Executive Summary
The paper discusses and analyzes human resource planning and its impact on an organization. Special attention is given to industry analysis and current HR strategies used by Unilever. The research methodology used is extensively discussed. Both primary data and secondary data were collected for the purposes of this paper. From the data collected, the paper analyses Unilever’s HR department and its performance, current policies, and strategies used by HR professionals, recruitment and selection techniques. In addition, based on the research finds, using theoretical materials and current studies, a recruitment and selection plan is developed. The aim of this proposed plan is to provide Unilever with innovative, more effective, and efficient employee recruitment techniques.
Introduction
Good leaders have visions of the future that inspire performance. They are able to communicate their visions effectively to others while relating to others on an interpersonal level to ensure the achievement of their visions. The aim of the assignment is to collect the data and evaluate current HR practices and approaches used by Unilever. The objectives are to use current theories and methodologies in order to analyze Unilever’s practices and propose possible improvements for the HR department.
The report analyses current strategies and techniques used by the HR department of Unilever and proposes new methods and tools for recruiting and selection procedures. In a modern business environment, performance tests help companies to analyze and examine competitive moves and create unique practices in order to compete in the market. The primary objective of applying new recruiting and selection techniques is to supply management with the practices that deliver customer value. The increased competitive pressures created by markets have led to a number of new analytic techniques.
Research Methodology
For this research, primary and secondary data will be used. The research adopts a mixed methodology approach in data collection involving the use of both qualitative and quantitative methods. The primary data will be collected through the interview method and direct observations. This method is the most common in HR research and allows companies to gather information from different sources and diverse population groups.
The interviews will be conducted at Unilever and will involve 10 employees working in the HR department in London. Once interview data have been collected, one can determine how well the interview explains certain underlying constructs related to the purpose of the interview. The secondary data will be collected on the basis of theoretical literature about Unilever, and theoretical studies related to the human resource management and planning process.
Organizational Background
Organization planning is a systematic, planned change effort. Modern managers see a need for a long-range, coordinated strategy to develop organizational climates, ways of work, relationships, communication systems, and information systems in order to deal with both predictable and unpredictable occurrences.
To some extent, organization development involves a systematic analysis of the organization and recognition of the need to understand and effectively deal with change. It also involves strategic thinking and the development of a plan for improvement. Further, HR planning includes the entrepreneurial and entrepreneurial activities of resources to carry out the strategic plan. Organization development is an effort that is planned, organization-wide, and managed from the top.
Industry Background
The retail industry is one of the most dynamic and fast-growing industries in the world. At present, all the retailers have been affected by the emergence of the one-world marketplace. Some decades ago it was expected that by 1992 twelve nations of the European Community, namely Denmark, France, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg, Netherlands, Portugal, Spain, United Kingdom, and a newly united Germany would merge into a united market of 350 million people of different nations united by a common currency and a pent-up appetite for consumer goods and services.
This is almost exactly what the modern market can observe now. New retailing concepts which appear every day attract the attention of retail traders and consumers from different countries. This leads to a cross-border flow of ideas that is often expedited by personal visits and observations by retailers. Still, long-standing contrasts persist, rooted in deep-seated cultural differences.
The UK is strongly influenced by new concepts in the retail industry. Its regional free trade structure allows the government to address rural demands, stabilize expectations, and moderate domestic perceptions of the risks of trade liberalization. Unilever is one of the organizations through which these demands and expectations are met. This is why the department responsible for marketing activities of Unilever across the country was located in London. Currently, this division involves 1200 employees.
Company Information: The Company, the Product, the Market
Unilever is an Anglo-Dutch company founded in 1911 by William Lever. Today, Unilever is the largest producer of branded consumer goods operating in around 100 countries worldwide with 227,000 employees. Unilever is designed to assist this market by providing timely and critical market intelligence necessary to aid in strategic and tactical planning for the fast-growing market in the world. With time Unilever is planning to enter a new market that covers cancer patients.
