Abstract
Nurturing new ideas opens the way to innovate new ways for entrepreneurship. It has been assumed that to start a new business needs to develop ideas at first. There is no doubt that the most complicated thing to run a new business is to plan and implement its marketing programs. A company should concentrate on the basic concepts of marketing to be successful. In this paper, the key concentration has been adapted to develop and introduce a new business. To start a new business means to enter into a new industry and to nurture the newer marketing communication techniques. All these are depended on the analysis of the company and its environments. For this in this report at first, the external environment of a company would be analysed. This would continue from the industry analysis, competitor analysis, macro-environmental analysis, and analysis of the behaviour of the potential customer. After all this analysis has been completed, the scope of further research has been assessed
Introduction
This report would discuss the appropriate way to a new business in energy gymnasium industry as an extended business of the firm named “Amazing Ideas”. The selected country is Australia and thus the Australian energy gymnasium industry is the industry for the selected company. The entities who are providing gym facilities are the key competitors of the proposed Energy gymnasium.. For the proposed company this paper has presented the appropriate market segmentation, company analysis and finally drawn the recommendations with the selected positioning strategy.
Industry definition
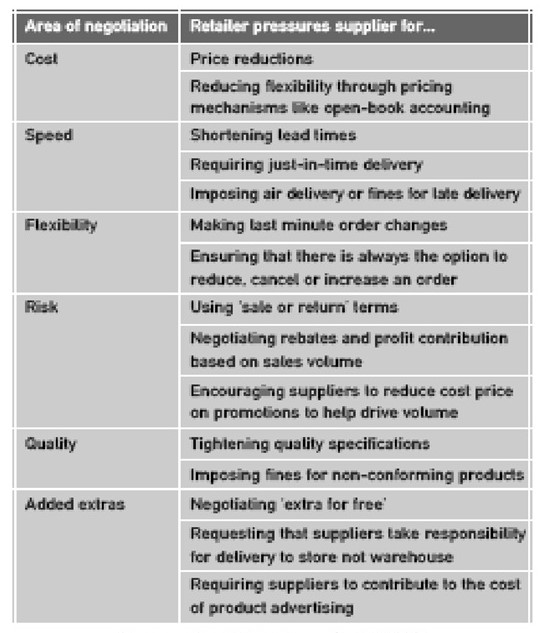
This segment of the paper would define the industry as a whole and conclude with an action plan with a tree diagram. The scope of the industry definition is to analyse the opportunities of a new gymnasium in the Australian market. It is about a health care or health betterment sensible practice to assess whether it is possible or not. This paper will assess the feasibility of the business and design a marketing-related activity schedule. Giving the industry definition for the energy gym can be assisted by the analysis of the industry-first (Fairfax Digital 2003, p.1). To analyse the industry, it has used Michael Porter’s five forces model analysis. These are:
- Entry barrier: There is almost no entry barrier in the industry. Many new gyms are opening in this market recently, which are from overseas. The local gyms are spreading their businesses from city to city.
- Bargaining power of the customer: The industry has a customer base of almost 1.6 million. It is assumed that the industry’s membership will be increased by 7% in this decade. Nevertheless, the customers have less bargaining power. The main cause is the nature of service, which gyms are offering. In most cases, people go to the gyms to caring for their health. SO, they became always ready to pay what they have asked for. Besides, the power harnessing technology ensures less customer control over the gym.
- Barraging power of the suppliers: The suppliers are dealing with some sophisticated products. That is why they have more bargaining power over the companies.
- The Threat of Substitution: There is almost no substitute for the gym. Here the power has been harnessed by the use of the equipment by the customers, which is a completely new idea, and no one in the country is using this. The gymnasium equipment is available to buy. However, the equipment is so expensive that for one person buying all the equipment is impossible. Rather, in the gym all types of equipment are available. Thus, gyms have almost no substitution.
- Competitive rivalry: Rivalry among the competitors is moderate and, in some cases, low. This is playing as the main cause of eased entry barrier.
Thus, the industry could define under the major industry of healthcare. Here the Tree diagram is showing the industry definition.
