Introduction
This essay is divided into two parts. The first part deals with the issue of increasing productivity with relation to market conditions. The two companies studied were Ford and Toyota. Ford has been able to increase productivity with lean manufacturing methods while Toyota has developed its own technique called Kaizen. Through this they have been able to increase productivity even in a competitive market through increasing demand for their products. The recent global recession has hit both companies hard. The second section compares characteristics of growing and mature markets. Some of the features that set them apart are sophistication and knowledge of customers, level of competition, pricing, commonality of product features. Companies can make use of techniques like the Boston Matrix to recover costs in growing and mature markets
Business analysis & decision making
This study deals with the Business analysis and decision making.
Increase the productivity is very important to every manufacturing company in the market. Productivity can be defined as the ratio of output against input. The perfect utilisation of resources will improve the ratio between this and reduction in cost. Efficiency is a tool to measure any industry organization’s performance while productivity used to measure this efficiency. (Saman and Ying 2002). “Car manufacturing is often associated with poor working environment resulting in Musculoskeletal disorders and high sick leave among assembly workers. Besides, a number of studies have proven that there is a clear correlation between assembly ergonomics and product quality and that poor assembly ergonomics result in impaired product quality and in decreased productivity.” (Annki, Roland and Dan).
To improve productivity, different techniques have been developed.To tackle obstacles from various areas like work study, quality improvement tools and line balancing techniques. Toyota is currently the world’s largest automobile manufacturer, a position it took from the former world leader Ford. The market capitalization of Toyota nearly five times more when comparing with the total market capitalization of both Ford and GM. The company’s policies are obliviously correct because of its superior productivity when compared to other auto manufacturers. This trend has been with Toyota for the last twenty years. Toyota’s example offers an excellent insights and a guide toward improving personal productivity. Toyota officially became the world’s number one automobile manufacturer by volume, by adopting the different techniques in productivity enhancement.
Methods to Improve productivity
Improvement in productivity is a challenge to every manufacturing industry but making it is not an easy job. There are some good methods that are proved to be very significant. Analyzing, measuring and setting goals is obviously one of the best ways to improve performance and productivity. (Improve Productivity. 2009).
Toyota motor company is adopting the Kaizen to improve productivity at its plants. Kaizen is a Japanese term which roughly means continuous improvement. Kaizen operates in a unique way in the sense that it brings about improvements in the process without adding more human components into the system. This will help to reduce costs while at the same time help to improve productivity. (What is the Goal of Lean Manufacturing. 2009).
The following are the greatest methods to improvement in productivity.
Increase productivity with Real-Time Goals: The main problem is that reduces productivity is that the floor employees are not informed about the production goals. Thus to improve production they must be delivered with real-time production goals. Should display a shift or job based goal. Normally people respond to information which tells them about the production goals. This will increase the productivity to a great extend.
Monitor small stops and reduced speed operation: The problem in this subject is that the major down time events appear to be under control but the process continues to miss target production. To resolve this problem, getting a handle on small stops and reduce the speed of operation can be adopted. It is easy to determine the downtime because the equipment or process is simply not running small stops and reduced speed operation. One of the best ways to monitor performance in manufacturing is the use the OEE performance. (Improve Productivity. 2009). Tackling the Six Big Losses: The six Big Losses are the common causes of efficiency loss in manufacturing industries. By knowing what are they and how to tackle them is the key to fast and long lasting improvements in productivity. Reduce change over time through Training and awareness: Usually the changeover time is very much affecting the production efficiency. We can Reduce change over time significantly through training and awareness to the employees. Using color coded data (say red and green) will reveal change over time to employees in the shop floor. This will help to reduce the time required to complete tasks in the shop floor. (Improve Productivity. 2009).
Productivity at Ford and Toyota is highly related to the sales volume they have generated. To become the world leader in car sales Toyota has innovated quality improvement techniques like the Kaizen technique. The Just In time and jidoka are the famous tools they have adopted for the quality production. Toyota also rely upon the cost management –that is reducing production cost and increase productivity. It is stated that productivity and sales volume or the growing car market is inter related. To come to the point we have to analyse the sales volume and produced units in the market for a particular period. For example. Profit at Toyota Motor jumped 29 per cent in the quarter of August 2004 as result of increase in the sales volume increase. As a result the company has raised its production in all the units. Thus it can be proved that a growing market is necessary to increase productivity at plant. In fact Toyota was able to stimulate sales volume in all the major markets shows that Toyota’s market demand.The company could achieve this much profit by doing the production improvement techniques like cost reduction and just in time methods. ”Toyota said such cost-saving measures increased its operating profit by 40 billion yen ($361 million) for the quarter just ended.” (Zaun 2004).
By adopting relevent marketing strategies Toyota achieved its aim of 9 million for the year 2006. According to Koji Endo, an auto analyst who works for Credit Suisse Japan, it is difficult to for Ford to overtake Toyota’s momentum. “Toyota sales are booming because of its good image around the world about reliability and ecological technology. (Toyota Overtakes GM in Global Vehicle Sales. 2007).
