KSA Financial Market Introduction
Essayyad and Madani argued that the financial market of KSA has evidenced massive change by two intergovernmental expansions that would influence competition in the Saudi capital market as well as the banking sector. The first one is the government’s decision to uphold the unified financial market system in accordance with the GCC (Gulf Cooperation Council) and the second one is KSA’s interest to joining WTO (World Trade Organization) where the basic condition is to the liberalization of the market for foreign entries. These initiatives would facilitate enhanced competition among the players that expand the market size and bring benefits for the borrowers and investors of the public and private sector as well as individuals in the financial market of KSA (Essayyad & Madani 4).
In 2003, the Capital Markets Law was introduced and derived to the founding of the Capital Market Authority of Saudi Arabia regulate and administer the capital market that ultimately ensured the establishment of the Saudi Arabian Stock Exchange that currently facilitated the online trading. The widespread reform to boosting the financial markets as well as easy access to financial services has sustained the faster growth and increasing employment opportunities and contributed the national economy significantly.
The new legislation introduced by CML has provided a vital proposal that will modify the landscape of financial services to a larger extend. The SAMA and CMA are mounting the harmonization measures to resolute conflicts and challenges of increasing market risk and structural reformation of the market.
Rabindranath and Gupta pointed out that the Saudi capital market faced a number of dilemmas due to religion-based outlook, for instance, it lacks a number of basic crises of the market, where independent issues required to having pricing benchmarking and also take steps as anchor securities aimed to portfolio management as well as trading in the secondary market.
Due to most recent acceleration of the capital market, it has integrated information technology and added online trading but there are not enough trading happens for very poor number of issues (Rabindranath & Gupta 3). Moreover, the number of listed companies is also inadequate. Another limitation of the market is that the bans and institutional investors are willing to invest in the secondary market; they do not get enough securities to invest, thus the short of a liquid secondary market, investors and fund managers loose their interest to invest in the secondary market.
Introduction to Saudi Banking Sector
Al-Muharrami mentioned that Kingdom of Saudi Arabia is a county where there was no national currency before 1952. In early stage foreign banks were strictly prohibited but after the world war – II in 1939, the exploration of Saudi oil has turned enormous opportunities to allow branches of foreign banks for negotiating oil payments and three foreign banks were allowed to open their branches in KSA. In 1951, SAMA was formed to conducing banking activities and it introduced paper money in exchange of foreign payment receipts, though the present Saudi currency Riyal was introduced in 1960.
IMF scrutinized the Saudi Banking sector and added that the capacity of the KSA banking sector to take action to the macroeconomic shocks has gained a great deal of potency through out the last decade. KSA banking sector has integrated with a modern and well-organized payment system and defrayal infrastructure by improving its governance and to managing liquidity risks. The central bank SAMA has been enthusiastically keeping its eye on various promising portfolio tendencies and supporting collective corporate performance and implications of prospective resource mobilization. The wide-ranging reforms in the KSA banking sector are on the move to intensify the financial market and to enlarge the opportunities for new entries to access to financial services sector.
Al-Muharrami pointed out that at the beginning of 1970s; a large number of foreign banks started their operation in KSA to take the advantages carried out by the expansion of Saudi economy resulted from growing oil revenues. This well-built presence of foreign banks has influenced the Saudi authorities to set up a guiding principle that would support the foreign banks to turn themselves into listed companies collaborating with of Saudi citizens whose shares would publicly traded in the Stock exchange.
In 1975, the Saudi authority has generated new legislation ensuring the optimistic opportunities for foreign banks that facilitated them to keep fifty percent ownership by them and rest for local (Al-Muharrami 1). Through this legislation, foreign banks had empowered to keeping original name, uphold management responsibilities, and enjoying similar treatment like local banks.
Financial statement analysis of three Banks of Saudi Arabia
Bank 1: The Arab National Bank
Arab National Bank (ANB) is one of the ten largest bank in whole gulf, started its business in 1979 as a joint stock company. Currently it has 168 branches in Saudi Arabia including 31 women sections and one foreign branch in UK that started in 1991. The banking activities of ANB mainly spread through three broad areas like Retail Banking, Corporate Banking and Treasury Banking and it covers every aspect of modern banking.
Retail banking also known as the consumer banking includes deposit collection, loan sanction, debit, and credit offering etc for the general individuals. Corporate Banking of ANB includes deposits, loans and other banking activities focus on the business organization range from large business giants to small enterprises. Finally, Treasury Banking focuses on trading, investment portfolio, liquidity, funding, currency conversion etc.
ANB currently has 3600 employees, 90% of which are the Saudi nationals and this number is increasing due to the continuous expansion of the bank. The current capital of the bank is USD 1.73 Billion and almost in every rating of the banking, industry ANB got A+ to A. As a bank of Saudi Arabia, it has a high concentration on Islamic Banking system and every branch of the ANB provides Islamic banking facilities to the customers.
Financial Statement Analysis
Balance Sheet
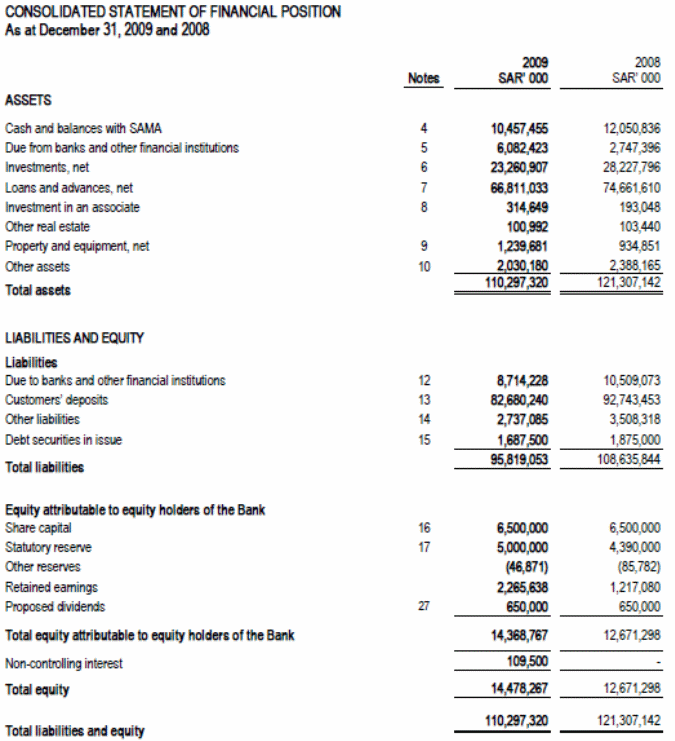
From the following balance sheet of Arab National Bank, the assets and liabilities shows the long-term financial position of the bank. In the assets side, cash and balance with SAMA has shown at first and SAMA stands for Saudi Arabian Monetary Agency. According to the government rules every banks need to keep a portion of its deposit on current, saving and other accounts to the SAMA from the balance of each month.
The total amount of assets of the bank at the end of the year 2009 was SR 110,297,320000 that was SR 121,307,142000 in the year 2008 (Arab National Bank 3). From the asset perspective, the bank showed the net decrease of asset, which was due to the downturn of world economy and the price fall of oil. In the liability side of the Arab National Bank, total liabilities of the bank in 2009 were SR 110,297,320000 that was SR 121,307,142000 in 2008.
The liability of the bank also decrease followed by the total asset. The liabilities of the bank mainly composed of liability arisen from the deposit and other receiving from the customers and the liabilities of the shareholders. However, the overall financial position of the bank was very strong and it contributed largely to the national economy of country and helped in the development of the banking sectors of whole gulf.
Income Statement
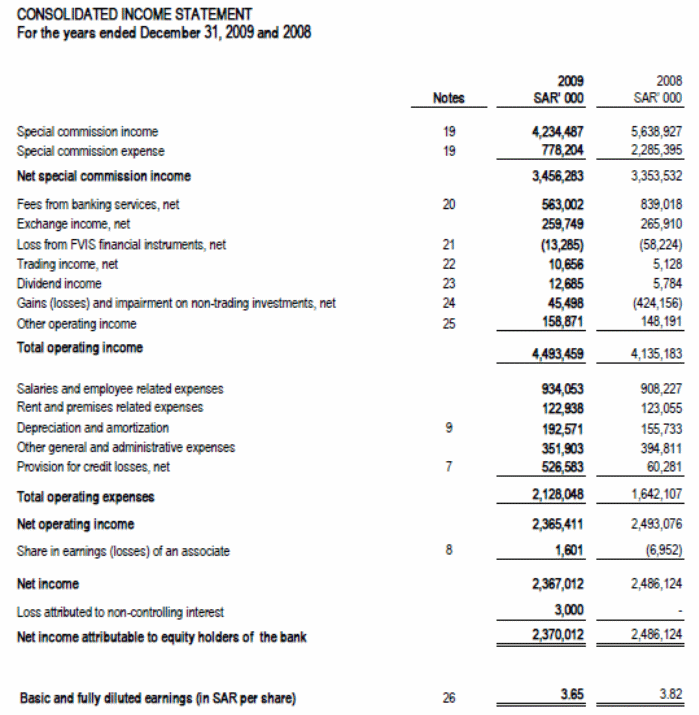
The consolidated income statement of the Arab National Bank presented the income and expenses of the bank for the year 2009 that compare with the financial statement of 2008. In 2009, the bank earned net income of SR 2,367,012 that was SR 2,486,124 in the year 2008. The net income of the bank slightly fluctuated from 2008 to 2009 due to the price lag of oil and the financial crisis hit the whole economy of the world.
The income of the bank mainly consists of special commission income and other income including the fees received from the customers, trading income, dividend income, income from exchange of currency etc. On the other hand, the main expenses of the Arab National Bank includes salaries of the employee, rent and premises, general expenses, depreciation, amortization, bed debt and so on. Moreover, earnings per share of the company for the stockholders ANB was SR 365 in 2009 whereas EPS was SR 382 in 2008 that indicates that the level of decrease in income affected the earning per share of the bank.
Though there is slight fluctuation in income, the overall income generation and financial condition of the bank is more or less stable in nature. This income generation directly contributes to the national GDP and per capita income of the people of Saudi Arabia.
