Introduction
Ryanair started its journey in 1985 with 25 employees and its first flight departure was from Ireland to London in April 1985. From 1990 until today, Ryanair established itself as a low fare and no-frills airline in Europe followed by the business model of South West Airline of the USA. The current CEO of the company, Michael O’Leary is considered as the pioneer for the success of this airline as he made it one of the most profitable businesses in Europe. Ryanair currently has 35 bases and 950+ routes, offering low fares to the passengers and it has 7000 employees and approximately 66 million passengers per year. In the year 2008, the total number of fleets of the company was 181; it increased the bases to 39 and started 223 new routes in Europe. In 2010, the company planned to generate more revenue rather than expanding the business by purchasing new aircraft.
As a result, the contract with Boeing for purchasing 200 new fleets terminated in the year 2009. It still holds the position of low fare and no-frill airlines reducing its fare by 20% due to the price reduction in fuel (Ryanair, 2010).
External Analysis
The macro-environment or PESTLE analysis
Political Factor
The following political factors affect the business of Ryanair while expanding its flights outside the home country.
- Most of the countries prefer to assist their own airlines than the airlines from other countries. When Ryanair started its flights in Ireland, the main competitor in the country was the national flight Aer Lingus and the government always favored the national carrier instead of Ryanair.
- Nowadays countries are more concerned about the noise made by the planes and are taking actions to minimize it. In the western world, people and the authority are much concerned about pollution; hence, they suggested big craft with long haul, whereas, Ryanair uses small aircraft and short-haul.
- An increasing number of terrorist attacks around the world forces the governments to look over the existing airlines. After the 9/11 attack in the USA, the government of various countries got more concerned about their safety and security and took a substantial amount of time from the visitors to check them as a precautionary measure; delaying passengers is against the policy of Ryanair.
- When entering a new market in any Muslim country of Asia or Africa, and the advertisements and promotional campaigns do not match with their cultures, the govt. can take steps against the company.
Economic Factors
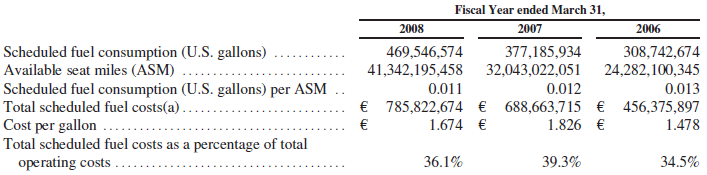
- The frequent fluctuation of oil prices is one of the most alarming and challenging issues for low-fare airlines like Ryanair. Ryanair’s policy is to reduce the cost to provide more economic fare to the customers. The implementation of this policy would be hampered if the fuel costs fluctuate.
- The integration of European countries in the EU creates a real opportunity for low-fare airlines. Ryanair could use this opportunity to enter and operate in all EU member states without the intervention from governments.
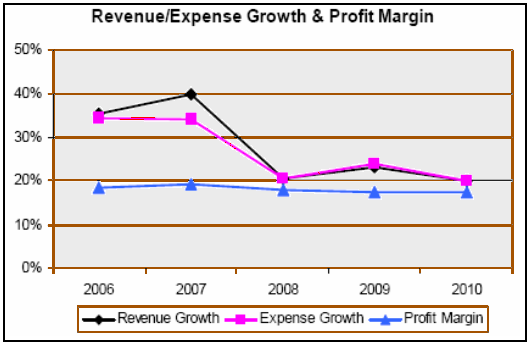
- The current economic downturn along with the decreasing unemployment rate worsens the market, and as a result, Ryanair faces a loss in the year 2009. Because of the economic insecurity, people are not willing to spend on traveling which directly affects the business of Ryanair.
Social Factors
- Since the European community is facing a low population growth rate, the numbers of customers are decreasing. If Ryanair wants to focus on earning revenue by increasing customers in order to achieve economies of scale, it would not be so easy to do this.
- The customers of Europe are attracted by the price reductions, which is an emerging trend. This trend benefited Ryanair as it is a carrier that concentrates on low costs.