In the case of Ford Motors, even though the market in the Europe faces a declining trend could make a growth in market share. Ford Europe sold 1149800 vehicles in its main 19 European markets in the first nine months of last year. They could achieve this high production because of the market growth in the industry. The sales volume growth indicates that a high market demand is inevitable for achieving high production.
For achieving this superior productivity both Ford and Toyota has adopted improvements in production methods, Methods like just in time and cost reduction, and real time production techniques have been used.
Discussion regarding whether growing market is a precondition for superior productivity
The discussion can be started with how the market growth affects the manufacturing units.It is noted that all the products in the markets are affected by market demand. Thus the production of units is related to market growth. But productivity in the other sense is not directly related to market demand. Companies normally produce more if there is more demand in the market. In the case of Ford ,they have reported significant losses through the first half of 2008 and Toyota could managed to increase the market share to 16.8% and made a $3.8 billion profit for the second quarter in 2008. But the company is predicting a total sales decrease in the year 2009. Toyota was forced to bring down its sales targets on a global level to a relatively small extent. The target was brought down to 9.5million from9.85 million. (Ireson 2008).
A study on the subject stated that in the US the General Motors is contracting as it losses sales.But Toyota is expanding as it takes more market share in the US. Toyota is gaining ground at the same time. From 12.2 to 13.5 per cent increase has been expected in the market share. Toyota could achieve this sales volume in the middle of crashing market conditions. Toyota can produce more units in the middle of down word market conditions. Their productivity is increased during the low market period also. Thus the condition of growing market is not at all a precondition for productivity. Above all Toyota is very methodical about growth.It doesn’t want anything to do with growth in leaps and bounds because, that is the only thing a company can grow sustainably. There should be a long term vision and a commitment to stick to it. In the case of Ford motors across all the 51 European markets the company has sold 157700 units in the year 2008. The company is facing a down ward trend in their market share. But the productivity in not at all affected by the declining market.In a difficult economic environment Ford could improve the overall market share last year with the help of the strongest product lineup.The company feels that the above measures will help them to cope with the current economic crisis that is facing the global market and even managed to increase market share in 15 of the 19 European markets it operates in. Even with a deep economic crisis for as long as it lasts, the company did not reduce the production capacity in plants. Thus we can conclude that productivity is not related to market conditions.
Growing and mature markets
Marketing is a complex task because of the nature of the markets in which the company operates. There is wide diversity with regard to the stature of a market. The main classification that markets are divided into in this respect is growing markets and mature markets. Growing markets as the term signifies is a place where there is enough scope for all the players in the market to make profits. There is demand for the product and the levels of competition are not very high. A mature market on the other hand is a situation where there is no scope for growth and similar products are marketed by a large number of companies. There was a period soon after marketing was seen as profession where all markets were highly conducive to growth. The advent of industrialization and mechanization resulted in the introduction of a diverse variety of goods and commodities. At this time there were only a few companies engaged in manufacture and marketing of these goods. Moreover, the economy especially in the United States and UK were growing especially during the period of reconstruction after the World War II. Marketing was not a very sophisticated function during this stage and companies could succeed by implementing basic marketing strategies. But over the years, this situation changed. “The most significant change to impact on Western companies since that time has been the maturing of the markets in which they compete.” (Christopher and Peck 2003, p.2).
This section will compare and contrast the characteristics of the two types of markets mentioned above. Examples of such markets will also be provided.
Comparison of characteristics of mature and growing markets
As is expected, each type of market whether it is a mature or growing one will have its own characteristics. This section will focus on the characteristics of mature markets. There are four characteristics that are seen in mature markets. It can be said that if these four are present in a market to a large extent the market can be considered to be mature.
Experience and sophistication of the customers
Mature markets are characterized by high level of experience of the products and also the need for higher levels of sophistication in them. The colour television can be given as an example. By the 1980s the market in the USA was matured with regard to the number of models in the market. By contrast, the market was nascent in other areas, for example in India. In India, colour television broadcasting began only in the first half of the 1980s. At that time and for almost a decade later, almost every manufacturer (or assembler) could find a market to sell their products. Many small and medium sized units emerged during this period and they could survive to a large extent because the market was growing at a phenomenal rate. Almost every single black and white TV in the country was now being replaced by colour televisions. Many of them had only standard features and limited number of channels. In other words the product was quite unsophisticated and users had very little experience. There was only government owned channel and viewers were ignorant of the vast entertainment potential of the TV broadcasting industry. Once the skies were opened to private players with the introduction of cable and satellite television, the situation changed dramatically. Now there are a plethora of local and international channels. Broadcasters now talk in terms of prime time and viewership ratings. People take part in opinion polls and now want specific entertainment content which is being provided by different broadcasters in a highly competitive market.