Cash Flow Statement of ANB
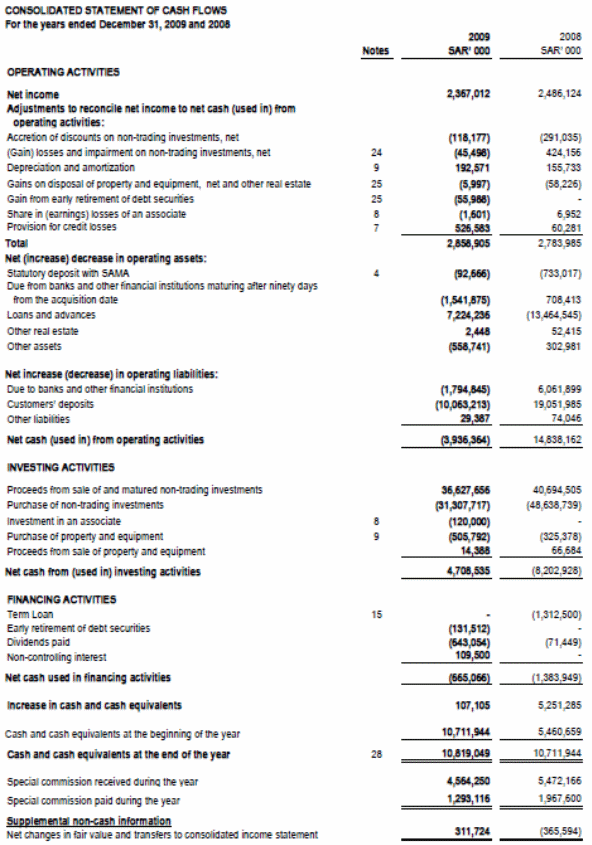
Cash is the lifeblood of any bank and bank makes profit through dealing with the cash, therefore, this statement work as the main financial indicators for any bank. In the above cash flow statement, the cash inflow and outflow of Arab National Bank had compared the financial data of 2008 with the fiscal year 2009. The main areas of cash inflow and outflow include cash flow of net income, operating asset, operating liabilities, investment, financing etc.
In the cash flow statements, the position of net cash of the bank in 2009 was SR 311,724000 that was negative in 2008. On the other hand, in 2008, the net cash outflow was SR 365,594000, which dictates the net cash outflow overlaps the net cash inflows. The position of the cash was much stronger in 2009 than in 2008 and economic crisis did not able to hit cash flows of the bank. In 2009, net income showed positive results after deducting the other cash outflow relating to it and in operating assets and operating liabilities, the result demonstrated the negative results.
On the other hand, the cash inflow from investment activities is positive that indicates good performance of ANB in short term investment. In financing activities, the cash outflow overlap the cash inflow as bank spends money on loan interest, dividend payment etc. Finally, the overall cash inflow is higher than the cash outflow of ANB.
Bank 2: The National Commercial Bank
The NCB (National Commercial Bank) is one of the most prominent banks of KSA and the citizens recognized it as the earliest commercial bank in the nation and started its operation in 1953 along with the decree of the KSA government with an initial capital of only US$ 8 millions paid up by the entrepreneurs. Initially NCB started as a partnership business but in 1997, the bank converted into Joint Stock Company and subsequently the government of Saudi Arabia acquired the majority stocks of the bank. Because of government takeover, there had changed in the board of directors of the bank including the chairman and the new chainman was Abdullah Bahamdan.
The paid up capital of NCB is SR 15000 million and the amount of total at the end of 2009 was SR 257452 million that is highest in Arab world. Currently, the bank has 282 branches in Saudi Arabia and the total number of customers of the bank is more than 2 million. NCB is fully dedicated to Islamic Banking and it solely operates in Islamic banking system besides commercial banking. The total number of employees of the bank is 5399 in which more than 80% are Saudi citizens. All modern banking facilities have integrated in this bank including the ATM, internet banking, telephone banking etc.
Financial Statement Analysis
Balance Sheet
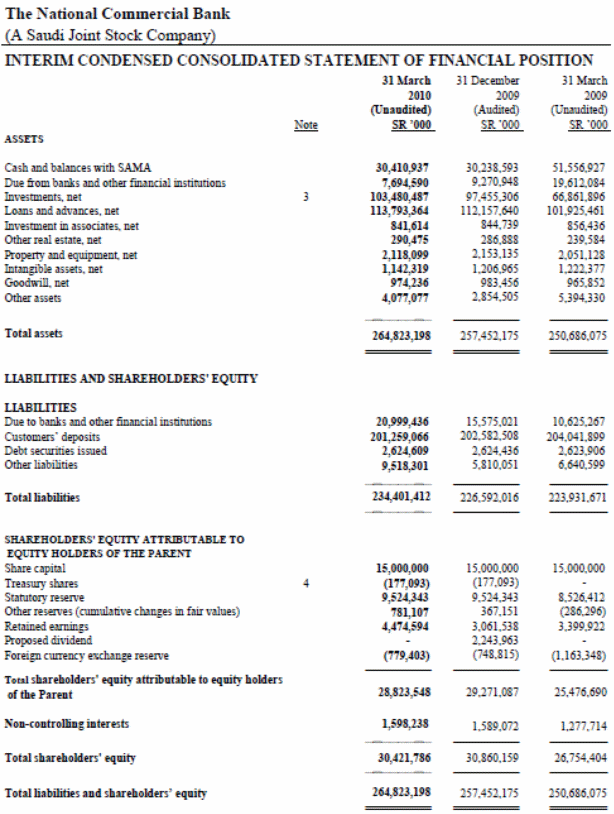
The balance sheet of National Commercial Bank (NCB) shows the current condition of long and short-term asset and liabilities of the bank on March in 2010. In the year 2010, the world economy including the Saudi Arabia turn back and the banking sectors also able to develop the condition of balance sheet through increasing assets and decreasing liabilities. In first quarter of 2009, the total assets of the bank were SR 250,686,075000 that increased to SR 257,452,175000 in the last quarter of the same year. Subsequently, at the first quarter of 2010, the amount of total assets increased to SR 264,823,198000, which is an evidence of gradual increment of the asset position of NCB.
The total amount of cash in hand including the balance with SAMA is SR 30,410,937000 and the total amount of investment of the bank in the first quarter of 2010 is SR 103,480,487000 (National Commercial Bank 23). Another important part of the balance sheet of NCB is the loan and investment of the bank that constitutes SR 113,793,364000. The volume of loan and investment of a bank is one of the main operations of the bank and profit of the bank largely depends upon it. In NCB, the loan and invest comprises a large part of its asset portfolio and substantial amount of profit come from this area.
In the liability side of the balance sheet, customer’s deposit with the bank is most important area and the volume of deposit is SR 201,259,066000 in NCB. The other liabilities include the equity of shareholders, due to other banks and financial institutes etc.
Income Statements of NCB
The profit and loss of the National Commercial Bank has shown in the following income statements. The main income of NCB come from the special commission, charges from the customer on various services, return from investment, dividend income etc. On the other hand, the expenses of the NCB include salaries of the employees, rent, and premises expenses, depreciation expenses, amortization and so on.
The net profit of NCB after the first quarter of 2010 is SR 1,442,395000 that was SR 1,050,798000 in the last quarter of 2009. The Earning per Share for the shareholder is SR 940 for this year, which was SR 700 in 2009, and it clearly illustrates the profit acceleration of the bank. The growing profit of NCB not only contributes to the growth of the bank itself but also to economy and banking industry as a whole. Within the time of economic downturn, the NCB shows consistent profit that ultimately encourages the investors to invest in the various areas and helps to build confidence of customers on the bank.
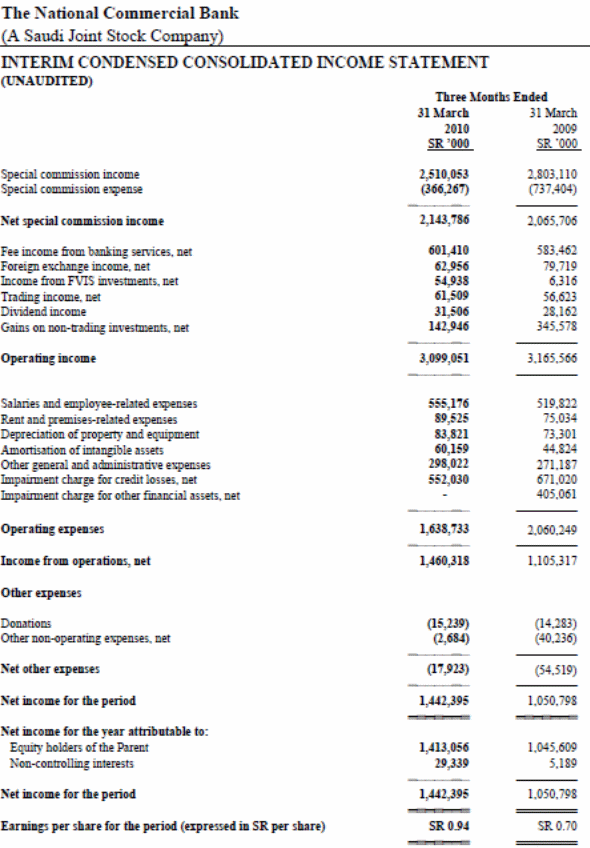
The Statement of Cash Flow of NCB
NCB added that its statement of cash flow has clearly demonstrated the cash inflows as well as outflows of the NCB for the first three months of 2010 and the income statement of NCB has indicated focuses up on three wider aspects that including cash flow of NCB, its operating activities as well as cash flow for its investment initiatives. Within the operating activities, there are mainly two main sources of cash inflow that are inflow from net income and inflow from the operating asset. In NCB, the main sources of cash inflow are the operating activities and it contributes SR 5,396,549000, which was SR 36,962,360 in the first quarter of 2009.
The reason behind this distortion is that customers withdraw deposit from the bank and it disburse huge amount of loan and advance to the customers. Investment activities are the major area where the bank spend most of its cash and in turns investment generated for the bank in long term. NCB mainly spend on purchasing property, equipment and other financial instrument that comprises the total outflow in investment activities are SR 6,651,442000 in 2010. Financial cash flow of NCB in 2010 is SR 1,076,566000 that expending on various areas of financing of the bank.
Bank 3: The Riyad Bank
Riyad Bank is one of most growing bank in Saudi Arabia that has operation in both corporate and retail banking and doing banking business as a joint stock company. The bank operates fully under the Islamic Banking System and brings services to the customer under four broad areas. These areas are –
- Corporate banking: In this banking, Riyad bank offers credit, cash management and other services to the corporate clients.
- personal banking: Under the personal banking, the bank provides loans and deposits, ATM services and other services to the individual customers
- Treasury & investment banking: In treasury banking, the bank offers exchange services, government bond proceeding, investment activities etc.
- International banking: Finally, in international banking, Riyad bank offers various international services to the clients through international offices and branch (Riyad Bank 8).