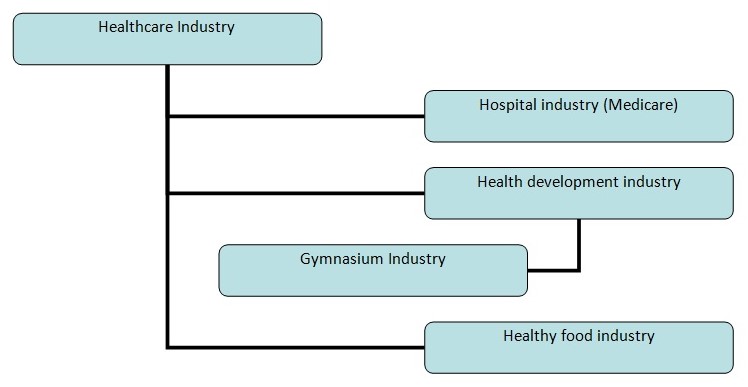
Competitor Overview
Anon (2008, p. 1) argued that the key competitors are gyms that have extraordinary customer awareness. Local Fitness Pty Ltd (2009, p. 1) reported that in an industry like gymnasium, it is difficult to enlarge anyone’s competitive advantage as every competitor has almost the same strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Here is a brief discussion of some key competitors along with their competitive advantages.
Come Alive Gymnasium
It is a gymnasium sited in New South Wales, established in 1984. It has the foremost concentration on securing the health conditions of the community and the members (Local Fitness Pty Ltd 2009, p.1). It ensures a friendly atmosphere to do gym works and for its care towards the people, it is more familiar as “people’s gym“. It has a wide range of fitness programs, which are offering maximum consistency and quality. Its core fitness programs include:
- Club training introduction
- 1 on 1 results training
- Gym support
- Les mills fitness classes
It is also providing some special programs that comprise Body-for-life challenge, Hatha Yoga, nutrition evening and many more.
The key weakness of the gym is its opening hours that differ day to day. For this reason, people may not find it effective to work out with come alive as they are often busy and want flexible time.
Muscle & Body Shape Gym Prahran
This gym is serving its members since 1998 with a wide range of fitness programs, located in the centre of the most famous cafe and shopping centre Prahran. Its services include:
- Personal training
- Casual gym use
- Fitness classes in group
- Skin and hair clinic
- Massage
- Other supplements.
The major weakness of the firm might be the entitled brand awareness with the café and the shopping centre. It should have its own brand elements to attract potential customers.
Body World Balaclava Gym
The vital strength of this gym is that it operates by industry experts, who have expertise in professional and personal gym works. It designs its fitness programs according to the customer base and before starting; the programs are equipped with the actual goals of the member. It has a variety of offerings and its bigger infrastructure than the others allow them to afforde many fitness classes.
Macro Environmental Analysis
According to the marketing management, every organisation has a macro or remote environment in their operations, which are also imperative for “Energy Gymnasium”. These are the PESTE factors, and are described as follow:
Political Factors
Kotler, Saunders & Armstrong (2006, p. 77) said that when the governmental policies, like tax policies, laws and regulations, and trade barriers are affecting “Energy Gymnasium” to continue its business in Australia these would be the political factors, specifically:
- Fiscal Imbalances in Australia: Any company in Australia may face the problem of fiscal imbalances in managing equity and efficiency without any political bias. There are specific purposes, like maximising electoral support with the willingness of political efforts in public finance and public choices (Dollery, Brian & Worthington 1996, p.83).
- Trade Agreements: The political leaders of Australia are making decisions on trade agreements to deal with Australia and the US market. Therefore, if the business needs any connection with the US market, then it is difficult without the help of political leaders.
Economic Factors
The factors that bring changes in economic growth, interest rates, exchange rates and inflation rates, are the economic factors (IPIN. 2008, p. 1). The Australian economic factors have focussed in below:
- Rise in Interest Rates: According to the Reserve Bank of Australia, the interest rates of dollars are raising at stock markets, which is affecting the business.
- Growth of Capital: In Australia, the investment opportunities are high with excellent offerings, and these are beneficial for Energy Gymnasium,
- Ease of Currency Exchange: The exchange rates of Euros, dollars are very easy in Australia for foreign investors, which have increased the ability of a business in the foreign purchase of equipment, for example.
Social Factors
The cultural aspects, like health consciousness, population growth rate, age distribution, and buying patterns are the social factors of Australia in the context of this business, with some issues like:
- Poor Health Conditions of People: According to the previous report, most Australian children are suffering from chronic conditions, which must be a focal area of the Gymnasium business.