Equality in product functionality
In a mature market, many of the competing products have similar functionalities. The electronic products industry is an ideal example. Mobile phones come in a variety price ranges. Each price range is perceived to be attractive or affordable for the people with differing income levels. But in most cases, products that are seen as acceptable in the market have more or less similar functionalities. The most basic model across made by all manufacturers will only have basic features. For a higher price range, the functions that are common will include a camera, and facility to play music. Another price range will be characterized by the inclusion of features like Bluetooth and GPRS or web browsing facilities. In mature markets, companies often bring in new features to bring about product differentiation. But this will soon be copied by competitors bringing balance into the product functionality. It can be seen that within a price range features will be more or less similar across all competing models. In a growing market, the demand for the product will be so high that only basic functionality is needed. Additional features will be made available for select models and will be bought by only those who can afford the high price of such sets.
Buyers’ and sellers’ market
A mature market is a buyer’s market while a growing market will usually be a sellers’ market. In a buyers’ market there will be many companies trying to market the products to a limited market while in the latter case, there will be more buyers than what the companies produce. In a mature market, the buyer has the option to choose from many similar products having commonality in features. This is not found in growing markets. This is because companies can sell products that have only basic features because the demand for the basic functionality is high. The transition from growing market to mature market is characterized by the fact that buyers will have more choice in the products giving them more power. This transition from a seller based market to a buyer based market is a critical feature in marketing.
Pricing
In a growing market demand for a product often outstrips its supply. In such a scenario sellers can price the product higher than what it is really worth. Even so, there will be demand for the product. But in a mature market, the level of competition will be high and pricing will be kept to a minimum (with maximum features) in order to market the products. Pricing is also the result of the effect of the earlier three factors.
The current marketing scenario is seeing a major change. The concept of globalization and free trade has made the level of international competition very high. In that sense the global market place is shifting from a growing stage to a mature stage very quickly. Government policies that once protected domestic trade has now changed in many countries. Branded international products once unavailable in such markets are seen freely and have led to an increase competition. In that sense, globalization is speeding up the transition of many markets from growing to mature ones.
Cost recovery
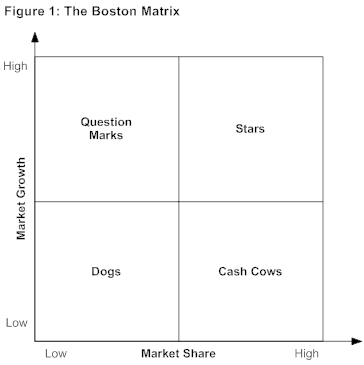
This area of finance can be done with the help of the Boston Matrix. “Also called the BCG Matrix, it provides a useful way of looking at the opportunities open to you, so that you can pick the ones that will give you the best results.” (The Boston Matrix. 2009). With the help of this matrix it is possible to identify which products are making good profits, and also those which are becoming outdated and hence not worth putting investment into. The BCG Matrix has four quadrants (as shown in the figure below). The individual components in the quadrant have been named dogs, cash cows, stars, and question marks. The X axis shows decreasing market share as it moves towards the right. The Y axis shows increasing market growth (moving towards a mature market stage) as it moves upwards.
Companies should first see in which quadrant their individual products (or class of products) lie. The dogs lie in the bottom right quadrant indicating low market share in a low growth market. It is difficult to recover costs (if not already done so) and hence should be removed from the company portfolio. A new product which is not needed in a market during low market growth will also come into this category. The cash cows come in the bottom right quadrant and denotes high market share in a low growth market. This product is generating lot of profits for the company even without any additional investment (or even advertising) because they are well accepted in the market. In most cases, the cash cows do not stay that way for long especially in a growing market. The stars are those products that enjoy a high market share in a high growth market. The point is that a lot of investment and promotion will be needed to maintain them as stars. The question marks are those enjoying low share in a high growth market. They can become dogs or cash cows depending on many factors and hence shown as question marks. The cash cows should be maintained as long as they are profitable. The dogs should be taken out as soon as possible. Stars also should be maintained like cash cows. The question mark product should be maintained for a short while until the company understands the way in which the product will move. It will also depend on the resources of individual companies.
Bibliography
ANNKI, Falck., ROLAND, Ortengren., and Dan, Hogberg. The Influence of Assembly Ergonomics on Product Quality and Productivity in Car Manufacturing a Cost Benefit Approach. [online]. Web.
CHRISTOPHER, Martin., and PECK, Helen. (2003). Marketing Logistics. [online]. Butterworth-Heinemann. P.2. Web.
Improve Productivity. (2009). [online]. Vorne: Visual Displays & Productivity Tools. Web.
IRESON, Nelson. (2008). Toyota: Sales Down But Market Share up. [online]. Motor Authority. Web.
SAMAN, Muhamad Zameri Mat., and YING, Law Cheak. (2002). Work Improvement at a Car Manufacturing Company. [online]. Web.
The Boston Matrix. (2009). [online]. Mind Tools: Essential Skills for an Excellent Career. Web.
The Boston Matrix: The Matrix Itself. (2009). [online]. Mind Tools: Essential Skills for an Excellent Career. Web.
Toyota Overtakes GM in Global Vehicle Sales. (2007). [online]. Msnbc. Web.
What is the Goal of Lean Manufacturing. (2009). [online]. Gembustu Consulting. Web.
ZAUN, Todd. (2004). Global Growth Gives Toyota 29% Rinse in Profit. [online]. The New York Times: Business. Web.
