Introduction
Forever 21, formerly Fashion 21, is a global fashionretailer headquartered in Los Angeles, Californiapopular for its low priced and trendy offerings onwomen, men and children’s apparel, shoes, style accessories, beauty products and home goods (About Us | Forever 21, 2020). From a small shop founded in 1984 by South Korean husband-and-wife immigrants, Do Won Chang and Jin Sook Chang, the company grew as a chain of stores (Ciment, 2019), eventually perfecting the fast-fashion model whereby it appeals to customers through itsinexpensive clothing assortment
Forever 21 flourished in the early 2000s and successfully peaked in 2015, with $4.4 billion in annual global sales, 43,000 employees in over 600 stores worldwide and its founders’ net worth reaching $5.9 billion(Ciment, 2019).
However, the downhill route began soon after, when mall traffic and sales were significantly decreasing due to consumer shifting preferences associated with the threat of rising fast-fashion competitors and online retail, undesirable brand reputation from originality and copyright lawsuits, environmental concerns and labour rights issues (McCarthy, 2019). Combined with increasing rental costs resulting from rapid brick-and-mortar stores overexpansion in the past two decades and the seemingly unsuitable family-run management structure and style of a massively expanding company (Maheshwari, 2019), Forever 21 lost grip of its success.
What started as a rapid rising family-run teenage clothing retailer deteriorated in liquidity, operations and sales, forcing it to filefor Chapter 11 bankruptcy protection in the US in September 2019 (Meyersohn and Isidore, 2019). The move for bankruptcy filing protects Forever 21 from its creditors while allowing them to retain operations under supervision and until a concrete repositioning and restructuring plan to revive the company financially is finalized and approved (Berfield, Ronalds-Hannon and Coleman-Lochner, 2020).
This report aims to provide an overall strategy that will help turnaround Forever 21’s current condition and continue as a going concern company with improved liquidity and profitability. The first part of the report will discuss the relationship of strategy, stakeholder expectations and organizational performance using Porter’s Generic Strategy, analyse the internal and external factors using SWOT and TOWS matrix, outline the overall business strategy and implementation plan. The second part will primarily focus on the recommended organizational redesign of the company.
Linking Porter’s Generic Strategies to expectations and performance
The foundation of Forever 21’s brand value and organizational success, as it is seen in its mission and vision,continue to stem from itscustomer commitment to deliver the latest fashion at affordable prices, consistently challenging its overall supply chain to be aligned while maintaining strong favourable relationships with its vendors, landlords and creditors. With the current state of Forever 21, it is crucial to re-evaluate its strategy to learn about new stakeholder expectations, proactively bridging them towards an upward company performance despite varying environmental and general conditions.
Porter’s Generic Strategy
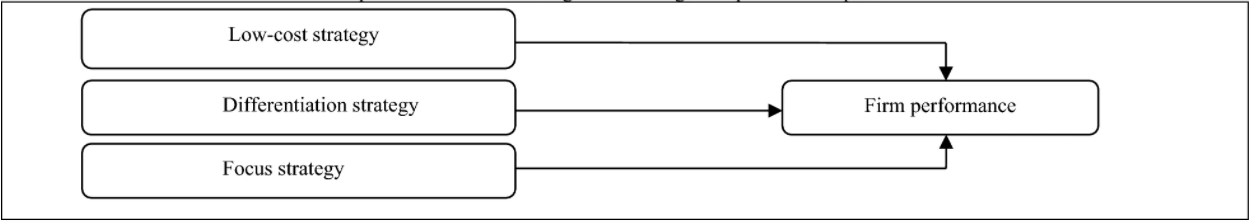
We choose to execute Porter’s Generic Strategiesas an effective strategic management theory to determine Forever 21’s direction and achieve competitive advantage above the average industry performance and will be based on three generic strategies for meeting customer requirements: cost leadership, differentiation, and focus. This theory emphasizes that solid company performance strongly relies on a singular focus of a generic strategy (Dombrowski, Krenkel and Wullbrandt, 2018), however other researchers would argue how an Integrated strategy may be required due to dynamic market situation and emerging market opportunities (Stages and Types of Strategy | Principles of Management, 2020).
