Introduction
The world’s largest cell phone Manufacturer Company Nokia is the selected company for this research paper. Nokia Corporation is familiar as a popular Finnish MNC of communication and in 2008, its annual revenue was € 50,710 millions, net income was € 3,988 millions and it produced 3.5% share in the home country’s GDP. It is essential to have a clear concept about this along with the global economic features with the company context as the net income is decreasing (in 2007, its net income was € 7,205 million).
This research paper will provide a short description of the Company, the reason behind to choose this particular company, its target market, and current situation of Nokia. This paper will assist to analyse internal and external environment by using several framework such as PEST factors, Porter’s five forces, SWOT analysis, industry analysis, and marketing strategy analysis (e.g. current marketing program and product positioning). Finally, major competitors, current trends in the industry and customer characteristics will be asses to provide a future marketing plan, which consists of a proposal for a future marketing program.
Background of Nokia Corporation
Nokia has established in 1865 by Fredrik Idestam and now it is the world’s largest cell phone manufacturer company, which makes a broad range of devices for all major customer segments and provides Internet services. According to the Annual report 2008 of Nokia Corporation, it is a market leader by market share as it holds 40.30% of total market share of Global Mobile Market and it has operation in more than 150 countries and for its global network of sales, in 2008 its net sales was totaled €50.7 billion and net income was € 4.0 billion.
History & Major Events
- In 1967, Nokia took its present form as Nokia Corporation;
- In 1982, Nokia introduced the foremost fully digital local telephone exchange in Europe,
- It entered the telecommunications equipment segment in 1960;
- In the early 1990s, Nokia made a strategic decision to formulate telecommunications its core business;
- In 2007 and 2008, Nokia continued to develop its services as well as software offering with the acquisition of main technologies and expertise, for example, NAVTEQ.
Target market
Nokia has customer all over the world but its main target market in developed countries as the people of that zone like luxurious products but Nokia has big market in developing countries for the large population like India, China, and Bangladesh.
Current position
Nokia deals with three segments as a market leader but due to global financial crisis customer’s capacity to purchase its products has decreased, which is the cause of declining profit margin.
External Environment or PEST analysis
- Political Factors: The political factors such as government policies, trade policies, pressure groups, political trends, and shareholders’ demand, rules and regulations or global financial down turn have a huge influence upon the success of Nokia.
- Economic factors: the deteriorating global economic conditions and related financial crisis has a negative impact on its profit margin, for example, in 2007, its annual revenue was €51.1 billions, net income was €8 billions, and comparing the data with the fiscal year 2008, net income has decreased up to 50% within a year.
- Socio-cultural factors: Pursuant to the provisions of the Finnish Companies Act and its Articles of Association, shareholders and Board of directors are controlled the company, who are annually elected by a straightforward majority of the shareholders’ votes. It has more than 125,829 employees those have equal rights and they get payment comparing with similar corporation and post.
- Technological factors: technological development and innovation is the only way to survive as a market leader so it has capability to implement and commercialize new products, services, solutions, different design approaches, and alternative technologies.
SWOT Analysis of Nokia Corporation
Strengths
- Nokia is a renowned brand clutching consumer loyalty and upholding the eminence of the company.
- It possesses inimitable expertise and incessant competitive advantage over competitors, along with economies of scale, remarkable performance in consumer care and successful adaptation of promotional tools that instantly draws the attentions of buyers.
- The company always appreciates recruitment of paramount R&D personnel. In 2008, R&D operating cost were € 5 968 million, which was a 6% rise since that in 2007; and this rise represents the 11.8% augmentation of net sales in 2008, from 11.0% in 2007.
- Nokia is the one of the leading global business with a sturdy financial position and last year, their profits were 34.3% against 33.8% in 2007.
- The merger of Nokia with NAVTEQ, besides of strengthening the technological rudiments, also enhanced the formation of the globe’s foremost assortment of customer internet services.
- The company is efficient in running low cost production.
Weaknesses
- Recently, there has been a decline in Nokia’s adroitness to foresee the improvements of the business correctly and designing its actions consequently.
- Wrong estimation often leads to problems like waste of time or inadequate expenditure in some prevailing market divisions and failing to regulate the expenses properly.
- The resolution of Nokia to outsource a few actions, led to the breakdown of assuring quality and safety of some goods making them undesirable to consumers.
