Executive Summary
General Motors is one of the largest automobile companies in the world. It provides all transportation-related solutions. The company has been facing negative profits and sales revenue in 2005-07. There are various reasons which are portrayed to be the main reason behind this problem.
One problem that we identified is due to the decline in the market share of GM in North America. Another problem is high operating cost and structural cost and low demand for vehicles in the market.
This paper tries to ascertain the problems which the company has been facing ad suggest possible recommendations and solutions to the problems presented.
Introduction
General Motors (GM) has recently declared a cut in white-collar jobs after the US economy hit the recession and there was a major slump in automotive demand in the US market (Barkholz and Sherefkin). There has been a decline in the sales revenue and net profit of the company since 2006. With the US economy in recession, the reason seems apparent. But are the negative profit figures attributable to a recession or there are other structural causes ingrained in the internal environment and operations of the company which result in this poor performance? In this paper we will discuss this problem that GM faces and will try to ascertain the reasons, not considering the US recession as the primary factor.
GM has been undergoing various problems which are comprised of both internal and external problems. The internal problems which troubled the company were excessive structural cost, producing cost-effective vehicles, market expansion, trade union problems, etc. the external problems included low market demand, reduced consumer spending, economic recession, government policies, etc. But do all these problems qualify to be the problem of the company? No. the reason being some of them are arising out of reasons which were not the outcome of an unattained objective or goal. So of these arise only due to exogenous causes on which the company has no control. So the problem which we will analyze in this paper will be an outcome of a goal that could not be attained.
The problem that the company is said to face is slowing market sales in GMNA which has caused a decline in market share and profit. To reach this problem extensive research has been conducted through the company website and peer-reviewed articles. Given this statement, the paper will aim to analyze the various aspects of the slowdown and try to ascertain a specific reason why the revenue fell in this region. But before we start our analysis we will conduct brief background research on the company to understand its operations better.
Company Background
GM is one of the world’s largest automotive companies. It was founded in 1908 in the United States and presently manufactures cars and trucks in 34 countries around the world (GM). The company is headquartered in Detroit and has an employee strength of 252,000. The company has its presence in 140 countries where the company sells and services vehicles (GM). The vehicles brands that GM has under its umbrella are Buick, Cadillac, Chevrolet, GMC, GM Daewoo, Holden, Hummer, Opel, Pontiac, Saab, Saturn, Vauxhall, and Wuling (GM). GM’s market share is largest in the United States followed by China, Brazil, UK, Canada, Russia, and Germany (GM). The company’s regional operations can be divided into five regions namely North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, Africa, and the Middle East.
The vision of the company is to be the global leader in transportation and other allied areas (GM Corporate Responsibility & Sustainability Report, 2006). To achieve the vision, GM embraces a corporate mission that embraces the following:
- “Anticipate external trends and changes that could affect GM’s business decisions
- Support corporate business and cultural objectives
- Develop and execute coordinated public policy strategies
- Ensure that GM’s strategic plans and operating practices take into account the changing public policy environment.” (GM Corporate Responsibility & Sustainability Report, 2006)
In order to the above stated vision and mission the company fosters a set of values which are ardently followed in the organization and forms a part of the company’s corporate culture. The core values which drive the business of GM are:
- Striving for continuous improvement by setting ambitious goals and trying to meet them, even if it means to do everything “better, faster, and more effectively in a learning environment” (GM Corporate Responsibility & Sustainability Report, 2006).
- They intend to make products which will make customers enthusiastic about the product they make.
- They believe in the virtue of integrity and honesty.
- Team work is an essential part of GM becoming the global leader with highly skilled and people and cultural diversity.
- Individual respect and responsibility becomes a common value which helps keeping a diversified company together.
GM culture prioritizes performance which may be in cars, parts, management operations, or culture. The main essence is to create a work culture based on high performance which aids to promote business results. Thus, their culture is customer centric, unity among the teams, work hard to attain big targets, and do the work fast. Clearly, the corporate culture creates a sense of “performance” based environment.
In 2008, there were rumors that after the bankruptcies of Merill Lynch and Lehman Brothers, GM too would file for bankruptcy, but the fear soon subsided (Whistle). The reason behind this was dwindling profits of the company and had major structural problems like high wages and benefits, pension costs, and health care obligations (Berko). So we see that the reason which the company reports state that due to the bad economy the company profits are suffering. This fact cannot be denied but it does not present the whole picture. Though there are affects of a bad economy on the company’s profit but the problem of reduced margins due to high structural cost had been a major issue for GM for a long period (Berko). Given this background on GM, we will now proceed to understand the main problem which has been ailing GM.