The management of the company keeps to an idea that “the greater the perceived consumer value, the better the strategy”. Currently, Unilever employs about 180,000 people around the globe; each of these employees takes care of consumers and their needs through manufacturing products of high quality. The company produces food, personal care, and home care products. The most famous food brands of Unilever Company are The Becel/Flora which offers consumers heart-healthy products, Lipton, the world-famous tea brand, Knorr, Bertolli, Rama, Hellman’s, and others. The company’s personal care brands include Axe, Dove, Rexona, Lux, Sunsilk, etc. The main home care brands are Cif, Omo, Radiant, Domestos, Sunlight, and Surf.
There exist numerous global markets in which the company operates. The most widespread are North America, Africa, the Middle East, Asia, Western Europe, and Latin America.
Vision & Mission
The Unilever management made vision and mission a core philosophy of the company: “Our mission is to add Vitality to life. We meet everyday needs for nutrition, hygiene and personal care”. Unilever has a strong statement of mission because this ensures consistency and clarity of purpose and stimulates understanding and support from without. The vision of Unilever can be expressed in the following statement: “Vitality means different things to different people. Some see it as energy; others view it more broadly as a healthy state of body and mind – of feeling alive”.
HR Department and its Role
The HR department in London (England) consists of 10 employees. The task of the department is to recruit, train, motivate, promote, reward, and support employees. Each dependent manager is responsible for the complete operation of his/her organization, including planning its growth in sales and profits. These managers constantly get ideas for improving their respective product lines either through internal developments or through the acquisition of other companies in related businesses. This is an important part of their general management function. However, unless their authority to investigate, evaluate, and negotiate for the acquisition of a promising company is circumscribed thoughtfully, unforeseen and undesirable company liabilities can be created quite innocently.
My role in the Department
I work in the logistics department. My duties at this department include:
Monitoring and reporting growth opportunities for staff.
On a daily basis, I can internally for opportunities that would help employees in the department advance their careers or experience their work in a new way. To this end, I monitor transfer and rotation files so as to respond adequately to employees’ need for skill development and advancement. My roles of monitoring and identification of growth opportunities also involve being averse to the new skills employees in the department are acquiring and how the same can be put to use in the organization, which would add to the job satisfaction for the employee. Another aspect of this role is that I am always following the exit trends in and out of my department so as to identify the possible growth opportunities related reasons for the exit of otherwise very productive employees.
I also actively participate in employee job posting and the formulation of policy that guides employee posting in the department. As a result of the given role, my day-to-day duties include discerning operations towards identifying possible necessary improvements in posting policy. Whenever there is an opportunity for growth, I duly communicate the same in the department or to the employees that could be affected.
Identifying skills shortage
Skill shortage is identified through monitoring of daily operations and from reports submitted from the different executives in the department. My work is to discern from given reports, official complaints, and sometimes through observation, the kind of skill lacking in given areas or scenarios. These skills could either be technical or soft ones e.g. personal etiquette. Skill shortages are often occasioned by technological changes, personnel exits, or retirement.
Identifying motivation problems and rewards
Employee behavior is critical to identifying motivation-related problems. We monitor employee enthusiasm and general behavior e.g. absenteeism by keeping records that are reviewed after some time. We also identify motivational needs and problems through regular surveys run over the intranet. Through consultation within the department, we identify reward packages e.g. shopping vouchers or holiday packages that boost employee motivation.
Reporting training needs and identifying future needs of the department
We have an ongoing training needs assessment plan. Training needs are identified largely through scanning changes in the external environment or internal changes such as technological development or transfers respectively. My work is to discern the skill needed in the department and propose training that would respond to the identified need.
Organization’s HRP & Strategy
Organization’s Strategic Plans and Objectives
At the core of the strategic objectives of Unilever, is a general-purpose or theme, which is “To achieve the highest standards of corporate behavior towards everyone we work with, the communities we touch, and the environment on which we have an impact”. This is the spirit that informs all the strategic objectives of Unilever.
The human resource department plays a crucial role in the achievement of the organization’s strategic objectives. The policies, and procedures or activities in the human resource department are all aimed at ensuring organizational strategic objectives are achieved.
The basic function of the Human Resource department or division is to take care of personnel or manpower needs in an organization. Manpower or skilled workers are critical towards the development of a competitive edge. It is the ideas that employees generate and the processes that the personnel supervise or conduct that give an organization an edge in the market. The human resource department ensures there is personnel and they are happy to be working for the organization. This is achieved through personnel recruitment, performance management, training planning, and execution, designing employee compensation and rewards packages, and handling of any personnel-related legal issues or grievances.
