Introduction
Emirates Telecommunications Corporation [Etisalat] is the market leader within the Gulf Cooperation Council [GCC] telecommunication industry. The firm was established in 1976 and it operates as a public limited company. The firm has optimally positioned itself as a blue-chip multinational corporation. The firm’s headquarters are located at Abu Dhabi in the United Arab Emirates [UAE]. Etisalat has established operations in over 19 countries in Africa, Asia, and the Middle East (Beltone 2008). The firm specialises in offering diverse telecommunication services and media. Its core products and services include wireless communication, voice communication, and data communication. The products and services are provided via the firm in collaboration with its subsidiaries, viz. e-marine and e-vision. Moreover, the firm also offers consultancy services to local and international companies.
Over the past few years, the firm has been focused on improving its performance by restructuring its internal operations. The restructuring led to the establishment of three independent divisions, which include Etisalat UAE, Etisalat International, and Etisalat Services. Etisalat UAE deals with the provision of cable television, Internet network, and telecommunication in the UAE. Conversely, Etisalat International specialises in international activities such as identification of business opportunities in the international market, while Etisalat Services is focused on improving the company’s efficiency in its non-basic telecommunication business units.
Etisalat is focused on improving and sustaining leadership in the global telecommunication industry. Thus, the firm has adopted best practices in strategic management such as the formulation and implementation of business and corporate level strategies. One of the corporate-level strategies that the firm has incorporated entails merger and acquisition (Johnson, Scholes & Whittington 2008). In 2010, Etisalat announced its merger and acquisition process with Reliance Communications Limited, which is the largest telecommunication company in India. The merger and acquisition intended to enhance Etisalat’s entry into the Indian market, which is ranked second amongst the largest wireless market (Behmann & Paton 2010).
The firm’s long-term competitive advantage will be determined greatly by its success in formulating and implementing effective strategic management process. According to Hitt, Ireland, and Hoskisson (2009, p.77), ‘the strategic management process is a logical approach for helping a firm effectively respond to the challenges of the 21st century competitive landscape’. Strategic management process involves the decisions, actions, and commitment that an organisation integrates in order to earn high returns for investors and create higher value compared to competitors (Kazmi 2008). Therefore, it is imperative for organisations to evaluate the internal and external business environment continuously and utilise the information gathered in formulating strategies that will lead to higher competitive advantage. This case study illustrates how Etisalat has integrated the concept of strategic management processes in its operation. The case study is based on a number of models, viz. the Value Chain Analysis, SWOT analysis, and the Boston Consulting Group [BCG].
Value Chain Analysis
Firms should focus on enhancing their strategic position in order to promote their competitive advantage by integrating value-chain analysis. Value chain analysis enables an organisation to formulate effective business-level strategies (Ungson & Wong 2007). Furthermore, value chain analysis provides an organisation with insight on the activities that can be outsourced. Lowson (2002, p. 87) affirms that identifying and ‘exploiting internal and external linkages with the objective of strengthening their competitive advantage’. In a bid to exploit the linkages successfully, it is imperative for an organisation’s management team to evaluate the costs and non-financial factors because the different bundle of activities undertaken. Hitt, Ireland, and Hoskisson (2009) are of the view that businesses must ensure that the value created in its operation is greater than the cost incurred in producing and distributing its products and services to the final customer.
Value chain analysis is comprised of two main categories of activities, viz. the primary activities and the support activities. Gholson and Schloegel (2006) assert that the primary activities involve the tasks that are directly involved in the creation and delivery of the product, hence offering customers high value. The primary activities can be categorised into
- Operations.
- Inbound logistics.
- Outbound logistics.
- Marketing and sales.
- After sales service.
The support activities aim at delivering value to the customer indirectly (Huse 2007). The support activities relate to technology development, procurement, firm infrastructure, and human resource development activities. Etisalat has integrated primary and support activities in its strategic management process as illustrated herein.
Primary activities
Inbound logistics
Etisalat is committed to attaining a strong competitive edge in its provision of telecommunication products and services. The firm appreciates the importance of ensuring that its customers receive high-quality services. In a bid to achieve this goal, the firm is cognisant of the importance of implementing a strong telecommunication network. Thus, the firm has established a strong relationship with other suppliers within the telecommunication industry. For example, Etisalat collaborates with well-established credit card companies such as MasterCard in an effort to improve its capacity to offering mobile payment solutions. The collaboration aims at improving the company’s efficiency in delivering services by enhancing the level of security and speed. The collaboration is expected to transform electronic payment system in the UAE (Mohammed 2014).