Problem Identification
This section is dedicated to understand the nature of the problem that GM presently faces. Here we will try to understand the nature of the problem. Here we will provide the validity for the problem thus identified. The problem has been chosen keeping in mind that an issue can be stated to be a problem only when there lays a gap between the desired goal and the unfulfilled results. In order to come to a specific problem, extensive research has been conducted through thorough study of the company’s present condition and the goals that the company strived to achieve. This was done by reviewing the annual reports of the company and analyzing peer reviewed sources.
Where is the Problem?
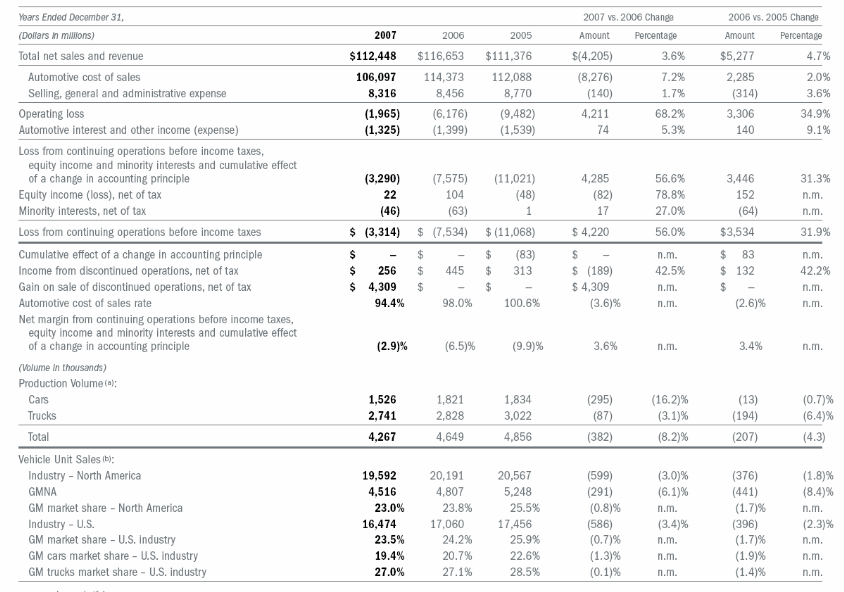
In this section, we will analyze the company reports and try to ascertain what the problems that the company is facing are. For this purpose, we use two Annual Reports, for 2006 and 2007. The results show that GM has been experiencing a decline in the total revenue sales and profit over the years. But the problem was more acute in GNAP i.e. General Motors in North America. Table 1 (see Appendix) show that the overall performance of the company was dwindling. The total sales revenue in 2007 had reduced by 12.6 percent from 2006 data. The figure was lowest since 2003. The sales revenue further dipped in 2008 to $149000 (GM). The net income of the company has been running into losses since 2005 which currently in an all time high of $168000 loss in 2008. The net income (loss) had fallen by 76 percent from 2007. So we see that the overall company is facing a reduction in sales figures and there are signs of shrinkage of the profit. Further analysis into the regional operations of the company reveals that there has been a change in the share of market of GM and a shift in the revenue base for the company. As figure 1 shows that share of revenue in overall revenue has been declining for only one region i.e. GMNA, where the share of revenue of GMNA to total revenue has declined from more than 65 percent in 2005 to 59 percent in 2007. But apparently, from the figure the share of other regions like GMLAAM, GME, and GMAP has increased. This demonstrates that the share of revenue of GMNA has been declining in the overall revenue of the company implying that the sales performance of the region has declined considerably while other regions have done a better performance.
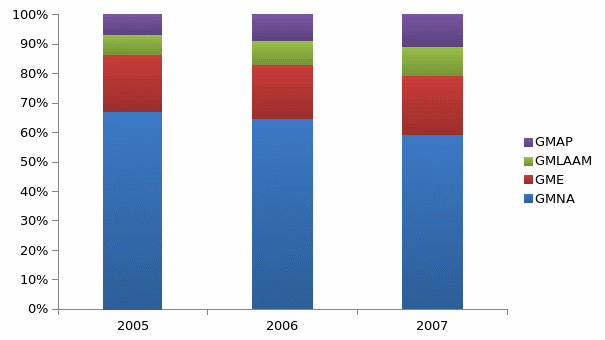
To deal further into the situation we take a look at the market share of the regions in the regional markets. This study shows that the share of GMNA in North American has gone down from 25 percent in 2005 to 23 percent in 2007, whereas the market shares in the other regions has increased especially in GMLAAP and GMAP. The increase in market share in Europe is marginal. This shows that the company’s share in the emerging markets of Asia Pacific and Latin America has increased as targeted by the company. So the problem was not in the emerging markets, but in GME and GMNA. As for GM’s operations in Europe are concerned, the company holds that the prices of the cars in Europe are lower due to stiff competition. So even though there has been a rise in volume sales, the market share has increased but only marginally. Further, the market in Europe is a secondary market for GM, the primary being its home market in North America. It has been observed that the sales in the company’s North American operations have declined considerably. This further shows that the company’s market share in the region has declined and so has the sales volumes. Clearly, the North American operation of GM has been suffering due to various reasons.