The bank currently has 216 branches in whole Saudi Arabia, one foreign branch in London and agency office in USA and Singapore. The bank has a strong financial performance in the Saudi banking industry that was possible due to the in depth understanding of the Saudi financial market. Riyad bank has all modern banking facilities including internet banking facilities, mobile banking etc. and it has more than 2435 multi function Automated Teller Machine (ATM) that enable the customer to contact with the bank from anywhere of the country. Riyad Bank achieved highest rating in many international bank rating and the results range from A+ to A. The financial result of the bank also proves the success of this bank
Financial Statement Analysis
Balance Sheet
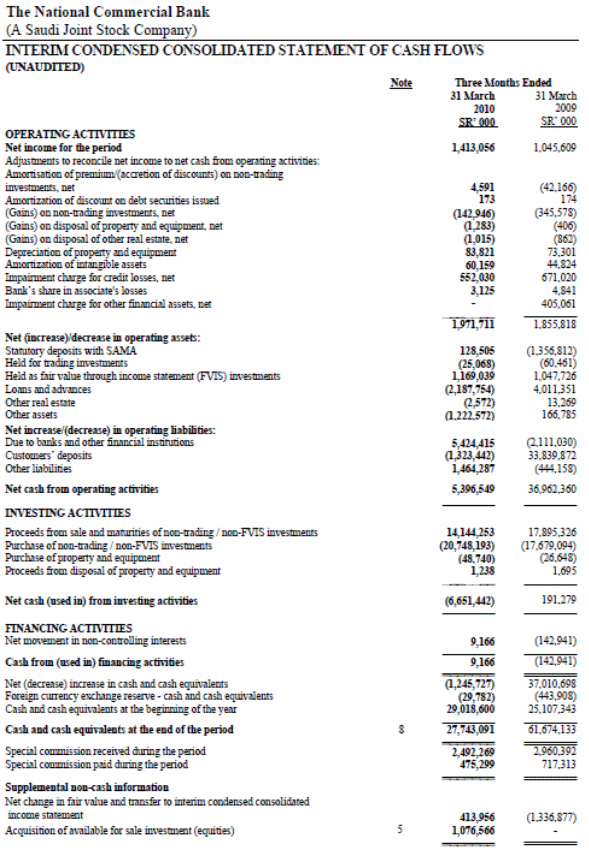
In the following balance sheet, the amount of total assets and liabilities of Riyad Bank had shown for the first quarter of 2010. The bank has strong liquidity as the cash and statutory deposit with SAMA in 2010 is SR 22,153,181000 that is less than the cash of 2009. The reason behind this is that the bank invests in various sectors, disburse loan, and advance to the customers. Other assets of the bank include receivable from the other bank, loan and advance, properties and equipment, real assets etc. Total assets of Riyad bank at the end of the first quarter of 2010 are SR 174,287,524000 that was SR 176,399,258000 in the last quarter of 2009. The amount of asset decreases from the previous year due to the economic crisis and oil price that thump the Arab market beside the world economy.
Most of the Saudi bank involved in general and corporate banking, large portion of profit and assets come from the sources of oil market transaction. Price fluctuation of the oil price directly affects the banking sectors and it reduces the profitability of the bank. In the liabilities side of the balance sheet of Riyad bank, it showed total liabilities of same amount of the asset. The liabilities include the liabilities to the customers and other banks and liabilities to the shareholders. Under general liabilities, the items are payable to the other banks, customers deposit, debt securities etc. From the balance sheet of the company, it is apparent that the bank has strong asset and capital that able to make them a key player in the banking sectors of Saudi Arabia.
Income Statement
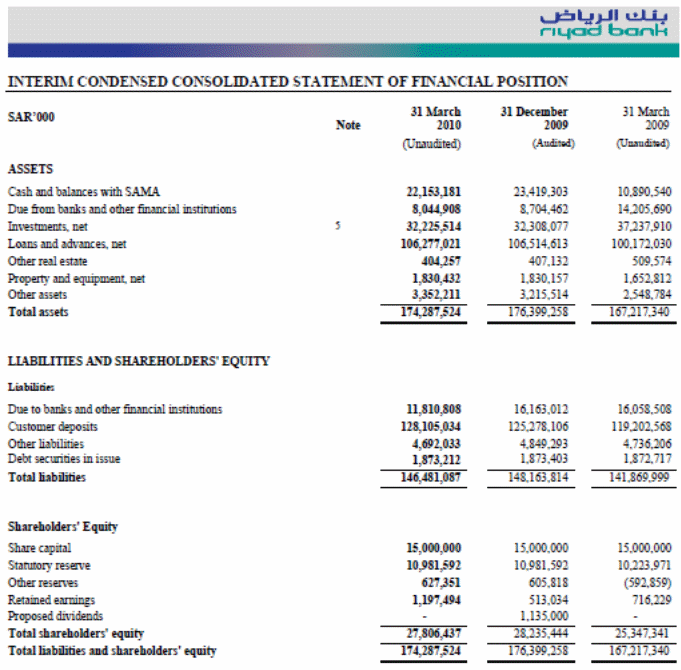
The income statement shows the net income including the earning per share that is available for distributing to the shareholders. It also explains the income and expenditure of a company where the expenses deducted from the income to get the net income for the company. In the income statement of Riyad bank, the total income of the bank in the first quarter of 2010 is SR 1,469,411000 that was SR 1,459,360000.
In spite of financial crisis of last year in global economy, Riyad bank able to recover the downturn and increase its income in 2010. The income of the bank mainly comes from the special commission, fees, and charges from the customers, trading income, exchange income, non-trading investment income etc. On the other hand, the expenses of the bank include salaries of the employees, rent and premises, depreciation, administrative expenses etc. that comprises SR 784,951000 for 2010. The net income of Riyad Bank for first quarter of 2010 is SR 684,460000 and in 2009, the income was SR 441,059000.
Within one year, the bank able to increases substantially the net income in spite of the high economic pressure. The Earning per Share of the bank was SR 2900 in 2009 that increased to SR 4600 in 2010. From the income statement it is clear that the bank has a strong presence in the financial and stock market, as a result, the investors are encourage to invest in the Riyad Bank’s share.
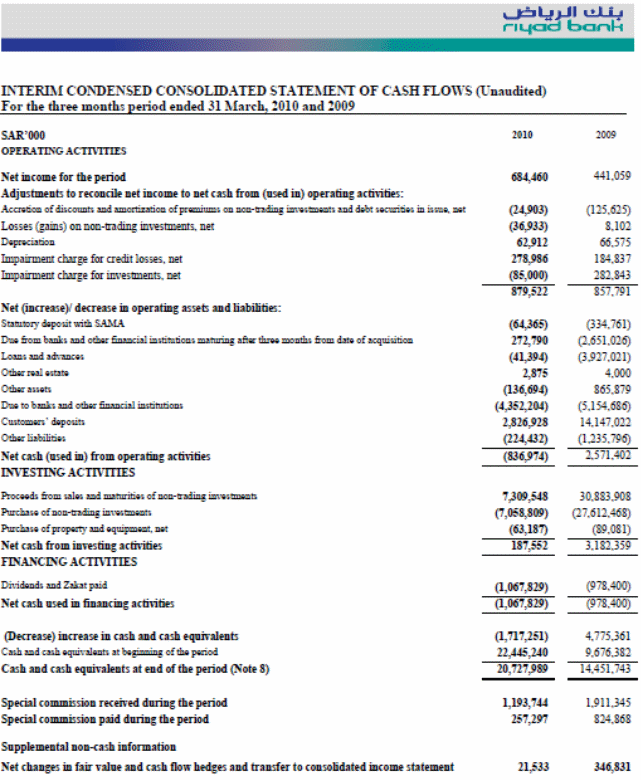
Statement of Cash Flows
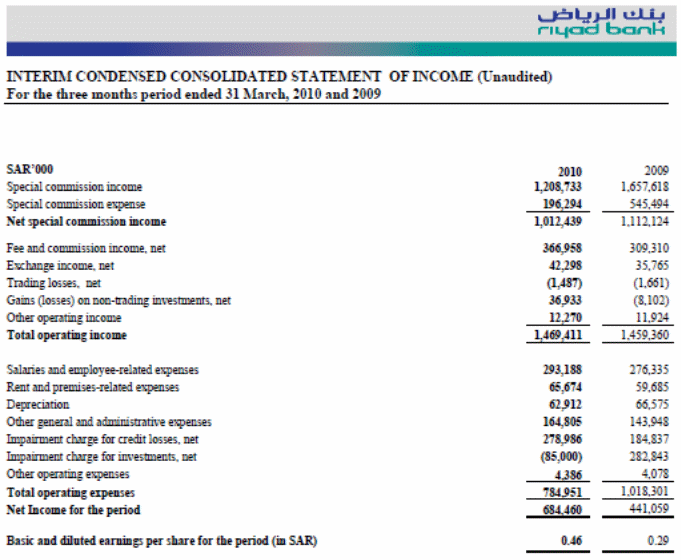
According to the figure no 8, the data focuses on the cash-inflow and outflow of the Riyad bank for the first-quarter of the fiscal year 2010. Operating activities include net income of Riyad bank, discount and amortization of non-trading investment, statutory deposit, loan and advance, investment, deposit of customers, payable to other bank and financial institutes, miscellaneous liabilities etc.
The cash outflow in operating activities for the bank is SR 836,974000 but in 2009, the operating activities generated cash inflow for the bank that was SR 2,571,402000 (The Riyad Bank 32). The inherent reason of these changes is in current year the bank spend more on operating activities like asset acquisition, paying charges to the other banks, and most importantly reduced amount of deposit and high withdrawn of cash by the customers. Customer only deposits SR 2,826,928000 in 2010 whereas they deposited SR 14,147,022000 in the first quarter of 2009. The cash inflows from investing activities in 2010 is SR 187,552000 and the return from the investment overlap the expending on the new investments.
In the financing activities, the only area of expenditure is zakat and dividend fund, which incurs an expenditure of SR 1,067,829000 that is the cash outflow for the bank. At the end of the first quarter of 2010, the net cash inflow of the Riyad bank is SR 20,727,989000 that was SR 14,451,743 in 2009. In the cash flow statement, it shows that Riyad bank gets progress in generating cash contrast to the previous year.
Concluding Remark
From the analysis of the three top banks of Saudi Arabia, it observed that the banking industry is much developed in this country like the other sectors of the economy. Arab National Bank, National Commercial Bank and Riyad Bank all showed very strong asset portfolio, operating profit, net income, and cash flow that enable these banks to earn this huge profit without compromising the services provided to the different set of customers.
Arab National Bank (ANB) generated SR 2,367,012000 profit in 2009, which is less than the profit of the previous year, and it is due to the economic crisis. The total asset of the company is SR 110,297,320000 at the end of the year 2009.
National Commercial Bank earns SR 1,442,395000 in the first quarter of 2010 and it is an increment over the last quarter. The amount of total asset of the bank is SR 250,686,075000 and it also grown over the last quarter. In Riyad bank, the amount of net income in 2010 is SR 684,460000 and the amount of total assets is SR 174,287,524000 in the same time. This huge amount of income and assets make the position of the banks in the stock market is powerful, the prices of the share of these banks are demanding, and the price is always upward.
Saudi Insurance Introduction
The Saudi Gazette reported that the insurance industry of KSA has come forward as a faster growing industry through out the world while the credit crush and global recessionary economy has rigorously shocked the other segments, the insurance industry evidenced about 25-30 % growth due to the order of compulsory insurance (1). The concurrent opening of obligatory health insurance for the private sector employees has boosted the volume of the insurance companies working with medical insurance in KSA and recorded as 44% of the aggregate insurance market in 2008. On the other hand, general insurance companies have the greater part of insurance premium in KSA, and the sector has evidenced an extensive growth under the global financial crisis.
The industry has anticipated for a targeted growth of 13% by 2013 through the increasing number of motor insurance, property insurance, energy, and liability insurance including ocean and aviation insurance. This Saudi Gazette also added that a number of researches have demonstrated that in 2014 the Saudi insurance market would generate a premium of Saudi Riyal 42,968 million if market growth continues at the present rates but the rate of premium paid for the insurance would increase more 1.07% to 1.71% for general insurance within the predicted period (2).