Operations
Etisalat has ensured that its telecommunication infrastructure aligns with the highest international standards. The firm has also invested in cutting-edge technological expertise, which has improved its capacity to offer its telecommunication services to customers. Furthermore, its technological expertise has significantly contributed to the improvement of the company’s market share (Etisalat 2014a). Despite the remarkable technological changes being experienced in the global telecommunication industry, Etisalat is committed to developing and sustaining its competitiveness. One of the aspects that the firm has focused on entails improving its operational efficiency. Subsequently, the firm has invested substantially in research and development.
The company’s investment in research and development has played a remarkable role in improving the firm’s operations. Thus, the firm has been in a position to offer advanced and innovative networks. On 25th February 2014, Etisalat announced its decision to launch trials on its innovative technologies, viz. the Radio Dot System and LTE Broadcast solutions. Additionally, the firm has also collaborated with Huawei in an effort to improve its operations. The strategic partnership is aimed at improving the firms’ operations in new areas such as Software-Defined Networking [SDN], Public Cloud, and Network Function Virtualisation [NFV]. Additionally, Etisalat has also partnered with SAP in an effort to provide customers with diverse mobility services. This aspect illustrates that the firm is focused on delivering value to customers by improving the quality of its products and services (Emirates News Agency 2014).
Outbound logistics
The company intends to become a customer-centric organisation in the telecommunication industry. One of the techniques that the firm has adopted in its pursuit for this objective entails improving its distribution efficiency, hence its ability to reach a large number of customers (John 2003). Consequently, the firm has positioned itself as a pioneer in the provision of next-generation network with reference to wireless and fixed-line services. Moreover, the firm has established an extensive fibre-optic cable network in the UAE. Furthermore, the firm intends to launch the 4th-generation long-term evolution network in its Saudi Arabian and the UAE markets. Currently, Etisalat dominates with reference to the provision of the fastest fixed-line broadband network in the Middle East (Etisalat 2014a). In a bid to improve its outbound logistics, Etisalat has announced its decision to develop a 5G telecommunication network in the Gulf region. The 5G network will enable Etisalat to offer customers quality broadband services such as speeds of up to 10 gigabytes per second. Thus, customers will enjoy premium high-speed services. Furthermore, improvement of the telecommunication network will foster the firm’s future sustainability in an industry that is incessantly changing.
Marketing and sales
Creating brand awareness comprises a fundamental element in developing a strong competitive advantage. Doole and Lowe (2005) affirm that the level of awareness affects the level of brand loyalty and preference. Doole and Lowe (2005) further affirm that brand awareness is critical in the consumers’ purchase decision-making process. In the course of its operation, Etisalat recognises that brand awareness constitutes the first step in the process of generating sales (Fombrun, Tichy & Devanna 2000).
Moreover, the firm has been focused on improving the size of its customer base over the years. However, the firm recognises that the attainment of this goal will depend on the level of brand awareness (Craven 2002). Thus, the firm has incorporated different marketing strategies in an effort to create brand awareness. The firm has adopted different techniques such as advertising, sales promotion, and public relations in an effort to create awareness of its products in both the existing and new markets (Webb & Gorman 2006).
In its advertising process, Etisalat has incorporated diverse mediums such as television, print media, and radio. Furthermore, the firm has adopted outdoor advertising by posting billboards in strategic locations. In its quest to attain a global reach, Etisalat has adopted web-based mediums such the company’s official website, wikis, and blogs. Additionally, the firm has appreciated the impact of social media in spreading the word of mouth. Thus, the firm has integrated diverse social media platforms such as YouTube, Facebook, Twitter, and Google+ amongst others in creating product awareness (Sahaf 2008).
Etisalat recognises the importance of entering new markets in order to maximise the level of profitability. The firm appreciates the importance of public relations and sales promotion initiatives in its quest to launch its operations successfully in the new markets. For example, in the process of entering some African countries such as Cote d’Ivoire, the firm has adopted a public initiative dubbed ‘WEENA’. The initiative aims at encouraging women within the rural areas to appreciate the benefits of using mobile technology. The company’s investment in this initiative has played a fundamental role in improving its entry into new markets especially Africa (Etisalat 2014b).
The firm’s public relations effort are evidenced by its participation in major telecommunication events such as the Mobile World Congress 2014 whose objective is to illustrate the role of mobile technology on individual and institutional customers in both the developed and the emerging economies. By participating in such events, the firm highlights its products and services, latest technological developments, and its focus in shaping the global communications industry. Creating such awareness is fundamental in attracting potential customers (Nedelea 2006).
