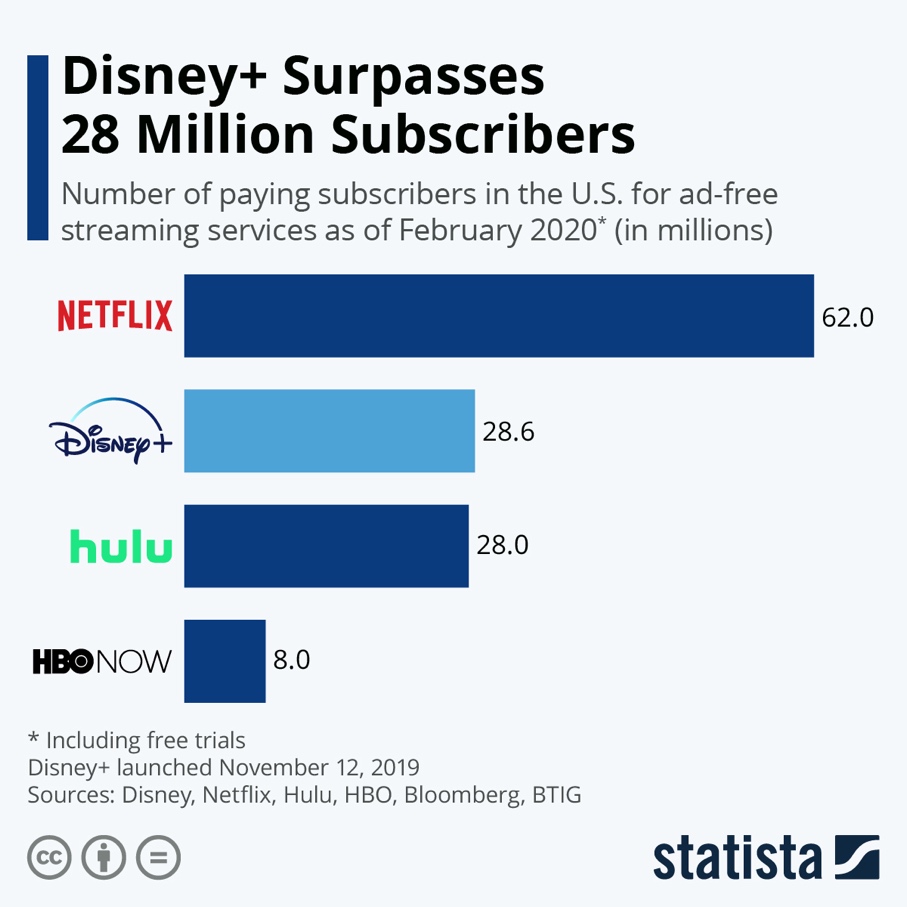
Evaluation by Perception Map
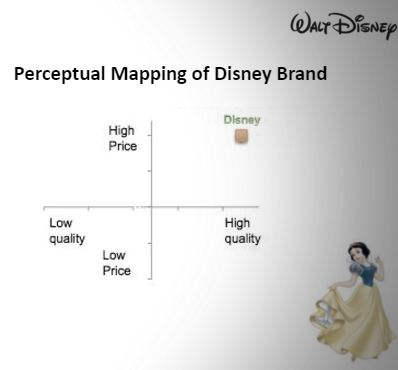
Perception maps are a tool that can be used to gauge how a business is perceived by its audiences. In the case of the Disney Company, the organization is overwhelmingly viewed as combining high quality and high prices. This puts the entertainment organization at a luxury-like level where value is created from commodities and goods created by the organization. The combination of both good quality and high prices keeps the reputation of the company high in the eyes of its audience.
Evaluation by Competitive Profile Matrix
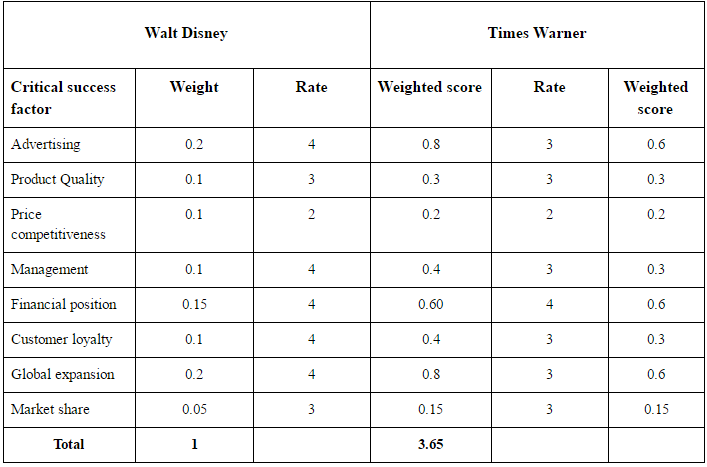
The competitive profile matrix is a useful measure to compare the organizational and market performance of competing organizations. In the case of the Walt Disney Company, it is reasonable to compare the business with Times Warner, which is another multimedia entertainment company operating in the US and overseas. In terms of product quality, prices, financial position, and market share, both companies are similar, operating as established faces in the industry. In the advertisement department, Disney wins, largely due to a variety of recognizable properties for customers to get attached to. Customer loyalty is higher for this company due to the same reasons. In terms of management and global expansion, one can note that the Walt Disney Company has managed to secure a strong international presence and a distinct identity.
