Background
Operations management is one of the most important aspects of an organisation because it determines the capabilities of an organisation. Most companies have an operations management function that aligns the processes in the workflow to fit the requirements of the management and the stakeholders. Operations management is also one of the areas that face the highest number of challenges in an organisation. Wal-Mart is one of the renowned companies that have faced crises in its operations management function. The challenges at Wal-Mart have greatly affected its competitiveness in the retail industry. Over the years, Wal-Mart has used its comprehensive marketing strategy to promote its brand across the globe, but a recent negligence on the part of the operations management function of the company has led to adverse effects on business performance for Wal-Mart. This issue is particularly highlighted by the shift of many customers to Wal-Mart’s close rivals like target. The main cause of the migration of consumers from the retailing giant to other companies is the lack of some basic products in its shelves. Over the recent past, Wal-Mart has faced challenges in its pricing system. While the company looks to offer its customers the cheapest products in the market, it has failed to standardise prices for some basic commodities. This challenge has forced the management to forfeit stocking some products instead of raising their prices. Empty shelves have become commonplace at Wal-Mart. This paper focuses on the issue of empty shelves that has recently faced the operations management function at Wal-Mart, its underlying causes, and the possible techniques that can be used to solve the underlying issues.
Operation management technique
Wal-Mart has embraced the use of technology in its inventory operation management system. The electronic system also relies on the human assets because they are actively involved in placing transporting the inventory from the suppliers to the shelves. The first step is always to calculate the required amount of inventory, which is fed to the database. The database gives every item in the inventory a unique bar code, which is used to calculate the amount of inventory in the stores. The bar code also highlights the number of specific products sold from the shelves. The management is, therefore, always aware when the shelves are empty. The system also alerts the management when the number of inventory reduces to a critical point. In addition, Wal-Mart’s suppliers can check the database and send the required inventory. This strategy indicates that the issue of empty shelves in the company is just a malfunction of the operations management system.
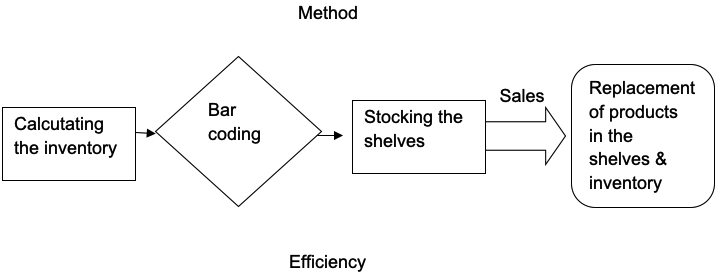
Supply chain
The current issues at Wal-Mart stem from its supply chain management process, which is a part of the task of the operations management function. This issue is part of the sustainability problem faced by the operations management department at Wal-Mart. It is apparent that Wal-Mart has traditionally looked into developing a supply chain that enables the company to offer affordable prices to the consumers. In addition, Wal-Mart has established a supply chain comprised of companies operating in the impoverished nations to minimise the cost of production. Until recently, Wal-Mart enjoyed a supply chain with numerous companies across the world, which operates with very low financial liabilities. The ethical issues behind this approach to production led to negative criticism of Wal-Mart, and it has been forced to shift to other suppliers who uphold morals. The company is in a dilemma about whether to increase the prices of its products or to look into other strategic plans to lower the cost of operation. One of the strategies that have already been implemented is the reduction of the human asset base, but its repercussions are dire because the quality of customer service in the company has diminished. Moreover, Wal-Mart has been placed under close surveillance by policy regulators to ensure it maintains a supply chain that upholds ethical production processes (Ketchen Jr and Hult 574).
