The automotive industry is not perceived with extremes of higher competitiveness, although it is an essential component in formulating a stable economy. Tesla, General Motors (GM), and Ford are among the best fortune 500 ranked automobile companies globally. The companies’ successes lie in their set strategic business plans, creation, and implementation of effective marketing plans and organizational structures. This paper will focus on organizational assessment.
After an assessment on structural organization, the has handled the planning and budgeting concerns arising from the three companies. The report has provided comparison in the company financial ratios and an industry comparison of the ratios, main products of each company for comparison, financial strategy and or overall strategy of the companies (SWOT), prospects in the automotive industry, and current stock prices and plotting of the stock price for Tesla, GM, and Ford.
A brief history about Automotive Industry
Todays’ world markets have continued to experience stiff competitive natures of environment. Survival is now entirely based on effective strategy in management and supply chain in the products produced. The competition has further grown roots in the automotive industry at a fastened rate. Fuel-driven, diesel and solar-powered companies have evolved to create a competitive nature in varied nature and improved features of their products. For instance, Tesla, General Motors Company, and Ford are among the most eye-catching companies in the fortune 500 companies that tend to bring competitive nature with the proximity in the automotive industry.
However, while competition is staged towards profitability, aspects of social responsibility are spearheaded towards creating and promoting environmental-friendly technologies in every emerging company to evade risks of degradation in the long run. For this reason, innovative inventions towards sustainability are the driving factors that most entrepreneurs and investors consider as competitive basements for their products besides financials budgets and costs. There is stiff competition realized by each company in the automotive industry, starting with Tesla, General Motors Company (GM), and Ford General Motors in the 20th century.
Organizational Assessments
Tesla
Tesla, Inc.’s organizational structure has become a favorable factor that encourages continuous expansion and growth. It is of significant benefit for a company’s organizational design, corporate, and layout that effortlessly defines healthy interactive patterns in its foundational components. For Tesla, the company still incorporates the traditional structure from managerial control levels and focus (“Tesla Inc.’s organizational structure & its characteristics (Analysis),” 2018). Besides, the structure still paves the way for limited and expansive operation in the world global market. Tesla, Inc. is renowned for its leading chains in manufacturing electric vehicles, solar power panels, batteries, and other transport system substitute energy solutions (Tesla Inc., 2018). Leadership is an important aspect that guarantees organizations more thriving abilities and opportunities in the global operations in business activities.
The leadership style and strategic key plays presuppose that they intermarry with an appropriate structure. Thus, Tesla’s owner Elon Musk’s mode of leadership efficacy is dependent on the corporate nature of the strategic organizational structure. The corporate structure plays a significant role in supporting the disseminating integrated improvements and growth in the business. Therefore, the organizational structure at Tesla has led to the company’s maximization of its ability while implementing new strategies and management of corporate objectives, goals, and activities (Thomas & Maine 2019). Operations Management at Tesla, Inc. is subject to the company’s organizational structure effectiveness to support various implementations and strategic changes required.
Tesla’s nature of its organizational structure is the key motivator for managerial monitoring of the company despite its international networks. However, a global expansion might bring in challenges and complexities because international development requires broader network considerations. The corporate structural basis is essential in helping Tesla maximize their managers’ information, highlighting the drawbacks, and acting out appropriately (Tesla Inc., 2018). Hence, through Tesla’s corporate structure, it established its vision statement and corporate mission of emphasizing leadership in the energy solutions and automotive markets.
Tesla’s features and the type of organizational structure are made up of a U-form functional structure. The U-structure employs the functions of an organization as the primary determining factor. Grouping in Tesla is significantly intertwined to business function such that there are engineers and other employees whose primary focus is on services and sales. Function-based hierarchy, centralization, and divisions are significant to Tesla’s organizational structure. Function-based ranking helps the company run n smooth activities in international and domestic operations with strict management. In a function-based hierarchy, Tesla’s organizational structure comprises Chief Executive and Chairperson, technology, Engineering, Finance, legal, and global service and sales (Tesla Inc., 2018).
