Introduction
The purpose of this report is to analyze the dividend policy of General Dynamics Corp. and other related factors. The report will cover what has happened to the company’s dividend payout, dividend yield, and dividend per share in the last three years and provide explanations for the same. The report will also provide an estimate of the company’s dividend for the following year. It will also make comparison between the company and its peers, note any similarities, observable trends and finally present a company that eliminated or reduced its dividend and related impacts on its stock price.
General Dynamics Corporation was established in Delaware in 1952 (General Dynamics Corporation 1). Between the period of incorporation and 1990s, General Dynamics offered “rockets, tanks, missiles, warships, submarines, fighters, and electronics for military services” (General Dynamics Corporation 1). The company is now a leading player in the global aerospace and defense. Today, it has a wide portfolio of products and services, such as C4ISR, combat vehicles, business aviation, weapons systems and munitions, IT solutions, and shipbuilding.
Several thousands of employees can be found spread across 43 countries in which General Dynamics runs its operations. The company appreciates contributions made by its employees, who are considered the key asset. It has created four business divisions for product and service delivery to maximize revenue generation. It is based on a balanced business model, which offers every division the flexibility and agility required to deliver to customers.
As mentioned above, this report focuses on dividend. Dividend, from a simple perspective, refers to the distribution of a fraction of a firm’s earnings, as decided by board of directors, to its shareholders. Firms usually pay dividends to shareholders because such actions attract positive views from both shareholders and the company. On the other hand, companies that do not pay dividends are poorly rated among investors and, therefore, they experience poor prices in stock markets noted in low share prices (Masum 9). Hence, a dividend policy in a firm is extremely important for shareholders. Proponents of dividends believe that firms that pay dividends significantly eliminate uncertainties in shareholders. That is, a firm’s earnings have low discount rates, thereby leading to increased market value. Failure to pay dividends, conversely, leads to increased uncertainty and low market value of a firm.
Analysis of what has occurred with company’s dividend payout, dividend yield, and dividend per share over the past three years and any explanations for what these events
Dividend Payout
Dividend payout ratio is used to assess the percentage of the firm’s earnings paid out as dividends to shareholders.
Dividend Yield
The increasing percentage of dividend yield noted in the company’s performance shows pay out in dividend every fiscal year based on the share price. As such, any income investor can use this simple approach to gauge the relative attractiveness of General Dynamics. From these figures, an investor will understand yield to expect from General Dynamics after purchasing the company stock.
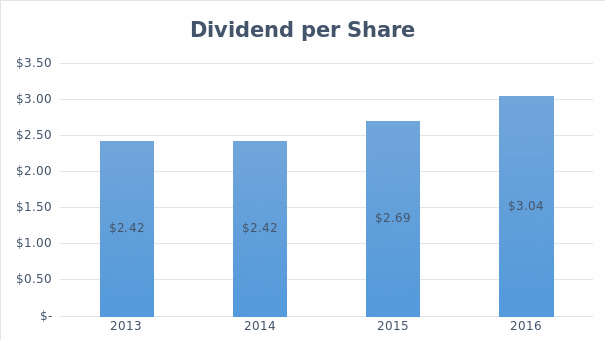
Dividend per Share.
Note: all data for General Dynamics were obtained from StreetInsider.
For the last three fiscal years, General Dynamics has consistently declared dividends on quarterly basis. For instance, in the year 2013, the company declared quarterly dividends of $ 0.56 for all the quarters and later increased to $ 0.62, $ 0.62, and $ 0.62 for every share held for quarter one to four respectively for year 2014, which annualized to $ 2.42 dividend per share.
The company has consistently declared dividends every quarter, which have increased from $ 0.56 to the current $ 0.76. As a result, the annualized dividend per share for the last three years has risen from $ 2.42 to $ 2.69 and now stands at $ 3.04.
General Dynamics’ dividend yield has also risen steadily from 2.175% in the fiscal year 2014, albeit with a marginal decline in the fiscal year 2015 to 1.96 percent. The dividend yield then rose to 2.2 percent in the fiscal year 2016.
