Introduction
Problems are part and parcel of man in day to day life hence there is need to devise proper ways and means of addressing problems (Skogan, 1999). Managers are the ones that are endowed with the responsibility of problem solving. Many approaches of solving problems have been devised depending on the nature of the problem and people affected (Tang, 2008). The rationale and commonly used approach is where a problem is defined, causes are analyzed, alternative solutions are identified, assessing the chosen alternative, choosing one alternative, implementing it and evaluating whether the problem was solved or not.
The purpose of this research is to present appropriate techniques or techniques that managers use or should use in problem solving. Managers have the responsibility of ensuring that whatever problem that comes up are solved within appropriate time before it causes havoc (Thierauf, 1987).
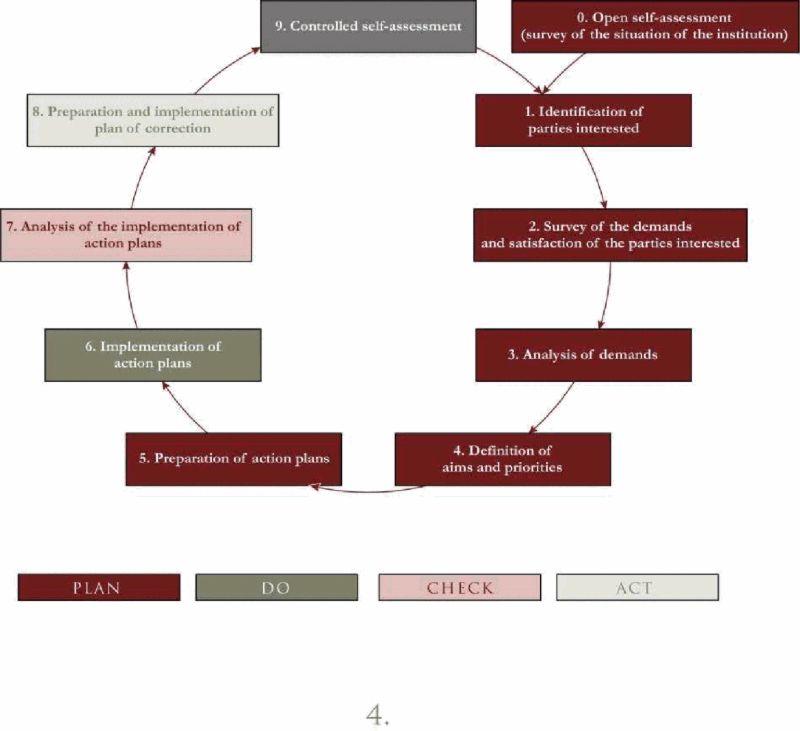
The twelve steps PDCA cycle provides the surest technique in problem solving. When embraced by managers and applied in good faith it’s bound to work since the steps tend to stem the problem at the bud. This report will address the problem of low customer turnout in a restaurant.
Literature Review
According to Bushell (1992) in implementing the Plan, Do, Check and Act 12 steps of PDCA cycles, the cycle is a scientific decision making tool that is very suitable for managers. This cycle is divided into four major steps: mainly plan, do, check and act. Bushell says that before defining a problem and planning a solution a manager needs to understand how the process is carried out under the plan stage. A manager needs to do anything that affect the process. A consensus should be reached in understanding the problem as it is practiced. Documentation of all explanation should be done. A manager must avoid fixing things he does not understand.
What follows is data collection on areas of process operation which are problem areas and analysis of the data collected. The next step is selection of solutions and evaluating them before implementation. He advises that the solutions should be prioritized accordingly.
The small scale test needs to be planned once a solution is selected. Bushel further asserts that when considering a solution, the following points need to be taken into consideration: the usefulness of the solution should be evaluated; employees also need to be educated on the solution and some improvement for the customers should be considered. Measures to establish success should be established whether 100% of customers are satisfied or 100% of employees used the solution.
According to bushel, appropriate measures to collect data on the expected out comes from both the employees and the customers should be put in place in order to evaluate how you did against your measures of success: to find out whether customers services were improved, to have data to support the implementation decision, to gather information to be used to upgrade solution and to build customer and employee feedback. A manager should use his or her understanding of the process to assign a suitable time for the test.
The test group should be selected and trained to work on the test. Employees also need to be trained on the test before the implementation is done. Once that is achieved the next course of action which is implementation should be taken. The next step is to train the test group, start the test and do it for a specified period then collect data on the test. The Check step involves collection of data on the do step and organizing it into information. At this stage the team either decides to implement the solution or retreats to the plan step. In the act step, the solution is modified in order to incorporate whatever is learnt on the check step.
Main responsibilities of managers and supervisors is making decisions and solving problems (Davis, 1973). New managers are faced with a problem of solving one problem and the same problem keeps recurring. This is because they make decisions or solve problems by simply reacting to the problem (Namara, 2010).
Managers are therefore encouraged to use scientific and rather more organized approaches in solving problems since it will help them to effectively find proper solutions to their problems. Namara (2010) gives seven steps or guidelines in solving a problem which are more like a summarized version of PDCA cycle. According to Namara, the first step towards solving a problem is by defining a problem.
As a manager you need to understand why you think there is a problem then asks yourself and your team what it is that you can see that imply there is a problem, where, how, when, with whom and why is it happening. At this stage it is not wise to think on who is causing the problem. It is advisable to verify your understanding of the problem analysis and if you find several related problems then prioritize them and come up with the most urgent and important one.