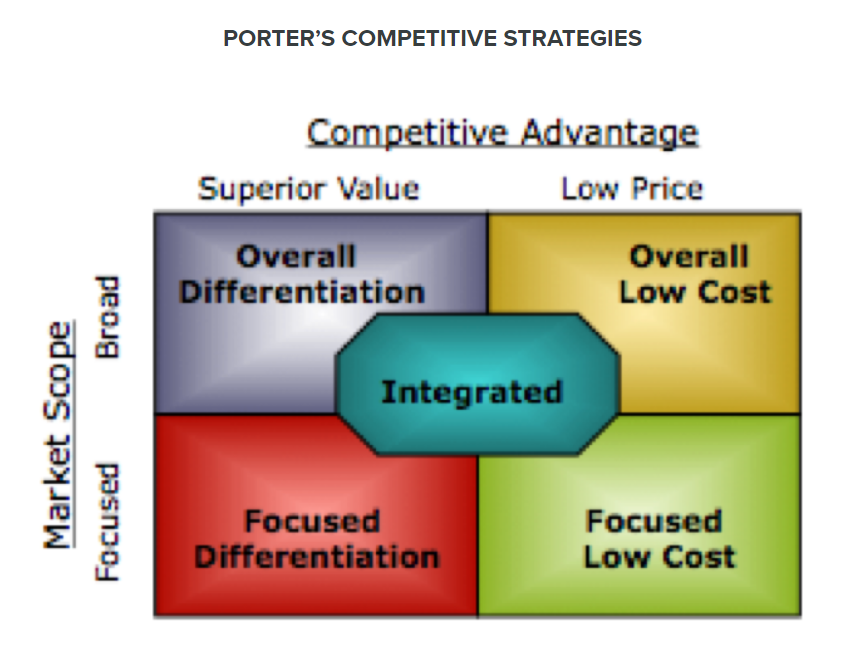
Cost leadershipstrategyimplies that Forever 21 targets a large market by offering lower product costs to a wide group of customers than its competitors. The ability to sell at low cost is dependent on how well it exploits all sources of cost advantage to enhance low-cost production:from preferential access to labour costs and raw materials, proprietary technology, and economies of scale and how well the company streamlines its internal processes encouraging high efficiency, low wastage and overhead (Islami, Mustafa and Topuzovska Latkovikj, 2020).
Differentiation leadershipstrategy, on the other hand,aims to develop and market unique products for different customersegments in the industry based on its varying criteria like product or quality feature and customer service, never sacrificingconsumer preference and leveraging this to the company’s benefit through premium pricing strategy or consumer loyalty(Dombrowski, Krenkel and Wullbrandt, 2018).
To be differentiated amongst its fast-fashion competitors, Forever 21 has to invest in competent market research to harness consumer preference, capitalize on innovation, high-quality delivery and effective marketing that will communicate the benefits of the unique product and features to the broad market. The focus generic strategy is determined with the option between cost focus or differentiation focus that is applied towards a certain geographical area or a segment of customers termed as niche market (Tanwar, 2013). Forever 21 can create exclusive product features and services to match its unique target market segment. However, in today’s competitive market, customers expect unique products at low cost, hence companies have adopted the Integrated strategy to provide more value for money by satisfying customer desires for appealing quality and features yet maintain relatively low-cost pricing compared to its competitors (Edwards, 2014). Integrated strategy is often termed as best-cost strategy as its hybrid approach particularly favours an extremely competitive market situation where product differentiation is normal because of the diversity in customer preferences.
Forever 21’s current Cost Focus strategy
Since its founding, Forever 21 has primarily used a cost focus strategy by selling low-cost apparels to young customers aged 18-30 as their target market, with a blend of segmentation across all product areas and demographics in this niche (Bhasin, 2019). They have been seen to maintain long lasting vendor relations that gave them favourable trade terms allowing them to offer inexpensive clothing quickly to the market. Forever 21 became the cost leader in the industry for several years, but not until their own growth strategy in terms of brick-and-mortar stores and customer base expansion caused them to lose touch with their niche, that despite the efforts, sales and profitability were unpromising as the company ignored essential differentiation factors such as the quality and delivery of their products, their ability to see trends and create appealing styles that resonate to customers (Bamberger, 2021), their neglect of supply chain that failed their ability to provide fresh designs speedily in the market (MacCollum et al., 2020), their delayed digital redesign and online adoption, and while competition and shifting customer taste and preference to mall shopping and sustainability has also massively increased (McCarthy, 2019). This was a clear indication of the interdependence of strategy, stakeholder expectation and company performance (Maheshwari, 2019).
Adopting the Integrated Strategy
Fundamental to the going concern objective in this crucial stage is an integrated cost and differentiation strategy focused on a back to basics merchandising initiative that will reinforce the company’s core strength of identifying trends and offering core product categories that are low cost and trend right to customers. Forever 21 will continue to leverage on the brand of low pricing and trendy offerings, but will combine it with differentiation strategy, turning around its reputation and sales, by improving quality of the apparels making it comparable to its peers in the industry(Ziggers and Henseler, 2016), adopting a slow shift from replicating current trends to creating its own brand identity and authenticity in design as part of innovation (Roll, 2018), and promote sustainability across its products and processes (Joy et al., 2012).
Low-cost strategy is good but being trend right and aligned to customer taste and demand is a tactic that will meet consumers right at the core of their expectation – and this should never be neglected this time. How well the strategy will sustain and cater the appropriate product to their customers at the right time at the right price more effectively and efficiently than its competitors in the industry, will allow Forever 21 to gain a competitive edge in the face of affordable designer market in the fast fashion industry (Karimi and Huatuco, 2019). If implemented the right way, the use of this Porter’s strategy presents a positive effect on Forever 21 performance.
