Executive Summary
The company selected for analysis is Hong Kong Greenking Food Stuff Co Ltd. This company specializes in frozen food distributed through traditional stores and the Internet Web Site. Both of these retail channels are applied successfully to Hong Kong market needs. Both are effective tools for specifying, coordinating, and integrating activities, situations, and resources that are interwoven in order to reach project aims on time. The main advantage of these distribution channels is that they do not require large-scale computers except for complex situations. The positive economic and political situation in the region suggests fast growth during the next 12 months. Skimming pricing, effective advertising based on cultural messages and emotional appeals help Greenking Food attract repeat customers and deliver high quality services and products to diverse target market. Greenking Food is a B2C company.
Introduction
In Hong Kong, food industry is one of the profitable industries today and in future. Frozen food is a part of food market specialized in frozen meet, vegetables and bakery products. Hong Kong Greenking Food Stuff Co Ltd is a company which follows the structure of successful traditional and Internet-based companies located in Hong Kong (Drejer, 11). The company mission is to deliver high quality services to diverse customers. Its strategy is to develop a unique image and deliver unique food for all customers. The company vision statement is to be a great business that is based on principles of:
- Profitability
- Friendliness
- Creativeness
- Consistency
- Great Value
- Cutting Edge
- Community mindedness
At the beginning of the new century, Greenking Food looks for ways to deliver customer satisfaction at a lower cost, smaller size, and higher speed.
Analysis the Industry Macro and Micro Environment
Following Hooley et al (2004), various kinds and levels of strategies can be carried out in a corporation. “The state of national and supranational economies affects business directly” (p. 97). Strategy development may be concerned with basic corporate objectives and fundamental functions, or with more minor activities. Long-range planning is distinguishable from short-run and intermediate planning. From the standpoint of organizational impact, planning may be classified as functional or departmental, strategic or tactical, and convergent or divergent. In order to link a strategy to operations, the organization needs an accurate analysis and assessment of the environment it operates in. The model analyses the environment into four areas of focus. It should be used flexibly to reflect the nature of the relevant country/market environment. This means that for a large corporate, with a significant spread of operations, it is appropriate to separately map the different environments in which the various parts of the organization operate. The facts are normally identified by the senior management of the business from their personal knowledge and experience. Naturally this assumes that they have sufficient background in the environment to generate accurate data.
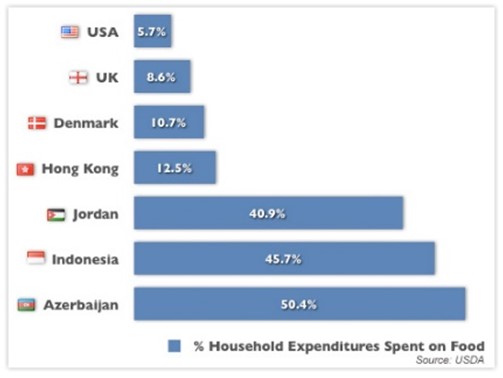
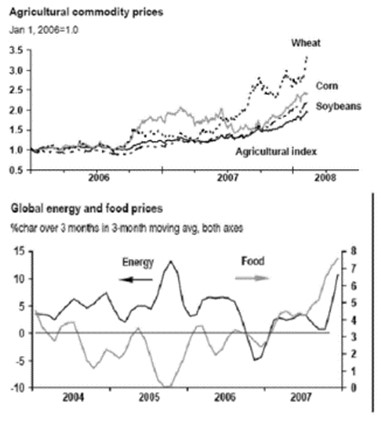
In Hong Kong, political and legal environment is favorable for food industry because of stable political situation and protective legal measures. Hong Kong is a non-sovereign partial democracy (Hooley et al 2004). The region is ruled by Executive Council. In spite of political battles and conflicts, Hong Kong maintains stable political climate favourable for international companies. Greenking Food operates in high dynamic political environment which requires continuous optimization of a product mix and new ways of doing business. Price competition, backed by improved efficiency, is the main feature of Food industry today. Many Hong Kong based companies fight for survival in markets faced global competitor ion. Within rapidly changing environment, this kind of development ensures that long-term survivors are those firms who are more competitive and are better able to satisfy consumer needs and adapt to the new competitive environment. Greenking Food obtains a strong brand image in the food industry proposing high quality products. Nevertheless, the weakness is lack of strategic vision, high labor and economic declines (Drejer 13 Hong Kong Fact Sheet, 2009). “The total value of goods and services trade, including the sizable share of reexports, was equivalent to 404% of GDP in 2007. The territory has become increasingly integrated with mainland China over the past few years through trade, tourism, and financial links” (Hong Kong the World Fact Book 2010).