- Due to the economic downturn, a huge number of populations shifted from expensive airlines to low-cost ones in various regions of Europe and the USA. As a result, low-cost air carriers like Ryanair was quite benefited by gaining more customers.
Technological Factors
- Wireless internet service is vital in recent times as it eases communication technology, prompting the operations of Ryanair. Currently, technological advancement helped Ryanair through fast communication with various terminals and flight schedules.
- Online ticket reservation system saves time and improves the quality of service. Currently, most of the flights of Ryanair are reserved and confirmed online, reducing the cost of Ryanair and saving the time of customers and consequently, improving the quality of services.
Legal Factors
- The legal framework of the country asserts environment protection charges to the airlines, which may limit the operations of Ryanair in various regions including Europe. For this reason, the company is searching zero carbon-emitting carriers for running the flight.
- Sometimes the hackers might hack the customers’ accounts due to the pitiable protection of Ryanair’s website, which in turn would adversely affect the company by alleging legal penalties.
Environmental Factors
- Environmental protection is a major concern of recent times. Customers may reject aircraft contributing to air and noise pollution and the company that causes environmental contamination. Ryanair needs to be more cautious about this.
- Environmentalists exert more stress on long-haul flights than on short-haul flights for minimizing pollution. However, although Ryanair is an operator of short-haul, this would be depressing for its business as it may also force to shut down some flights in short-haul.
The industry environment Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
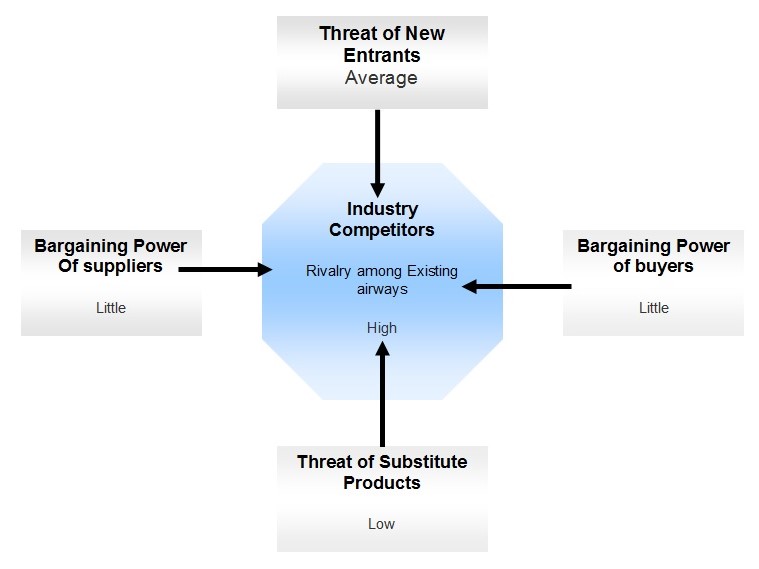
Bargaining Power of Supplier
- Boeing and Airbus are the only suppliers of the industry so that Ryanair has to buy whether from Boeing or Airbus. All aircraft of Ryanair are brought from Boeing as it provides quality airbus. Therefore, the braining power of Ryanair is low compare to Boeing.
- The supplier of fuel has a strong bargaining power as the price is uniform everywhere. As a result, Ryanair was affected by the hike in the oil price and it cannot bargain for a price reduction.
- The local small airports have little bargaining power than the big airports. Because the small airport has a little number of flights and international flights do not use this place. Therefore, they have little bargain power and Ryanair can bargain over this airport authority.
Bargaining Power of Customer
- Customers are mainly concerned about the price than the quality where Ryanair provides low fare no-frill service where the service is not extraordinary. As a result, customer has the bargaining power over Ryanair.
- The switching cost of the customers is very nominal as a customer can easily change his or her flight from Ryanair to Easyzet or British Air. For this customer need not expand any pound.