Without a proper and well-functioning human resource management function, an organization can neither achieve an edge in the external market nor efficiency in the internal organizational processes or procedures. It is the human resource function that assigns or gives each employee his or her job description. The job description is critical towards being clear on what each person is doing thus avoiding confusion or overlapping of roles.
The main goal of HR at Unilever is to create a positive and favorable environment for diverse employees. Its strategic plans are to support all the employees and eliminate gender and racial differences. The management of the company is perfectly aware of the diversity of its personnel: “Unilever understands the importance of diversity and that’s why it is a critical component of our business strategy and an integral part of everything we value and do”. At Unilever, aspects of corporate identity include such values as the history, the coping and defense mechanisms, the decision strategies, the self-imposed rules and regulations, the habits, the norms, the goals, the attributions, and the self-evaluations. Its manifestations include symbols, rituals, ideologies, language, stories, myths, assumptions, relationships, and humor. The goal of Unilever is to keep and support this unique corporate culture and positive employee relations.
Role of Different Departments Staff in Achieving the Objectives
Each of the staff members contributes to organizational objectives and goals fulfillment. Different departments are provided to workers during orientation and specific job training. It is one of the management’s ways of providing leadership, particularly if the procedures and their methods of presentation and follow-up are consistent with policies and principles. “Good” corporation values, in broad terms, might include closeness to the customer, respect for the individual, innovations, and entrepreneurship, leadership, and the organization’s impact on society.
Definition of HRP
Human resource planning basically refers to the efforts or measures, the human resource department puts in place, on how to maintain the right employees and ensure they are doing their jobs well. This function is carried out through planning or scheduling or putting in place mechanisms for staff retention, staff replacement, and employee search. This function of the human resource department goes hand in hand with training needs assessment, skills analysis, and development of recruitment procedures.
Human resource planning can be looked at as an increased ability of managers to evaluate, select, and implement alternative approaches to the financing and delivery of the public services which the company requires. It can positively influence the efficiency of the company, the improvement and simplification of selected service delivery functions, and the financial viability of individual agencies and jurisdictions.
In an organization, planning is done at different levels. Whether at the operational or strategic level of management, there are distinct steps that are followed. The steps generally followed are situational analysis, formulating vision and mission, formulating strategic or departmental objectives, resource mapping and creation of an action plan, implementation plan, or basically scheduling. Once a plan has been made at the strategic level of management, the different departments and arms of the organization have to also make their plans. These are widely referred to as support plans.
The human resource plan is one of the support plans or departmental plans. It reads into the strategic plan of the organization and in line with the strategic objectives, the human resource plan stipulates what is to be done with regard to recruitment, performance measurement or management, compensation and rewards, and other administrative issues related to personnel.
HR Policies and Procedures of Unilever and Strategic Objectives
Employees at whatsoever level of employment desire to get the most out of organizations. The organization on its part also strives to get the best out of its employees. It is this mutual need or desire that cements relations between employees and organization. The game is that the employee wants to get the most out of the organization at minimal cost while the organization would most happily get the best out of employees with minimal cost.
Human beings are very creative and this stems from the fact that they are rational and thus free animals. It is not unusual to human nature to test boundaries and limits. Therefore, employees unless fully motivated will constantly seek the lower limit or the minimal to give to the organization for their pay. Organizations can also at times go to the extreme in the way they deal with employees i.e. overworking employees or exposing them to risks at minimal pay.
The work of human resource policies and procedures is to harmonize the interests of the organization and those of the employees. This is important towards ensuring an organization has skilled, enthusiastic, motivated employees who help it towards achieving its strategic objectives or a competitive edge in the market. The harmonization is set through establishing basic standards of procedure that employees should follow, establishing key action points in each job description and providing key performance indicators for each post or role played by an employee.
Unilever’s human resource standard procedures and policies are as summarised in the table below.
Unilever has got well laid down policies and procedures with regard to human resource recruitment and selection. The recruitment starts with an application form that contains a number of questions. The forms are assessed by a qualified assessor before the senior managers see the successful forms.