After sale services
Developing a strong relationship with customers is vital in an organisation’s quest to sustain and improve its level of profitability (Duam 2003). Etisalat has incorporated a number of after sale services. The firm has incorporated a call centre in an effort to improve its effectiveness in serving customers. Thus, customers can contact the call centre, which is toll-free, in case of any question, complaint, or compliment. The call centre services are available 24 hours a day. Furthermore, the firm has established an online portal through which customers can seek support related to the firm’s products and services. Other web-based technologies that customers can utilise in communication with the company include e-mail and through chatting (Etisalat 2014a). The firm’s decision to integrate diverse points of contact has considerably improved its interaction with customers.
Support activities
In addition to the above primary activities, Etisalat has integrated a number of support activities as explained herein.
Human resource management
The quality of an organisation’s workforce greatly affects the firm’s productivity. Thus, the importance of developing a strong human capital base cannot be underestimated (Hill & Jones 2010). Etisalat recognises its human capital as one of the most important organisational assets. Thus, the firm has integrated effective human resource management practices. For example, Etisalat ensures that its employees are rewarded fairly and equitably by integrating a reward system that is comprised of financial and non-financial rewards. Some of the non-financial rewards adopted include providing employees with training and development and an opportunity to progress in their career paths. Furthermore, the firm has integrated work-life balance into its HRM in an effort to improve the level of satisfaction amongst workers (Porter 2008). Its effective HRM practices have significantly improved the employees’ level of productivity, hence improving its position as the pacesetter within the telecommunication industry in the Gulf region.
Infrastructure
Etisalat’s operations are undertaken through various functional departments, which include research and development, accounting, marketing, legal, finance, quality assurance, public affairs, and planning. Despite the integration of these divisions, the company appreciates the importance of developing synergy in order to attain a high competitive advantage. Therefore, Etisalat ensures that the various departments work in collaboration with each other.
Technological development
Etisalat continuously improves its telecommunication technology by investing in research and development. Moreover, the firm collaborates with other telecommunication companies such as Ericson and Huawei in an effort to gain a high competitive edge with regard to technology. Thus, the firm has gained competitiveness with reference to its innovative capacity. Furthermore, investment in research and development has considerably improved its effectiveness in delivering value to customers. The company has developed one of the most comprehensive infrastructure networks by incorporating emerging technologies such as the fibre optic technology, the 4G, and 5G broadband technologies.
BCG analysis
Wit and Meyer (2004) emphasise that it is critical for organisational managers to evaluate the performance of the respective business units in order to assess their contribution to the general organisational profitability. Gaining such knowledge enhances the managers’ capacity in making decisions on how to allocate resources. The Boston Consulting Group matrix is one of the models that organisational managers can adopt. The matrix evaluates business performance based on two main dimensions, viz. the relative market share and growth rate. Peng (2014, p.77) argues that the ‘matrix classified the types of business in which a diversified organisation can engage as dogs, cash cows, question marks, and stars’.
Etisalat’s provision of broadband services can be categorised within the ‘stars’ category due to the high growth rate potential characteristic. Additionally, Etisalat has attained a high market share in the provision of broadband services. The company’s ability to exploit the opportunity within the broadband market segment is dependent on its investment in research and development. Etisalat must ensure that it invests in continuous research and development on how to improve its broadband network capacity. For example, investing in 5G technology will enable the firm to attract a large number of customers. Furthermore, the firm will be in a position to exploit the emerging trend whereby consumers are increasingly consuming data services.
On the other hand, Etisalat operations with regard to the provision of electronic payment services can be categorised within the question mark category. Etisalat has not been in a position to exploit the market potential successfully despite the fact that mobile payment market segment is undergoing a high rate of growth. Thus, the firm’s market share with reference to mobile payment services is relatively low. However, Etisalat’s strategic partnership with electronic payment companies such as MasterCard can improve its market share by developing an effective electronic payment platform. The partnership will enable Etisalat to exploit the opportunity associated with the development of e-payment especially in the retail sector (Reuer 2004).
Despite the high growth opportunity, the firm might not be in a position to sustain a high market share in the electronic payment market segment due to the high rate at which companies established in different sectors are diversifying their operations into electronic payment services, for example, by issuing credit cards. Furthermore, the firm’s ability to sustain its market share within the electronic payment segment might be affected by intense competition from financial institutions.
Etisalat dominated the UAE market with regard to the provision of voice services. The firm had managed to position itself as a monopoly in the UAE telecommunication industry. Subsequently, the firm was in a position to generate a high level of economic profit. Despite the loss of monopoly power due to the entry of competitors such as Zain and Du, the provision of voice services continues to be a source of income for Etisalat.