How General Dynamics’ dividend payout, dividend yield, and dividend per share compared to other companies in its industry
Some major competitors of General Dynamics in the industry include Lockheed Martin Corp., First Aviation Services Inc., Raytheon Co., Northrop Grumman Corp., Rockwell Collins Inc., and L-3 Communication Holding Inc. among others. For comparison purposes, only two firms are preferred.
Lockheed Martin Corp.
Dividend Payout.
Dividend Yield.
Dividend per Share.
Note all data from StreetInsider.
Northrop Grumman Corp.
Dividend Payout.
Dividend Yield.
Dividend per Share.
Note: all data from StreetInsider.
Any similarity of the company’s dividend strategy to other companies in its industry
Lockheed Martin Corp is among the best performing companies in the industry. It generally has higher dividend per share relative to General Dynamics and Northrop Grumman Corp.
In addition, Lockheed Martin Corp. also has high dividend yield compared to other two companies. General Dynamics and Northrop Grumman Corp. have almost similar rates in terms of dividend payout, dividend yield, and dividend per share.
Overall, companies in this industry have a policy of paying their shareholders dividends every quarter. The figures are then annualized for effective comparison.
The company’s earnings (USD Mil).
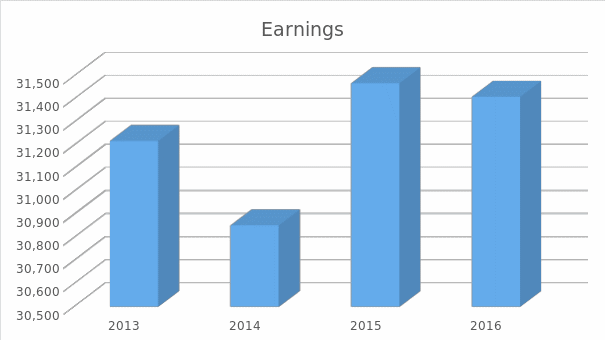
Between the fiscal year 2013 and 2016, General Dynamics has consistently increased its dividend per share from $ 2.42 to $ 3.04. At the same time, the company has also noted a growth in earnings from $ 31,218 to $ 31,469 until the year 2015.
Despite fluctuating earnings noted in the fiscal year 2014, General Dynamics maintained dividend per share at $ 2.42 (same amount as the previous fiscal period). While the dividend per share has grown on annual basis, one must understand that the company leverages earnings every quarter to achieve or increase payout. Hence, it is imperative to note percentage variations in dividend amount every quarter.
According to Annortt and Asness, historical evidence has shown that the possible future earnings increments are quickest when the prevailing payout ratios are high, but sluggish when the payout ratios have declined (70). This association does not account for other influencing factors, such as changes in earnings (Arnott and Asness 70).
It is observed that the relationship between earnings and dividends remains unresolved and complex (Farsio, Geary and Moser 1-5). Different studies have presented various outcomes, including using dividends to predict potential earnings. However, Farsio, Geary, and Moser have argued that some studies presented a causal relationship that could not be consistent if all other factors were considered (1-5). From a practical perspective, there is a notable increment in dividends followed by an increment in earnings. Conversely, an increase in dividends may lead to reduced earnings during some financial periods. Consequently, it is concluded that “no significant relationship between dividends and earnings is expected in the long run” (Farsio, Geary and Moser 1). It is possible for researchers to use data from short periods to present empirical evidence that suggests a causal association between dividends and earnings, which could be misleading for investors.
An estimate for the company’s dividend per share next year and justification for the decision made
General Dynamics’ expected dividend per share is most likely to be $ 3.04. From the available data on quarter amounts for the last three quarters, the dividend per share approximates $ 3.
It is observed that between the year 2013 and 2015, the percentage dividend per share increased by about 17 percent. When this percentage is considered, the possible dividend per share for the fiscal year 2016 is most likely to be approximately $ 2.9. As such, the lowest dividend per share is expected to be $ 2.9 while the highest figure is expected at $ 3.04.
A company that has reduced or eliminated its common stock cash dividend over the past year, why the company reduced or eliminated its dividend, and effects on the company’s stock price over the year
While Chesapeake Energy (NYSE: CHK) is not in the same industry as General Dynamics, the company is a perfect example of a company that recently eliminated its common stock cash dividend from the fiscal year 2015 third quarter.