Insurance industry of Saudi Arabia has unique feature in context of growing insurance market in the world. This industry is growing more aggressively than any other insurance industry of rest of the world. To justify this statement, it can say that, while many other industries are suffering severely of the financial crisis of the recent recession, the insurance industry of KSA gained an unexpected growth in the concurrent years and this growth rate has recorded on the rear of essential insurance lines. There are many sectors of insurance industry in KSA. Such as –
The fastest growing part of this industry is the protection & savings and the health insurance sector while the other sectors have also shown a better performance. The boom of the health insurance makes it able to attain around 44 percent of the overall insurance industry sectors. Along with this, the protection and savings insurance sector has expected to grown at 55 percent in 2009 to 2013. Recently the health insurance sector has also grown aggressively as the compulsory health insurance for the private employees have introduced (Saudi Gazette 1).
In recent years, the Saudi Insurance industry has experienced the highest growth, in 2007; it was 24 percent with the gross premium of about 8.6 billion Saudi riyal. This amount was only 6.9 billion in 2006 and after that; this number is being increasing year by year. The main reason of this booming condition is the favorable economic condition along with the expansion of motor insurance and health insurance.
The motor insurance has also made compulsory for many private organizations and the expansion of insurance industry in KSA has been increased by 15 percent from 2006 to 2007. In 2007, there were about 42 insurance companies in the industry. The recent regulation like Cooperative insurance companies Law of 2003 has regulated the insurance practices. The level of insurance penetration has been increasing rapidly along with the insurance density (Arab News 1).
Insurance companies in Saudi
There are many insurance companies in Saudi Arab among them there are huge numbers of insurance companies who are operating worldwide. Three big players in Saudi Industry are Tawuniya, Medgulf, and Bupa Arabia. Here the selected three companies for this report are ACIG, CIGNA, and IIIC.
Allied Cooperative Insurance Group:
ACIG is a registered company under the commercial company as a Saudi Joint stock company. The Islamic Development Bank (IDB) is the leading shareholders of this company. The objective of this company is to carry out cooperative insurance activities and related operations in KSA. In August 27, 2007, it became a listed company and was listed in Saudi stock market in 1july 2009. The organizational chart of the branches of ACIG is show below:
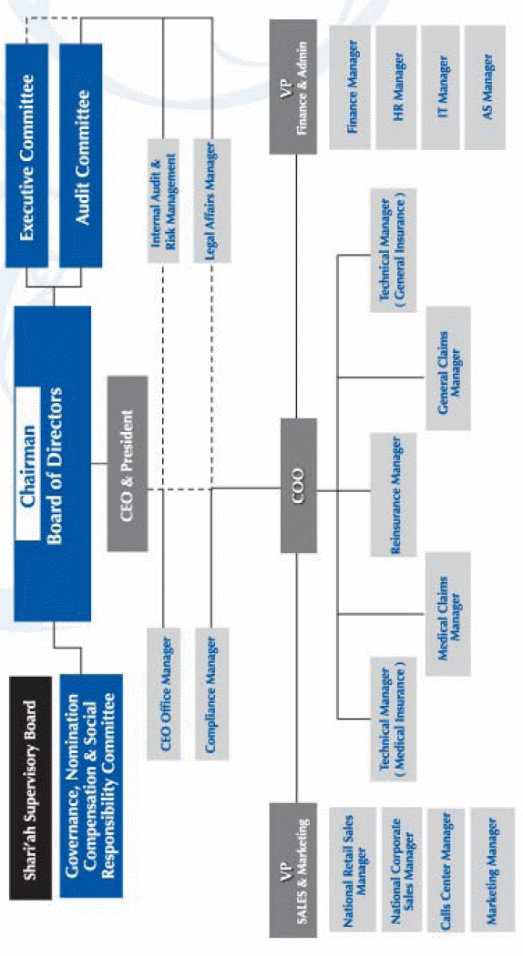
According to this chart, it is clear that the operation of ACIG has assisted with many bodies and the accumulated effect of these bodies are availing the success. However, this structure is not simple though Chairman of the board of directors is the top of all management bodies who monitors the provision of Islamic laws (ACIG 11). He is the chief of the executive committee, Audit Committee, Governance, nomination, Compensation and social responsibility committee.
He is also the chief of the Shari’ah supervisory board. Under him, there is a CEO & President of the company (ACIG 11). Under the CEO, there are four managers as CEO office manager, internal audit and risk manager, compliance manager, Legal affairs manager. The chief operating officer (COO), vice president of sales and marketing and the Vice president of Finance and admin are also working under the CEO. According to the annual report 2010 of ACIG Under the CEO, there are 4 managers as technical, reinsurance, medical claim, and general manager. Under the sales and marketing department, there are national retail sales managers, national corporate sales manager, call center manager, and marketing manager.
- Vision of the company: The vision of the company is to be the preferred cooperative insurance company in the region that provides security to customers and deliver value to employees and shareholders applying the highest international standards. ( ACIG 2009)
- Mission: Delivering values to all stakeholders by managing the risks along with providing Sharia compliant solutions for the community ( ACIG 2009)
- Values: There are seven things which ACIG values. These are:
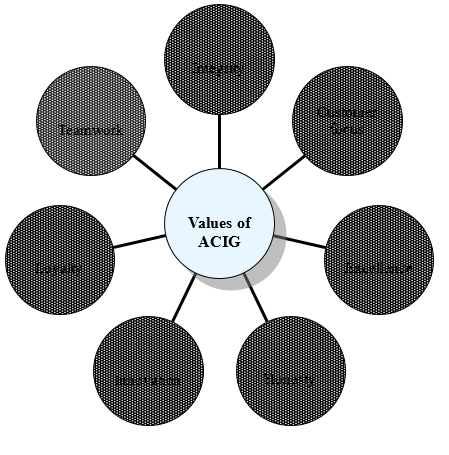
ACIG is committing to provide the highest level of professionalism in conducting business operation and to maintain the ethical standards along with treating all the entrusted resources as the own assets which is termed as the integrity of their values. Customer focus means the eagerness of the company to listen, understand, and respond to the wants of the customers and to serve the customers as they became satisfied to be with the company. This value is actually the main concern of ACIG. Excellence in all over the operation is another value where the company is striving to provide the quality products and services ensuring the excellence of providing the “best in class” in case of value delivery to the customers.
Honesty in all over the operation of the company is another value, which is termed as uncompromised and ACIG is actually creating a workplace where the communication with the stakeholders will be transparent and direct. Innovation is the key competitive advantage for the company as a value. ACIG is creative and innovative in case of its business practices. Not only this, the company is creative in case of creating a dynamic and flexible working environment, which make the employees to become innovative and creative.
Teamwork is a value, which ensures the working condition of the employees by creating a favorable environment to work in a group, which brings extraordinary results. Thus, the success is not individual rather as a team. Finally, the loyalty means to become loyal to the company, to the employees and to the customers and this loyalty is the key of the success as it brings the customer loyalty.
Financial position of ACIG
Financial position of ACIG
Key challenges of the company
- Table no 1 shows that ACIG has suffered huge losses for last two years, which is the main risk of the company;
- It has already spends 20% of its reserve;
- Delay in decision making process The business level strategy;
- It is great challenge for the ACIG to recover the confidence level of shareholders, customers and employees;
- The accountability of the employees should increase;
- Current liabilities as well as operating costs have increased dramatically, for example, in 2009, ACIG was paid SR 1,763,100 as zakat, and paid SR 954,487 as insurance of Staffs;
- However, there are very few competent human resources in this country for insurance market;
- Finally, it is great challenge for ACIG to hold the existing market position.
Key issues for future development
- This company has 10 independent and non executive directors who are responsible to monitor the performance and prepare audit report;
- It has taken many new initiatives to recover the ACIG from recessionary impact;
- ACIG had reshape its organization structure to make losses;
- It should develop new products to sustain in the market;
- It is important to meet up the conflict of interests among the directors;
- It should properly utilize its assets as its reserve is decreasing.
Products and services
There are eight insurance related products and services provided by ACIG and the major insurances served by ACIG are:
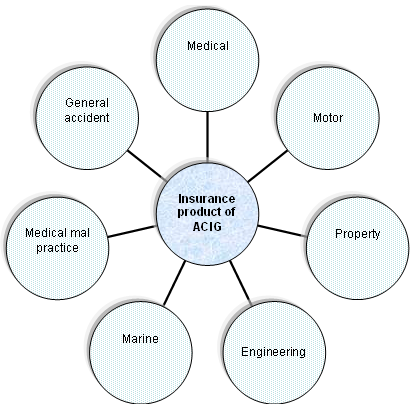
Medical Insurance of ACIG is covering the costs and risk of medical treatment and medical care facilities for the recovery of the sudden medical needs of the corporate sector in compliance with the rules and regulations of the government. The main driver of this service is the call centre of the ACIG. The centre is well equipped as per the state of the art technology to take the distance call from anywhere of the country. IN case of medical insurance, the company is ensuring the optimization of the service level and the resources. Along with the call centre, the company answers any medical questions of the customers or provides the services of insurance as per the need of the customers.
The Motor vehicle insurance of ACIG is a policy to provide a comprehensive protection of the vehicle of the customers. The damage or loss of vehicle due to accident covered with this service. Along with this, products and service will also cover the liability of body injury or even death of the people for car accident and also provide protection of the injury of the other people by the car or any property loss of others by the car.
The extension of this policy has extended to cover the personal accident benefits of the car owner, driver, and the passenger of the insured vehicles. It is also providing a third party liability as a payer of the all related loss accrued by the insured car along with discharging the liabilities of the insured to pay for any other loss of the other party.
The general accident insurance is a service of the company, which has mainly seven sub categories. These are:
- Money Insurance: The coverage has provided to the loss of money and securities of an insured person for any accident like robbery within a specified premise. The other services include giving protection to the money, which is in transit with the bank and can extend to the safety damages and premises damages by thieves.
- Fidelity Insurance: The business owners, who face severe losses, as a result fraud or dishonesty of employees have protected under these services and scheme;
- Personal Accident Insurance: ACIG would provide security fund for accident and this provision only for those customers who have insured in case of full or partial disability, in addition, the extension of this scheme is to pay for the loss of medical fees due to the result of accidents;
- Public liability insurance: ACIG reported that this covers when a third party claims for injury or damage of his property. ACIG provides protection against this claim as per evidence for the insured.
- Workmen’s compensation insurance: It is general rule of insurance that company will compensate for the injury of employees, moreover, to save the employees from unfair prejudice, this compensation will impose if the companies break any rules of the employment law;
- Medical malpractice insurance: It is also an important segment as this damages available for any medical malpractices;
- Burglary/Theft Insurance: This scheme is giving protection against any sort of theft and robbery within the premises of the insured person or organization.
- Marine Insurance: The Cargo or vessels traveled by the sea are facing risks, as there are many uncertainties to loss the assets or any other things for the storm and many more. It is covering the general merchandises, household goods, and appliances along with complex cargos like machineries and equipment.
