Introduction
The growth of athletic events and recreational activities in the world has faced several challenges, including the appropriateness of attire to enhance performance. Several companies have attempted to promote on-field athletes’ conditions and enhance sports performance through diverse efforts to provide quality attire to accommodate various weather conditions. Under Armour (UA) invented the manufacture of high-quality performance sports attire with a mission to enhance athletes’ performance. The main goal of the company is to provide athletes with alternative all-season high-quality gears in the form of footwear, all-season gears, accessories, and apparel.
UA’s product-line expansion targets to provide various sports attire to match the diverse athletes’ needs. North America is an established market for the company’s products with strategic business plans to expand internationally. The marketing strategies to global penetration and brand awareness include the team manager’s buyer acceptance, sponsorship of sports events, individual athletes, and sports teams. Online, website, live media broadcast in the form of sports, recreational activities, and television programs act as additional marketing channels to promote customer awareness and develop a global brand. The company faces several global market setbacks in the form of the political climate that includes a travel ban to some Islamic countries by the United States and Brexit. The unfriendly political climate and the presence of global market competitors with strong financial muscles and brand loyalty make foreign market expansion difficult. Nevertheless, the industry is still in its growth stage with space for business growth and profitability.
Strategic Issue
In the case study, the company’s strategic plan is to control market share, revenue position, brand awareness, market expansion, and challenges. The company has a strongly established market with current revenue of $60 billion in the United States alone. The established horizontal integration in the United States promotes customer brand awareness and product sales. High school, sports teams, colleges, and individual professional players’ sponsorship has enabled the company to build a strong buyer relationship enhancing the achievement of the yearly target growth objective. Foreign market penetration of product-lines promotes the company’s competitive advantage in the global market. The company has expanded its global market by funding and designing concept consumer shops, increased company outlets, qualified personnel along with the concept shops, and specialty stores. The company enjoys additional marketing strategy and revenue generation through license agreements with other manufacturing firms contracted to manufacture and sell UA’s high-performance sports attire across the global market.
UA faces critical business challenges in both local and international arenas covering dynamic customer needs, unfriendly political climate, license agreements, and stiff competition. The dynamic needs of customers lead to uninformed order and product manufacturing, which burden stocking and increase storage cost. The global political climate is an additional problem obstructing the company’s expansion to the foreign market. Short-term license agreements do not provide a long-term solution for global market expansion and company growth. Established local companies providing substitute products and strong global market players pose stiff competition to the company’s strategic plan of expansion and penetration into global market segments. Thus, the issue concerning the company’s strategy is, ‘which company objective needs to be revised to enhance the company’s global market competition and penetration?’
External Environment
The external environment comprises factors that influence the strength and the potential of a company to grow, compete, and expand in a given market niche. According to Mahesh (2014), the external environment refers to factors that set business challenges and opportunities in any given business industry. Thus, the external environment refers to all conditions that exist in both macro- and micro-environments of business. Macro-environment has factors such as economic, legal, socio-cultural, technological, political, and environmental forces, while microenvironment has factors such as supplier bargaining power, threats of new entrants, buyer bargaining power, rivalry by other firms, and the presence of substitutes.
Macro-Environment
The emergence of health lifestyle awareness that revolves around sports and exercise activities have a positive impact on the socio-cultural environment of the sports industry. Indris and Primiana (2015) hold that lifestyle changes among populations influence the demand, the market needs, and the purchasing power of consumers. The young generation’s love for sports and recreational leisure activities has changed the direction of the sports industry to embrace indoor and outdoor sports product requirements. Thus, the current world lifestyle changes directed towards exercising promote the growth of the sports industry and the company’s profitability. The diverse environmental conditions in the global market provide different sports and recreational activities. Weather and climate change influences human activities in every aspect, including sports and recreation activities (Litavniece & Znotina, 2014). Different weather conditions promote the industry’s product diversification among firms and enhance creativity.