Stock capabilities
The underlying issues at Wal-Mart’s operations management department are the lack of stock capabilities, which is a result of the business strategy used by the company. Wal-Mart has traditionally focused on the provision of the cheapest consumer products in the market. The company prides itself on the ability to provide cheap products associated with high quality, and this has been the main attraction to customers. Over the recent past, customers at Wal-Mart have complained about empty shelves when they visit its stores to purchase basic products (Dudley par. 2). Consumers have developed the culture of purchasing specific products based on their quality, and the lack of these products in Wal-Mart’s shelves is disappointing. While Wal-Mart has embraced the globalisation of products, most consumers would rather purchase their basic products elsewhere than try the available alternatives and substitutes. This phenomenon has led to a significant decrease in Wal-Mart’s local market share. The stock issue in the company is an indication that the people in charge of logistics processes in the company have failed in their tasks. The operations management function in the company is supposed to be aware of the stock crisis in the company, but the associated members of the company have demonstrated the inadequacy in skills. There are also reports that claim that Wal-Mart has the required merchandise is piled at the back of its stores, and the main issue behind this is the lack of adequate staff members. According to business analysts, Wal-Marts small human asset base is a strategy to lower its financial liabilities in the quest to provide low-cost products. It is evident that this strategy is not as effective as it should be because some of the operations within the organisation are being neglected.
Pricing system
Financial sustainability at Wal-Mart is currently under threat because the company is not only losing suppliers, but also potential consumers of the products produced by these suppliers. The pricing system in the company is on the brink of collapse because of the business strategy assumed by the company. The prices of products in the company have stagnated for a long time because Wal-Mart focuses on providing the cheapest prices for the basic product. This approach is the main marketing strategy that has seen the company rise to success, and abandoning it is not considered as an option. However, there are few options left for the operations management department in the company. Wal-Mart will have to start increasing the prices of its products because other efforts like reducing the number of employees have proved ineffective. The company’s profit margins are still diminishing because of the high cost of operations. Wal-Mart will soon be forced to cushion the costs of offering low-cost products and this is not an option that the operations management can take because it is against the interests of the stakeholders. The issues with the pricing system in the company can only be solved by prioritising processes like supply chain management. The logistics of the company need to be evaluated to ensure the cost of operations is lowered. Financial stability should be the primary priority for the operations management department at the company. The company has claimed that the poor services and failure to stock the shelves are a result of the inadequate human resources. The cost of increasing human assets in the retailing industry points directly to the prices of the products.
Mapping
The process of stocking at Wal-Mart is facing a bottleneck effect. The workflow in the company is too much for the limited human assets. This amount of work makes it difficult for the employees to prioritise the stocking process. There is a clear uneven distribution of labour in the company, and this has led to the piling of inventory in the stores while some of the shelves remain empty during the business hours. The limited capacity of the employees causes the bottleneck. It is also important to understand that the bottleneck is just a part of the underlying issue in Wal-mart.
Solution
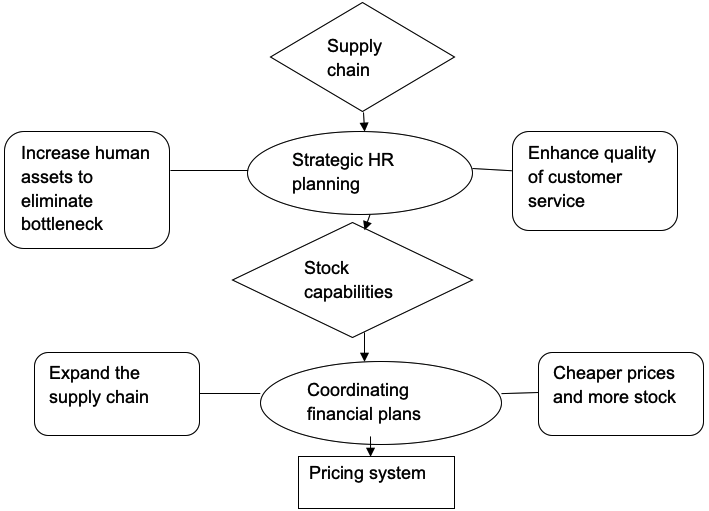
Strategic human resource planning
The underlying issue in Wal-Mart is the operations management department. The operations management function has failed in the development of equilibrium to the operational costs and the pricing system. While the company has always been focused on providing the cheapest products in the market, the external business pressures have forced Wal-Mart to break ties with some of its strategic suppliers. These suppliers were important in the maintenance of significantly lower process for Wal-Marts products. The main issue in the operations management department in the company is its choice of response to the internal and external pressures facing Wal-Mart. There are reports that most of the products missing on the shelves are piled at the back of the stores, and the main issue is the lack of sufficient human assets to fill the shelves. Wal-Mart should consider increasing its capabilities to provide quality services to the consumers by hiring more employees. The operations management function should be acquainted with the looming crisis in the company, and the appropriate response is to increase the number of employees.