Centralization in Tesla’s organization management entails emphasizing managerial control to the entire organization, and the decision stands evolving from a central team. Divisions are essential in evaluating global geographic business operations in implementing various and significant marketing campaigns and organizing financial performance and records. The primary divisions include Energy generation and sore and automotive. The geographical divisions of the company include the United States, Norway, and China.
Corporate structure employed by Tesla, Inc. has resulted to several advantages. It has acquired effective managerial control in its multi-national operations. It has also eliminated the tendency of implementing new strategies set by the company. The company has used its regional geographic records and report analysis in creating a foundation that shall be used for future tactics and strategies of regionalization of automotive markets. As a result, such advantages have helped the company employ its organizational structure while building and growing its competitive edge against Ford, GM, and other manufacturers.
Ford Motor Company
The company’s organizational structure is driven by the world’s varying conditions concerning the business needs of markets. The organization of every firm is, perhaps, concerned with the definition and configuration of the organization’s systems of interaction and components (Vernimmen et al., 2018). Ford’s organizational structure bears close correlative relations to the automotive industry nature. The company operates based on international scope that helps determine crucial elements in organizational structure that pose surety of withstanding market risks and competition. In this case, Ford’s ranking as the second-best automobile manufacturer company in the US indicates the effectiveness of the organizational structure in supporting the company to have a continuous business performance and growth. The organizational structure of Ford Motor Company (FMC) has divisions regarding regional markets, while other featuring characteristics are solely based on Ford Company’s nature of business and the global scope.
The organizational structure employed by Ford is entirely driven towards the need to controlling the company’s activities based on the market conditions in different regions (“Ford Motor Company’s organizational structure analysis,” 2018). Ford Motor Company’s organizational structure is characterized by corporate hierarchy, regional geographic divisions, and global functional groups. The corporate hierarchy employed by Ford follows a traditional structural hierarchy. In this case, the chief executive officer (CEO) Mark Fields receives a report from the Executive Vice Presidents. In turn, the executive vice presidents receive reports from middle managers. For this reason, Ford’s traditional organizational structure proves efficacy in managing business firms in a top-down approach manner of control.
FMC has extensive regional geographic divisions at the base of its organizational structure. Global companies are renowned for demarcating their operations into regions depending on preferential operability in different continents. Ford company’s organizational structure readily operates in only three divisions of its geographic business regions. Even though its regional geographic divisions are three, the organizational strategy has covered its entire market targets globally. Organizational structure and its effectiveness in a business are significant for easier integration into varied business strategies. Ford’s operations have covered America, Asia Pacific, Europe, Africa, and the Middle East, and an executive vice president heads each division. The company’s global functional groups serve essential roles in the entire organizational structure and operation of its processes.
Ford’s functional groups comprise global market sales and services, global product development, a global manufacturing and labor affairs, communications, accounting, global purchasing, legal, government and community relations, finance, quality, new model launch, and the human resource and corporate services. Ford Motor Company benefits from the corporate hierarchy deployed to realize a global sense of direction and control. The workforce at FMC showcases smoothness inflow due to available functional groups incorporated with human resource management personnel. The large integrated regional divisions enable the company to quickly integrate and implement its strategies and policies in the organizational layout.
The company further enjoys the advantage of extensive regional divisions in accessing a broader view of its potential markets. Consequently, Ford might become disadvantaged in the long run due to risking and disregarding unique and essential nature or needs in the domestic markets.
General Motors Company
The critical aspect in the management of a business entity lies in its organizational structure. Organizational structure attributes to the success, service delivery, and efficiency of a company. Various organizational structures selected by different firms affect fundamental operational factors such as cost, a chain of command, and human resources in a given organization (Sakhartov, 2016). However, companies are focused on deploying organizational structures that promote efficient allocation of resources, employee effectiveness, bureaucracy, and reduced costs.