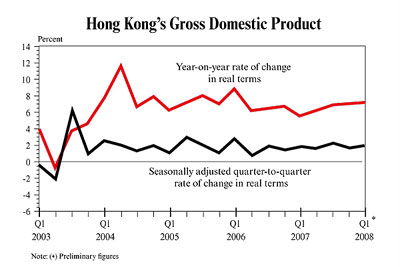
The average annual percent change in the population, resulting from a surplus (or deficit) of births over deaths and the balance of migrants entering and leaving a country. The rate may be positive or negative” (Hong Kong the World Fact Book 2010). In terms of technology and environment, Greenking Food relies chiefly on an efficient market system and product improvement. The region has 4.124 million Internet users (2008).
The original mission had made it clear that it was in the relatively unexploited sector that Greenking Food saw its clearest opportunity for innovation in food industry. As the most important, these basic lines of business allows Greenking Food set out to create a range of high-quality products that are distinctive in quality and technology (Dobson and Starkey 62; Hong Kong Fact Sheet, 2009).
At operational level, strategy is concerned with the establishment and reestablishment of basic objectives for all marketing activities. In perspective, functional plans are inclusive, integrative, and coordinative. This type of planning requires a systems perspective, and much of long-range planning falls into this category. Departmental planning, in contrast, focuses on one particular aspect of marketing activities — one segment of the total marketing plan.
It is designed to integrate and coordinate in sequence several closely related elements, such as the many components of advertising. Narrower in scope than functional plans, it greatly affects them. For instance, the sales forecast, which determines and is determined by the marketing program, affects all planning — production planning, financial planning, and personnel planning. It is the base of future operations. Marketing planning, then, becomes a guide for corporate objectives and for planning in all functional areas (Hooley et al 2004). Strategic plans affect a number of subsequent plans and establish the limits and ranges of optional choices.
Situation during the Next 12 Months
It is expected that during the next 12 months more and more people will be concern about their health and quality of water they use. Industry structure and market position of Greenking Food suggests that threat of entry is low. Food giants like Greenking Food resist strongly, so it makes it difficult for new organizations to enter the Food industry (Grant 24). For frozen food retailer like Greenking Food ability of a firm to use its resources and capabilities to develop a competitive advantage through distinctive competencies does not mean it will be able to sustain it. Two basic characteristics determine the sustainability of a firm’s distinctive competencies: durability and imitability (Hooley et al 2004)
Thus, it ensures that it obtains a leading position and is able to compete with direct and indirect competitors. New economic landscape, Greenking Food has to choose a new strategy aiming to address new market and environmental changes (Dunne and Lusch 54). Taking into account current situation, it is possible to say that Greenking Food has to develop a completely new vision of its marketing system based on global strategies. Specification in Greenking Food is determined as a result of an organization’s policy, which in turn resulted from decisions on its market policy, which in turn resulted from its consideration of the market or customer needs, requirements, and the activities of competitors. This is the process of designing quality into the service. Sales strategy is on a one-to-one basis (Armstrong and Kotler 65; Greenking Food Home Page 2009; Baudrillard 23).