The next procedure involves a telephone interview. The finance department applicants undertake psychometric test involving finance for them to qualify.
The selection phase involves the formation of a selection committee which undertakes a number of activities. These include simulation, discussions, individual interviews and presentations. The selection process also involves use of case study to ensure that the individual selected is conversant with the business environment.
Critical analysis of HR Policies and Procedures
SWOT Analysis
Contribution of My Department to HR Planning
The Logistics department plays a crucial role in the formulating of logistics related human resource plans. The human resource officers, in the department, monitor human resource related issues such as employee growth opportunities, skills requirements or shortages, employee motivation related issues and employee grievances. Basing on findings from the monitoring and evaluation, the officers are expected to report or advice senior management accordingly. In relation to each of the mentioned issues, the department prepares plans and proposal towards better operations in the department in line with the strategic objectives of the organization. It proposes new training programs for its employees and reports possible difficulties in staff training and skills shortage.
It is the work of officers from the department to discern future man power requirements in the department and propose the kind of individuals that would meet those needs. As such, job descriptions for employees in the department are largely designed by the departmental officers.
HR Planning and Success of Logistics Department
The nature of HR department makes it imperative for planning to be a continuous activity. Plans made have to be responsive to measurement indicators and feedback monitors. In the logistics department, each job title has its job description which states clearly what the performance indicators in that role are and the key action points. The key performance indicators and key action points are identified early enough so as to accord the logistics department an operating system within which the goals and objectives can be implemented and the impact on Workers and Work tracked. Activities informed by principles that reflect values, policies that augment the principles and procedures that implement policies are major features of day to day operations in the department. As Becker advises, a conscious recognition and means of resolving the problems that inevitably occur between various components of operations in the department is established.
HR Plan for the Organization/Department
7S Analysis
PESTLE Analysis
At Unilever, HRP depends upon internal and external factors. Such internal factors as personnel productivity and motivation seem to be of major concern of the company’s management, because they need experienced personnel able “to anticipate and respond to changes in the marketplace”. However, the external factors are considered with equal measure of significance as shown in the PESTLE analysis table below.
Impact of various Factors on HRP
Despite all the external factors presented in the PESTLE analysis above being important, the major ones that are of key concern at Unilever are technological developments and economic factors. The others can be easily coped with through basic standards of procedure that the human resource department aptly contributes towards. Technological factors are more complicated to deal with, because the company will have to spare money for technological development. The company does not have direct control over the different countries economies. Economic upheavals often mean fewer funds available for HRP processes.
Cultural Diversity in Unilever
Although it was indicated that technological changes and economic factors are the most challenging PESTLE factors, socio-demographic factors are critical in the HRP processes in Unilever. Socio-demographic factors fall are easily managed by the human resource department, however they determine the HRP processes in a big way. The labor market of Unilever is extremely diverse.
The company saw modification of recruitment policies already in 1980s when the concerns arose regarding the growing volatility in the labor market. This was when women started to be employed as managers and when management trainees entered the company. These days, due to company’s divisions functioning in underdeveloped and developing countries, such as India and Africa, it is often blamed for child labor. Unilever denies that any of its divisions use child labor because it is strongly opposed to child labor. The company’s labor market consists exceptionally of experienced professional workers entering the labor market at will.
A formal policy has been put in place to manage issues of socio-demographic diversity. In human resource planning, efforts towards appreciation of diversity and cultural differences are made.
Organization’s Audit Matrix of Current Staff
Vacancy Identification/ Demand and Availability Forecast
Man power demand forecasting is the estimating of future skill requirement in an organization. This function requires looking into the skills available and putting them on the scale against skill needs in the organization. This function also requires scanning the future to understand the trends in technology, social dynamics and economy so as to identify how to respond to the needs that may arise.
Personnel demand forecasting takes into account strategies that guarantee the availability of skills, which are necessary for attainment of the strategic objectives of an organization. Interpreting business strategies into how many employees and type of skills needed is not easy. However, there are a number of ways of approaching demand forecasting. Some of these methods are “Direct Managerial Input. Best Guess Historical Ratios, Process Analysis, Other Statistical Methods, and Scenario Analysis”.