The second step is to find the potential causes of the problem from people who the problem is related to directly or are affected by the same problem. The data is collected from individuals and peers but not groups and also as a manager you can use available resources to source important information needed. Stage three is identification of alternative solution through brainstorming. In stage four Namara suggests that the best approach is selected to be followed by implementation in the fifth step. In step six implementation plan of the best alternative solution is monitored for the best result. Finally on the seventh and last step, verification whether or not the problem has been resolved is carried out.
Methodology
The problem to be investigated was customer low turnout which posed serious risk to the restaurant. In trying to solve the problem and making appropriate and timely decisions, the management team was summoned and together they deliberated on how to identify and acknowledge the problem. Data was collected and interpreted before possible option or approach to solve the problem was initiated. It was found out that there was a sudden change in the customers attitude towards the restaurant while the neighbouring restaurants were always flocked with customers. Surprisingly the sudden turn of events was not expected since a few days before, the turn out of customers was normal.
After defining the problem an attempt to find alternative solution started. This was done in the boardroom through the brain by the management team. All sorts of opinions were entertained and the manager ensured that there was focus on the agenda. He also prevented the team from commenting on others’ opinions or suggestions. After problem definition, causes of the problem were sought using the resources and information or data to get to the root of low customers turn out in the restaurant.
After brainstorming atotal of five possible alternative solutions were arrived at. All the alternative solutions were critically analysed and weighed on the basis of their advantages and disadvantages. Eventually the most effective with the highest advantages was chosen for implementation which was followed by evaluation.
Findings
The manager was then able to identify the possible cause of the low customer turn out which was found out to be the negative attitude of two staff members towards customers. It was ascertained beyond reasonable doubt that they were rude to the customers and they could not take the customers’ orders accordingly. Alternative solution suggested were: rebranding of the business, relocating the business, firing all the employees, training the employees and improving customer services.
In a thorough session of brainstorming to determine possible alternative solutions, it was agreed that the most viable and appropriate alternative solution was to be implemented. All the staff members of the company were briefed on the decision and the reasons behind the decision to implement it. The resolution was then implemented and all employees was involved in the implementation process. After the period allowed for implementation expired evaluation was carried out and it was found out that the decision had worked and it was the best alternative the company could ever make in such a situation since the business flourish more than before.
Discussion
Relevant questions need to be aked at the very beginning of problem solving. When defining a problem it is paramount to be right from the very beginning or else the management will be acting on false foundation and that will be a waste of time and resources while the problem persisits. The management should use the resources available to get to the root cause of any problem(Proctor, 199).
They are a better place to use available machinery, information to collect helpful data that can reveal the root cause of any problem affecting their firms. It was determined that it was the deeds and the attitude of the two staff members that were driving away customers from the restaurant. Brainstorming as an attempt to come up with alternative solution to the problem is very crucial.
A well guided and controlled brainstorming will give suittable alternative solutions. Each alternative solution was analysed independently where advantages and disadvantages of each was sought. Eventually, the one with the highest advantages and least disadvantages was chosen. Other factors were also brought to focus like cost benefit analysis and effectiveness. The cost benefit analysis and effectiveness of each alternative solution was carried out and the solution was chosen. The one with least cost, most effective and the most advantageous one was implemted.
It is after this stage that the manager made a decision to implement the alternative solution. Employees were informed of the decision of the management and why the management came to the conclusion and the reasons behind the decision. This was to make employees understand the decision and hence implement the resolution based on information. For any decision to work it should be given enough time for implementation. After the implementation evaluation followed immediately with close monitoring by the manager. The implementation was given ample time to materialize and indeed after two months the business was back on its feet.
Conclusion
Good managers are know in times of problem because good managers will make good decisions when it is needed most (Kohnen, 2005). Therefore decisiveness is a very paramount quality of a manager. When faced with a problem, it has been ascertained that managers need to follow the 12 steps of PDCA cyle and they will certainly find solution to problems affecting their firms.
In solving a problem or making a decision, it is important that a manager starts being right from the first step of the 12 steps in solving a problem. When a mistake is made at the very beginning then it means that all the 11 following steps will be wrong since they will not be addressing the problem that requires a solution. Hence when defining a problem, caution should be taken to avoid taking symptoms of a problem for a real problem.
Recommendation
- Proper mechanisms should be put in place that accurately identifies the problem and the cause of a problem before the succeeding actions.
- During brainstorming, all team members should be given equal opportunity to deliberate without any interruption, disqualification or judgement.
- Care should be taken when choosing the best alternative solution to avoid implementing less effective and more costly alternative solution(Shibata, 1998).
- All employees should be informed and involved in decision implementation
- Alternative solution chosen should be given ample time during implementation.
- Managers should ensure proper follow up in decision implementation to ensure that it is implemented as per the expectations.
Reference List
Bushell, S. (1992) The Journal for Quality and Participation. ProQuest LLC.
Davis, G. (1973). Psychology of Problem Solving: Theory and Practice. New York: Basic Books.
Kohnen, J. (2005) the Quality Management Journal. Volume. ProQuest LLC.
Namara, C. Basic guidelines to problem solving. Web.
Proctor. T. (1999). Creative Problem Solving for Managers. London: Routledge.
Skogan, W. (1999).Police and Community Problem Solving. Contributors. Boulder: Westview Press.
Shibata, H. (1998). Problem solving. Web.
Smith, G. (1998). Quality problem solving. USA: Quality press.
Tang, J. (2008). The Implementation of Deming’s System Model to Improve Security Management. ProQuest LLC.
Thierauf, R. (1987). A Problem-Finding Approach to Effective Corporate Planning. New York: Quorum Books.
Young, R. (2004). The requirements Engineering Handbook. Norwood: Artech House.
Zabel, D. (1997). An International Guide to Materials and Resources. London: Routledge.