Opportunities
- The business released some controlled shares withholding the idea to employ, preserve, remunerate, and inspire some finest human resources, who would be significant to its future achievements.
- Working fortitudes, pioneering technologies, originality, and commitment of workforce would corroborate the potential triumph of Nokia.
- Dominant administration and the company’s uniqueness would open new dimensions for its further opportunities.
Threats
- The biggest apprehensive threat for Nokia is the concurrent economic crisis because long lasting recessionary period may lead to falling sales;
- It endures intense competition in the international market;
- Workers may lack motivation from the anxiety of being redundant.
- Considerable alterations on exchange rates might also influence the competency; for instance, in 2008, such an alteration assisted Nokia’s rival companies from Korea.
Industry Analysis
The major competitors: Nokia faces competition from different mobile manufacturers at diverse user segments, price points, and geographical markets and the majors competitors are Samsung Electronics, Sony Ericsson, Motorola, AT&T, Bird, Gionee, K- touch, AT&T, LG Electronics, NTT DoCoMo, ST Ericsson, Vodafone, non-branded manufacturers, and other competitors.
The current trends in the industry
- The sales of its products are somewhat affected by seasonality; for example, the first quarter of the year 2008 was the lowest quarter but the fourth quarter was the strongest quarter;
- Sales increase in holidays;
- Slowed growth in developed markets was due to declining investments;
- Annual report 2008 reported that the industry has evolved quickly during the past two decades and now people would like to use mobile for secondary purpose for example, send pictures, listen music, record video, watch TV, play games, check mails etc.
Industry Worth
Press Release (2008) pointed out that the Mobile phone industry worth almost US$ 1 trillion. Among them mobile voice transfer service is valued US$ 600 billion, messaging services gets US$ 130 billion, mobile data and content segment is valued is valued US$ 70 billion, while the hand set segment worth US$ 150 billion and network hardware valued US$ 50 billion. Nokia (2009) reported that that the company worth 39% of the mobile handset market and 33.8% of the both service and device market in 2008.
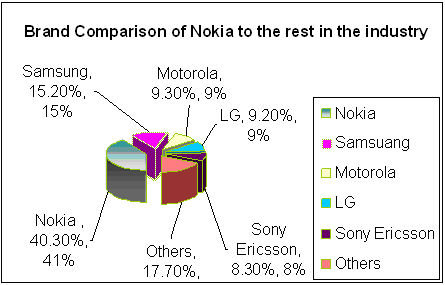
Brand Comparison of Nokia to the rest in the industry
Nokia is a market leader in terms of market share; however, participants in mobile communication and devices manufacture industry compete with each other mainly based on their product, service, solutions, and Brand awareness.
Table 1: – Market Share of Global Mobile Market
Customers: Nokia’s main target customers for its mobile items are upscale and middle- earning households, teenagers with particular importance on female buyers and people who would like to follow latest fashion trend or want to carry luxurious products regardless the price. Nokia always treat the customers as its main assets, therefore, Nokia determine the product price considering consumer’s ability and the design of the products are unique and meet all relevant safety standards.
Strategic Analysis of Nokia
Corporate- level strategy: Nokia generates 95% of its total revenues e from telecommunication segment, which indicates that revenue of Nokia is depends on a particular sector, as a result, it has followed the low-levels to moderate to very high-levels of diversification strategy. It is essential to mention that growth in one of its non-dominant product or service line is able to change the scenario of any Nokia’s diversification.
Cooperative strategy: Nokia Corporation has number of strategic alternative concerning this. As:
- By strategic alliances, it can formulate partnership with firms through a mutual interest of resources and capabilities from designing to distribution channel;
- By a joint venture or merger, it can promote a new venture and obtain potential economies of scale with other by combination of resources, for example, world’s largest network – Nokia Siemens Networks is result of merger;
- Through the acquisition strategy, Nokia can purchase, controlling or 100% interest in other business with an intension of utilizing an effective core competency through converting that firm as its subsidiary;
- Acquire NAVTAQ, which is the world’s leader in serving digital maps as well as public and corporate solution.
Marketing Mix
Kotler & Keller (2006) argued that a market is dividing into distinct groups of buyers with considering different needs, characteristics, or behaviour and in order to assess target market it is significant to consider product mix, price mix, distribution and promotion mix.