The overall corporate and business strategy will be further discussed in Section 4 of this report.
Impact of external factors on strategic management
This section will identify and evaluate the effect of external aspects on Forever 21’s strategic management using PEST analysis tool, narrowing to only political, economic, and cultural aspects. This analysis will equip us with the right understanding of the current environment that will be useful in implementing our strategy.
Political factors
The political factors affecting strategic management in the global context depends on how and to what extent the government interferes in the economy and impact the ease of conducting business in locations that Forever 21 choose to enter. It may comprise political instability or stability, government policy, tax policy, trade restrictions, environmental law, and labour law which can influence the economy as a whole, the consumer buying habits and eventually the sales and profitability of Forever 21 stores. As Forever 21 choose to enter and operate in a certain country, it has to consider regulations that can affect the import, export, sales and taxation of its products. In some countries, direct foreign investors are also limited making it difficult for Forever 21 to expand to these locations. Furthermore, in cases where trade embargo is introduced against imports from another nation would compel apparel retailers to look for different suppliers and change their sourcing strategies.
When imported apparels are expensive due to the trade tariff or taxation policy, promotion of locally made apparel brands and domestic designers becomes a common practice (Dobrosavljević and Urošević, 2020). Additionally, Forever 21 as it has employed approximately 43,000 worldwide, has to consider the varying labour law requirements in each location and ensure its employees are paid accordingly. Forever 21 has to properly weigh-in the consequences of prioritizing its internal cost structure versus being labour law compliant at all times. Additionally, in the recent trend and prioritization of online shopping, the government has also interfered by putting regulations on antitrust issues and data breaches, as such Forever 21 is compelled innovate and improve their e-commerce platform to comply with these regulations.
Economic factors
Economic aspects have a substantial effect on how firms in an industry conduct their businesses and how profitable these businesses are. These aspects comprise interest rates, economic growth, and disposable income of buyers, inflation, and employment. Growth in the international economy will also influence growth in the clothing industry, hence, provides higher opportunities for the globalization of apparel brands (Chavan, 2018).A rise in the disposable households’ income such as that seen in OECD nations for the past years implies more disposable income for customers to buy apparel that increases sales of fashion retailers like Forever 21, however, a declining rate of employment in the OECD nations implies lower purchasing capacity (Dobrosavljević and Urošević, 2020). As Forever 21 expands to various locations, the opportunity to provide additional employment down to its supply chain contributes and gives back to the economy.
Market conditions can also influence business operations positively or in adverse. The market recession leading to the real estate crash in 2009 may have been disadvantageous at certain aspects but it did also provide Forever 21 the best opportunity to increase its physical presence during that time, as landlords offered prominent locations at low advantageous price in order to survive multiple vacancies during the crisis.
Now in 2020, COVID-19 pandemic is also driving negative economic results from travel restrictions, mall and business closures, high unemployment rates, unpredictable consumers buying habits from malls to online and from cash to cashless payments. All of these has further impacted Forever 21’s sales and profitability and confused the company’s efforts from rising above bankruptcy to overcoming the corona virus situation (Clark, 2021). The uncertainty of when the pandemic ends is the same uncertainty shared by countries, economies and business as to how and when they can bounce back.
Socio-cultural factors
Cultural and societal changes and trends have an effect on Forever 21’s business based on how consumers’ choices and preferences shift over time, which can be linked to demographics, education, beliefs and a lot of other factors. The ability of the company to understand these social and cultural factors, to adapt and stay ahead in the industry and continue to be relevant in the customer’s minds. Fashion and styles are always changing, and this is interlinked with consumer preference and effective influential marketing (Matsoma and Ambe, 2016).
What is fashionable today might be outdated in the next year, so the ability of Forever 21 to harness the opportunities on varying preferences and use marketing as a tool to create a trend is critical to their success.Changes in demographics is also an important factor. For example, it has been noted for years that there is an increase in a global aging population. Such an adjustment in demographics can lead to a threat to teen-centered clothing companies since the competition for their market segment is declining, creating stiff competition(Chavan, 2018).
To be able to exploit the maximum opportunities Forever 21 has in the market, extensive market research is essential to understand the culture, beliefs of the country, including the behaviour, buying habits and attitude of its target customer base (Mazovic, 2018). There are two considerable changes in customer preference that continues to challenge Forever 21’s business: preference to technology and sustainability. The decline in mall traffic which led to the significant decline in Forever 21 sales created maximum pressure for the company to focus and improve its e-commerce platform and online presence in order to beat the significant shift of consumer preference from in-store to online shopping.Rising sustainability concerns also demands businesses nowadays to share and imbibe green conscious values and efforts in their products and processes, reducing wastage, upcycling, recycling and reducing devastating impact on the environment otherwise could potentially impact projected sales (Fashion Fail: Where Did Forever 21 Go Wrong?, 2019).
New Strategy Formulation
This section utilizes the TOWS matrix to depict the current internal and external environment of Forever 21, and provide a strong groundwork to evaluate, establish and ultimately formulate its new strategy.