The company’s provision of fixed line services can be ranked within the ‘dog’ category due to the potential low market share and growth rate. The entry of Zain and Du into the UAE’s telecommunication industry is likely to reduce Etisalat’s market share in the fixed line segment (Everington 2014). The firm expects to share its fixed network infrastructure with Du and this move will trigger intense competition between the two firms with regard to the provision of internet and landline services. Du stands to attain a substantial market share within the fixed line market segment if the network sharing agreement is reached. Therefore, the firm will gain remarkable dominance similar to what it has achieved in the mobile market segment.
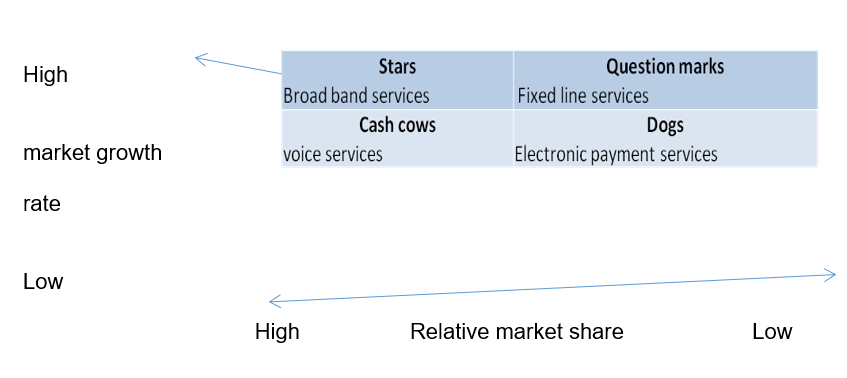
Relative market share.
SWOT analysis
Etisalat’s operations are subject to changes within the internal and external business environments. Thus, it is essential for the company’s top executive to understand the prevailing business environment. Gaining such insight will enhance the firm’s ability to formulate effective decisions (Sutherland & Canwell 2008). The SWOT analysis presents an effective model that the company can utilise in analysing the business environment. Below is an analysis of the company’s strengths, weaknesses, threats, and opportunities.
Strengths
Financial stability
Etisalat has developed a strong financial capital base, which has been enhanced by its local and international operations. The firm’s market value is estimated to be AED 90 billion [$ 24.5 billion], while its annual sales revenue is estimated to be over AED 39 billion [$ 10.6 billion] (Etisalat 2014a). Due to its financial capacity, the firm can invest in extensive international investment. Additionally, its financial stability is evident given the rating illustrated in appendix 1 (Etisalat 2014b).
Technological development
The company has penetrated the international market successfully due to its technological expertise with regard to telecommunication. Thus, the firm is ranked amongst the market leaders with reference to the introduction of new technologies.
Product diversification
Etisalat has developed an extensive product portfolio in an effort to serve diverse customer needs. Some of the telecommunication services offered include data services, video, cable television services, mobile services, and fixed-line voice services.
Strong management team
The firm’s market dominance in the Gulf and Middle East regions has been enhanced by the adoption of effective strategic management practices. Furthermore, the firm’s management team is proactive in formulating business strategies hence improving the firm’s long-term survival.
Customer focus
Etisalat has positioned itself as a customer-centric organisation. The firm appreciates the importance of understanding the customers’ needs in its service and product provision processes. Consequently, the firm has managed to develop a high level of brand loyalty in the Gulf, Middle East and the MENA regions.
Weaknesses
Weak control
The firm has outsourced management of its international operations to third parties, hence leading to loss of optimal control of its international operations.
Low level of profitability
Etisalat has not been in a position to optimise its profitability in the international market. Thus, a substantial proportion of its profit comes from the domestic operations.
Opportunities
Geographical markets
The firm can maximise its profitability by venturing into new markets through international market expansion. For example, expanding into emerging economies that are characterised by less developed telecommunication networks will promote the firm’s competitive edge.
Tariff
Etisalat can enhance its competitiveness against Du, which is its major competitor, by exploiting its financial capacity. The firm can set competitive tariffs of its telecommunication services. Through this strategy, Etisalat will improve its attractiveness to customers.
Growth in population
The high global population growth rate presents an opportunity for the firm to improve its customer base. Additionally, change in consumer behaviour with regard to technology also presents an opportunity for the firm to increase its customer base. Consumers are increasingly incorporating technology as a key component in their consumption process. Thus, the firm can exploit this trend by offering products that align with their needs.
Threats
Competition
The firm faces intense competition from local and multinational companies especially Du. In 2007, Du ended Etisalat’s monopoly in the UAE with regard to provision of fixed-line telephone services, cable television services, and broadband services (Smith 2014). The existence of intense competition might affect the firm’s capacity to sustain its level of profitability.