For long our company has relied on historical ratios as a method of forecasting the future personnel demand. This is a method in which headcounts are considered against issues like goods produced, clients served or items to be handled per particular employee. The operational budget comes in handy in determining the number of employees to be brought into the organization.
However, this method does not anticipate the future well enough. This has occasioned a general shift to the scenario analysis method. This is a method in which resource officers do environmental scanning and gather data force related data. From the analysis of the data, new workforce scenarios are discerned through brainstorming sessions. The brainstorming sessions consider possible future scenarios and the change points in established trends.
There are some sales managers and accountant vacancies currently identified in London division. Using Forecasting and Statistical Analysis methods, it is possible to say that Unilever will need additional number of IT professionals and sales managers. The company works on the new projects based on the Internet solutions and IT.
Forecast for Sales Managers and IT professionals in London
There is a high turnover rate with respect to sales manager which means that there is a creation of new demand within the company. The table shows that 5 employees in sales and 1 employee in IT field will retire during the next year. In order to avoid shortage of staff in future, Unilever should hire new people and train them in accordance with needs and demands of the department.
HR Budgeting with respect to Strategic Goals
HR planning should involve not only goal setting and environmental analysis, but it must also serve as a means of intervening in the policy-making process. Indirect influence techniques such as information dissemination, persuasion, and consultation provide a strong base for influence in the early stages of policy making. However, initiation of change in the public sector must evolve from creative strategic planning styles. Innovative and advocacy planning are two such styles. During the next year, Unilever will need £4 billion for salaries. Also, it will need £1 billion for advertising and training, career promotion and development programs.
Job Descriptions for Identified Jobs
Recruitment and Selection Plan
Recruitment is a process that involves identifying and choosing the right candidate to fill a given vacancy. Recruitment methods are largely grouped or characterized into two i.e. traditional recruitment methods and contemporary/internet based recruitment methods. Recruitment methods can also be looked at in terms of external methods or internal methods. The external methods rely on candidates from outside while internal methods tap into skill already existent in an organization. In external recruitment, an organization can do the selection itself or engage the services of an external recruiter or recruitment agency. Internal recruitment often involves posting information internally about availability of a vacancy
Selection is a latter stage in recruitment, which entails picking one out of many identified candidates. Interviewing is the most popularly used selection method. There are different forms or types of interviewing. Interviewing can be done directly or indirectly, individually or in a group. Sometimes interviewing is combined with other methods such as tests, presentations and exercises. Depending on post, practical tests to demonstrate skill are administered. If it is a technical post, interviewees can be asked to identify and fix a fault on a machine. If interviewing for a financial or knowledge intensive post, a case study or exercising involving interpretation of information may be employed. Presentations often require candidates to make a presentation on given topics or scenarios.
Existing Recruitment Process and Review
Unilever follows traditional recruitment methods or approaches. The traditional approach to recruitment involves posting job advertisements in newspapers or on websites. Those interested in the job sent in written applications which are reviewed before potential candidates being contacted for interviews or tests. This process is largely costly and time consuming. Applications come in many forms and sometimes at an overwhelming rate. Often sieving through the numerous applications to identify the right applicant is too arduous that the right applicants are often not given due consideration. In Traditional methods, interviewees could easily deceive interviewers by telling them what they think the interviewer wants to hear as opposed to the truth. Interviewers also waste a lot of time on non qualifying candidates thus undermining the whole process.
Employers need to share with prospective workers both the advantages and disadvantages of employment in their organization. This includes providing information about
- the job opportunity and the workplace setting in which it occurs;
- the vision and mission of the organization;
- the functional performance levels needed to accomplish the outputs;
- the working conditions: effort, responsibility, environment;
- growth opportunities: educational support, promotions, compensation;
- accommodations the employer makes to meet special needs.
This information can be provided by brochure, interview, video, or some combination of these modalities. This open and forthcoming approach at first meeting lays a foundation for trust that becomes a vital element in future productivity.
New Recruitment and Selection Plan
The main steps will involve planning, establishment of merit criteria, and assessment of the plan. In order to consider this basic information in some depth, HR managers should organize information into six main areas. These areas are:
- a description of the job position and place of work ;
- the vision and mission of the department and the aims that flow from its purpose;
- the functional levels needed to achieve the outputs of the department;
- the working conditions-physical, setting, social, as well as effort, responsibility, and type of management–in which the work will be done;
- the career opportunities, including training, personal development, promotion, and compensation; and
- the accommodations the department is prepared to make for disabilities, day care, flextime, and the like.