TOWS Matrix
Figure 3: Forever 21 TOWS matrix.
Formulating the Turnaround Strategy
The above diagram demonstrates how SWOT analysis and TOWS matrix is an effective tool in linking identified external and internal factors and formulating strategic options. In this section, we will describe the overall Turnaround Strategy that has been formulated to overcome the current challenges and meet the organizational objectives of Forever 21. This is also guided by the chosen Integrated Cost and Differentiation (Best-Cost) Strategy in Section 2C and was based on the result of the PEST analysis and TOWS matrix in the earlier sections.
Capitalize on strength to maximize of opportunities
- Creating a new brand identity of sustainable and uniquely designed product lines. The company should offer products that remain trendy always, and the reality to matter is always offering the latest trends for its consumers in all dimensions (Bhasin, 2021).
- Optimizing marketing and social media initiatives. Forever 21 should increase its marketing and social media interactions to get consumer feedback and comments on their products and suggested changes and ideas.
Take advantage of opportunities to overcome weaknesses
- Re-align merchandising approach based on integrated cost and differentiation strategy that will focus on product assortments that are trend-right and affordable. The company should focuses more on innovation and constantly provides consumers with something new in their stores daily (Rawung and Salindeho, 2020). The brand should be affordable for a majority of its consumers, and offerings are unique at fair values.
- Rightsizing physical store footprint and expanding e-commerce offering. The company need to reduce its brick and mortar stores and increase its online retailer business as it is easy to maintain.
- Streamlining the end-to-end supply chain business processes through innovation, technology, lean and agile methodologies to achieve operational excellence
- Reducing operational costs at store, field and corporate level. It can be achieved through advanced technologies application and online marketing through social media sites and email marketing.
Leverage strengths to avoid threats
- Investing in product development to capture existing market and product diversification to capture demands of a new customer base
- Optimize branding through good corporate social responsibility
Overcome weaknesses and threats
- Addition of new directors and executives in the existing family-run management team, plus hiring a strategy and change management team, to work on Forever 21’s restructuring and turnaround strategy
- Enhance customer experience through capturing their feedback in real time and creating emotional connection with Forever 21’s consumers.
Evaluate and justify why this is the best way forward
The above strategy of integrated cost and differentiation will be advantageous because of the current turbulent and dynamic business atmosphere where companies are constantly plagued with an urge to attain improved performance. This is expected to work as a catalyst for accomplishing optimum organizational performance and establishes synergy in the operations of the company in the market, and hence, offers an opportunity for Forever 21 to excel in areas not exploited by its competitors (Phung and Mishra, 2016). It will create a better chance for the company to bounce back into a leader in the fashion industry. Since cost leadership strategy has become untenable; the turnaround strategy grounded on Porter’s integrated cost and differentiation strategy will be the best way for the company.
Benefits of the new strategy
Forever, challenges leading to it filing for Chapter 11 of bankruptcy protection in the United States and eventual closure of 350 outlets from the over 800 global retail outlets. The blame has been pointed at the company’s lagging in sustainability and innovation efforts for its market decline. The brand failed to keep up with increasing business modernization, supply chain, and digital presence. Successful brands expand and change, and no brand can remain the same.
The company focused on the same strategy of cost-leadership, whereas the apparel market keeps on changing. The business also focused on one segment with the same products, which become more emphasized, leading to declining in sales and competition with others who implemented the same strategy (McCarthy, 2021). H&M implemented a cost leadership strategy that is being utilized at Forever 21, making it untenable for the company to continue using it alone to enhance its competitive edge in the market.
However, the adoption of the integrated cost and differentiation strategy at the company will be of benefit in attaining its competitive advantage. Product differentiation and diversification may be applied by a firm to improve profitability and attain higher revenue volume from selling the new products. The company can apply business-level product differentiation to permit it to expand its business into the new segment in the fashion industry where it is currently operating. Besides, there are many ways Forever 21 will opt to differentiate its product (Phung and Mishra, 2016). The company may opt to use product differentiation, service differentiation, relationship differentiation, price differentiation, reputation differentiation and distribution differentiation.
Furthermore, Forever 21 can add similar products to its current business offerings. For instance, the company has focused more on teen products. With the increasing needs of the youths, they can innovate or come up with the same products but with unique qualities and prices that favour their teen’s market. The approach will expand their consumer base and offerings, which in turn improve their performance.
Besides, differentiation with the same products and sell them to a familiar consumer base presents less risky other than creating a new different product for the new market. It is the best way the company can sustain business stability. Integrated cost and differentiation strategy presents Forever 21 with the opportunity to change and enter into business lines that are the same from existing operations that require innovations and change (Bamberger, 2021). Business growth entails a substantial increase in organizational performance objectives, and this should be far beyond the past levels of Forever 21’s performance. Product differentiation and price differentiation will permit the company to hedge its bets, and when one of its products or markets fails, they have another to support them until recovery.