- Engineering insurance: In case of engineering, the major sector covered by insurances is the construction industry. According to the annual report 2010, ACIG offers the major services are contractors, erection all risk insurance, contractor’s plant with equipment, machinery-breakdown insurance, deterioration of stocks and electronic-equipment scheme etc.
ACIG is providing the insurance coverage of fire and allied perils, property risk insurance and all level of loss insurance for all like business people, household and even for the houses plate and glasses under the personal property insurance.
CIGNA
CIGNA is a multinational company operating in Saudi Arabia. It is an American originated company named in KSA as ARABIA CIGNA. Its key services related with health and customers are highly relied upon this company for any kind of health perils and hazards. It is the only health service providing company, who operates for 24 hours in a day and seven days in a week (CIGNA 4).
Its vision and mission both is customer related and it is focusing the customer heavily to become a customer-oriented firm. As the financial crisis of the recent years, this company had also experienced some problems but still managed itself to do something for the customers. It has reinvented the customer experiences in recent years. In 2009, it has done six things to become a customer-oriented firm and to get success. These are:
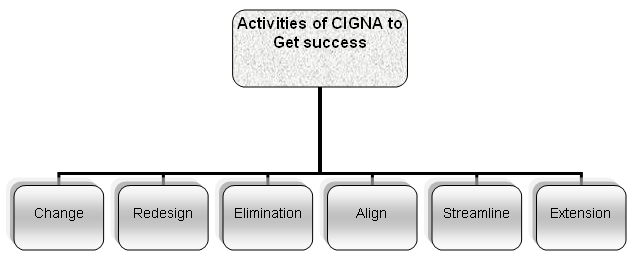
As a key task, it has changed the ways of communication with the customers to communicate with them with the messages related with the offerings of the company. Now it is communicating with the present and potential customers with more efficiency and effectiveness. It has redesigned the overall environment to reach the customers and to get the proper attention along with different operational process like coverage enrollment guides and explanation of benefits.
These are now more customer oriented and concise, informative and user friendly. The company has eliminated the confusion and clutter with the help of consolidation related with the collateral materials and makes it half of the amount of the materials by cutting the amount dramatically. It has also aligned the operation methods, which make sure of the acceptance of all types of people. It has streamlined many of its activities and technologies like the voice response program, which is helping the customers to get a quick advice from a live representative or a self-service option. Lastly, it has extended its service hours in all the branches worldwide.
As it is a multinational company and having its key concern over the health of the customers, the insurance policies are covering the possible perils and hazards of health of the insured person. It has it compensations plans to help and protect the health of the customers in the time of sickness or any other physical problems. If any customers face health related problems, the company tries to give solution with the help of its own physicians and doctors. All the medical expenses are covered by the plans and it provides plan to cover the disability caused by any sickness of the insurer.
According to the company profile, the mission of CIGNA is to assist citizens to improve the health, well-being, and sense of security of the customers. The customers get the support in the time of the injury and after the time of the injury, which brings the hope for the insured person. To improve the health of the customers, it has termed as a responsibility for the company and for this reason they have taken many initializes.
As it operates in many countries of the world, it has differentiated schemes and plans for different people as the term health has different meanings in different countries. In KSA, it is offering the same schemes and plans as it is offering in USA. It is offering people to get the nutritious food, clean water, and safe shelter with the help of many individuals, employees, volunteers, and charitable organizations.
According to the annual report 2010, CIGNA is providing mainly 4 types of services, which are Healthcare Life insurances, Disability-insurances, accidental case, and so on. CIGNA healthcare is the major insurance service of the company, which is covering the medical, dental, behavioral health and pharmacy options covering related health related perils and hazards. In case of medical insurance plans, it has customer directed health plans, health reimbursement accounts, health savings, stop loss, and much other coverage. The pharmacy plan designed to cover different pharmacy related perils. Dental and vision plans are related with dental and eye related problems. Other plans are also offering ways to cover different health related incidents making the loss of health and money.
The group insurance is also an insurance scheme of CIGNA through which many members of a family or an organization can get the coverage of health related perils and hazards. Like the group disability program, which minimized the employer’s costs and increased the productivity of the employees, other group insurance plans are insuring the health protection of the family members and the members of a company as a whole. The basic products and services offered by CIGNA ARABIA in group insurance sector are short and long term disability insurance and management, family medical and leave of absence management, disability along with advocacy and in many cases the group life insurance and accident insurance.
Economic position of CIGNA
Key challenges of CIGNA
- Future growth of the company depends on the strategic implementation, such as, introducing new products or programs, retention of qualified employees, and corporate governance;
- It has to careful about the maintenance of the integrity or security of its data;
- Controlling outsourcing projects and key vendors;
- A downgrade in the financial strength ratings may create problem for further development;
- Huge competitive pressure in this sector, mainly price competition is another risk factor for CIGNA;
- CIGNA always try to set up strategy to retain customer as Lack of loyal customers (CIGNA 12);
- Significant changes in market interest rates, global political as well as economic factors, guaranteed minimum death benefits, and increase litigation and regulatory investigations are the major threat for the company.
IIIC
Islamic Insurance Company is the first co-operative insurance company in KSA, which established in 1980 by the Faisal Islamic bank. The key shareholder of this company is Prince Mohammad Al- Faisal who is the son of the late king Faisal. It was 1992, when the company re-organized and termed as International Islamic Insurance Company. It is now a joint venture of Bahrain and KSA and the head office situated in the Medina Road in the heart of Jeddah.
It has also branches in Tabouk, Hail, and Al-Baha and has the expansion plan in gulf countries. The major insurance coverage provided by IIIC are Fire insurance, marine & Hull insurance, motor insurance, general accident insurance, Engineering insurance, medical insurance, and Takaful insurance. It is the founder of the cooperative Islamic insurance and covers the risks for not only the individuals but for the projects of the company and many other entities. It has contributed in the expansion of the holly mosques and attended in many other programs as a part of their corporate social responsibilities.
The concept of cooperative insurance has risen as many Muslim scholars have argued that if the insurance can be done cooperatively, then it can be legitimated. Taking this concept into concern, the operation of IIIC was started. In the every sphere of the operation of the cooperation, the Shariah has been ensured along with a strong Sharia Supervisory board. The company is also ensuring to innovative different Islamic insurance instruments and procedures in accordance with holy Sariah.
The cooperative insurance is a type of insurance, which is actually a welfare concern rather to be a business concern. The principle is to take the contribution from the policyholders and to compensate to others in case of need or loss. Thus, the company has a profit after deducting the claims, operating expenses and other expenses. The premiums are termed as “Contribution” which is invested according to the Shariah.
The fire insurance provided by IIIC is mainly providing the protection against the loss of fire. The customers in case of fire insurance are the factories, warehouses, and many other property holders like commercials, manufacturing and residential, machineries, equipment, and furniture, Office or any other household equipment against the risk of fire or lightning. According to the company report, it is including the extension of many fire related perils or natural crisis like storms, thunderstorm, rainfall water, bursting, overflow of waters in tanks, earthquakes, Hurricane, riots, strikes, volcanic-eruption, air-crash, vehicle impact, civil-commotion, many other hazards and etc. The perfection of overcoming the hazards has provided according to evidences.
The company is also providing coverage for the general accidents for all like personal and property losses. The sectors covered by this policy are cash, Public liability, fidelity guarantee, personal accidents, employers’ liability, and electronic equipment insurance.
The cash insurance is an insurance where cash required by an entity is compensated any sort of cash loss. There are two types of cash insurance available from IIIC and these are –
- Cash in Safe: IT covers the loss of cash where the cash is anywhere in an insured premise and in a locked safe when the premises are closed.
- Cash in Transit: It covers the loss of the cash when it is in a transition like in a transport or in a hand of a messenger.
The public liability insurance is a compensation plan to compensate an injured or damaged person by the insured person. The fidelity guarantee is another scheme which covers the loss of anything of an employee where in the premises or in the duty of the employer where the employer is the insured person. For instance, IIC offers compensation for accident, which may result to “disability, injury, or death” (annual report of the company). There is another scheme termed as employer liability insurance, which is also same as the fidelity guarantee.
The medical insurance provides extensive healthcare coverage against the accidents and illness of the insured. IIIC has some networked hospitals, clinics, laboratories, and pharmacy from where the insured can get the medical facility and the insurance company beards the costs.
The marine insurance has also provided by the IIIC, as the marine way has become one of the major ways to do business worldwide. The marine cargo insurance coverage is covering all types of cargos like containers, refrigerators and others. Besides, the marine insurance also covers the cargos in aircrafts
The engineering insurance is a type of property insurance. It is covering the perils and hazards related with plants and machineries in all possible forms. The major services provided by IIIC are contractor’s risks, erection risk, machinery breakdown risk, boilers explosion risk and many more.
Financial Market
Choudhury pointed out that interrelationship between financial market and the economy considering the scenario of Saudi Arabia where financial market indicates any marketplaces to purchase the product like equities, bonds, currencies, and derivatives, etc. Amadeo argued that it is also familiar the name of capital markets, Wall Street, or even markets. Some also call it as stock markets, although it is trading with stocks, bonds or other commodities.
Sometimes financial markets are allowed based on some features, or criteria, like amount of money held by market, geographical locations of investors, market knowledge, and participants’ professions etc. In every country of world, financial markets are found, with different in size, number of participants etc. For an example, New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) is dealing trade with trillion of dollars in every day (Amadeo 1).
Most of the financial markets are trading heavily with longer framework of time and high demand of securities, which has increased by times as historical norms. However, some factors has caused to fall the price level, which are based on low level of demand or other macroeconomic factors, like tax rates of any regions, having less national productivity, or unemployment level etc. Therefore, the financial markets are transacting any type of financial services, which are helpful for growing businesses and making money of investors.
The Financial System Stability Assessment has organized the financial market of Saudi Arabia and the government of KSA agreed to integrate this system due to the continuous pressure and prescription of International Monetary Fund (IMF) and World. The Financial System Stability Assessment has played the role of consulting as background documentation for definite times with their member countries.
The government of Saudi Arabia and the Executive Board of IMF had jointly prepared the reflecting documents of the markets according to available information. The publication policies of financial markets has represented by staff reports and other documents, which are allowing market sensitive information by IMF. On the other hand, The National Commercial Bank is associated with Dun and Bradstreet South Asia Middle East Ltd. (D&B), is also releasing Business Optimism Index for financial market of Saudi Arabia within 2010. It is also conducting global economic recovery, which has concerned by sovereign debt in Europe (Ministry of Commerce & Industry 1).