Marketing Strategy
Greenking Food follows a resource-based approach in marketing (Hooley et al 2004). For Greenking Food, food related products are defined broadly to include both products and services. Products are perceived as means of problem solving for both buyers and sellers. It means that “the issue is long-term performance, not simply short-term results” (Hooley et al 2004, p. 11). The discussion relates to both consumer and industrial goods. Product-line management involves the addition of new products to the line, and the deletion or modification of current products. Product diversification (horizontal, vertical, or heterogeneous), may be the result of internal product policies or mergers. Reasons for diversification vary from spreading risks to using by-products and increasing profits. New product policies and strategies may be offensive or defensive, convergent or divergent (Drejer, 44). Greenking Food may adopt a followership or leadership posture, and may choose a strategy of segmentation or product, differentiation. Each of the new phases of the product- process (conceptualization, exploration, development, marketplace preparation, commercialization, and appraisal), is considered. Technology related product development should be seen as one of the core foundations of corporate planning. Its success or failure shapes corporate destiny. Because of this, particular attention is given to a conversation of new products, technology related products and diffusion processes, the product life cycle, and new-product failures. Channel balance, which is difficult to achieve for Greenking Food, must be realized at various levels. The case of Greenking Food market position allows to say that marketing becomes an orientation for the total business, a way of business life. Customers and consumers are perceived as the reason for business existence and their wants and needs become the bases for designing total systems of action. A narrower conception, which is an extension of the business orientation, is concerned with the basic management activities — the entrepreneurial functions-that have to be performed to manage micro-marketing systems (Hooley et al 2004). Through marketing, the critical role of consumption is recognized and cultures become reoriented from Producers’ to consumers’ cultures (Elmer 44). Some critics state that the weakness of the food company like Greenking Food is lack of promotion campaigns aimed to attract new customers, and absence of competitive advantage. High labor and energy costs are the main threat for Greenking Food (Levy and Weitz 62). Economic recessions and industry declines affect Greenking Food and its market performance. The role of Strategic Alliances is made all the more complex and thought provoking because of the competition of ideas between different academic and political standpoints. Greenking Food proves that Strategic Alliances are the best form to reach global dominance and reduce competition. So, it creates new opportunities for Greenking Food on the global scale. Joint venture is another important part of Greenking Food’s international strategy. From the economic side Food industry has to spend its own resources in order to meet the requirements focusing on technological efforts, security. Greenking Food has also realized rapid expansion through capital injections. Greenking Food follows skimming pricing strategy which ensures core of loyal customers who buy products regularly (Goodstein et al 98). They involve the greatest risk, since they bound the decision and planning area and give direction to the total marketing effort. Strategic plans are broad and comprehensive; they are the master plans. Tactical plans are more flexible, and they can be viable. Strategic planning encompasses the search for market opportunities, the development of general guiding directions, the scope of activities, and the goals to be achieved. Tactical planning, on the other hand, is concerned with the detailed application of efforts — the plans for operations to carry out the strategic plan. It is shorter run in nature, is a form of partial planning, and is closely related to programming. It specifies detailed plans for the actual programs themselves. The logical planning sequence, then, is to go from marketing strategies to marketing programs and then implement them through marketing tactics. Both strategic and tactical planning refer to the advance specification of an action program (Aaker 43).
Following Hooley et al (2004), the core strategy involves resource-based view and long-term objectives. Some strategies are of a higher order than others. They control other strategies and may be referred to as constraining or strategic influences. The strategies that are more minor in character may be referred to as tactical plans, since they do not directly affect the framework within which other plans are formulated and decisions are made. Also, it is possible to use competitor profiling which provides for a direct ranking of the relative performance of the organization versus that of its competitors. It should be used to take a broad view of the relative competence of the firm and the analysis must deliberately be driven from a customer perspective. It is therefore important to take into account both facts and perceptions (Aaker 43).
Current Market Diagnosis and Problem Analysis Greenking Food
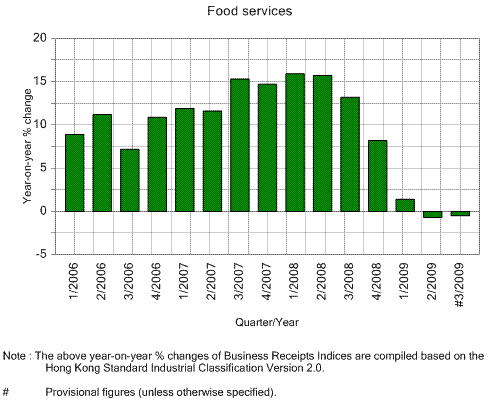
Following Hooley et al (2004), increased competition on the international arena threatens profitability of such giants as Greenking Food. The main problem was that imported Food accounted for 20 percent of the food consumption which limited price level and competition in the home market (Hong Kong Fact Sheet 2009). In this case, Greenking Food develops multidimensional strategy to cover three competitive segments: local (national), international and global. This strategy involves brand positioning, market segmentation, strategic alliances and value pricing strategy. New competitors may find it difficult to gain access to delivering service, which will make it difficult to provide their service to customers or obtain the inputs required or find markets for their outputs. On the other hand, these ‘mega-Food markers’ represent the main threat for Greenking Food in Hong Kong (Thompson and Martin 65). Employees, who have perhaps worked within the traditional system for a number of years, must now learn a new methodology using technology with which they may not be too familiar (Hong Kong Fact Sheet 2009). Resistance to change often occurs within businesses that are seeking to introduce an Internet component. If it successfully navigates this balance, it will find that it can not only maintain its current position but also expand into new territories and possibilities for profitability/growth (Armstrong and Kotler 24; Hillis 65).