Through integrated cost and differentiation strategy, Forever 21 can modify or change its advertisement approach and invent the modern ways to reach a wide consumer base. For instance, the company may opt to use social media in its advertisement as its products mostly centre on the youths. It will create an opportunity to receive feedback on the increasing needs of the teens. Hence, create an avenue to develop new products that suit the needs of the market. The avenue will call for change in the company management and operations (Bamberger, 2021).
The feedback will help the company develop sustainable ranges whereas keeping its primary value drivers. It assists Forever 21 in retaining relevance and venture into a projected shift towards slower replacement patterns in the fashion industry.
The cheap fashion model was a competitive advantage during the 1980s. In this modern time, that is not the case, hence cost leadership strategy fails. There is a need to diversify its product offerings to the current youths who keep on changing their needs. Diversification will facilitate the company to create a competitive platform because competitors have ensured that developing a brand is far beyond the single strategy of cheap fashion model offerings (Bamberger, 2021). Forever 21 need to add some dimensions to remain relevant in the fashion industry. Hence, investing in research and innovation will help to bring the change needed through product differentiation.
Integrated cost and differentiation strategy needs to ensure that Forever 21 sustain advanced physical retail consumer experiences. Consumers shopping for apparel fashion models are an experience of looking for something that corresponds to the bill for the new job, a night out, or a date. The company needs to maintain a laser concentration in the retail store, developing settings and well-trained workers that blend pop customs with the pop fashion design. Through such innovation and change, the company will experience growth in the market share and overall organizational performance to meet stakeholders’ expectations.
The firm needs to change from the tired featureless ranges of cheap apparel. Forever 21 should management and stakeholders need to understand that running the largest store in the world requires that pressure of change and innovation. Hence, integrated and differentiation strategy acting as a catalyst spearheads innovation and change in product offerings from the company. Consumers will be availed of a wide range of products to select from through continuous innovation and improvement (Phung and Mishra, 2016). Integrated cost and differentiation strategy, therefore, is of benefit in ensuring that this is achieved and improves organizational performance.
Currently, Forever 21 is playing safe as a retailer that is slow to embrace change and innovate. However, through the implementation of a product diversification strategy that enhances growth as successful organizations are pursuing more than one growth strategy. Besides, the perception held by a majority of executives and investors is that “bigger is better” in the business world. Hence, an increase in sales will be a great measure of organizational performance (McCarthy, 2021). The emergence of digital empires that serve a youthful population of Forever 21 in a dynamic and new way has made this target segment a saturated space. Hence, the implementation of a diversification strategy at Forever 21 allows it to remain relevant and competitive in the apparel industry.
Strategy Implementation Plan
The goal and objective of the plan
The goal of the company is to implement a integrated cost and differentiation strategy. The objective here is to enhance the company’s growth and save it from its immediate collapse in the fashion industry. Therefore, this integrated and differentiation strategy implementation will promote the achievement of long-term objectives such as growth and attaining a competitive edge in the fashion industry. Integrated cost and differentiation strategy implementation aims at improving Forever 21 conditions for long-term organizational performance.
Milestone and implementation phases
Forever 21 will have to add new products to its related markets or products to accomplish strategic fit in the apparel industry. Strategic fit permits the company to attain synergy. This is the capability of two or more sections of the firm to accomplish higher total effectiveness and efficiency together than might be encountered when the endeavours of the independent sections were totalled. Forever 21 can attain synergy by merging retail stores with complimentary financial, marketing, management, or operating efforts.
Forever 21 will be able to attain marketing synergy via global distribution and advertising. However, this may be met with opposition from the management as currently, the company spends less on marketing and advertising (Phung and Mishra, 2016). By merging several retail stores into a national network, the company will be capable of producing and selling more clothes and other offerings than had independent regional retail stores.
Phase 1
Forever 21 will need to empower and train its store managers and workers to be specifically sensitive to consumer wants and needs and how consumers enact them on the store floors. The company should facilitate these training and empowerment programs offering them free to avoid resistance from the employees when it requires them to pay for the training. It should also be communicated efficiently and effectively to stress the importance of training and empowerment to the workers to avoid misinterpretation and resistance to it. The company’s store managers and sales associates should be at the forefront of consumer research. Forever 21 workforces should intently listen to their consumers, and record comments, ideas for fabrics, cuts, or the new line, and keenly observe new trendy styles that its consumers are wearing that have the possibility of being translated into unique Forever 21 styles.
Phase 2
Forever 21 should implement complex technology-driven processes that facilitate information to move rapidly from the outlets back to its headquarters in Los Angeles in the US since it has empowered and trained its workforce to handle needed change. The company must also ensure that its consumers and designers are inextricably connected in its brand strategy (Bamberger, 2021). It will facilitate expert teams to get persistent feedback on the resolutions its consumers are making at every Forever store that persistently inspires the Forever 21 creative team.