- Living Costs: The living costs of the largest cities of Australia, like Melbourne, Adelaide, and Perth are surprisingly less than other largest cities in the world, but the quality of living standards is almost the same.
Technological Factors
Technological factors relate to the innovations, ideas of R&D activities, automation, technology incentives, and technological changes in the market. For example, internet adoption has increased in Australia day by day for the ongoing survival approach. Therefore, Energy Gymnasium should also adopt this facility with service info, etc. in detail form online.
Ecological Factors
In Australia, it is an important social responsibility to collect wild seeds and cultivate edible legumes, with maintaining a continuous relationship with Asia. As a social responsibility, Energy Gymnasium should also maintain an ecological system in Australia by saving seeds, wildlife, and species.
According to Marketing Mix of 4P’s, macro-environmental factors can be classified for Energy Gymnasium, which are:
- Product: a gymnasium business needs high quality products, so trading is important considering political and economical factors in PESTE analysis.
- Price: Customers in Australia are living with low costs, so they obviously want the service costs of Energy Gymnasium at possible low costs.
- Place: Considering social and economic factors, the business should launch in big cities in Australia
- Promotion: For attracting customers, appropriate promotional tools should use for the business.
Consumer Behaviour Analysis
SDSU (2009, p. 1) stated that the behaviour and analytical tradition of interpreting complex behaviour within a conceptual network are known as Consumer Behaviour Analysis. In this model, the intersection of consumer behaviour and an individual’s history of learning has created consumer behaviour in a market. So, some specific marketing strategies should adopt for modifying consumer behaviour to the organisation’s product/ service. Consumer Behaviour can be analysed with the help of Decision-Making Process by the customers. There are mainly five Steps in DMP, which are:
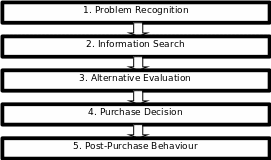
For Energy Gymnasium, the decision-making process would be the same, in the context of a service organisation, such as:
- Problem Recognition: When the target customers perceived the need for gymnasium services in their life, then the problem of lack of a gym would find out. The perceptions of customers are different from a person’s ideal and actual situation, which has to remove by the organisation by triggering a decision. High promotional activities can create the need of gym of target customers’ life.
- Information Search: Customers are seeking quality or value of services by recalling or scanning memory from their experience related to products or services. Energy Gym is new in the market, so the customers would not evaluate the experience. However, the customers may feel high risks in making decisions to have the services of organisation if the information is not properly available in the market.
- Alternative Evaluation: When customers are getting alternative services in the market, which might meet the value perception of customers then alternative decisions occur. In this sector, customers are evaluating brands, prices, past experiences, etc. There are many Gym services in the market, so the organisation should be aware of losing this section.
- Purchase Decision: When the target market is getting services, which would depend on location, pricing, and other factors of services.
- Post Purchase Behaviour: As, this is a service organisation, so post-purchase behaviour would depend on the satisfaction of services to repeat purchase behaviour. The value and quality of services of the organisation can drive this section.
Further Marketing Research Requirements
In this part, the organisation has to make some strategic decisions for making further improvements to the study. For this reason, Porter’s generic forces model would be best to describe different strategies and implementation towards potential customers (Kotler & Keller 2006, p.211). There are three forces in this model, which are:
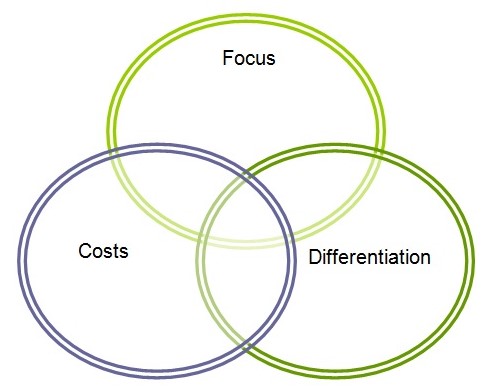
- Focus: By Energy Gymnasium, target customers and quality of services should focus area of the business to survive in a competitive market.
- Differentiation: This organisation should be different in terms of services provided to customers, the location, the decoration, different equipment and other facilities, which make it different from competitors.
- Costs: As customers always want to minimise the costs of having services, so this organisation should also consider this factor to keep their customers.
Justification for Choice of Segmentation Base
According to segmentation base, customers and other segmentation can be classified into many sections for this organisation, which are discussed below: (Kotler & Keller, 2006)
- Region/Country: Australia
- City/ Metro: Melbourne, Perth, Adelaide etc.
- Density of Population: Urban Area
- Climate: Tropical
- Age of Customers: Over 18 years- 40 years
- Family Size: 3-4+
- Family Life Cycle: Young, Single; Young, Married
- Gender: Male, Female
- Income: Over $10,000
- Occupation: Any kinds
- Education: Graduate, College going Students
- Religion: Any
- Race: Any
- Generation: Young
- Social Class: Working class, middle class, upper-middle class
- Psychographic Lifecycle: Sports/ Outdoor Oriented
- Personality: Compulsive, Ambitious
- Benefits: Quality, services, economy, facility
- User Status: Non- Users, Ex- users, potential users
- User Rate: Medium/ High users
- Loyalty status: strong, medium
- Attitude towards Services: Positive
Profile of Segments
For the justification of segmentation, these segments have to frame under the profile basis of customers to understand more clearly about the market segment, which shows in the following table:
Table: Profile of Customers according to Market Segments:
Target market choice and justification
From the above discussion about the segmentation of the market, it is clear that the suitable and more attractive market segments are age base market segmentation (Kotler et al. 2006, p. 79). The proposed energy gym must target people of an age limit from 18 to 40. The reason behind choosing this segment will be judged according to the three factors of segment attractiveness.
- Potential competitors: most of the potential competitors have no concentration on the age differentiated fitness program. For this, targeting a segment based on the age limit can be an attractive market segment. Potential competitors have no specialty for an age group so having specialty over an age group will ensure the consumer thinking that this gymnasium is designed only for them who has specialized expertise.
- The relative power of the customers: The energy gym users are not priced sensitive and they will go with the gym though the service charge is higher so they have less control over price. Besides, people of the segmented age limits have the ways and possibilities to earn more money. Therefore, they have extra money to spend on gym works.
- The relative power of the suppliers: he suppliers of the gym equipment have less power over the gyms and the gym has control over the suppliers because the price of the equipment is the same for every supplier and thus to buy equipment from a supplier has no extra benefit than to buy from other.
Assessing the above three criteria, the attractiveness of the segment is justified and it becomes clear that segmenting based on the age limit is not only attractive but also effective for the energy gym.
Proposed positioning strategy
To assess the proposed positioning strategy, perceptual mapping is a widely used tool in strategic marketing management (Anon 2009, p.1-7). Here the energy gym industry has many dimensions based on which the perceptual mapping of the consumers can be drawn.
Here two dimensions have been taken to draw a perceptual map. These two dimensions are the equipment availability and the quality of training.
Another map can be drawn taking another two-dimension- Brand awareness and price.
Conclusion
Consumers are the key strength for a company. Just to acquire consumer’s satisfaction should be the major concentration for the company. In the gymnasium industry, the industry boom has expected to be occurring. Therefore, a new gym must take the proper segmentation and proper positioning strategies effectively.
References
Anon. 2008. Come Alive Gymnasium. [Online]. Web.
Anon. 2009. Perceptual Mapping. [pdf]. Web.
Dollery, B & Worthington, A. 1996. A note on political factors in federal fiscal arrangements in Australia. Economic Papers 15(4):pp. 81-87., [Online]. 2009. Web.
Fairfax Digital. 2003. “A pointless exercise”. The Sydney Morning Herald. [Online]. 2009. Web.
IPIN. 2008. Economic Factors in Australia. [Online]. Web.
Kotler, P. & Keller, K. L., 2006. Marketing management. 12th ed. New Jersey: Pearson Prentice Hall.
Kotler, P., Wong, V., Saunders, J. & Armstrong, B. 2006. Principles of Marketing. 11th Ed. New Delhi: Prentice-Hall of India Private Limited.
Local Fitness Pty Ltd. 2009. Body World Balaclava Gym. [online] Web.
Local Fitness Pty Ltd. 2009. Muscle & Body Shape Gym Prahran. [online] Web.
SDSU. 2009. Consumer behaviour. [Online]. Web.