The political environment is closely tied with economic repercussions on the growth and life of the sports industry. The current political climate in the foreign market hangs at a critical balance and risks financial damage, and several businesses fall out. Indris and Primiana (2015) aver that political climate influences consumer perception and purchasing behavior of consumers in different political zones. The United States travel ban and Brexit influence marketing and promotional approaches in the sports industry. Affected and associated governments may form local political policies to block foreign companies from trading in their markets. Thus, the unfriendly political environment has a significant impact on the sports industry that is currently enjoying a global market.
The expansion and the growth of the sports industry rely on the economic conditions of diverse global market segments. Litavniece and Znotina (2014) hold that various economic factors such as currency fluctuation and economic growth rate influence the economic potential of a market segment. Thus, economic factors are a product of the political and technological environment. Therefore, the political environment poses a great challenge to economic conditions surrounding the sports industry. Brexit causes negative effects on exchange rates and trade terms in the global market. From the case study, the leading global market competitors control a big market share and enjoy huge profit and revenue turnover, with Nike’s 2012 sales of $24.1 billion. The competitors’ huge sales indicate that the industry is still at its growth stage despite the stiff competitive environment.
The invention of worldwide web and the advancement in technology around the world has a positive impact on every business. Technological pace and transformation enhance the industry’s competitive environment (Litavniece & Znotina, 2014). Technology promotes various recreational activities and sports. Foreign markets have varied business regulations. Litavniece and Znotina (2014) argue that legal jurisdictions dictate governments’ interests in the welfare of its citizens. Diverse legal jurisdictions present varied legal regulations that influence sports, recreational activities, and business activities globally. Adverse weather conditions influence a country’s governance and the sports managing bodies to create regulations that describe the requirements for social sports events, thus affecting the growth of the sports industry in different market segments.
Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
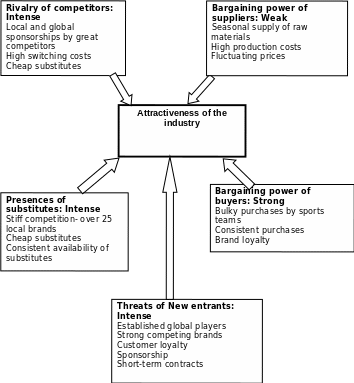
Porter’s five forces analysis offers a descriptive analysis of factors that control forces in the microenvironment (Tehrani & Rahmani, 2014). The immediate environmental factors include buyer bargaining power, substitute products, threats of new entrants, rivalry, and suppliers bargaining power. According to Khan and Khalique (2014), analysis of the industry’s internal environment enables firms to research on factors relevant to strategic planning. The analysis provides adequate knowledge on the status of the company’s immediate business environment that shape competitiveness and growth of the industry (Appendix A).
The sports industry faces a strong buyer bargaining power due to bulk purchase by big sports organizations and athletic teams. Kraja and Osmani (2015) affirm that an industry that has a high buyer bargaining power grows rapidly. In the sports industry, the market segments include individuals, sports teams, college, and high school. Sports organizations are the most powerful buyers of bulk and consistent purchases, and thus, they increase competition among rival firms. Horizontal integration among the top firms for sponsorship and professional athlete endorsements build a brand loyalty that locks out competition from potential new entrants with inadequate financial strength to compete.
In the sports industry, the supplier bargaining power is weak. The bargaining power of suppliers dictates the production cost (Kraja & Osmani, 2015). The high-quality fabric supplies in the sports industry rely on oil prices for Storm fleece fabrics and cotton harvest for cotton-charged garments. The industry companies have a hard task of maintaining production cost that ultimately dictates product pricing through bulk production. The bulk product manufacturing results in high inventory and random consumer order resulting in increased cost of product storage for unspecified market delivery. The price fluctuation associated with the seasonal oil prices and cotton harvest determines the bargaining power of suppliers and the industry’s ultimate profit potential.