General Motors (GM) is ranked among the top entities in the automobile industry (“General Motors Company (GM),” 2021). It is appraised of its robust revenues. The company entity has a network of assembling plants in different geographic regions globally. Plants in each region are specific to serving the given region. The company’s vision to serve its target potential customers in its regions has raised the need for strategic location and positioning of its production plants. The organizational structure of GM Company is hybrid. Thus, it can blend regional forms and primary forms associated with organizational structures. The financial department is housed in Michigan headquarters. GM departments include North America, Europe, International, and South America. As a primary player in the world automotive industry, GM should implement strategies that specifically solve the market conditions in its regions.
General Motors follows a regional, divisional organizational structure. Thus, the core business is contained in grouping business operations based on their geographic operation areas and segments. Advantages of GM regional division organization structure and design include flexibility of the business to provide affirmative action to trends in market variations (“General Motors’ organizational structure for flexibility in regional markets,” 2018). It also helps to create focus on the financial and business services of the company as separate entries. The company enjoys optimized effectiveness in the growth of automotive sales in the global market. However, the major disadvantage of GM’s organizational structure is the constrained support towards brand consistency in the international market.
Planning and Budgeting Concerns
Planning and budgeting concerns are significant factors for the success in the financial performance of every business entity, organization, or company. Planning helps companies to come up with expected expenditure budgets. Budgets serve as a crucial financial roadmap of a business’ working goals and objectives. Besides, planning and budget are pivotal in determining economies of preferences and priorities for planned and better spending. The rise in the market’s competitive nature has put top brand companies such as Tesla to plan and budget for their products in the market. Ford is America’s second-ranked automobile company that has heightened the competition that is nearing Tesla. Also, the GM entity is a crucial player in the automotive industry that poses greater chances of outperforming Tesla in certain aspects.
Thus, for Tesla to remain at par with performance, it has laid down budgeting and planning concerns to remain consistent in the automotive market competitions. Tesla has planned to unleash new electric-powered vehicles that it budgets to be relatively cheaper than the previous price tags (Gaya Ferre, & Tresserras, 2016). Elon Musk has also aired out that the firm’s sole purpose is to try and manufacture cheap and affordable electric vehicles. Ford CEO has also proposed to cut down on the cost of their vehicles, trucks, and electric-powered vehicles. GM Company’s planning and budgeting objectives are to rise spend per customer by sourcing new suppliers, promotion and marketing, expanding product offering, and affordable pricing.
The Company Financial Ratios and an Industry Comparison of the Ratios
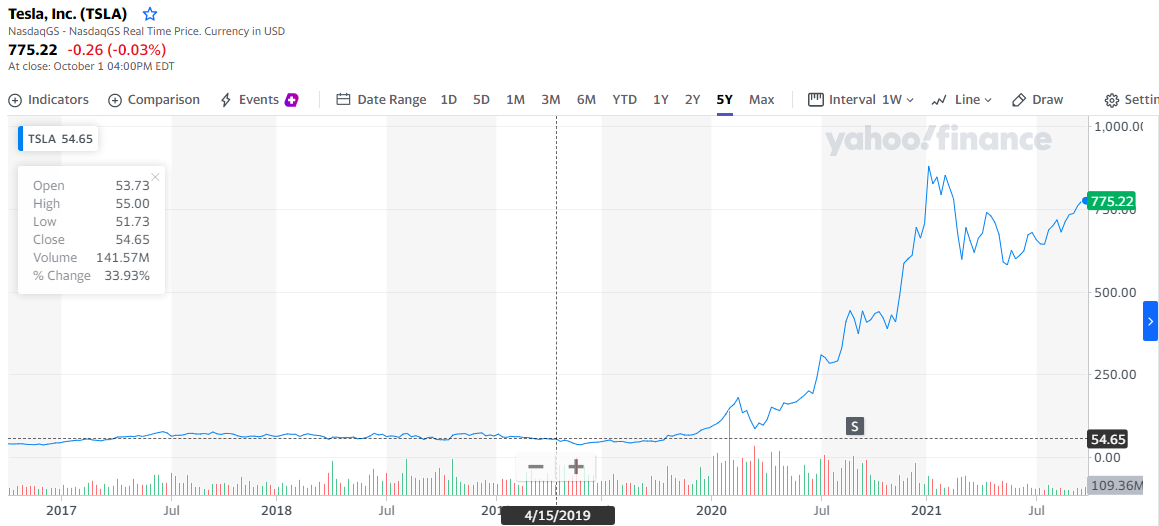
The financial position of Tesla, Ford, and Gm is a result of their company financial ratios. By February 2021, Tesla’s financial ratio was at $0.74 in earnings per share, while their earnings per share were at $ 0.64 diluted earnings per share. According to their 2021 accounts, Tesla has a total debt of $11.69over $ 22 billion, where accrued long-term debt was valued at $9.56 billion and the current debt at $2.13 billion (Figure 1). The figure was issued days before the Q2 earnings call, and therefore the figures are most likely to have changed since then.
