Introduction
“Motivation determines what employees do, how they do it, and how hard they work” (Graves & Sarkis, 2018, p. 6)
Employee motivation is one of the most important aspects of a successful business. It consists of the desire of the staff to take an active part in the company’s activities, to provoke innovation and positive change, and to create creative and practical activities (Robbins & Coulter, 2018). Research shows that “motivation determines what employees do, how they do it, and how hard they work” (Graves & Sarkis, 2018, p. 6). Regardless of external and internal market factors, an organization must constantly find ways to maintain employee motivation. In this aspect, theories of employee motivation can be useful and provide valuable insight into how to maintain this indicator.
Among the positive aspects of employee motivation for the company, a higher level of productivity can be distinguished. This is because good working conditions awaken the staff to work for the company’s benefit. Moreover, motivation brings more innovation and significantly reduces the number of absenteeism in the workplace. Organizations recognizing the importance of motivation recognize that support and care are the keys to satisfied personnel. In addition, staff turnover decreases and the company’s reputation increases, due to which qualified specialists are attracted.
Expectancy Theory
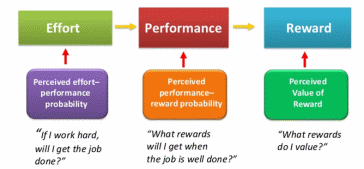
The first theory that will help to understand better the motivation of employees in an organization is the theory of expectations. This theory is one of the most widespread among all and focuses on the relationship between motivation and human behavior (Baumann & Bonner, 2017). Thus, proponents of this theory believe that the degree of involvement and commitment of employees depends on their belief in the correctness and effectiveness of the intended action. The theory of expectations has several essential components that must be observed and taken into account when studying employee motivation. These aspects include expectation, performance, and reward. All of them are directly dependent on each other and show how the desire of employees develops.
Like any scientific approach, the theory of expectations has its drawbacks and advantages. The strength of this theory is that it is based on the personal interests of employees. They consist of a person’s desire to reduce unsatisfactory conditions as much as possible and make them the most acceptable and preferable. The second advantage is that the approach is based on the expectations and perceptions of employees who are accurate and relevant to this situation. The last aspect that is positive in this theory is the emphasis on staff rewards, which are a great way to increase motivation.
Therefore, in addition to the advantages, the theory of expectations has its limitations. One of them is the idealistic nature of the employees’ expectations under consideration. This is due to the fact that some members of the staff may perceive a high degree of correlation between results and rewards differently. Another limiting factor is the discrepancy between remuneration and employee productivity. The factors influencing this aspect are the position, qualification level, and interest in the work performed.
Equity Theory
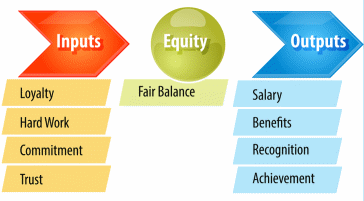
The second theory of motivation that can provide organizations with a better understanding of the employee is the theory of equality. This approach is based on the opinion of employees about how equally they are treated compared to other company personnel. The two main components in this theory are outcomes and inputs. The first implies that the organization gives its employees in return for their activities. Examples of this aspect are wages, bonuses, and various bonuses for the work done. Inputs imply that the staff is ready to give the company, for example, a time resource, qualifications, commitment, trust, or desire. Therefore, according to the theory under study, these two indicators are used to measure the difference between employees.
Negative Consequences
If employees have a feeling of unevenness and unfair treatment compared to others, they can significantly change their behavior and attitude toward work. Moreover, other negative consequences may be the desire to increase recognition for their activities, for example, the requirement to raise wages or to leave the company altogether. The latter is the most undesirable consequence since dismissal is always much more costly for business in many respects than the introduction of measures to change the situation. Thus, the theory of equality is applied to increase the level of employee satisfaction with the workplace, environment, and relationships in the company. In addition, this theory emphasizes the need for equal treatment of all employees, which is critically important.
Goal-Setting Theory
This theory of motivation is based on the opinion that people’s desire to work towards a goal is the main source of motivation (Locke & Latham, 2019). This action helps to clearly define what people want to achieve from their activities and what benefits this action will bring. The theory, as previously mentioned, has several aspects that need to be taken into account. The first is that more specific goals with precise conclusions have greater effectiveness than more extensive ones. Also, the more complex the final goal, the more positive the result will have. In the end, feedback on progress towards the goal enhanced performance. The latter aspect is unique due to the fact that feedback about the work and goals of the staff can set the boundary between the expected and real result.
One of the advantages of this theory is that motivation based on goal setting is characterized by a significant increase in the desire of employees to bring changes to the company. Moreover, this approach leads to increased productivity and improved feedback quality. Among the limitations of the goal delivery theory, one can distinguish the contradiction between the goals of the organization and its employees. This may affect the occurrence of conflicts of interest, reduced productivity, and other negative consequences. Although complex goals may have more effective results, they can also provoke more risky and reckless behavior. Moreover, there may be a situation when the desires of employees may not correspond to their skills and qualifications, which will lead to the non-fulfillment of goals.
Reinforcement Theory
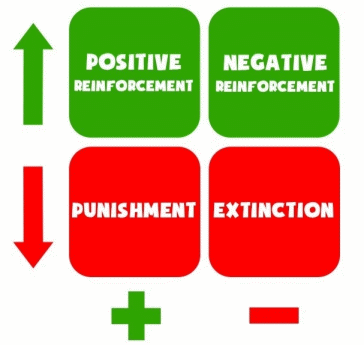
The last theory to be given in this research paper will be reinforcement theory. This approach pursues the concept that any behavior has its own specific consequences; that is, people have a clear understanding of what can follow their actions (Fayyaz et al., 2021). Thus, the assessment of the set goal occurs when considering whether the results will be negative or positive.
A feature of this theory that can cause difficulties is that it is functional. In other words, all its components are determined from the functional side and not from the structural side. Henceforth, the consequences of certain decisions depend on each person individually, that is, on behavior, level of motivation, ability to assess the situation, and qualifications. This theory will be particularly effective in training personnel to adhere to the correct behavior and avoid the other.
Conclusion
Therefore, this presentation provided information about various contemporary theories of motivation. Among them, expectation theory, equity theory, goal-setting theory, and reinforcement theory were highlighted. All of them have their own characteristics, which, if properly and thoughtfully applied, will help regulate and increase staff motivation. This aspect is essential for the organization since the productivity of personnel affects the productivity of the company and the preservation of competitiveness.
References
Adams’ equity theory. (n.d.). Free Management Books. Web.
Baumann, M. R., & Bonner, B. L. (2017). An expectancy theory approach to group coordination: Expertise, task features, and member behavior. Journal of Behavioral Decision Making, 30(2), 407-419. Web.
Chouhan, S. (n.d.). Expectancy theory of motivation. Info4Mystery. Web.
Davidson, P. (2021). When using goal-setting theory to motivate employees, managers should. World Review. Web.
Graves, L. M., & Sarkis, J. (2018). The role of employees’ leadership perceptions, values, and motivation in employees’ provenvironmental behaviors. Journal of Cleaner Production, 196, 576-587. Web.
Locke, E. A., & Latham, G. P. (2019). The development of goal setting theory: A half century retrospective. Motivation Science, 5(2), 93. Web.
Robbins, S., & Coulter, M. (2018). Management. Pearson.
Time management and productivity. (n.d.). What is reinforcement theory | Explained in 2 min [Video]. YouTube. Web.