The presence of substitute products presents an intense challenge to the growth and attractiveness of the sports industry. UA faces stiff competition from substitute products of approximately over 25 local brands. The low cost of substitute products and the consistent availability throughout all seasons influence customer-buying behavior and reduce industry profit and growth potential. Companies with high-quality performance products must face product price cuts to compete alongside the substitute products. The presence of the substitute products thus reduces industry’s profit and growth potential.
The industry faces intense barriers to entry from established global market players with large economies of scale, strong brand preference, and customer loyalty. Nike and Adidas enjoy an established global market. These big market players have a large revenue base that gives them a competitive advantage of endorsements and sponsorship without straining their profit margins. The unwillingness by other manufacturing firms to make a long-term commitment to new entrants and challenges of establishing factory outlets in global market segments are additional barriers in the industry (Tehrani & Rahmani, 2014). Small firms with low financial strength are unable to cut through these high barriers enabling established firms to enjoy almost a market monopoly and minor competition with huge profit margins.
The sports industry faces intense stiff rivalry among top market players and upcoming local firms. Rival firms have local and global sponsorship programs with international sports organizations and individual professional athletes as a marketing strategy. These sponsorship and contractual agreements place high switching costs on the industry firms and not the end consumers of the products. Additionally, low cost of rivals’ substitute products is a threat to the growth in the industry. Diverse consumer needs for recreational and sports activities pose a great threat of rivalry from locally available cheap and low-quality substitutes.
Key Success Factors
Key success factors are business elements necessary to achieve a company’s objectives. Khan and KHalique (2014) explain that key success factors are key drivers influencing company growth and expansion. The three key factors in the sports industry are highly designed performance apparel, contractual licensing, and sponsorship agreements and technology. Improved technology promotes the manufacture of highly performance sports attire that enhance athletes’ performance and consumer satisfaction and enables companies to meet sales targets under low cost. Sponsorship and licensing agreements with sports teams and other manufacturing firms present reliable marketing strategy to push brand awareness and market penetration. The agreements also act as company selling points and product distribution channels enhancing growth and expansion.
Industry Profile and Attractiveness
Sports industry faces numerous growth challenges ranging from unfriendly political climate to unstable economic conditions in the global market. These two factors threaten growth and profitability of the sports industry. However, technological advancement together with socio-cultural shift and diverse climatic conditions presents a great deal of wide and exploitable market segment. Lifestyle changes directed towards healthy living and discovery of new recreational activities promote the industry’s profile and attractiveness for future growth and expansion.
Company Situation
The inception and growth of UA is a result of the primary objective to provide athletes with high-quality sports attire. The sports attires include apparels, accessories, and footwear designed to meet optimum comfort in all weather conditions. The company product quality targeted to improve athletes’ performance acts as an alternative to the poor quality cotton sports fabrics. The quality provided a competitive edge against the other company’s athletic apparels. UA entered into licensing and contractual agreements with high schools, colleges, sports organizations, and team equipment managers as marketing, distribution, brand awareness, and sales strategy to promote product penetration and company growth. This approach positively promoted the company’s growth and expansion within a considerably short period. The company’s growth potential had reached a high of $2.2 billion sales revenue in 2013 with a projected 2016 growth to $4 billion.
Financial Analysis
Financial analysis of UA regarding profitability ratios, liquidity ratios, leverage ratios, and activity ratios indicates that it has robust financial status (Appendix B). From 2008 to 2012 profitability ratios, such as return on assets, return on equity, and profit margin, have increased considerably, which means that UA increases its profitability with time. Return on assets ratios were 7.841%, 8.575%, 10.139%, 10.544%, and 11.130% in 2008 through 2012 respectively. Comparatively, return on equity ratios were 11.546%, 11.696%, 13.779%, 15.228%, and 15.764% while profit margin ratios were 5.271%, 5.463%, 6.436%, 6.581%, and 7.018% in the same period respectively. However, gross profit margin ratios show stability in earnings from sales for they were 48.679%, 47.889%, 49.863%, 48.404%, and 47.920% in the consecutive period of five years (2008-2012). Thus, profitability ratios reveal that UA is a profitable company.