- Customer loyalty is absent in the industry and they are well known about the operations and costs. In the case of Ryanair, the traveler use it because of low fare and if they get a flight lower than Ryanair then they will choose it.
New Entrants
- A huge amount of investment is required to enter the market currently as to buy a new aircraft is a matter of huge investment. Ryanair currently dismiss the contract with Boeing of purchasing 200 aircraft due to the extra cost. As a result, this amount of investment is risky on the part of investors.
- The newcomers cannot charge low prices due to the huge cost of investment, which may drive out them from the market especially when competitors like Ryanair compete on low fare.
The threat of Substitutes
- There are no close substitutes to the aircraft and long haul airlines cannot be substitutes of short-haul. Besides this other modes of transport are not close substitutes for the aircraft. As a result, the fear of substitutes is absent in the business of Ryanair.
- Cars, trains, and buses are the other modes of transport but are not close substitutes because it requires a long time and jerking which made the traveler exhausted where as aircraft is not in that nature.
Competitive Rivalry
- The air market is highly competitive as there are competitors like Easyjet, British Airways, etc. To compete in the market Ryanair needs to be more efficient and it cut the prices though made loss.
- The competitions are based on price, and another such as when Ryanair reduce its fare can easily imitate the steps taken by one company then easy jet can easily reduce the fare to be competitive in the market.
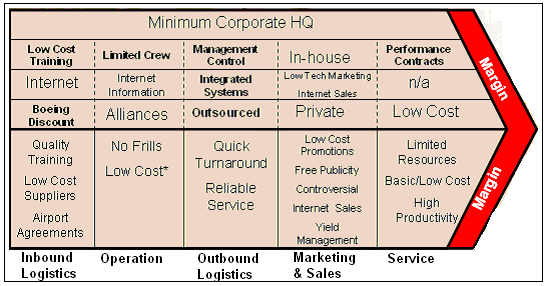
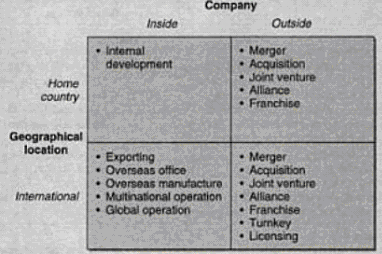
Value networks and business partners
The value network starts with the suppliers of fuel, the airplane manufacturers, and the airports. On the other hand, oil prices directly affect the aviation industry and some companies supply fuel for the airplanes. The value network is described in the following figure.
Resources and Capabilities
Valuable Resources and Strategic Assets
Physical Resource
Ryanair’s physical resources include more than 192 Boeing aircraft to serve the customers in different destinations and a huge amount of funds of the company is spent for maintaining these resources. In Europe, Ryanair possesses the younger fleets and the fleets are more energy-saving and less carbon-producing, which is friendly for the environment.
Financial Resources
Ryanair’s profit after taxes in 2008 was € 390.7 million and net profit in the same year was 18%, which was approximately 300% more than that of the competitors and the earning per share was higher too. At the end of the year 2008, the net cast worth of the company was € 2170 million (Ryanair, 2009).
Human Resources
The human resource is the main strength of Ryanair and it has 7000 employees now, which had been 25 when the company started its business. The employees are working hard to take the company in number one position in Europe and trying their level best to retain the company’s core strategy of cost-cutting. The top-level management of the company is working there for more than ten years, which was an added advantage and a contribution to the success of the company (Butler, 2006)
Capabilities, knowledge and intellectual assets
The main capabilities of Ryanair are its ability to run flights through low price and cost control. These capabilities are achieved by using cost-effective measures such as increasing the number of flights and expanding the market by increasing the number of destinations. Another capability of Ryanair is ‘on-time flight moving’ and more than 90% of the flights arrive and departures on time. The approach of the company is not profit-maximizing rather minimizing the cost. The various value-added entertainment facilities during the flights is an added advantage and it can easily advertise the company through these programs, which require no cost at all (Itami & Noto, 2007).