Towards the end of July 2021, Tesla was valued as the 9th most valuable company with a market cap of 631.26 billion. The company’s financial growth is evident considering its market cap. Tesla’s gross margin was valued at 21% and gross revenue at $31.5 billion in 2021. Based on the Return on Investment Capital, Tesla had – 4.55%, and its profitability started in 2020.
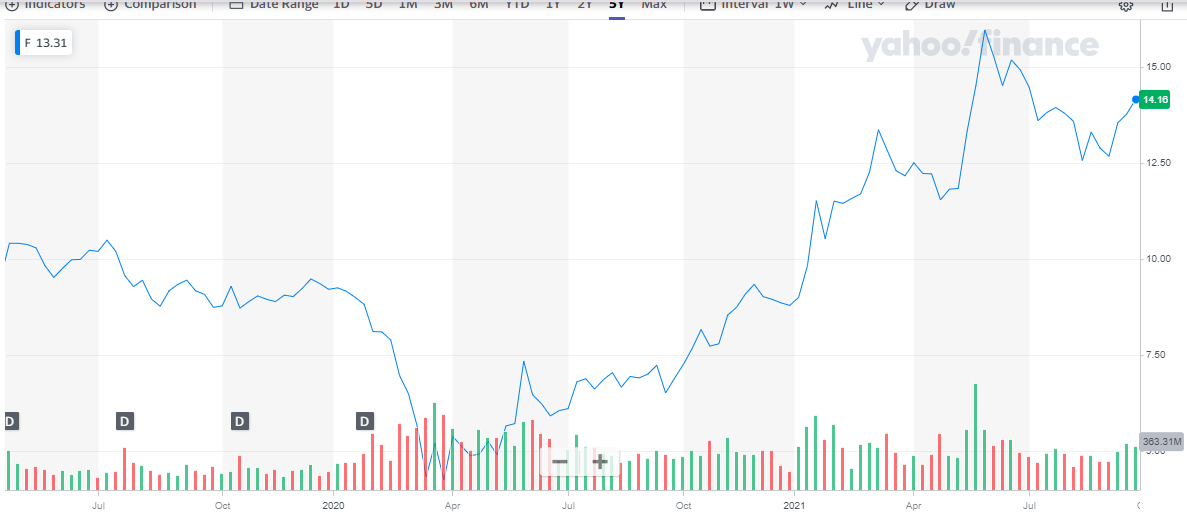
On the other hand, Ford had a total debt of $152. Sixty-seven billion in long-term and short-term debts are valued at $103.20 billion and $49.47 billion, respectively. As of July 2021, Ford’s market cap was valued at $55.64 billion before the market opening (Figure 2). Based on the market cap, Ford was listed as the 344th most valuable company. Their gross revenue was estimated at $127 billion and the gross margin at 11.3%. The return on capital in investment capital is valued at 5.92% as of 2020.