Liquidity ratios indicate that the ability of UA to meet its short-term liabilities fluctuated with time. Working capital ratios were 10.694, 26.979, 42.365, 11.827, and 18.696 whereas the quick acid ratios were 2.238, 9.262, 12.788, 2.256, and 5.523 in 2008, 2009, 2010, and 2012 correspondingly. Under Armor had the highest quick acid ratio in 2009 (9.262) and the lowest one in 2008 (2.238). Comparatively, UA had the highest working capital ratio in 2010 (42.365) and the lowest one in 2008 (10.694). Thus, liquidity ratios show that UA can offset its current liabilities using both cash and current assets.
Leverage ratios of UA are favorable for investment for they are less than one. Equity ratios were 0.679, 0.733, 0.736, 0.692, and 0.706 in 20008 through 2012 while debt ratios were 0.094, 0.037, 0.024, 0.085, and 0.053 in the same period. Moreover, debts to equity ratios were 0.138, 0.051, 0.032, 0.122, and 0.076 the similar period. The equity ratios indicate that assets constitute about 70% of equity and debt to equity ratios shows that debts constitute less than 14% of equity. Debt ratios indicate that liabilities forms less than 10% of assets.
The activity ratios reveal that UA utilized its resources effectively in the past five years, 2008 to 2012. The ratios of total asset turnover were 1.488, 1.570, 1.575, 1.602, and 1.586 while the ratios of inventory turnover were 2.042, 3.006, 2.477, 2.342, and 2.993 in 2008, 2009, 2010, 2011, and 2012 respectively. Further analysis shows that the average of total asset turnover was about 1.5 and the average of inventory turnover was about 2.5. The activity ratios show that UA utilized its inventory more efficiently than total assets.
The overall financial status is promising as the financial ratios reveal favorable and progressive growth. The profitability ratios show that UA is a profitable company and the liquidity ratios indicate that it can offset its current liabilities using cash and current assets. On the aspect of leverage ratios, UA is favorable for investment its ratios are less than one. Moreover, the activity ratios show that UA utilized its inventory and assets efficiently in generating revenue. Therefore, as financial status is promising, UA has great growth potential for it can leverage its resources, augment profits, and venture into competitive markets.
SWOT Analysis
UA’s horizontal integration is a strength that promotes the company brand awareness and on-field consumer reach. The design and manufacturing of high-quality sports attire promote product differentiation and competitive advantage. The expansion of the market segment through licensing agreements is a robust element of market penetration and product distribution. Distribution channels in various market segments together with factory outlets, specialty stores, and retail concept shops and online and website portal expand the market coverage and act as research and development points for new consumer needs. The company also enjoys a strong local market share and established sponsorship of sports organizations and professional athletes.
The expanding sports and recreational activities together with the growing diversified consumer needs of different market segments provide the opportunity for the growth and expansion in spite competitive rivalry in the foreign market. The possible long-term licensing manufacturing agreements with other manufacturing firms to manufacture, use, and sell UA products is an untapped opportunity to for the company. These opportunities together with the established local market share support the company’s expansion into the global market.
The company faces great growth risks threatening its foreign market operations. The short-term licensing agreements limit the company control of foreign market brand awareness and penetration. Lack of long-term strategic sales objective to guide foreign market penetration is the leading factor of market fall-out. The company faces uncertain pricing of its performance attire due to inconsistent fabric supply and fluctuating oil prices. The uncertain consumer needs with the bulk manufacture of seasonal products Increases company’s storage expenses leading to low revenue returns. The loss of two top management staff has a negative impact on control of operations and strategic planning.