Phase 3
After training its employees on the new approaches needed to implement in the company, the company, therefore, has an opportunity to introduce new products to diversify its offerings to the market. It can successfully diversify from its core apparel business to other products that are deemed relevant to consumers in its niche market (Bamberger, 2021). Forever 21 can utilize its power of the Forever 21 brand to develop unique experiences far from the clothing industry. The company may venture into chocolates, hotels, and flowers using diversification strategy and segmentation (Phung and Mishra, 2016). Besides, Forever 21 may segment its brands to react to various consumer grades in the fashion pyramid.
Phase 4
Forever 21 should also implement IMC (integrated marketing communication) combined elements applied to promote its product offerings. This will ensure that their potential clients and consumers get the relevant and right information concerning their service or product on time. It will help to reach out to a wide range of consumers and broaden its consumer base (Ziggers and Henseler, 2016). On its online stores, Forever should embrace consumers’ subscriptions.
Resource allocation
Forever 21 need to consider collaborating with the private-equity company to finance its large-scale restructuring plan to execute its integrated cost and differentiation strategy to achieve its objective of company growth and competitiveness in the industry. The resources need for strategy are human resources, capital, and consultation expenses.
Metrics for success
The metric of success is determined through attaining sustainable corporate profitability and growth. Successful implementation of the strategy demands management to convey the significance of growth and support the circulation and creation of new ideas to Forever 21’s workers. Since true success is found in understanding the business and creating the different parts that work together efficiently and effectively to achieve a common goal (Bamberger, 2021). Stakeholder expectations will be fulfilled through increased profitability and growth of the company in the fashion industry. This assures them of a stable share of dividends for the long term.
Adapting to change and overcome barriers
Forever 21 could avoid employees’ resistance to implementation by offering free training and empowerment. The company can adapt to change through the implementation of consumer research capabilities that will enhance innovation and change. The company’s product offerings in its outlets globally will depict unique consumer wants and needs in terms of their cultural, climate, or physical differences (Ziggers and Henseler, 2016). Through regular interactions between Forever 21’s local store executives and its innovative team, the company can offer different products.
In this clothing industry, a trend commences small even though it develops fast. Forever 21 workers need to be trained to watch, listen, and be attentive to the slightest seismographic signals emanating from their consumers that may be an initial indicator that a new trend in fashion is being created. This will require employee engagement in the decision-making to avoid resistance (Ziggers and Henseler, 2016). The company needs to understand that the swifter it may react to, and then most probably, it will thrive in supplying the correct fashion products at the right time around its international retail chain and gain a competitive advantage over others in the industry.
Forever 21 has to lean into being consumer-centered, distinctively motivated, and ruthlessly pragmatic as well as pervasively innovative to remain relevant in the fashion industry. However, establishing the leading brand requires sustainability and hard work through embracing a cost strategy while also following creativity and innovations in the product offerings to the target consumer segments. The company, therefore, has an opportunity to introduce new products to diversify its offerings to the market. It can successfully develop and diversify its product offerings that are deemed relevant to consumers in its niche market (Bamberger, 2021).
Forever 21 can utilize its power of the Forever 21 brand to develop unique experiences and may segment its brands to react to various consumer grades in the fashion pyramid. Consumers may buy the most expensive apparel at Forever 21 but also affordable and luxury clothes at the same stores based on different unique qualities (Phung and Mishra, 2016). Considering consumer insights in product design and development will increase their capability to compete and innovate new and unique products to the market.
Recommendation and conclusion
It is recommended that Forever 21 should retrace back to find and define its niche in its segments. The company had established its empire by offerings unique products line for the underserved niche-younger population at affordable prices. It can be recommended that the company should think of ways of product differentiation and price differentiation, it currently offers to its current consumer base. It may be tempting to perceive a wider product hub as appealing to a broader array of consumers. The company should be capable of fostering faster growth whereas keeping its initial niche –serving the youths (young adults) market.
It is recommended that rather than creating apparel to appeal to a wider audience, they should introduce accessories and clothing lines that centered the youthful that underpins the essence of the Forever 21 brand and creates them appealing to its target market. The company should also continue listening to its consumers. Forever 21 need to listen to their consumers’ pain points and create a life-improving product other than offering them another problem. Losing valuable insights from the consumers could end up harming the brand in the market. For instance, the concept of sustainability and sourcing apparel from greener options is increasing in population among the people.
In conclusion, Forever 21 should implement the integrated cost and differentiation strategy as it will spur its growth in the fashion industry. Forever 21will be capable of offering different products with unique qualities because of innovation. Forever 21’s should understand that its business model is a living document requiring revalidation and frequent update, mostly when they learn more about their target market-young adults are ever-changing. Hence, integration of the revision processes into its routine may re-build the core values that connect with its niche and initiate a positive consumer experience with Forever 21.
Organizational structure
An organizational structure refers to the system that highlights how specific tasks are directed to accomplish the company’s goals. The tasks may comprise roles, rules, and responsibilities. Besides, the structure determines how information flows between management and operations levels within Forever 21. Currently, Forever 21 apply a centralized organizational structure where resolutions flow from the top-down movement. Forever 21 is designed with centralized management and leadership aligned with a defined command chain.