Recommendations
Ansoff Matrix
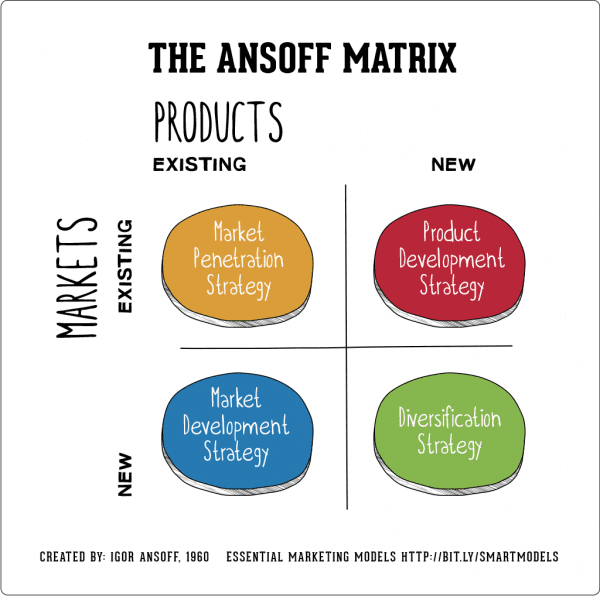
The Ansoff Matrix for implementing change can be used to identify and classify potential areas of improvement for the Disney brand, as well as for the process of finding suitable recommendations for its further growth. The current market penetration strategy for the company focuses on expanding the number of companies and properties used under the Disney name, as well as continuously producing media in connection with the existing ones, keeping them in rotation in the public mind (Williams, 2019).
For future development, it would be beneficial for the company to embrace new concepts and ideas instead of reusing older ones from its existing collection as a way to both attract new potential audiences and increase the number of potential opportunities for the future. As seen by the feedback on the majority of live-action Disney remakes, the public opinion of the company is starting to shift unfavorably due to the general inability to take more risks. With the creation of new media and the incorporation of novel intellectual properties, the Disney company can deliver better value to its customers.
In terms of Market Development, the move towards new emerging markets by the company has been more and more evident in recent years, with a particular focus on China as a large source of revenue. Despite some pushback and cultural differences, a constant effort to penetrate the Chinese market can be tracked, with many of Disney’s classic movies and upcoming releases being specifically made to suit this new audience (Yu, 2015). In the future, even further utilization of China as a source of revenue would be favorable due to a big potential audience and spending potential in the country (Khankasi, 2020). To properly adapt to the cultural and historical tradition of the new market, the Disney company has to integrate Chinese values into its regional approach, further understanding the desires of this market and its subjects.
Product development has always been something that the company excelled at, offering its customers merchandise, personal experiences, and stories based on the existing intellectual properties and creation of Disney. Amusement parks and toys, in particular, can be seen as a great way to expand upon the brand’s product line and keep it in the minds of the public. However, due to a large overall number of properties under Disney’s wing, not all of them get the same treatment and exposure, leaving a lot of missed potential in terms of audience creation and revenue. The venture into streaming services has successfully shown that the company can take a risk and reap big rewards in turn (Cox, 2020).
Expanding the line of merchandise and products connected with less popular Disney properties can be an effective and novel way for improvement, allowing the company to gain more public support and recognition.
Diversification, similarly to the process of market penetration and market development, involves a better understanding of the audiences a brand has and finding the proper way to gain more of them (Markides, 2014). For the Disney Company, this would mean expanding into countries and territories where its influence is much smaller than the US, especially the quickly growing Asian market. Once again, bringing up the example of China, the business can be more successful in that segment of the global economy by diversifying its public image. Currently, Disney’s image is intrinsically connected with its home country, the US, which alienates potential audiences and makes it less likely to be accepted overseas. Disney should strive for a far more neutral, nationless public image, one that highlights its entertainment value while also not being in connection with any particular country.
Brand Identity Elements
Throughout the years, the Disney company has established itself as a family-friendly, inclusive and positive sphere of entertainment for all ages. Its ability to create engaging narratives and experiences presents its unique market value, and an array of unique intellectual properties further bolsters Disney’s appeal. In the process of improvement, the company must continuously take into account the public perception it has gained and the influence of its actions on it. To maintain a cohesive and inclusive public image, the Walt Disney Company must demonstrate its values to the customers in both public and corporate actions and in the products it creates (Shanly, 2021).