Threats of substitute products from the many local companies in the foreign market offering low prices discourage foreign market expansion. The great rivalry and barriers to the entrance by established global market players such as Nike and Adidas with the foreign market monopoly of sponsorship and strong financial position project possible tough expansion results. The summary of SWOT analysis is shown in Appendix C.
Recommendation
Strategic Issue
The strategic issue entails the company’s objective of market expansion and growth. The critical steps required in strategic planning must target exploitation of the market opportunities, reduction of cost and threats of substitute products, and increased global market penetration while maintaining high local market share. Therefore, the company requires changes in its marketing and sales strategy to boost its global market penetration and growth.
Strategic recommendation
The company should set long-term sales objective indicating the company set sales target and percentage of global market share within a given period. The global market set target and percentage market share act as a blueprint to guide and drive the company’s market share through contractual agreements and expansion of distribution channels that are critical to the company’s growth and expansion. The sales objectives provide measurable steps to help assess the company’s market position and sales growth in a periodic manner. The blueprint must address issues relating to plans to control prices of seasonal products and ways to curb the fluctuating oil prices. Price controls indicate a marked production, distribution, and storage of the cotton-charged apparels and oil-based storm fleece products in expanded distribution stores and factory outlets.
UA must break barriers to entrance in the foreign market by increasing production of the all-season gears to gather for unpredictable consumer needs during diverse weather conditions. The all-season gears enhance the company’s competitive advantage and consumer brand authenticity and subsequently promote the company’s foreign market share.
Objectives
Quarterly assessment of foreign market sales and percentage of market share provides critical knowledge on company’s market position and the rival firm’s strategic steps. This will then provide a platform for adjustments and an opportunity to devise new strategies to match the changing competitors’ steps. Licensing and sponsorship agreements need a periodic review to assess market coverage and plan improved sales approaches to lure the sports organizations and tame managers while maintaining cost reduction of brand marketing.
Strategic Justification
The setting of long-term sales objective reviewed quarterly will guide the company in taking the measurable steps to penetrate the market. The review will provide top management with an opportunity to assess the company’s market standing and competitive position and revise the targets to meet the long-term goal of growth and expansion. Additionally, sales objectives provide a stepwise approach to follow in realizing the company sales goals. The assessment provides knowledge on licensing and sponsorship agreements that hugely enhance on-field product authenticity, product distribution, and company sales.
The large production of all-season sports apparel builds consumer trust on company’s brand reliability. Moreover, an increase in company’s retail and other distribution channels such as factory outlets promote wider product coverage and increase company sales. Controlled prices of seasonally produced goods through supplemented increased production of all-season apparels promote customer loyalty.
Appendices
Appendix B: Financial Ratios
Table 1
Table 2
Table 3
Table 4
Appendix C: SWOT Analysis
References
Indris, S., & Primiana, I. (2015). Internal and external analysis on the performance of small and medium industries (SMes) in Indonesia. International Journal of Scientific & Technology Research, 4(4), 188-193
Khan, M., & Khalique, M. (2014).Strategic planning and reality of external environment of organizations in contemporary business environment. Business Management and Strategy, 5(2), 165-175.
Kraja, Y., & Osmani, E. (2015). Importance of external and internal environments in creation of competitive advantage to SMEs. (Case of SMEs, in the Northern region of Albania). European Scientific Journal, 11(13), 120-128.
Litavniece, L., & Znotina, D. (2014). External business environment problems and opportunities in Rezekne city. Journal of Social Science, 1(7), 107-119.
Mahesh, D. (2014). The industrial environment analysis. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Business Management, 2(5), 1-6
Tehrani, M., & Rahmani, F. (2014). Evaluation strategy Michael porter’s five forces model of the competitive environment on the dairy industry (case study: Amoll Haraz Dvshh dairy company). American Journal of Engineering Research, 3(5), 80-85.