The company operates as a military organization because it is highly centralized with the specific and long hierarchy of subordinates and superiors(Puranam and Maciejovsky, 2017). Forever 21 in its centralized system where there are defined responsibilities and duties for each department role with its subordinate roles defaulting to their supervisors’ guidance.
In Forever 21, the organization relies on the owners to create decisions and offer guidance for the firm. Hence, they apply functional structure. It is also known as bureaucratic organizational structure breaking up the firm according to Forever 21’s workforce specialization (Puranam and Maciejovsky, 2017). The company has been divided into units comprising operations, marketing, and sales.
The figure below depicts Forever 21 organizational structure (Orgio, 2021).
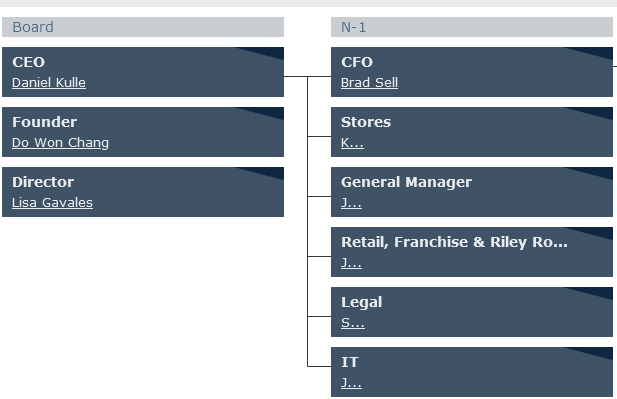
Forever 21’s centralized organizational system is effective in meeting the company’s objectives. The company is efficient concerning its business resolutions. Forever 21’s owners normally formulate the firm’s vision, mission and set objectives for their management team and workers to follow when accomplishing the goals. The command and decisions arise from a single source, and this enhances efficiency and effectiveness in its operations. Workers and management teams are obliged to follow one source of decisions emanating from the business owners. This avoids issues of confusion in the company’s direction.
However, Forever 21 has failed to succeed in its use of the current centralized organizational structure. Centralized systems reveal the negative impacts of many bureaucracy layers in the company that hampers the implementation of any designed change to the business model, mostly if it arises from the subordinate team. The company has many management layers that stretch from the business owners down to the line supervisors (Vitez, 2019). Further, the owners are accountable for initiating every resolution in the firm can demand more time to achieve the activities that may lead to slow business operations. It is typical for Forever 21’s decision-making to be from top to down push towards individuals closest to the company’s frontlines.
However, adopting a decentralized control will make Forever 21 operate faster and nimbler in initiating integrated cost and differentiation strategy recommended to enhance its current business model and improve its growth in the fashion industry (Puranam and Maciejovsky, 2017). Therefore, restructuring this centralized system is needed to implement the diversification strategy at the company. The company needs to restructure its organizational structure and adopt a decentralized organizational structure. A decentralized system allows its business units to function autonomously.
The best restructuring plan that Forever 21 can implement is right sizing its centralized decision-making system. It may be meaningful for the company to commence with deciding which resolutions should be maintained in a centralized system. It can begin with four features most managers want their company to have: reliability, responsiveness, perennity (continuity dependably in perpetuity or quality of being perennial), and efficiency. The company needs to think through all of these and select the most significant to each of its business (Vantrappen and Wirtz, 2017). In departments in which reliability is the most significant, for instance, consider maintaining autonomy centralized. In management or employees’ teams in which responsiveness or efficiency is most significant, then decentralization is the way forward.
Right-sizing needs a proactive approach other than a reactive practice that permits Forever 21 to shun fire-drill method cost reductions form of downsizing efforts. Rightsizing initiatives should be and can be initiated if there is no imminent pressure on the profitability or cost position. Downsizing can be an emergency procedure; fire-drill method cost-cutting actions typically creep into play if it is the most stakeholders that ideas cannot continue as they normally. However, ideas have turned out to be bad that resizing the Forever 21 is risky and painful.
Forever 21 is a large organization that seemed to have developed wasteful bureaucracy and operational inefficiencies over time. Hence, they can develop opportunities to review their company for waste, rightsizing them consequently, and establish additional, sustainable value for the long-term propensity and their stakeholders’ benefits (Batra, 2019). Proactive practices towards rightsizing begin with establishing the capabilities to recognize and implement opportunities that demand leaders to create the case worthy.
Evaluation of the restructuring plan and the proposed organization chart
Expected positive outcome
Rightsizing restructure plan will permit for a participative method to identify unnecessary cost, mistaken priorities, and waste. The restructuring will also help the company make good use of its talent and enhance its competitive edge while improving its profits and operational efficiency (Batra, 2019). Forever 21 will also reduce the company costs.
Anticipated challenges and possible risks
Restructuring demands centralized practices during the emergency cost cuttings to change implementation. Restructuring stress at times takes away the focus of the staff from their actual activities. Workers are worried when Forever 21 is not forthcoming with information about its restructure (Vantrappen and Wirtz, 2017). Rightsizing is a complex approach as compared to downsizing since it is a more sensible method. The complexity of the approach creates a possible risk of delay in restructuring. High levels of resistance and lack of stakeholders’ commitment to restructuring can also be the possible risks to experience. Further, Forever 21’s may experience budgeting risk for the restructuring process.
Ways to overcome and risk management plan
Forever 21 top executives should assume the lead, and specialists use external-in judgment (benchmarks) to affirm painful cuts (Puranam and Maciejovsky, 2017). The company may involve decentralized actors to contribute their best into the dialogue of how to be more efficient and effective (Batra, 2019). Conducting the resizing work before one is compelled to do it permits for productive stakeholders’ involvement, broad capacity building, and buy-in that reduces resistance to change issues.
Rightsizing Forever 21 implies mastering the process of rightsizing end-to-end. If cost cuttings exercises fail, this is because of the implementation failure. Therefore, the company needs a robust governance structure, committed leadership focus, enough resources, and metrics (Orgio, 2021). Forever 21 should look for a continuous focus on a restructured plan based on rightsizing because the method is complex.
The company needs to initiate a continuous rightsizing method that offers them an opportunity to implement adaptations and align them with the development plans (Vantrappen and Wirtz, 2017). This will help to address any risks that come with restructuring through rightsizing approach. In their risk management plan, Forever 21 and its human resource management will have to observe individual potential and skills, capabilities, and worker demographics as part of their work process as transformation is established to the processes and structure of the company to prevent resistance from employees and court cases for unfair dismissal.
Furthermore, Forever 21, in its risk management plan, can use management functions to allow self-directed organizational teams. Basic functions of management offer an initial point for the company to design, intending to allow self-directed groups and to improve decentralized decision-making in the firm to avoid resistance to restructuring (Vitez, 2019). Rather than leaders, expense reduction analysts and cost reduction consultants have to assess through and implement the critical process steps to accomplish cost reduction success.
Reference List
Bamberger, N., 2021. 3 Key Business Plan Components That Forever 21 Fatally Missed. Bplans Blog. Web.
Batra, A. (2019). Downsizing, Rightsizing or smart-sizing: A potion for organizational performance. Delhi Business Review, 20(2), 57-66. Orgio. (2021). Forever 21. THE ORG. Web.
Berfield, S., Ronalds-Hannon, E. and Coleman-Lochner, L., 2021. The failure of the Forever 21 empire – BNN Bloomberg. BNN. Web.
Bhasin, H., 2021. SWOT analysis of Forever 21. Marketing91. Web.
Chavan, R., 2018. Analysis of Fashion Industry Business Environment. Latest Trends in Textile and Fashion Designing, 2(4), pp.212-218.
Ciment, S., 2021. How Forever 21 went from a fast-fashion powerhouse to a brand reportedly eyeing bankruptcy and a troublesome future. Business Insider Africa. Web.
Dobrosavljević, A. and Urošević, S., 2020. CONTEMPORARY MANAGEMENT OF BUSINESS PROCESSES WITHIN THE SUPPLY CHAIN OF FASHION INDUSTRY. Fashion Industry, (2), pp.36-39.
Dombrowski, U., Krenkel, P. and Wullbrandt, J., 2018. Strategic Positioning of Production within the Generic Competitive Strategies. Procedia CIRP, 72, pp.1196-1201.
Islami, X., Mustafa, N. and TopuzovskaLatkovikj, M., 2020. Linking Porter’s generic strategies to firm performance. Future Business Journal, 6(1), pp.1-15.
Matsoma, N. and Ambe, I., 2016. Factors Affecting Demand Planning in the South African Clothing Industry. Journal of Economics and Behavioral Studies, 8(5(J), pp.194-210.
McCarthy, J., 2021. Forever 21 has aged: now it’s outflanked on sustainability, fast fashion and relevance. The Drum. Web.
Phung, D. and Mishra, A., 2016. Corporation Diversification and Firm Performance: Evidence from Vietnamese Listed Firms. Australian Economic Papers, 55(4), pp.386-408.
Puranam, P., and Maciejovsky, B. (2017). Organizational structure and organizational learning. The Oxford Handbook of Group and Organizational Learning, 5(4), 520-534.
Rawung, S. and Salindeho, M., 2020. Small-Scale Industries Development Strategy in Bitung City Using SWOT Analysis and TOWS Strategy. Society, 8(2), pp.783-793.
Vantrappen, H., & Wirtz, F. (2017). When to decentralize decision making, and when not to. Harvard Business Review. Web.
Vitez, O. (2019). Centralized vs. Decentralized organizational structure. Small Business – Chron. Web.
Ziggers, G. and Henseler, J., 2016. The reinforcing effect of a firm’s customer orientation and supply-base orientation on performance. Industrial Marketing Management, 52(2), pp.18-26.