Product: Nokia produces mobile devices, and offers customer Internet services, GSM, EDGE, and 3G/WCDMA/HSPA radio access networks and provides digital map information worldwide through NAVTEQ with maps, music, media, messaging and games, and the user interface etc. According to the annual report 2008 of Nokia, it also produces multimedia computers, enterprise applications, Television, imaging, and so on
Price: Pricelists have planned according to the local necessities and choices of various marketplaces. A number of players are adopting further antagonistic pricing policies preferring diminutive turnover than usual, causing strain to Nokia to lower its charges and turnovers; besides, because of the existing recession, the prices might be falling more awfully
Place: It is operating in about 150 countries having 300 000 stores all over the world, and the modes of distribution consist of retail placements, e-commerce sites, earpiece and cell phone appliance producers, other wholesalers, and redistributors. Having one of the biggest supply channels, Nokia has significantly better delivery systems predominantly in Asia, Middle East, and Africa other than the rivals in these areas
Promotion: Advertisement plays an essential part in enlarging the market of a product, amplifying the revenue. Nokia’s takeover of Enpocket and merger with NAVTEQ reinforced a course of sales programmes, such as participation in trade fairs and symposiums, promotions in journals, direct mails, e-mails, websites, and television, as well as sponsoring events
Proposal for a future marketing program
As it has operation in all over the world, distribution channels and strong financial resources and capabilities, it can introduce new products easily. Moreover, though it has many employees to promote its new product but due to global recession, it should not drive to launch new products because it may suffer huge lose, if the new market sectors Nokia target and invest in raise fewer or are less beneficial than predicted. In this context, it should prepare future marketing plan considering present economic environment, foreign exchange risks, competitive position, and cost efficiency. In addition, competitors of relevant products will reduce the price to increase sell in recession, which may adversely affect its business, which will pressure the company to change its strategy or introduce new products for further prospect.
However, in order to solve these problems, Nokia can improve its consumer Internet services business, and communication industry by increasing promotion activities as it fails to be market leader in this sector. However, it can follow Ansoff’s new product development matrix, if Nokia introduce new product in the existing market to develop its business profit, and diversification strategy can apply if it introduce new product in new market.
- Service and software can be developed by Ad business, Intellisync E-mail, music store, maps etc
- In order to adding ultra value, It should provide additional care on software “Ovi”, Nokia 6300 GSM device, 3110 Evolve, 6110 Navigator, 6500 classic, 5310 Xpress Music, 7900 and 7500 prism etc;
- introduction of e-marketing campaigns and reformulation of the pattern of distribution channels take a major role in marketing of the company, so it should continue it.
Recommendation
In order to increase its market share and become more effective in operation, Nokia should concentrate on:
- As a result of the global financial crisis, many customers may replace their handsets with less expensive mobile phones, so it should more concentrate on its audit procedure for external and internal control of the company;
- It should follow the recommendation of board of directors to holds its number one position;
- According to the annual report 2008, it spend sufficient money for advancement of R & D and it should increase the budget for research on changing demand, logistics and outsourcing issues to improve the effectiveness and flexibility of its manufacturing and logistics;
- To overcome the adversely affect the U.S. dollar value fall due to economic down turn, Nokia should continue to transact in the overseas market with a strong and stable currency like Euro;
- It should focus on mass customization, functions and co- branding with other companies;
- Nokia’s cost management is mostly imperative to look after price erosion by analyzing the next generation pricing of the company through the introduction of cost saving devices;
- Its wide expansion of suppliers, efficient and effective execution of logistics required to be more ensuring customer’s safety trust as well as values;
- Formation of products, services, and solutions portfolio based on competitive operations appearing as balanced offerings of design, aesthetic image, and value- recognition;
- It should asses the risk factors, as multinational company it should monitor the market in all countries where it has operation;
- It requires the linking of all the monetary functions for having greater visibility as well as control on financing activities.
Conclusion
This marketing analysis of Nokia has used the tools of strategic analysis to weigh up the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats involved in the business process of Nokia including a situational analysis marketing mix, and a proposal for a future marketing program recognizing the internal and external factors, which are critical and encouraging to attain the objective of the company.
Reference
Kotler, P. & Keller, K. L. (2006) Marketing management. (12th ed.). New Jersey: Pearson Prentice Hall.
Nokia Corporation. Annual Report 2008 of Nokia Corporation. Web.
Nokia (2009), Nokia: Interim Report. Web.
Press Release (2008) Mobile Phone Industry close To Trillion-Dollar Baby. Web.