Customer Wants and Needs
Hooley et al (2004) underline that a competitive position depends on market structure and segmentation. “Domestically a company must weight the power of various pressure groups determining market vulnerability” (p. 49). The mission of Greenking Food is to reach wider target audience. Vision is that food quality is used as a strategic weapon and the aim of Greenking Food is to maintain high quality standards at costs lower than competitors. Marketing strategies are the broad approaches Greenking Food intends to adopt in the longer term to achieve its marketing objectives in accordance with its marketing policies. Strategies are developed for the following: The market segments in which Greenking Food will concentrate and the marketing position it proposes to adopt in each segment (i.e., the extent to which it positions itself close to a competitor but establishes differentiation through product features and price distinction, or the extent to which it attacks markers established by gap evaluation) (Drejer 43; Thompson and Martin 51).
Following Mckinsey 7-S model, strong corporate culture is one of the main strengths which help the company to compete. The culture and structure of Greenking Food develop over time and in response to a complex set of factors. Usually large organizations like Greenking Food have more formalized structures and cultures. Increased size is likely to result in separate departments and possibly split site operations. Another important feature of Greenking Food is the non-price competition which takes form of branding, advertising, promotion, and additional services to customers and product innovation (Poster 77). Speaking about the nature of competition it is possible to say that Greenking Food has a competition advantage. Greenking Food uses e-commerce for selling purposes only. Greenking Food creates web-sites in order to popularize their brand and attract potential consumers. A good example of the use of the Internet in this way is to keep rapidly changing catalogues on-line. This enables, for the first time, the opportunity to bring grocery shopping out of the grocery store, supermarket and superstore. By uploading the daily catalogue of goods and prices that are available, stores can now enable consumers to buy their goods without having to go round the store to collect them. In an environment in which time is precious the advantage to the consumer is undeniable. Not only that, but the concept can reduce costs too. For instance, Pea Pod that stores the goods which a customer wants can sort and pack these goods considerably more efficiently than the store and can be located out of town in an industrial park or other area where cheap rents are available. Moreover, staffing requirements are lower, the incidence of in-store theft is reduced, and the hours of operation can be extended. For small business companies like Greenking Food, the opportunities of Internet-based commerce seem considerable, but few companies have yet succeeded in exploiting them profitably. Such success is dependent on acquiring an in-depth understanding of the characteristics of the Internet and matching these with the characteristics of existing products or services. In contrast to Greenking Food proposes better catalogues and more vivid visual representation of its products. It is easy to find a product and its price. Pea Pod has poor design and simpler structure; it is difficult to navigate and use this site.
Price competition involves businesses trying to undercut each other’s prices; this will be dependent upon their capability to reduce their costs of production. Brand equity represents the added value that accrues to a product as a result of Greenking Food prior investments in the marketing. Brand equity is thought of as an asset representing the value created by the relationship between the brand and customers over time (Mintzberg et al 54; Walsh 82).
Evaluation of Strategic Options during the Next 12 Months
Vision of cultural and social values has a direct impact on Greenking Food and its market performance. Hooley et al (2004) state that “cost leaders typically need market share to achieve the economies of scale and access raw materials” (p. 50). This factor could be interpreted as strength but globalization process and changing international relations show that cultural and social values become opportunities rather strategies for global food industry. A solid understanding of cultural preferences is important for any company that markets such products internationally. Greenking Food leverages superior cultural understanding to compete effectively with large foreign firms. It is possible to say that it has an advantage drawing from tradition (Bartnatt 72).