According to the view of Choudhury (7), the financial market of this country is reforming to comprehensive underway and mounting the access of pecuniary services. According to all banking sectors, and other supporting financial infrastructures of this market are limited, which is 29% of GDP in Saudi Arabia’s economic condition and most of these percentages are generated from private sectors of financial service institutions. The following table will help to show the provisions and financial indicators of Saudi Arabia in details:
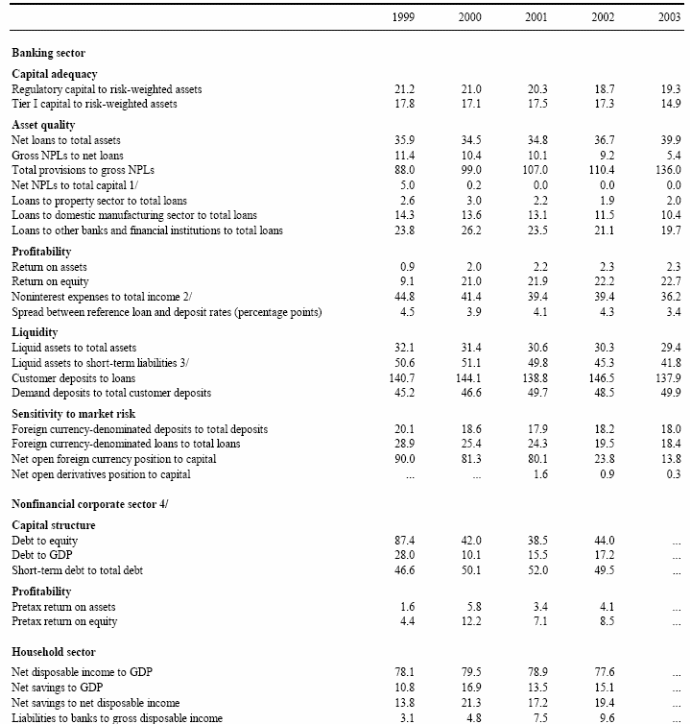
Therefore, diversified intermediation framework is helping to indicate financial needs of participants or investors, who are being invested and considered as participants, should supported by institutional efforts of Saudi Arabia. These institutional efforts has regulated and implemented by some following regulatory bodies of financial markets, which would discuss in below after showing it by figure:

Supervision of Bank
According to Banking Control Law (BCL) of 1966 and ministerial decisions on the rules-enforcing provisions of BCL (Banking Control Law), financial system developments of Saudi Arabian financial market has conducted including some modern prudential practices, or consolidated supervisions. The authority and accountability arrangements are definitely make clear by the amendment, Inter Alia, which is exchanging information under Article 19 of BCL for domestic and foreign supervisors.
Financial Market Infrastructure
Financial market infrastructures of Saudi Arabia is considered when it is conducted repurchase and reverse repurchase operations on the basis of secondary market transactions of Saudi Government securities and facilitate the Saudi Arabian riyal (SRI) yield curve in order to use as benchmark against other markets operated in worldwide. This market is also establishing formalization of ultimate responsibility for defining and implementing payment system policy, which has regulated by board of governance of Saudi Arabia. This payment and settlement system is also facilitating Saudi Arabian Riyal Inter-bank Express (SARIE).
These works have been facilitated board of governance, which is considered to set up a dedicated payment and settlement system to analyze policy, regulations, and other payment and settlement systems, which are monitoring and operating in the country. Here, it is important to mention that the analyses are including SARIE, SPAN (Saudi Payments Network), Clearing House, the stock exchange’s securities settlement systems, and other payment systems of KSA (IMF report);
Capital Markets
Capital Market Authority (CMA) of Saudi Arabia is building the credibility of good market practices and integrity by ensuring clear and transparent arrangement and coordination of Saudi Arabian Financial Markets and Ministry of Commerce and Industry. According to Companies Law, new development of capital markets and insurances are focusing on particular corporate bond issuance with removing caps.
Financial Services
The framework of housing finance with proper mechanisms, which are facilitating execution of collateral and ensuring the arrangements to recognize creditors by having owner occupied residential property and permission with effective, transparent, and predictable resolution process for enforcement in financial markets. These features, which have related with collateral enforcement, also promoting expansion and reducing the costs of market related financing to small and medium scaled enterprises (SME) and leasing in financial markets.
Stocks Introduction
SAMBA reported that ‘Tadawul’ the stock exchange of KSA is the most powerful and the top largest stock exchange among the GCC countries by integrating a strong market capitalization of US$ 325 billion that has accounted as seventy percent of the country’s GDP in 2008. In 2009, the main index of the Tadawul evidenced a promising hold-up in the market that benchmarked with a few margins together with concerns regarding the corporate balance sheets as well as enhanced sentiments for the investor. In context of the Saudi stock exchange, Kuwaiti stock stands in the second position in GCC region that demonstrated the market capitalization of US$ 94 billion.
The index on 31 December 2009, TASI scored at 6121.76 points, which was 4802.99 points in the same time of 2008 and evidenced an increase of 27.46 %. Under the credit crush of 2008, Saudi stock exchange placed second position nest to London stock exchange. At present Tadawul, the stock exchange of KSA has only 134 listed companies that have nine industries including hydrocarbon, telecom, consumer’s goods, and services industries (SAMBA 5).
However, stocks of financial markets are defined as common and preferred stock of any company, which is authorized to issue in financial and capital markets according to company’s corporate charter. These stocks are also called as Capital Stock that normally listed on company’s balance sheet as shareholders or owners’ equities. In financial statement analysis of a company, the increased capital stock value indicates good sign of economic health, which is also proceeding to invest in projects or machinery that increases corporate profits and efficiency of a company and its operations in the financial market.
According to dual-purpose fund of any company, stocks and shares are entitled that used as appreciation on the company’s further investment for development and improvement. To handle with dual-purpose funds in the stock exchange, it is obligatory to understand for the concerned traders or investors that there are two types of shares such as –
- Capital Shares.
- Income Shares.
Both the shareholders are legally entitled to the company’s ordinary income but first one would distributed before tax and the second one is later than capital expenditure and it may bring advantages for shareholders by the opportunity to reinvestment in the same company with the goals and procedure that investment-vehicles would modify without any complications.
According to the view of Essayyad & Madani, the issuance of new equity is attached with particular legal clauses, which are differentiated them from previous issues (8). Some common stocks may not have any voting rights, and some special rights have treated as importance by investors on basis of special and unique rights.
According Capital Market Authority (CMA) of Saudi Arabia, it is very restricted to stocks in financial markets, where any delay payment of announcement on stocks of a company could fine 100,000 riyals that come into practice by the announcement in 2009 first. The Investment Bank of Saudi Arabia already fined for delay disclosing of CMA changes in Saudi Arabian boards and management (CMA 15). The stock exchange of Saudi Arabia is a subject to manipulate its stock prices, and where investors and executives of companies are heavily fined for stocks violations in financial markets of Saudi Arabia, like jail sentence, revoked license, and clamp down on irregularities with heavy fine.
For these reasons, the authority has to establish provisions on relevant regulations with establishment of standards and conditions to the auditors of companies, brokerage firms, investment funds and joint stock companies, which are listed in Saudi Arabian’s financial and capital market. The responsibilities have imposed to verify by Saudi Organization for Certified Public Accountants
As a result, establishment of KSA trading securities, which will be known as Saudi Stock Exchange with legal status of joint stock companies according to the law of provisions. The Kingdom is even trading with market originates by telephonically or electronically, or other foreign authorities. In Stock Exchange of Saudi Arabia, the board will consist of nine members, which are showing in below –
The stock exchange of Kingdom will perform following functions, which are listed in below:
- Ensuring fairness and transparency of financial markets, which is operated by Stock Exchange.
- Admitting brokering and clearing affiliates;
- It also responsible to illuminate the requirements as well as conditions for listing of securities (CMA 1);
- CMA pointed out that promoting ethical standards to Exchange members, its staff, and market participants is one of the most important tasks;
- It is also significant to maintain standards for corporate governance.
- Ensuring timely and accurate market information;
- Operating nation based securities trading system, settlement clearing and depository to protect investors and maintain fair financial market according to definite orders;
- Providing modern communication and data processing facilitate with foster efficiency to enhance competition, which are available as market participants.
Companies in the market
In accordance with the rules of the audited financial reports, two major bodies are mainly regulating the laws for the listed joint stock companies of the stock market of Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. The first one is the Companies act administration under the ministry of commerce, which argued that the time limit is 90 days from the end of the financial year for the subscription of the audited annual financial statements to make available for all the stakeholders. The second one is the Capital market authority namely CMA which has designed the regulation asking every company to file the annual audited financial statement along with other financial information mainly the auditor’s report within 90 days after the end of the fiscal year in CMA.
In the supply side, the Saudi Arabian audit market has many firms and entities that are playing significant roles. These firms are of various kinds including local firms and international organizations. There are 4 major international firms operating in this market (Yahoo Finance 1). The forms of the local firms are mainly partnership but there are some exceptions in many cases like a single owned firm or joint subsidiaries or auditors. No other local firms are linked with the international firms besides the big 4 firms and for this the stock market is being dominated by the local firms mainly (Almosa & Mohammad 12).
There are two types of Joint stock companies in terms of incorporation with licensing. Firstly, there are some companies licensed and regulated by the royal decree by the royal government of the kingdom. Under this category, there are franchise companies, the companies who run public utilities, the firms who receive state subsidies and the companies having the government as a shareholder except social insurance and retirement pension department and the companies engaged in banking. Secondly, the companies subscripted in terms of capital subscription which includes the companies where the founder subscribe part of corporate capital and the companies which has subscribed for all its corporate capital.
SHUAA is such a company, which has the operation including investment, banking, asst management, brokerage, private equity, and finance. It also assists the other companies to enter into the market of KSA and help them in stock market activities like buying shares.
Saudi Arabian Monetary Agency (SAMA)
The central bank of Saudi Arabia SAMA established in 1951 to develop the financial system of Saudi Arabia and the purpose of this bank was to offer services serve national or public interest while other commercial bank only considered profit. Only for the liberal financial system, it was possible for SAMA to play a vital responsibility for development of the Saudi economy, for example, free movement of goods, capital, services, and human resources helped to promoting growth and ensuring the soundness of the monetary system.
Major Responsibilities of SAMA
- In early stage of SAMA, the genesis of a modern the banking system in Saudi Arabia, introduction of paper money instead of precious metals and foreign currencies, save the commercial banks from the rising pains for insolvency problem, and strengthening of the regulatory framework were the main responsibilities of its operation;
- maintenance of domestic price and exchange rate stability;
- As a central bank, it controls monetary policy with policy in coordination with the fiscal policy;
- Increase banking business in Saudi Arabia by reviewing all applications for banking licenses;
- It is responsible to submit regular financial and statistical statements according to the national law;
- The major duty is to carry out on-site and off-site banking supervision;
- According to law, banks cannot change the composition of their capital without approval of SAMA, so SAMA responsible to provide approval;
- SAMA does not activate a deposit insurance scheme;
- However, SAMA integrated e-commerce facilities to offer quality of consumer service, electronic funds transfer system, reducing expenses, and strengthen controls;
- Its Board of Directors occupies the central position of CMA;
- SAMA six up minimum cash margins for banks’ credits or guarantees;
- SAMA issues regulations concerning the liquidity of banks and money-changers;
- Islam pointed out that it monitors closely banks’ lending activities broad reporting, on-site examination, and constant communication with the banks (Islam 2).