So we see that the actual performance of the company has been bad in North America. This is after the fact that the company implemented a turnaround program for the GMNA specifically as this region was their stronghold (GM Annual Report 2006). This indicates that the company’s intended goal to alter the poor performance of the region has not been successfully fulfilled. Thus, we find a gap between the company’s desired outcome and the actual performance.
Problem Statement
So we can state that problem faced by GM is primarily for its North American operations. The GMNA has been facing dwindling profits as well as declining market share even after the company has aggressively tried to turnaround the regional market performance. As this region has a huge impact on the total revenue of the company being the major market for the company, it is important to put more emphasis on the performance of this region. Further, this is the region where GM has maximum market share. This indicates that the overall company performance was getting affected by the slow performance of GMNA’s low performance. The problem assumes greater stature due to the planned goal of the company which aimed to revive growth in GMNA and improve revenue. But this did not occur showing a failure in the company’s desired goal. This reason exemplifies the severity of the problem which GM faced due to a bad performance of the company in GMNA.
Why did the problem arise?
In this section, we will try to understand the reason behind the problem. Why did the revenue of GMNA fell? Why did the market share fall? In order to do this we will need to understand the overall operations of GMNA. The reasons are elaborated in the following paragraphs.
GMNA Turnaround Plan
The GMNA turnaround plan aimed to improve business in North America and achieving competitiveness. In doing so, the company aimed to position itself for sustained growth and profitability in the long run, as well as maintain liquidity. In order to implement this GM aggressively took measures to turnaround the North America operations into a profit making unit and ensure positive cash flow. The key factors which the company identified that needed attention were providing quality product, altering the marketing strategy, reduce cost and maintain high quality, and reducing structural costs (GM Annual Report 2007).
Structural Cost
In GMNA, the structural cost like labor, pension and other post-retirement costs in GMNA was reduced to certain level by $9 million in 2007. There are various reasons for which this may have been happening. In the following section, we will try to ascertain the reasons for which the problem arises. As North American is the core market area of GM, they intend to increase their market share in GMNA (GM North America): “…one of our top priorities has been improving our business in North America to position GM for sustained profitability and growth in the long-term and to achieve competitiveness on a global basis in an increasingly global environment.” (GM Annual Report 2006) For this purpose, they have launched a program to turnaround their market share and revenue from GMNAC (GM Annual Report 2006). But according to the sales figures, GMNA suffered a declined vehicles sales of 6.1 percent and a decline in Net revenue Sales of 3.6 percent (GM Annual Report 2007).
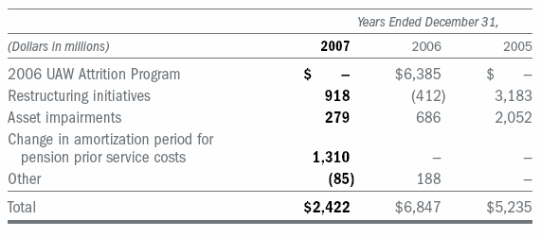
GM has tried to decrease their structural cost, as this will increase their profit margin. This they have tried since 2005. As the priorities set for 2007 was set by Rick Wagoner, Chairman, CEO, General Motors Corporation: “Our priorities for 2007 are very straightforward. First, we will stay focused on our turnaround in North America. We will stick with discipline to our sales and marketing strategy, and we expect to benefit from better sales mix, residual values, and more launch product. In 2006, nearly 30% of our U.S. retail sales volume came from launch product. That is up from about 20% in 2005. This year we expect that number to grow to nearly 40%. Bob will show you some of the reasons why in a few minutes…. Last year I said that we thought we could get to the range of 31% in ’06. In fact, we reduced our global automotive structural cost to between 29 and 30% of global revenue in 2006. We expect to improve on that in 2007” (Fair Disclosure Wire). But in 2007 annual report, they stated that their structural costs have increased to $53 billion in 2007, an increase of $2 billion from 2006. So we see that even the structural cost for GM has increased from $51 billion in 2006 to $53 billion 2007. Thus, we see that an increase in structural cost may have reduced profits. But in GMNA, there has been a decline in the structural cost by $ 6 billion.
Figure 2 shows that the overall structural cost has declined in case of 2007 from 2006. But giving a closer look at the data in figure 2, we see that the reduction in the cost from 2006 is mainly due to the absence of the cost of UAW Attrition Program. As the attrition program was an initiative taken by the company to reduce its cost in terms of compensation and benefits, taking this cost in trying to find the reduction in cost is not a wise idea. So if we take out the cost of the attrition program the total structural cost in 2006 turnout to be $462 million, which is much less than the whooping figures of $ 2422. So we see that the structural cost, even though apparently reduced actually increased during 2006-07. Structural cost, thus, is one of the reasons which had driven down sales by increasing cost of production, and so increasing price.