Coordinating financial plans
The supply chain management process has yielded to the external pressures from consumers to rely on partners that uphold morals. Wal-Mart was previously involved in numerous scandals about its supply chain. The main issue was the nature of the manufacturing companies in relation to the observation of ethical business operations. The issues involved employee exploitation by Wal-Mart’s suppliers, which enabled them to offer quality products at very low prices. Wal-Mart has already shifted to ethical suppliers, but their bargaining power is significantly higher, and this increases the cost of operations. There are two possible solutions to this issue. First, Wal-Mart may opt to increase the size of its supply chain. According to the laws of business, the more the suppliers, the lower their bargaining power gets; hence, Wal-Mart can effectively decrease the cost of stocking its shelves. This reduction in bargaining power for the suppliers has been the main competitive advantage of the company over the years. Second, the company may opt to change its business strategy by increasing the prices of the products. Increasing prices will enable the human resource function to acquire more human assets to add value to the services offered to the consumers. This approach will effectively solve the issue of empty shelves (Dudley par. 2). However, it is likely that a change in business strategy for Wal-Mart will result in loss of market share because customers are loyal to the company because of the low prices.
Comparative analysis of current process
The productivity level of the employees at Wal-Mart has been greatly challenged by the current human resource reduction strategy. The employees at the company are not motivated to enhance the quality of the services of the company. It is also apparent that the small number of workers in the stores receive very low wages, and this is also a contributing factor in the low productivity. Increasing the workforce in the stores is an inevitable process that must be advocated by the operations management. The issue of empty shelves is clearly propagated through the lack of enough personnel to handle the restocking tasks. The effectiveness of the proposed solutions to the issues facing the operations management function at Wal-Mart depends on its business strategy. By increasing the number of employees required to handle the workflow of the company, Wal-Mart will solve the service quality crisis. The issue of empty shelves with products lying at the back of the stores will be effectively eliminated by increasing the number of human assets (Barney 4).
Six Sigma (DMAIC)
The efficiency of the suggested plan to eliminate the issues in the operations management function at Wal-Mart depends on the company’s commitment to changing its business strategy. If the company chooses to increase its human resource base, it will have to come up with a plan to meet the excess cost in operations. The most probable and feasible strategy would be a slight increase in the prices of the products. This approach may translate into the loss of a percentage of loyal clients, but the resultant quality in services will add value to Wal-Marts products. The second option entails the development of a larger supply chain to reduce the bargaining power of suppliers (Ketchen Jr and Hult 577). This approach is a risky response to the current crisis in operations management because it will only solve part of the issue. The lack of products in the shelves will be solved by decreasing the prices of some of the products that Wal-Mart is currently avoiding. The company will have the capability to continue with its traditional business strategy, which entails the provision of the cheapest basic products in the market. However, the issue of inadequacy of the personnel will still continue to haunt Wal-Mart if it chooses to implement this approach exclusively. The quality of services at Wal-Mart needs to be improved to attract more customers, and to prevent the existing market share of the company from decreasing. This goal can only be attained through the increment of the number of employees at Wal-Mart stores.
Conclusion
The operations management team at Wal-Mart has failed in the development of an effective internal response to the external factors affecting the company. Since the period that Wal-Mart was faced with negative criticism because of the immoral conduct of its suppliers, the company has broken ties with many suppliers. A possible solution to this issue is the development of a larger supply chain for the company to reduce the bargaining power of the suppliers. This strategy will enable Wal-Mart to continue purchasing the stock and availing it to the shelves. It is also vital for the company to increase its human resources to add value to its products through quality services.
Works Cited
Barney, Jay B. “Purchasing, supply chain management and sustained competitive advantage: The relevance of resource‐based theory.” Journal of Supply Chain Management 48.2 (2012): 3-6. Print.
Dudley, Renee 2013, Customers Flee Wal-Mart Empty Shelves for Target, Costco. Web.
Ketchen Jr, David J., and G. Tomas M. Hult. “Bridging organization theory and supply chain management: the case of best value supply chains.” Journal of Operations Management 25.2 (2007): 573-580. Print.