Major challenges of SAMA
Before attempt to proceed with the recent problems, it is important to consider the challenges of the era of 1970s –
- Deficiencies of the 1970s: Initially, SAMA had to depend on expatriate foreign employees due to lack of Saudi nationals in banking sector;
- Decreasing oil price: the oil price had been reduced from 1981, so the growth rate of the bank decreased dramatically that time;
- Slowdown in Economic Activity: SAMA (5) pointed out that frequent up and down of oil prices changed the economic activities in 1980s, as the oil revenue decreased for credit crunch in 1980s;
- Another challenge for the Supervisory System: In addition, irregularities appeared in Saudi Cairo Bank’s operations, so SAMA faced financial crisis.
However, SAMA suffered many other difficulties from 1990s and take appropriate measure to minimize banking risks –
- The Challenge of the Gulf Crisis: Despite of the high growth in 1990s, the monetary situation and the Saudi banking system adversely affected by the invasion of Kuwait by Iraq;
- The economic boom with bank recapitalization:
- Strengthening of Capital Base of the Banks in difficult political condition;
- To recover from crisis by applying mergers and acquisition strategies;
- Arrange fund for investment to develop technological infrastructure;
Two recent challenges for the operation of SAMA are –
- Global financial downturn;
- Unstable condition of the oil price.
The Financial Position of SAMA
According to the forty-fifth Annual report of SAMA, the growth rate of the world economy declined from 5.2% in 2007 to 3.2% in 2008 because of recession whereas Saudi financial system recorded remarkable growth in 2008 taking benefit of the constructive developments oil market (all-time high of $147 a barrel) though this scenario has slightly changed subsequently. However, the following table shows strong economic situation of SAMA where its total assets and liabilities amplified from SR 347.87 bn in 2004 to SR 1608.42 bn in 2009 and the growth rate for the last two years was 35.31% and 42.89% accordingly.
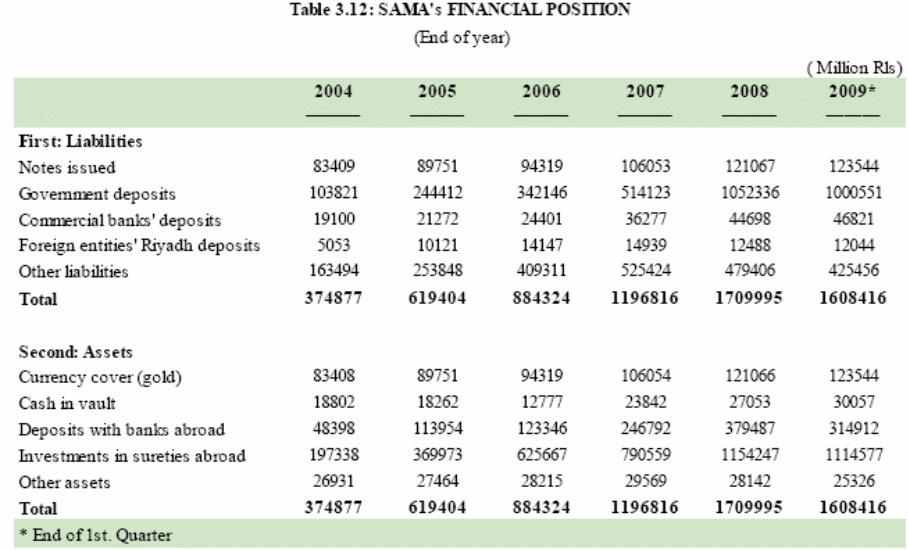
However, government deposits also increased by 104.7% in 2008 while it was 50.3% in 2007 and some other issues are:
- Notes issued enlarged from 14.2% to 48.7%;
- In addition, its investments abroad grew by 46.1%
- On the other hand, commercial banks’ deposits with SAMA raised by 23.2%
- Its deposits abroad improved by 53.8% and the amount was SR 132.7bn;
- Net cash value increased by 13.5% compared to a rise of 86.6% in the previous year.
CMA (Capital Market Authority)
Mission
The mission of CMA has noticeably stated that it acts to expand the Capital Market of KSA by taking care of investor’s interest, saving them from market risks and make use of all resources to reinforce equality for all, transparency to the public and disclosures of the listed companies (Capital Market Authority 7).
Vision
The Vision of the CMA has aimed to lift up the competence of the capital market and to boost the market strength by means of introducing the excellent standards parallel to global context shape the KSA capital market as an attractive place for foreign investors (Capital Market Authority 1). For liquidity, market performance, transparency including rules and regulations, CMA would like to achieve world’ number one position
Background of CMA
The CMA (Capital Market Authority) of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia was introduced in 2003 under the Capital Market Law to regulate and administer the capital market of KSA by issuing relevant legislation to improve the market. The CMA has been treated as a public body of KSA with full administrative and financial autonomy which is essential for free fair and impartial capital market implication in this region but accountable to the prime Minister.
The Capital Market Law has clearly defined it as a legal personality and prohibited its right to conducting any profit-making initiatives such as trading, browning, lending, and issuing securities. The CMA Board enjoys all exemptions and power practices like government agency and its employees are subject to the KSA’s Labor Law. The ultimate concern of CMA is to regulate capital market of Saudi Arabia ensuring a health investment atmosphere both for local and foreign investors.
Organizational Structure of the CMA
The CMA consists of a board of five members with highly professionally skilled Saudi nationality by birth and provides fulltime service to the organization. The appointment of all board members, their remunerations, and state facilities would settle by the royal assent. Among the five board members, anyone would be the Chairperson and another would be selected deputy Chairperson upon the decision of the royal order. The duration of a selected board is five year from the date of appointment and possibly will reappoint for another term. After completion of their working session, the board members would responsible to continue their office until the new members are appointed.
The CMA board would determine its employees, advisors and auditors and their salaries to extend which is needed to conduct it functionalities. The Board will identify the way of CMA’s working, its responsibilities, coordination of different subordinate bodies and departments. It also has power to introduce new regulation to initiate market mobility and conflict resolution with any existing law.
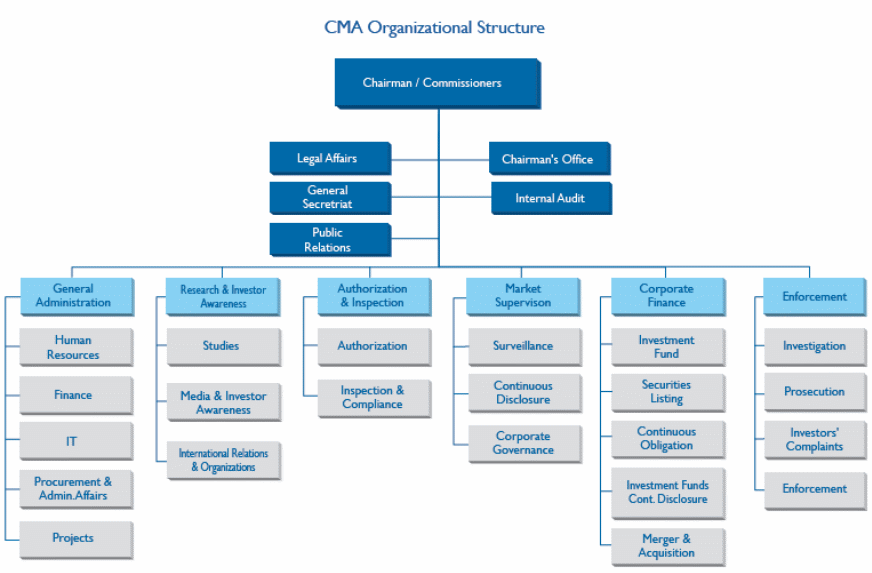
CMA has eight essential wings to coordinate the functions of the organization and these are as follows –
- Enforcement Department: The foremost task of this wing of CMA is to inspect the violations of CML, put into practice of regulations, conducting legal proceedings, disputes resolution. It may sometime organize subcommittee to handling the investors complains and to resolute them.
- Corporate Finance: This department of CMA scrutinizes the applications from the companies for their issuance, offering and listing stocks assessing their compliance CML and confirms the investment funds.
- Market Supervision Department: The duty of this department is to acts for put into practice the instructions and to administer the concerned corporate information such as interim and annual financial statements, publication and maintenance of accounting standard.
- Authorization and Inspection Department: This wing is responsible to reading applications placed for authorization, to carry out business inquiry on the applicant. It also look after the company’s dealing, management and give an opinion and custodial services to the investors as covered under CMA.
- Research and Investor Awareness Department: CMA conducts researches on financial market, investor’s trend, and economic tendency of the country and publish journal those are available to the stakeholders, academies, and public. It also generates regular publication to build the awareness of the investors including data with statistical presentation.
- The General Administration Department: It is the most common department of CMA like any other organization that builds up with the skilled Human Resource, interrelated policies.
- Internal Audit Department: This department concerned to improve performance and efficiency of the CMA and ensure the internal compliance policies for the transparent accounting standards.
- Legal Affairs Department The major feature of this department of CMA is to put in order the existing regulations, giving explanation and producing new direction for further market development. To amend and mineralize capital market of KSA it works with both the local and foreign partners simultaneously.
Functional Area of CMA
CMA works to implementing the Capital Market Law by producing necessary regulations, rules, explanations, and direction in accordance with the provisions of CML (Capital Market Law), and to do so CMA identifies its functional areas as —
- The basic functional area of CMA is to introduce a dynamic trading system in the stock exchange dipping the transactional risks of investors and to regulate the market in global context;
- CMA would carefully control, monitor, and adjust the issuance of Stocks and Securities and their trading;
- CMA would strongly supervise the market, performance of the concerned parties subject to the regulation.
- It will keep its keen eyes to control and prohibit all sorts of market manipulations, and ensure a free fair and transparent trading environment in the stock exchange.
- It also scrutinizes the disclosers of securities and related issues by ensuring free flow of information for both public and shareholders by publishing regular bulleting, market updates, and research findings;
- Another significant function of CMA is to regulate proxy and buying orders as well as public offers of shares and effectively prescribes in accordance with CML provisions;
- It would also look after the compliance of law by the listed companies
Executive Power of CMA
Under the Article- 6 of Capital Market Law, it has clearly mentioned that the CMA has the power to convey its activity complying with regulations, and if required, making new rules and introducing diverse instructions for handling the following power practice
- CMA has empowered to move forward planning, carry out market research and take necessary initiatives to gaining the objectives.
- CMA is authorized to resolve any market dilemmas and to do so it can amend any controversy of existing law and the put into practice the regulations those are essential to enforce under CML.
- Before coming in the market for trading, all the offerings of securities needed to have the approval of CMA.
- CMA time to time provides suggestion to the government to take necessary steps to improve the capital market and attracting the investors for risk free entry in the stock exchange.
- For any crisis, CMA has the right to postpone the activity of the stock exchange for a single day and if needed, the suspension can be extended for any longer with the permission of the Minister of Finance.
- CMA also can postpone the trading of any issuance if any discrepancy or manipulation arises and at the same time, it determines the brokerage charges that the broker takes from the investors.
- It has the authority to investigate and scrutinize the listed company’s books and audit reports and fix up the auditing standard,
- Moreover, CMA settles on the stuffing of financial statements and reports that produced by issuers, make decision, appoint licensed auditor to audit the final accounts that may impact on the capital market situation,
- CMA has the rights to approve the establishment, award the essential licenses for merge ring and bankruptcy of investment funds so far the law facilitates.