Operating cost
The operating cost had declined in North America. But given our logic in case of calculating the structural cost, we see that the operating cost increases by $ 462 million which makes the new operating cost to be $2.3 million, which is still less than 2006 level. The main reduction in structural cost arose due to a reduction in the cost of automotive sale which declined to $0.5 million from $6.2 million in 2006. So the operating cost also declined. A decline in operating profit indicated an increased efficiency. So GMNA was said to become more efficient in North American market.
But there were increase in cost due to additional expenses which arose due to an increase of $1.3 billion due to accelerated dispersal of pension unamortized prior service cost. A higher material and freight cost occurred which increased cost by $0.8 billion. Warranty related costs also increased by $0.5 billion. There was higher engineering cost attached due to increased investment. GMNA faced higher foreign exchange losses of $0.3 billion mainly due to appreciation of Canadian dollar against US dollars. So these were the factors which drove the cost of production higher in GMNA.
External Causes
The present crisis of economic recession was one primary reason for the decline in car sales. Due to the recession, consumer demand in North America dampened, declining the sale of vehicles. Further, increased trade union problem of GM was one reason for the company to face such high risks of closure.
Solution & Recommendation
Now the question arises, how the sale can and revenue of the area can be increased which will in turn increase the revenue and profit of the overall country. The sale can be increased by following these methods:
- First, continue with restructuring of the organization which will give the regional unit more operational and efficient.
- Improve the operating performance of the plants. Here we must mention that the production of GMNA had declined since 2005 to 2007. The reduction in production is related to the inefficient time management of the company.
- Implementing structural changes, as downsizing is a major work that GM may put their attention on. Downsizing is necessary for the company, as the company is too big to be managed.
- Further the brands of the company must be rejuvenated to appear to the customer as a new proposition with loads of added features. Thus, what so required is an alteration of the corporate image as most of the customers have the impression that GM implies the vehicles are gas guzzlers.
- Another aspect that GM must look at is reducing the stress that the company plays on the US market and concentrates more on the emerging markets. Though GM is already doing this, but with a wrong strategy. Emerging markets, like India and china demand for more small cars. GM has very few offerings in term of small cars, which makes their brands loose a battle against other company’s small cars.
- Foreign competition has ceased the demand for US made cars in the home market. There were Japanese and Korean makes like Honda, Toyota, Suzuki, and Hyundai which had already made their strong hold in North American market with their fuel efficient cars. Recently there were Chinese made cars which have been launched in the market. Foreign competition with higher efficiency is eating away the market share of GM.
Conclusion
General Motor’s operations in North America will undergo a change if the company undergoes a complete make-over. The company analysis shows that the company’s performance has been grossly affected due to a slowdown in sales in GMNA. This aspect led us to try and identify the reasons which may have caused these problems. We come to three causes: (a) operational costs are still high, (b) unfavorable market conditions, and (c) GM’s dwindling market demand due to low fuel efficiency in GM’s cars.
The recommendations that we present are those related to increasing efficiency so that cars become more fuel efficient. Our analyses showed that there is a need to reshuffle the company’s brand portfolio as this will increase the company’s image and offering to the market. Further, as GM has become the number one automaker in china it must try to take china example out try to fit it in other situations with certain modifications based on regional differences. Apart from this, there must be a strategy to increase operational base in GMAP and GMLAAP. In GME, the company must increase its operations and increase profit. Further, the increasing thrust of the company must be to increase the market share in the emerging markets which have growth potential than a mature market like North America.
Works Cited
Barkholz, David and Robert Sherefkin. “Sales slump, globalization claim white-collar auto jobs.” Crain’s Detroit Business Vol. 24 Issue 36 8 September 2008: 23.
Berko, Malcolm. “New management May Put GM back on the right road.” Des Moines Business Record 6 February 2006: A30.
Fair Disclosure Wire. “General Motors Corp. at Citigroup 2007 Auto Analysts of New York Conference – Final.” Citigroup 2007 Auto Analysts of New York Conference l. New York: Fair Disclosure Wire (Quarterly Earnings Reports)
GM Corporate Responsibility & Sustainability Report, “General Motors Corporate Responsibility & Sustainability Report” General Mstors. Web.
GM Annual Report 2006. “GM – Corporate Information.” 2007. GM. Web.
GM. GM Company Profile. 2009. Web.
“GM Reports Preliminary Fourth Quarter and Calendar Year 2008 Financial Results.” 2009. GM Corporate Information. Web.
Whistle, Mark. “GM Woes A Warning To All Automakers (GM, F).” 2008. Investopedia Advisor. Web.
Appendix
Figure 3: