Mission and Vision
Mission and vision are crucial to companies operating in the healthcare sector, as they define the organisation’s priorities and assist in planning strategic moves at all stages of organisational development. The vision of NMC Healthcare is “to be the trusted healthcare provider across the globe, driven by excellence in innovation, quality, teamwork, advanced technologies, patient safety and customised care offerings” (NMC, 2020a, para. 4).
There are two critical components of this vision: future development and everyday practices. On the one hand, the company strives to grow its presence internationally, thus gaining access to more geographical markets. This has been supported by NMC’s current strategy, which involves geographic expansion through specialised services. For instance, NMC has developed its maternity, fertility, and long-term care services to establish a presence in Saudi Arabia, Europe and Latin America (World Branding Forum, 2019). On the other hand, the stated mission also identifies the practices that support NMC’s current and future growth, including the use of technology, quality improvement, teamwork and customisation. These practices are part of the company’s strategy and its value proposition to customers.
The mission of the company also involves several components. First and foremost, the company is committed to providing advanced healthcare services to people from all sections of society (NMC, 2020a). Secondly, the company seeks to uphold ethical medical practices and prevent malpractice, thus maintaining a high level of service quality (NMC, 2020a). Thirdly, NMC Healthcare seeks to gain customers’ trust through providing “personalised care in a compassionate and friendly environment (NMC, 2020a, para. 4). Hence, customer orientation, service quality and organisational culture are the primary components of NMC’s stated mission.
Marketing Mix Strategy
Product
NMC’s core product is healthcare services, which include examination, diagnostics and treatment of patients in acute, primary and long-term care settings. The company provides a wide range of services that allow rendering comprehensive care to persons of all ages. NMC’s specialities depend on the region since, in some areas of operation, NMC only serves limited populations of patients, such as infertile couples or elderly persons with chronic illness (World Branding Forum, 2019).
However, in the UAE, the company’s facilities employ a full scope of specialised personnel and feature paediatrics, cardiology, pulmonology, endocrinology, physiotherapy, general practice, psychiatry, immunology and other specialisations. The wide range of specialisations is part of the company’s value proposition to customers, and it contributes to NMC’s marketing because it enables customers to obtain primary health care from one preferred NMC facility.
Price
Price is a crucial component of the marketing mix for private healthcare companies since it shapes the organisation’s competitive position and its image in the customers’ minds. Moreover, private healthcare usually is part of various corporate and individual health insurance plans, and thus NMC’s prices can influence the demand for its services among insurers. Service prices set by NMC are considered affordable for the large part of the population (NMC, 2020a). This enables the company to attract customers with medium income, thus addressing a more extensive customer base as part of its strategy.
Place
The primary area of operations for NMC is the United Arab Emirates. The company is headquartered in Abu Dhabi and has a number of branches throughout the UAE, including Dubai, Ajman and Sharjah. NMC has also expanded to some other regions of the Gulf, including Oman and Saudi Arabia. As part of its strategic growth effort, the the organisation has also targeted Europe, Africa and Latin America. According to NMC (2020b), the company has hospitals in Spain, Slovakia and the United Kingdom, as well as in Brazil, Nigeria and some other countries. The company works with global insurance providers, including Allianz, Connex, Inter Mutuelles Assistance, and Vanbreda, which supports its growth in different locations.
Promotion
NMC uses a variety of methods to attract customers, including digital advertising, TV, social networks, and poster ads. For instance, the company used Google Search ads campaigns and has an active social media presence on Youtube and Twitter. Local branches of NMC have also released video and poster ads to raise awareness about its services. Partnerships with insurance providers can also be considered a part of the company’s marketing strategy since they attract new patients to its facilities. Corporate insurance provides a way for customers who are hesitant about private health care to use NMC services, potentially retaining clients who were impressed with service quality in the future.
Segmentation, Targeting and Positioning Model
Segmentation
Segmentation is an essential part of NMC’s marketing plan since it affects the strategies used to attract new customers and the services provided by the facilities. Based on the strategic information about NMC, the company relies on geographic segmentation. This is justified by the fact that people usually chose to obtain primary care from their local providers, and thus focusing on local customers is beneficial for NMC. Additionally, there is evidence that the company uses demographic segmentation based on income and nationality. The services provided by NMC are affordable, meaning that they target people mostly from medium-income backgrounds.
National and ethnic identity is vital to NMC, too, and this approach to segmentation often affects strategic decision-making with regard to new facilities. According to Healthcare Business International (2018), NMC evaluates its patient base based on nationality, which has supported some of the company’s branding decisions in the past. Hence, the two approaches to segmentation used by NMC assist the company in tailoring its marketing strategy to meet its strategic needs.
Targeting
From the description above, it follows that NMC’s market is represented by adults from diverse nationalities who have a medium to high income and live in the area of NMC’s facilities. The targeting strategy corresponding with this market is differentiated marketing, which involves targeting large groups from the primary market. As explained by Porral and Stanton (2017), differentiated marketing focuses on the needs of several market segments, and thus it enables companies to cover a large share of the general market for their product or service.
Targeting individual segments might require new approaches to marketing that would make a company attractive to new consumers from a previously underserved population. For example, when NMC found that the vast majority of patients from its patient base were Indian and that other nationalities perceived it as an Indian healthcare brand, the company sought to attract more UAE nationals and Western expats by focusing on experiential marketing and leveraging service delivery (Healthcare Business International, 2018). Therefore, the differentiated targeting strategy enabled NMC to achieve a significant market share in the UAE and other regions by making its services appealing to diverse customer groups.
Positioning
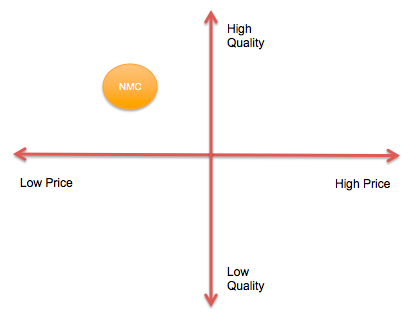
Private healthcare companies are usually positioned depending on their prices and the quality of services provided. NMC has affordable prices and offers a reasonably high quality of service with a good range of specialisations, which places it into the top left quadrant of the positioning model (Figure 1). These are the functional aspects of positioning as they reflect the actual services provided to clients and their costs (Porral & Stanton, 2017).
However, NMC also engages in experiential positioning, wherein customer experience is a significant aspect of the company’s value proposition. The company’s mission and vision reflect its patient centricity, which is an essential part of every patient’s experience with a care provider. NMC’s experiential positioning also targets various demographic market segments at once; while older adults would appreciate the friendly atmosphere and patient focus of NMC’s facilities, younger customers would be attracted to innovations in service delivery and technology use. This means that NMC’s approach to positioning is in line with its segmentation and targeting strategies and has a significant impact on NMC’s marketing.
STEEP Analysis
Socio-Cultural Forces
One of the main aspects of NMC’s macroenvironment that deserves attention is the socio-cultural environment. Due to the increased access to healthcare in most regions, people all across the world have become more aware of their health needs and view health care as an integral aspect of self-care. This is particularly evident in younger populations, where the levels of health-consciousness are at record high values. For example, a recent study indicated that millennials are more concerned about their health and usually rank it as their second priority in life (Nermoe, 2018). While previous generations showed concern for their health mostly at times of illness, younger people are more engaged in prevention, health screening and lifestyle health promotion (Nermoe, 2018). This creates excellent opportunities for the development of healthcare companies, particularly with respect to primary care institutions and organisations.
Technological Forces
Technological trends also have a crucial impact on health organisations from two different perspectives. On the one hand, contemporary patients have become technologically savvy, meaning that they use modern technologies actively to improve their lives on a daily basis. The healthcare sector is affected by this change since there is a certain pressure on care providers to remain on track with technology developments and use them to patients’ benefit (Allen, 2019).
On the other hand, the development of new technologies has also facilitated operational effectiveness in healthcare institutions (Allen, 2019). Today, hospitals and clinics can use technology to reduce workers’ paperwork, improve patient data storage, exchange information with other care providers and more. This has a positive effect on the operational efficiency of healthcare organisations. However, the development and implementation of technological innovations come at a cost, and many institutions face additional expenses related to hardware and software needed to stay innovative.
Economic Forces
The economic environment concerns NMC since it affects whether or not patients or corporate insurance clients can afford private healthcare services. Hence, there are some worrisome economic trends in the UAE, and globally that could affect the company’s performance. For example, the UAE economy showed a decrease in output growth and payrolls, marking a low point in business activity (Fattah, 2019).
Other regions where the company operates are also affected by the lack of economic stability, including Nigeria, Brazil and the United Kingdom. This might affect both corporate and individual clients utilising NMC’s private health care services, and thus the company requires a strategy that takes potential economic challenges into account.
Environmental Forces
The current state of the environment globally is concerning due to the increase in pollution and climate change. There are two distinct ways in which this influences healthcare organisations. Firstly, poor environmental conditions have a negative effect on people’s health, thus raising the demand for health care services. For instance, air pollution has a significant impact on the incidence of respiratory diseases, whereas ozone layer depletion affects the rates of skin cancer by enhancing the amount of UVB reaching the Earth’s surface. Secondly, organisations in all industries are pressured to become more environmentally friendly by reducing waste, introducing green energy sources and supporting local and global green initiatives. This creates an important opportunity for NMC to improve its image among target customers while also becoming more cost-efficient.
Political Forces
Finally, the political environment in which NMC operates is beneficial for the company due to the increased concern of international governments with health matters and improved support of healthcare organisations. As explained by Stolz (2019), the UAE government has increased its support of private care providers over the past years and plans to develop this sector even more. Moreover, specific policies, including hospital privatisation and mandatory insurance, contribute to the demand for private health services in the region. Similarly, in other locations, governments are focused on achieving population health targets and improving people’s well-being in general, leading them to support both public and private medical institutions.
This means that the current political climate is favourable for NMC’s future growth and development. Nevertheless, future global expansion of NMC may be affected by local policies on international businesses and other regulations that do not target the healthcare sector in particular.
References
Allen, S. (2019). 2020 global healthcare outlook. Web.
Fattah, Z. (2019). U.A.E. economy falters with first-ever drop in new orders. Bloomberg. Web.
Healthcare Business International. (2018). NMC healthcare – Best building of a brand finalist – 2018. Web.
Nermoe, K. (2018). Millennials: The ‘wellness generation’. Sanford Health News. Web.
NMC. (2020a). About us. Web .
NMC. (2020b). International patients. Web.
Porral, C. C., & Stanton, J. L. (2017). Principles of marketing. Madrid, Spain: ESIC.
Stolz, R. (2019). UAE leading the healthcare sector. Web.
World Branding Forum. (2019). NMC healthcare. Web.