When the applicants are interviewed, the HR manager will analyze their personalities and make appointments. After the waiting period, the person who fits the position best will be hired.
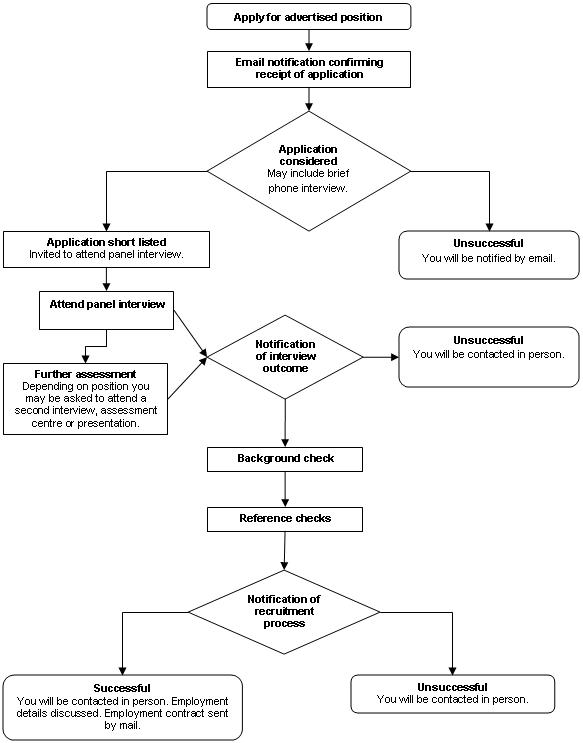
Process Chart for the Plan
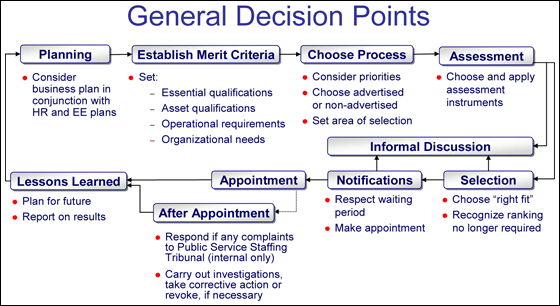
The recruitment process chart above is adapted from the Canadian public service commission. Adapted to recruitment for the vacancies mentioned above, first there was planning for recruitment based on demand forecasts. A clear merit criterion was made and a job description prepared. The next step will be to advertise the position or devising a way of reaching the right candidates. What will be novel about the process is the inclusion of assessment instruments that test behavior, past experience, and performance related issues.
Such instruments would include well tailored psychometric tests, technology averseness tests and experience tests. Those who pass the tests, done anonymously, will be invited formally to meet with interviewers. From the interviewer’s judgment based on assessment tests and personal interview, the right candidate for the job will be chosen. There will be room for feedback for the applicants and from applicants on their performance in the interviews.
Key Result Areas and Timelines
In order to introduce the new recruitment and selection techniques, Unilever will have to spend 1 month and recruit 2 HR professionals in this field. It is highly suited for structured interviewing and performance testing, as well as for types of paper-and-pencil testing that focus on past experience or task preference. This behavioral predictor ensures reliability, validity, and little or no adverse impact against minority groups. The reliability of these methods consists in anonymity of the testing system, which will help to avoid biased attitude towards the candidates; the validity consists in the fact that the information will be obtained from the candidates themselves both orally and in writing which would minimize falseness regarding the previous working experience and already existing skills.
Choice of Selection Methods and Rationale for These
The main selections methods are unstructured interviews and CVs analysis. Unstructured interviews lack focus and are poor at identifying the best candidates for a job or promotion. Structured interviews, on the other hand, ask job-relevant questions that can considerably improve an employer’s ability to select the best candidate. This section discusses how FJA (Functional Job Analysis) can be used to structure an interview so that employees selected or promoted the right person. It also shows how to use FJA to present a realistic job preview during the interview, thus promoting applicant self-selection and contributing to a more satisfied worker.