Technological changes
The telecommunication industry is characterised by a high rate of technological change due to investment in research and development. Therefore, the firm’s failure to invest continuously in technological innovation might affect its competitiveness.
Overreliance on third parties
Etisalat might lose its competitiveness in the international market due to its continued reliance on third parties in managing international operations
Strategic development
In a bid to sustain its long-term competitiveness, it is imperative for the firm to invest in extensive strategy development. Some of the strategic options that the firm can consider are highlighted in the table below.
Conclusion and Recommendations
Etisalat has successfully attained an optimal market position in the UAE telecommunication industry. Its success has arisen from the adoption of effective strategic management practices. However, the firm faces a threat arising from changes in the telecommunication industry such as intense competition and technological changes. In order to develop long-term sustainability, Etisalat should consider the following aspects.
Exploiting market intelligence
Etisalat should evaluate market changes continuously in order to gain insight on how to adjust its products and services. Gaining market intelligence will improve the firm’s ability to deliver value to customers. Subsequently, the firm will foster development of a high level of brand loyalty.
Human resource management
The firm should focus on improving its organisational culture in order to develop a strong workforce in a bid to enhance its innovative capacity. The firm should train its workforce incessantly in order to enhance its ability to respond to market challenges. Some of the values that the firm should consider in developing a strong organisational culture include teamwork, integrity, employee inclusion, trust, and diversity.
Reference List
Behmann, E & Paton, J 2010, UAE’s Etisalat looking for mergers, acquisition in India within next year. Web.
Beltone, J 2008, Emirates Telecommunication Corporation (Etisalat), Etisalat Incorporation, Cairo.
Craven, R 2002, Customer is king: how to exceed their expectations, Virgin, London.
Duam, J 2003, Intangible assets and value creation, Wiley, Hoboken.
Doole, I & Lowe, R 2005, Strategic marketing decisions in global market, Thompson Learning, London.
Emirates News Agency: Etisalat and Huawei sign MoU to identify new areas of cooperation. 2014. Web.
Etisalat: Company profile. 2014a. Web.
Etisalat: Investor relations; credit rating. 2014b. Web.
Everington, J 2014, Etisalat set for network share challenge with du. Web.
Fombrun, C, Tichy, N & Devanna, M 2000, Strategic human resource management, Wiley, New York.
Gholson, N & Schloegel, M 2006, Driving growth and shareholder value: the distribution value map, Oxford Press, London.
Hill, C & Jones, G 2010, Strategic management theory: an integrated approach. Houghton Mifflin, Boston.
Hitt, M, Ireland, & Hoskisson, R 2009, Strategic management: competitiveness and globalisation; concepts and cases, South-Western, Mason, OH.
Huse, M 2007, Boards, governance and value creation: the human side of corporate governance, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
John, J 2003, Fundamentals of customer-focused management; competing through service, Sage, Westport.
Johnson, G, Scholes, K & Whittington, R 2008, Exploring corporate strategy: text and cases, Prentice Hall, London.
Kazmi, A 2008, Strategic management and business policy, Tata McGraw Hill Education, New Delhi.
Lowson, R 2002, Strategic operations management: the new competitive advantage, Routledge, New York.
Marchand, D 2000, Competing with information, John Wiley and Sons, New York. Mohammed, S 2014, Etisalat, MasterCard join forces to unveil future of mobile payments in the UAE. Web.
Nedelea, A 2006, The concept of marketing in the public administration, University of Suceava, Suceava.
Peng, M 2014, Global strategy, Cengage Learning, Mason, Ohio.
Porter, M 2008, Competitive strategy; techniques for analysing industries and competitors, Simon and Schuster, Chicago.
Reuer, J 2004, Strategic alliances: theory and evidence, Oxford University Press, Oxford.
Sahaf, M 2008, Strategic marketing; making decisions for strategic advantage, PHI Learning, New York.
Smith, M 2014, UAE’s Etisalat sees fixed line telecom competition by year end document. Web.
Sutherland, J & Canwell, R 2008, Essential business studies for Aqa As Le, Folens Ltd, London.
Ungson, G & Wong, Y 2007, Global strategic management, M.E Sharpe, Armonk.
Webb, M & Gorman, T 2006, Sales and marketing the six sigma ways, Kaplan Publication, Chicago.
Wit, B & Meyer, R 2004, Strategy: process, content, context; an international perspective, South-Western College, New York.
Appendix 1
Etisalat’s long-term rating and outlook.