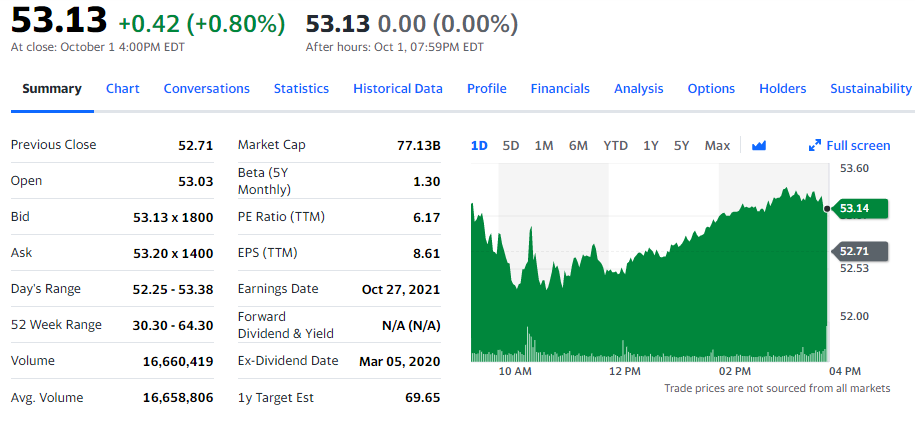
Lastly, the financial ratio of General Motors is as follows. The total debt was valued at $108.89 billion. $ 72.98 billion are in the long term, while $36.91billion is in current debt (Gaya Ferre, & Tresserras, 2016). As of July 2021 pre-market ratings, general motors had a gross margin of 11.2 % and a market cap of $82.76 billion (“General Motors Company (GM),” 2021). Based on the pre-market ratings and listings, Tesla has the least debts and has the highest rating at the 9th most valuable company in the industry. The return on investment capital was rated at 6.52%.
Main Products of Each Company for Comparison
Tesla is one of the most selling brands. The company is well known for its products which are electric cars and solar energy (Tesla Inc., 2018). Tesla’s products include; Tesla model 3, Tesla Model X, Tesla Model S, Tesla Model Y, and Tesla Cyber track. Besides manufacturing vehicles, Tesla also specializes in the production of storage and energy systems (Agarwal, 2021). Ford specializes in the manufacture of automobiles as their main products, including Ford Series, Ford Trucks, Lincoln Luxury, and utility vehicles. General motors specialize in car brands such as Chevrolet, Cadillac, Hummer, Saab, Saturn, and other car brands (Cole, 2020). Based on their products, Tesla has a broader range of products. Besides, it is more equipped to address the emerging market needs, which might increase demand for electric cars and solar systems.
Financial Strategy and Overall Strategy of the Companies (SWOT)
Companies rely upon their strategies to survive in diverse markets. Their SWOT analysis is as follows. Tesla’s strengths include; innovation and diversification of their products (Gaya Ferre, & Tresserras, 2016). Additionally, Tesla is the top automotive company with considerable dominance in the production of electric vehicles. Tesla’s weakness includes limited production volumes, manufacturing complexity, and limited global presence due to their pricing. Tesla’s available opportunities are the future of sustainability and the ability to expand globally. Impending threats are product deficits and intense competition from other companies in the industry.
Future Prospects in Automotive Industry
The automotive industry is a rapidly growing industry that linearly corresponds to millennial integration in technology and population. The prospect in the industry races towards a new market. The industry’s future outlook is purposefully aimed at sustainability and increasingly changing consumer trends in behavior while encompassing electric and solar-powered vehicles, mobility sharing in the fleet, advanced business models, connected cars, always-on connectedness, and onboard sensors (Azam & Yusoff, 2020).
A higher rate at which the world population is growing poses higher forces in demand and supply. As a result, the demand for automobile products like vehicles is gradually growing at a faster rate. Leading and emerging automotive companies are, therefore, seemingly to outperform each other shortly. Technology is evolving each day, and more automobile products are overflowing the market. Thus, it is the need for automotive stakeholders to keep up with the pace at which technology is growing to remain competitive.
Current stock prices and plotting of the stock price for Tesla, GM, and Ford
By February 2021, Tesla’s financial ratio was at $0.74 in earnings per share, while their earnings per share were at $ 0.64 diluted earnings per share. According to their 2021 accounts, Tesla has a total debt of $11.69over $ 22 billion, where accrued long-term debt was valued at $9.56 billion and the current debt at $2.13 billion (Figure 1)
Ford had a total debt of $152. Sixty-seven billion in long-term and short-term debts are valued at $103.20 billion and $49.47 billion, respectively. As of July 2021, Ford’s market cap was valued at $55.64 billion before the market opening (Figure 2).