Implementation and Monitoring the Effectiveness of the Proposed Recruitment and Selection Process
The interviews with 10 people will take place after standardized psychological and performance testing. The control technique will be based on comparison between previous methods and new methods introduced by HR department. The main criteria will include time, effectiveness, and effective assessment of skills and knowledge. This procedure will allow defining which methods applied by the HR department are more efficient and which give better results regarding the proficiency of the recruited personnel.
Introducing Changes into Recruitment and Selection Plan
In order to improve recruiting and selection methods, Unilever should introduce performance testing technique.
- Step 1 the applicants will be required to fulfill the task connected with their past job experiences
- Step 2 the applicants’ responses will be evaluated by trained observers according to criteria of effectiveness identified for that job.
For instance, the criteria for a salesperson in a work simulation would be to remain calm and polite in dealing with a rude and verbally abusive customer.
- Step 3 the behavioral sample will consist of an interaction between the prospective salesperson and a difficult customer–possible a trained actor –under conditions closely approximating the job.
The evidence for the person’s future job performance will be direct and behavioral.
This technique is advantageous for both the company and job seekers. Many applicants prefer performance tests, because they give a real-life preview of the job and encourage self-selection.
Recommendation
My research into the recruitment processes used at Unilever (England, London) shows that there is need to introduce some changes if the processes are to become cost and time effective. The company currently uses traditional recruitment methods. These methods are not only time and money consuming; they have loopholes that lead to a high likelihood of the best candidates not being picked. By relying on CVs and oral or telephone interviews alone, interviewers are easily cheated.
Based on the foregoing consideration, I recommend refining of the recruitment process as discussed in this paper. The new recruitment plan or method requires that Unilever introduces performance-testing techniques and behaviors assessment tools in its recruitment process.
These new plan will consist of 3 distinct steps. Step 1 the applicants will be required to fulfill the task connected with their past job experiences. Step 2 the applicants’ responses will be evaluated by trained observers according to criteria of effectiveness identified for that job. For instance, the criteria for a salesperson in a work simulation would be to remain calm and polite in dealing with a rude and verbally abusive customer. Step 3 the behavioral sample will consist of an interaction between the prospective salesperson and a difficult customer–possible a trained actor –under conditions closely approximating the job. The evidence for the person’s future job performance will be direct and behavioral. This technique is advantageous for both the company and job seekers. Many applicants prefer performance tests, because they give a real-life preview of the job and encourage self-selection.
Conclusion
The analysis of the Unilever (England London city) revealed that HR planning is vital for its success, effective performance, and recruiting and selection procedures. New recruiting programs, proposed for HR department, will inevitably lead to job changes and recasting of employee skills. It is advised for the management of the company to follow all the abovementioned techniques to ensure proper development and performance of the company.
Appendices
Questionnaire
- What are the most important requirements you seek in your selection plan?
- What method of communication with job seekers do you prefer?
- What are the most important requirements you seek in your selection planning?
- What are the main problems you have encountered with job seekers?
- Does selection tools’ processing include tracking internal candidates?
- What are the types of job postings (continuous, internal, etc.)? Please provide examples of each type you use.
- Are job descriptions and/or qualifications for postings standardized?
- Are preferences for filling jobs and special requirements specified on the job?
- What is the average number of job positions per month? Highest month?
- Describe the process when a job seeker wants to apply for additional positions.
- Describe the selection process. Please give examples of manuals or references used for screening and selection at Unilever.
- Describe the job seeker interview process. Attach examples of interview documentation.
- Describe the hiring process as it pertains to recruitment.
- What is the average number of requisitions filled per month? Highest month?
- Do you perceive recruiting process at Unilever as effective?
- What would you change in the selection process?
(Note: Answers for each question are collected from 10 employees of the department).
Bibliography
AMS. Marketing. 1999. Web.
Armstrong, M. Human Resource Management. 8th Ed. New York: Kogan Page, 2001.
Armstrong M., Baron A. (Eds.). The job evaluation handbook. Eds. London: Institute of Personnel and Development, 1995.
Bandt, Allan, and Stephen, Haines G. Successful Strategic Human Resource Planning. Oklahoma: Systems Thinking Press, 2002.
Barney, J. Firm resources and sustained competitive advantage In Journal of Management, 17 (1991) 99-120.
Basu, Ron. Implementing Quality: A Practical Guide To Tools And Techniques: Enabling the Power of Operational Excellence. Hampshire: Cengage Learning EMEA, 2004.
Beardwell, Julie and Tim Claydon. Human Resource Management: A Contemporary Approach. 5th Ed. New York: Financial Times, Prentice Hall, 2007.
Becker, G. Human capital. New York Columbia University Press, 3rd edn, 2003.
Campbell, D.J. (Organizations and the Business Environment. Oxford: Butterworth-Heinemann, 1997.
Campbell, A., Goold, M., Alexander, M. Corporate Level Strategy. London: John Wiley, 1994.
Company Profile of Unilever, Updated Report, 2004. Web.
Doyle, P., Stern, Ph. Marketing Management and Strategy. 4th Ed. New York: Financial Times/ Prentice Hall, 2006.
Drejer, A. Strategic Management and Core Competencies: Theory and Application. Oregon: Quorum Books, 2002.
Edenborough, Robert. Assessment Methods In Recruitment, Selection & Performance: A Manager’s Guide To Psychometric Testing, Interviews And Assessment Centers. New York: Kogan Page, 2005.
Fahy, J. Smithee, A. Strategic Marketing and the Resource Based View of the Firm. Academy of Marketing Science Review, 1999. Web.
Fill, C. Marketing Communication: Contexts, Contents, and Strategies. 2nd Ed. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall, 1999.
Grant, R.M. The resourced based theory of competitive advantage. California Management Review, 33 (1991), 114-35.
Green Peace. Unilever. 2009. Web.
Heene, A., Sanchez, R. Competence-Based Strategic Management. New York: John Wiley, 1997.
Kay, J. Foundations of Corporate Success. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2003.
Lynch, R. Corporate Strategy. London: Pitman, 1997.
Lawton A., Rose A. Organization and Management in the Public sector. 2 ed., London: Pitman Publishing, 1994.
Mayo A. Creating a Training and Development Strategy. London: Institute of Personnel and Development, 1998.
McDonald M., Christopher M. Marketing: A complete Guide. New York: Pal grave Macmillan, 2003.
Oppenheim, A. Questionnaire Design, Interviewing and Attitude Measurement, London: Pinter, 1992.
Paley, N. The Manager’s Guide to Competitive Marketing Strategies. New York: Thorogood, 2006.
Prahalad, C.K., Hamel, G. The core competence of the corporation. Harvard Business Review, 1990.
Reed A. Innovation in Human Resource Management. London: Chartered Institute of Personnel and Development, 2001.
Robertson, I.T. Smith, M. and Cooper, D. Motivation, London: Institute of Personnel Management, 2002.
Robbins, S. Organizational Behavior. New York: Prentice Hall. 11 Ed., 2004.
Rosow, J. and Casner-Lotto, J. People, Partnership and Profits: The new labor- management agenda, New York: Work in America Institute, 1998.
Salancik, G. R. “Commitment and the Control of Organizational Behavior and Belief” in B M Staw and G. R. Salancik. New Directions in Organizational Behavior, ed., Chicago, St Clair, 1977.
Schuler, R. Managing Human Resources. Cincinnati, Ohio: South-Western College Publishing, 1998.
Senge, P. he fifth discipline: The art & practice of the learning organization. New York: Currency Doubleday, 2000.
Smith R. Strategic planning for public relations.2nd Ed. New York: Routledge, 2004.
Stacey, R. Strategic management and Organizational Dynamics, 2 ed., London, Pitman, 1998.
Storey, J. New perspectives on Human Management, London: Routledge, 1989.
Taylor, S. Employee Resourcing. London: Institute of Personnel and Development, 1998.
Torrington, Derek, Laura, Hall, and Stephen Taylor. Human Resource Management. 7th Ed. New York: Financial Times Prentice Hall, 2008.
Ulrich, D., Lake, D. Organizational Capability: Competing from the inside out, New York: John Wiley, 1990.
Unilever Home Page. Web.
Unilever HR Page. HR Policies. Web.