Actions such as a more vocal and substantial ecological position would be greatly beneficial to Disney’s brand image and also contribute to its longevity as a brand. Climate change action can be seen as one of the potential avenues for a company’s development.
Country of Origin Effect
As previously noted in the Ansoff Matrix, the US has become a major part of Disney’s image and brand, hindering the company’s potential for connecting and establishing its presence in other markets. The Country-of-Origin effect, including the translation of American values onto the corporation, can be seen as a significant challenge. To combat this problem, the brand should have the capacity to identify its own set of values and goals and reinforce them as the primary motivator behind its action (Prats et al., 2017). Furthermore, the incorporation of other countries’ ideas, traditions, history, and insight could be beneficial in further diversifying Disney’s identity.
Conclusion
The Walt Disney Company, as a major media conglomerate and the creator of many beloved franchises, fills an important role in the lives of its customers. As a brand, it offers its audience a sense of love and belonging by creating unique media experiences and uniting communities that enjoy them. The various physical and online spaces facilitated directly by Disney, and its fans, have given many individuals an improved sense of connection with others and thus intimately connected their lives with the Disney brand. Through the creation of more value for the public to enjoy, the corporation will have the ability to further fulfill the needs of the people and remain in the public consciousness.
References
Anderson, C. & Andersson, P.M., 2007. Long tail, Stockholm: Bonnier fakta.
Beattie, A., 2021. Walt Disney: How Entertainment became an empire. Investopedia. Web.
China Labor Watch, 2010. Code of Conduct is No More than False Advertising, Disney Suppliers Continue Exploiting Chinese Workers. Web.
Cox, E., 2020. Disney and new product development: A case study On disney+. LinkedIn. Web.
Disney – LEADERSHIP, history, corporate social responsibility (2020) The Walt Disney Company. Web.
Disney PESTEL Analysis. (n.d). Edrawsoft. Web.
Disney plus revenue and usage Statistics (2021). Business of Apps. Web.
Environmental sustainability (2020). The Walt Disney Company. Web.
Goodman, L., 2021. From ?black Widow? And ?Avatar 2? TO ?STAR WARS?, here are 30 upcoming movies to expect between 2021 AND 2028. PureWow. Web.
Hornor, T. et al., 2017. How to take calculated risks in business to reduce losses. Bplans Blog. Web.
Khankasi, A., 2020. Ansoff matrix for Walt Disney. Ansoff Matrix. Web.
Ledger, P.byK., 2021. Supply and Demand, Disney-style: Why you shouldn’t copy their methods. Promotional Products Blog. Web.
Mănoiu, V.-M. & Crăciun, A.-I., 2018. Waste management on board Disney cruise Line company ships. Lucrările Seminarului Geografic “Dimitrie Cantemir”, 46(2), pp.77–100.
Markides, C., 2014. To diversify or not to diversify. Harvard Business Review. Web.
Ness, N., 2020. Innovation: The magic behind disney’s sales success. Profiles Incorporated. Web.
Pdugar, 2016. Perceptual mapping. T1 2016 MPK732 Marketing Management (Cluster B). Web.
Prats, J., AMIGÓ, P., & SOSNA, M., (2017) How to overcome a negative country-of-origin effect. Entrepreneurship. Web.
Richter, F., 2018. Infographic: Disney-Fox deal to shake up the movie industry. Statista Infographics. Web.
Richter, F., 2021. Licensed merch: Disney the clear number 1. International Business Times. Web.
Shahzad, 1970. Walt Disney – Competitive Profile Matrix. CSBAdmin. Web.
Shanly, C., 2021. How to maintain a strong brand identity on all your social networks. IMPACT. Web.
Stoll, J., 2021. Walt Disney revenue by region. Statista. Web.
Stoll, J., 2021. Walt Disney revenue by segment. Statista. Web.
VanDeBrake, J., 2020. How disney became the undisputed “king of the box office”. Medium. Web.
Vote with your Wallet: Consumer power as Activism. (2020) Medium. Web.
Vultaggio, M. & Richter, F., 2020. Infographic: DISNEY+ surpasses 28 million subscribers since launch. Statista Infographics. Web.
Wasko, J., 2020. Understanding Disney: The manufacture of fantasy, Cambridge: Polity P.
Whitten, S., 2019. Disney accounted for nearly 40% of the 2019 US box office. CNBC. Web.
Whitten, S., 2019. Disney is dominating the animation category and no other Studios seems to be able to compete. CNBC. Web.
Williams, A., 2019. Disney’s generic competitive strategy & Intensive growth strategies. Panmore Institute. Web.
World top broadcasting companies by market value as on 2021. Value.Today. Web.
Yu, H., 2015. From Kundun to MULAN: A political economic case study of Disney and China. ASIANetwork Exchange: A Journal for Asian Studies in the Liberal Arts, 22(1), p.12.