The total debt was valued at $108.89 billion. $ 72.98 billion are in the long term, while $36.91billion is in current debt (Gaya Ferre, & Tresserras, 2016). As of July 2021 pre-market ratings, general motors had a gross margin of 11.2 % and a market cap of $82.76 billion (“General Motors Company (GM),” 2021).
Recommendation on Stock-type
Underlying stocks in a business should be sold whenever there is a promising future increase in sales. Therefore, the automotive industry’s underlying stock is a sell stock (Nikowitz, 2016). There is a future expectation of an increase in demand. Technology is evolving to outdo existing brands; thus, the industry would have a sell stock that promises future expansion in demands. While evaluating companies, the rigidity nature of Tesla’s corporate organizational structure has limited the company from advancing expansions and adjustments within the organizational settings. For instance, global centralization is structurally characterized by limitations to an autonomous overseas office that responds to arising matters in different regional markets.
Thus, Tesla, Inc. should have a reformation in its structure and increase the degree of autonomy in its overseas office because corporate systems with more decentralization prove effective in creating competitiveness among local businesses in the overseas markets. GM Company can develop appropriate marketing strategies and campaigns to retain its consistency in automobile industry branding. This recommendation is aimed at improving the strength of the company’s brand.
Conclusion
The automotive industry has been growing at a faster rate since the 20th century. Technology is the thriving force that has evolved the increased growth in the automotive industry. Competition has come through incorporating technology in the industry to create innovative products for the market demands. Sustainability is a question across the globe. Every company evolving in the industry is striving to outperform each other through technological innovations that aim at global sustainability. Thus, Tesla, General Motors, and Ford are good competitive companies that prospect the staged campaign on sustainability.
These assessments reveal strategies that each company is employing to realize a favorable competitive environment. However, the prospects of the automotive industry are luminous. Profitability is propelled by sustainability and increasingly changing consumer trends in behavior while encompassing electric and solar-powered vehicles, mobility sharing in the fleet, advanced business models, connected cars, always-on connectedness, and onboard sensors in the automotive industry.
References
Agarwal, A. (2021). Equity research report on ford motor company: running out of´ gas´? (Doctoral dissertation).
Azam, S. F., & Yusoff, S. K. M. (2020). Investment and financing analysis: An investigation of the automotive industry of china. Systematic Reviews in Pharmacy, 11(1), 913-919.
Cole, A. (2020). Fundamental valuation of the general motors company: Assessing the value in the midst of a pandemic (Master’s thesis).
Ford Motor Company’s organizational structure analysis. (2018). Panmure Institute. Web.
Gaya Ferre, F., & Tresserras, V. (2016). Brand valuation-Tesla Motors, Inc.
General Motors Company (GM). (2021). Yahoo Finance – Stock Market Live, Quotes, Business & Finance News. Web.
General Motors’ organizational structure for flexibility in regional markets. (2018). Panmure Institute. Web.
Nikowitz, M. (2016). Advanced hybrid and electric vehicles. System Optimization and Vehicle Integration, Springer. Web.
Sakhartov, A. V. (2016). Selecting corporate structure for diversified firms. In Academy of Management Proceedings (Vol. 2016, No. 1, p. 11521). Academy of Management.
Tesla Inc., (2018). Formulating technological innovation strategy. Web.
Tesla Inc.’s organizational structure & its characteristics (Analysis). (2018). Panmure Institute. Web.
Thomas, V. J., & Maine, E. (2019). Market entry strategies for electric vehicle start-ups in the automotive industry–Lessons from Tesla Motors. Journal of Cleaner Production, 235, 653-663. Web.
TSLA interactive stock chart | Tesla, Inc. Stock. (n.d.). Yahoo Finance – Stock Market Live, Quotes, Business & Finance.
Vernimmen, P., Le Fur, Y., Dallochio, M., Salvi, A., & Quiry, P. (2018). Choice of corporate structure. Corporate Finance: Theory and Practice, Fifth Edition, Fifth Edition, 748-770.