Islamic Banking
The concept of Islamic banking is an old thought derived from Holy Quran and Islamic banks set up their operating system in accordance with the Islamic Sharia’h principles and equity participation.
Islamic Banking in Saudi Arabia
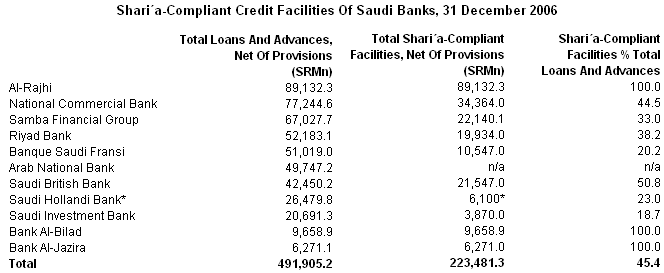
Khan & Ishaq reported that many conventional banks has restructured their business considering the success Islamic banks and they introduced new products like Sharaih compliant stocks, Sukuk issuance, bonds and so on (7). They further added that Islamic banking businesses hold 64%of the total market shares in Saudi Arabia though only two players Al Rajhi and Bank AlJazira lead this market (Khan & Ishaq 7). However, the following table depicts the position of banks in this segment and shows that three banks Al-Rajhi, Al-Jazira and Al-Bilad operate their system by implementing and maintaining 100% Sharaih law –
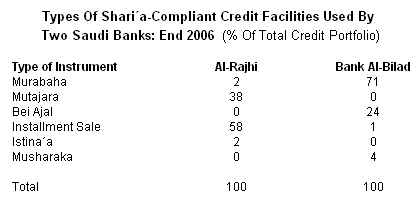
Cunningham (1) stated that the Saudi Arabia observed the development of Islamic banking from the 1990’s, though this practice started from 1980’s. According to Cunningham, these banks mainly offer the following products and services in financial market of this country –
- Sukuk issuance
- Shari’ah -compliant mutual funds
- Murabaha instruments
- Murabaha and Musharaka Sukuk
- Personal banking (credit and deposit)
- Corporate banking such as financial project, service industries, financial trade, and corporate account services,
- Brokerage
- Istisna’a, Ijarah and Tawaraq
- funds management
- Treasury
- Other conventional services etc.
Advantage of Islamic Banking
- Siddiqi pointed out that Islamic banking is a more effective way than other banking system to offer just and equitable distribution of assets;
- Sometimes borrowers failed to reach their goal due to high interest rate of bank loan whereas Islamic banking system prohibits both paying or receiving interest;
- Moreover, Saudi based organizations should encourage Islamic banking system as many large companies has collapsed due to pressure for high interest rate in global financial crisis in all over the world;
- On the other hand, the relationship between the bank and its customers become more closer for profit sharing provisions (Siddiqi 1).
- It enjoys many competitive advantages over the non-Islamic banking system;
- Some Islamic bank offer extensive foreign exchange services at competitive rates;
- Islamic banking system is easy and straight forward to attract the customers;
- Customers like to use this system to minimize the risk of inflation and financial crisis;
- According to the view of Siddiqi, “Islamic financial system claims to be based not on an excellent stroke of human ingenuity but on divine regulation and prophetic insights”;
- Finally, Islamic banking helps to reduce poverty level by introducing zakat (shares of assets of upper class for the poor) and prohibiting interest and gambling.
Reasons behind the prohibition of riba (interest)
Siddiqi argued that Islam and its laws strictly prohibits the provision of riba or interest as it has many drawbacks to maintain public morals or remove the inequality, injustice, or poverty from the society. He also added that the system of interest is directly conflicts with Quran and Sunnah as this system only change the financial position of upper class people, as a result, Islamic laws prohibits Muslims from paying or receiving interest on the grounds of equity (Siddiqi 15). However, the following points analysis the justification to forbid the prohibition of interest from baking system –
- The meaning of riba is growth or increase, which impose extra liabilities on the debtor and if they fail the interest on time, it may exceed the actual loan amount;
- Interest system may corrupt the society by creating fasad;
- Islamic law prohibits interest because it unlawfully appropriates the property of the borrowers;
- The crucial effect of interest is it can negatively affects on growth;
- It demeans and reduces human personality;
- Interest is unjust according to Islamic law;
- Bank should take responsibilities, as a business has chance to make profits and suffer losses.
Key challenges for Islamic Banks
- There are few issues, which need to set up by laws, for example, Islamic law should specifically mention the formation process of the board;
- Conflicts of interest is the existing major risks in this sector;
- Voting and approval system to manage the bank is not clear yet;
- Build up reputation is the great challenge for the Islamic banks though this banking system is recognized to the 75 countries;
- Some scholars argued that the bankers need more knowledge about financial system;
- Similar to commercial banks, global financial crisis is also threat for its operation;
- Lack of consistency on best practice;
- The competition in financial baking sectors is really high, so, these banks have to compete with similar Islamic banks as well as western banks;
- This system is less popular to organization for the zakat provision;
- There are no clear answer about disclosure and degree of compliance issues;
- In addition, it has many problems relating to the corporate governance.
Case Study of Al Rajhi
Al Rajhi Bank started its operation in 1984, and it is now market leader in Islamic banking segment in the world and it is the third largest financial group in Saudi Arabia. This bank has formed an independent Shariah Board to control the Islamic banking system in accordance with the directives of the Corporate Governance Rules duly reported by CMA where the board is responsible to take major decisions for further development like introduce of new services or laws, customer care issues, internal monitor and audit process, ensure Shariah-rule and so on. Al Rajhi reported that in 2008, its net profit increased 8%, and it generated highest profits from retail sectors though it has many other segments like corporate financing, Bai Al Ajel (direct cash to customers), Musharaka (partnership), Eirad (credit facilities), Akar (provide investment opportunity) and Istisnaa (financing large real estate projects) etc.
Case Study of Bank AlJazira
Bank Aljazira has incorporated with the joint stock company in 1975 and it turned the monopolistic market of Al Rajhi into a perfect competition by introducing its Islamic baking activities. Bank Aljazira is the first Islamic bank, which started with the unique differences by combing the traditional Islamic values with innovation of technology in the modern banking system in Saudi Arabia. It had entered into the market to provide a full range of banking services by following customer oriented banking with the help of close personal relationship and understanding their demands of the services. However, the customers of this bank are also satisfied with the dedication to flexibility, modern way of banking, innovation, solutions for financial needs etc.
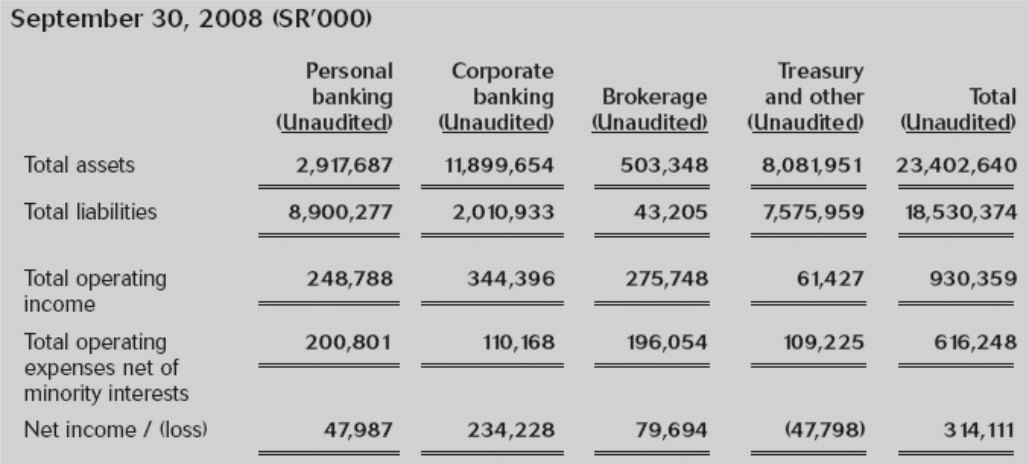
The table no 9 demonstrates that in 2008, its net income from personal banking and treasury and other segment has decreased dramatically comparing the data of 2007. On the other hand, in 2008, it introduced a new brokerage segment and earned SR796.9 million from this sector. However, its overall income has also decreased like non-Islamic banks due to global financial crisis.
Works Cited
ACIG. Annual report 2009 of Allied Cooperative Insurance Group. 2010. Web.
Almosa, Saad. & Mohammad Alabbas. Audit delay: Evidence from listed joint stock companies in Saudi Arabia. 2005. Web.
Al-Muharrami, Saeed. “The competition and market structure in the Saudi Arabia banking.” Journal of Economic Studies, 36(5), 2009. Web.
Al Rajhi. Annual Report 2008 of Al Rajhi. 2008. Web.
Amadeo, Kimberly. An Introduction to the Financial Markets. 2010. Web.
Arab National Bank. Annual Report 2009 of Arab National Bank. 2009. Web.
Arab news. Saudi insurance market grows 24 percent in 2007. 2007. Web.
Bank AlJazira. Financial Report 2008 of Al Jazira. 2008. Web.
Capital Market Authority. About Us. 2010. Web.
Capital Market Authority. CMA Report 2008. 2008. Web.
Choudhury, Masudul Alam. Culture, Finance and Markets in Saudi Arabia. 2001. Web.
CIGNA. Annual report 2009 of CIGNA. 2009. Web.
CMA. Kingdom of Saudi Arabia: Capital Market Law. 2009. Web.
Cunningham, Andrew.”How Big Is Islamic Banking? – A Snapshot From Saudi Arabia.” Middle East Economic Survey, 2007. Web.
Essayyad, Musa & Madani, Haider. “Investigating Bank Structure of an Open Petroleum Economy: The Case of Saudi Arabia.” Journal of Managerial Finance, 29(1), 2003. Web.
IMF. Saudi Arabia: Financial System Stability Assessment, including Reports on the Observance of Standards and Codes. 2006. Web.
Islam, Mazhar. Regulations and Supervision of Financial Institutions in GCC Countries. 2003. Web.
Khan, Mansoor. & Ishaq Bhatti. “Islamic banking and finance: on its way to globalization.” 2008. Web.
Ministry of Commerce & Industry. Application & Procedures. 2006. Web.
National Commercial Bank. Annual Report 2010 National Commercial Bank. 2010. Web.
Rabindranath, Vijay. & Gupta, Parthapratim. An Overview – Sukuk Market in Saudi Arabia. 2010. Web.
SAMBA. The Saudi Stock Market: Structural Issues, Recent Performance, and Outlook. 2009. Web.
Saudi Gazette. Saudi insurance industry one of fastest growing worldwide. 2010. Web.
Siddiqi, Mohammad Nejatullah. “Comparative Advantages of Islamic Banking and Finance.” Harvard University Forum on Islamic Finance, 2002. Web.
Siddiqi, Mohammad Nejatullah. Riba, Bank Interest and the Rationale of Its Prohibition. 2004. Web.
The Riyad Bank. Annual Report 2010 of the Riyad Bank. 2010. Web.
Yahoo Finance. Saudi stock exchange fines six firms. 2010. Web.