In order to control performance, Greenking Food applies financial measures and statistical control tools. In the long run, however, it may be possible for Greenking Food, through its choice of strategy, to change the strength of one or more of the forces to the company’s advantage. Taking into considerations the statistical data of Greenking Food it is possible to say that it is profitable because the value exceeds the cost of performing various factions which include: financial management, technology management, organization and human resource management, supply and bound logistics, operations, outbound logistics, sales and marketing (Buckley and Ghauri 65)
Conclusion
Greenking Food obtains strong market position introducing new ways of doing business. Communication, employed by Greenking Food, is affected by internal and external environment, by the nature of the task, and by technology. Difficulties in communication can arise with production systems where workers are stationed continuously at a particular point with limited freedom of movement. Greenking Food tries to penetrate deeper into current market. International expansion and global strategy is to aim at a particular target market. One of the main functions of global and international promotional activity is of course to influence the perceptions of the consumer. Greenking Food maintain policy of product standardization in order to sell them around the world under the same brand. In order to change and improve current situation, Greenking Food should attract more customers and introduce new product lines including related technologies and markets. This strategy will help Greenking Food to survive and remain competitive in spite of market changes and economic crisis. Since buyers are often other-directed, they are concerned with what other group members think of them and their taste. Taste is not an acquired or inherited phenomenon. Consequently, opportunity exists for designers, food companies, and marketers to upgrade tastes. For Greenking Food cooking implies repetition over time. What may be rejected in product design or color today may be viewed approvingly after a second, third, or fourth exposure.
Works Cited
Aaker, D. Managing Brand Equity, New York: Free Press, 2003,
Armstrong, G., Kotler, Ph. Principles of Marketing. Prentice Hall; 11th edition, 2005.
Bartnatt, C. Cyberbusiness: Mindsets for a Wired Age. Chichester: Wiley, 2002.
Baudrillard, J. The Vital Illusion. New York: Columbia University Press, 2000.
Buckley, P.J. Ghauri, P.N. The global Challenge for Multinational Enterprise. Pergamon, 1999.
Dobson, P., Starkey, K. The Strategic Management: Issues and Cases. Blackwell Publishing, 2004.
Drejer, A. Strategic Management and Core Competencies: Theory and Application. Quorum Books, 2002.
Dunne, P. M., Lusch, R. F. Retailing. South-Western College Pub, 2007.
Elmer, G. (ed.) Critical Perspectives on the Internet. Boulder, CO: Rowman & Littlefield, 2002.
Gardiner, P. Project Management: A Strategic Planning Approach. Palgrave Macmillan, 2005.
Grant, R. M. Contemporary Strategy Analysis, (3rd edn.). Oxford: Blackwell, 1998.
Goodstein, L., Nolan, T., Pfeiffer, W. J. Applied Strategic Planning: How to Develop a Plan That Really Works. McGraw-Hill; 6 editio, 2001.
Hooley, G. J,. Saunders, J.A. & Piercy N. F. Marketing Strategy and Competitive Positioning, Prentice Hall International, 2004.
Hillis, K. Digital Sensations: Space, Identity, and Embodiment in Virtual Reality, Vol. 1. Minneapolis, London: University of Minnesota Press, 2001.
Hong Kong Greenking Food Stuff Co Ltd. 2009.
Hong Kong Fact Sheet. 2009.
Hong Kong the World Fact Book. 2010. Web.
Levy, M., Weitz, B. A. Retailing Management. McGraw-Hill/Irwin, 2008.
Mintzberg, H., Lampel, J. B., Quinn, J. B., Ghoshal, S. Strategy Process. Pearson Education, 2004.
Poster, M. What’s the Matter with the Internet. Minneapolis: Minnesota University Press, 2001.
Thompson, J. L., Martin, F. Strategic Management: Awareness, Analysis and Change. Thomson Learning, 2005.
Walsh, B. Clear Blogging: How People Blogging Are Changing the World and How You Can Join Them. Apress; 1 edition, 2007.