Chesapeake Energy was interested in protecting its capital expenditure by eliminating the common stock cash dividend (Gara 1). The company currently operates in a difficult market characterized by low commodity prices that is noted in the oil and gas and natural gas liquid industry. As such, the company will note a significant reduction in capital expenditure available for investment to support the company.
It is imperative to note that the board of directors makes such significant decision to abandon common stock dividend of $ 0.35 per share every year. The company executives believed that eliminating the common stock cash was prudent to ensure that more cash was available for vital assets rather than paying investors. Chesapeake Energy observed that it could save nearly $ 240 million every financial year. The elimination of the common stock cash dividend was considered as a part of the wider disciplined strategy to reduce the firm’s financial complexity while increasing its liquidity position. As such, Chesapeake Energy was able to attain a stronger liquidity position with over $ 2 billion of free cash reflected in the balance sheet and another undrawn $ 4 billion of revolving credit facility.
The company therefore considered the elimination of the common stock cash dividend as one of the several opportunities to revamp its cash flow generation capabilities and create additional value through investment in assets.
It was observed that the company’s stock price had been rising since 2014 (Bandz 1). However, a major decline of 84% was noted in the past five years as noted in the drop of natural gas prices too. This downward trend changed once the company declared some vital changes in its approach to capital management. For instance, it was noted that immediately after the company announced a new financial strategy involving the elimination of common stock cash dividend and other measures, the stock price increased by 0.78 percent to $ 10.35 in pre-marketing trading (Schiavo 1).
In addition, it was observed that Chesapeake Energy stock price was rallying, and it was generally associated with the announcement to sale some assets in 4Q15 (Schiavo 1). The company declared asset sales that could reach $ 700 million. It was implied that the change in the company was associated with investors’ change of opinion on the possibility of Chesapeake Energy filing for bankruptcy (Schiavo 1).
Meanwhile observers have noted that multiple factors, specifically weaknesses, influence the company’s position. These weaknesses will outweigh any gains or strengths noted, and they could hinder possibilities of positive returns to investors relative to other stocks. A declining net earnings, poor return on equity, feeble operating cash flow, historical poor stock results, and weak performance in earnings per share are some of the major weaknesses that can undermine any gains made by the company.
Conclusion
The purpose of this report was to analyze the dividend policy of General Dynamics Corp. and other related factors. The report has demonstrated that the company’s dividend policy supports dividend payment to shareholders. General Dynamics has increased its dividend per share from $ 2.42 in 2013 to nearly $ 3.04 in the current fiscal year (2016). This trend has also been noted among the industry peers, such as Lockheed Martin Corp. and Northrop Grumman Corp. A complex relationship is still observed between earnings and dividends, but the company has been consistent with the increment in dividend per share. Hence, it is estimated that the company will increase its dividend per share in the next fiscal year.
Meanwhile, updated financial strategies, such as elimination of common stock cash dividend, could lead to rallied stock price as Chesapeake Energy demonstrates.
Works Cited
Arnott, Robert D., and Clifford S. Asness. “Surprise! Higher Dividends = Higher Earnings Growth.” Financial Analysts Journal (2003): 70-87. Print.
Bandz, Keisha. “Why Chesapeake Energy’s Stock Has Rallied since 4Q15 Earnings.” Market Realist. 2016. Web.
Farsio, Farzad, Amanda Geary, and Justin Moser. “The Relationship between Dividends and Earnings.” Journal for Economic Educators 4.4 (2004): 1-5. Print.
Gara, Antoine. “This Time Is Different: Chesapeake Energy Scraps Dividend Amid Oil And Gas Plunge.” Forbes. 2015. Web.
General Dynamics Corporation. About General Dynamics. 2016. Web.
Masum, Abdullah Al. “Dividend Policy and Its Impact on Stock Price – A Study on Commercial Banks Listed in Dhaka Stock Exchange.” Global Disclosure of Economics and Business 3.1 (2014): 9-19. Print.
Schiavo, Amanda. “Chesapeake Energy (CHK) Stock Up on Financial Strategy Announcement.” The Street. 2015. Web.