The intellectual property of Ryanair is also very rich, and so it archived the brand of the most profitable airline in Europe in the chart of ELFA. Ryanair possesses the most experienced senior management team in the industry and the CEO of the company Michel O’Leary joined this team in 1988 and acted as a CEO from 1994. The chief pilot of Ryanair Captain Ray Conway joined the company in 1987 and acted as a chief from 2002.
These capabilities and properties build up Ryanair’s core competency. Ryanair is a low fare and no-frills airline, where low cost is the central expertise of the company. The business models of Ryanair are constructed on the philosophy of low costs, which enables the company to charge low fares from the customers. On the other hand, a large number of aircraft enables the company to schedule more flights, which covers the cost of operation. The workforces of Ryanair are also competent enough to sustain its strategy of cutting costs.
Structure, Culture and Value Added
The culture of Ryanair is heavily leadership-based, and the leaders are the transformational organizers with a clear vision, empowerment, and strong commitment. The structure of the company is less complicated with low power distance and collectivism. The commitment of the organization is very important in Ryanair, and it requires leadership based on seniority, position, and authority. The value added to the customers includes the execution of flights on time, online booking systems, etc. The customers of Ryanair are pleased with the services provided by the company as no other airlines offer such low fare services along with additional benefits. It also introduced a maximum number of destinations with Boeing airbus to the customers.
The Strategic Situation
Currently, Ryanair operates in the European market where a low fare is the trademark of the company and its strategic situation will be clear from the examination of its current strategies.
- Business model: Ryanair has currently changed its business model; it relied on increasing the number of customers traditionally, but now it is trying to increase the revenue, and as a result, it terminates the contract with Boeing for purchasing new 200 aircraft from 2013 (M&C News). The CEO of the company stated that it would try to maximize the revenues for distributing it to stockholders (Ryanair, 2008).
- Addition Income: Ryanair plans to earn additional income through branding their aircraft with some B2B companies like Dell, IBM, etc. that will cover the cost of the company and generate profit.
- Price Reduction: Ryanair plans to reduce the fare by about 20%, which may reduce the income of the company. Nevertheless, it will cover the fare reduction cost through a 30% low price of oil in the international market.
- Low fare: According to the view of Johnson, Scholes & Whittington, (2005, p. 840), low fare strategy is the main reason behind the success of Ryanair and it targets those customers who are traveling to various destinations and much concerned about the fare. Sometimes the company offers free tickets to uphold the image of its low fare (Allé & Schmitz).
- New Route: Ryanair always tries to expand the business by introducing new routes at different places and currently it started its flights to Malta and Portugal (Ryanair, 2008)
- Short Haul destination: Ryanair provides frequent flights in short-haul destinations, which enables them to cut a huge cost. The minimum interval of flight in the short destination is only 1.1 hours and it allows the airline to reduce the cost of serving customers during the flights.
- Secondary Airport: Ryanair has chosen secondary and regional airports for landing because it entails low cost and prompts the processing of the flights, whereas in the big-crowed airport the processing takes a very long time. As a result, it can turn around flights within 25 minutes to maximize the use of its fleets and executes more flights than the traditional one.
- Cost of operation: The operating cost of Ryanair is lowest in Europe than any other airline company as because its concentration is on lowering the outlay. The company minimizes the cost of aircraft equipment by buying aircraft from one company and easily replaces the equipment from one fleet to another (Anon, 2005, Strategy of Ryanair).
- Maintenance and safety: Ryanair gives paramount importance to the safety of the customers and it maintains the highest standards of Safety in Europe. The company does not want to compromise on the issues of protection for the sake of cost; and during the history of the company, no fatal accidents occurred.
- Positioning in the market: In the airlines market, Ryanair positioned itself as a low-fare airline, and it is possible for the company to take the above-mentioned strategies. In every aspect of the operation, it uses the low-cost models for reducing cost and thus it differentiates the company from others.
Strategic Choice
Identification, description, and definition of a small number of Strategic Options open to Ryanair
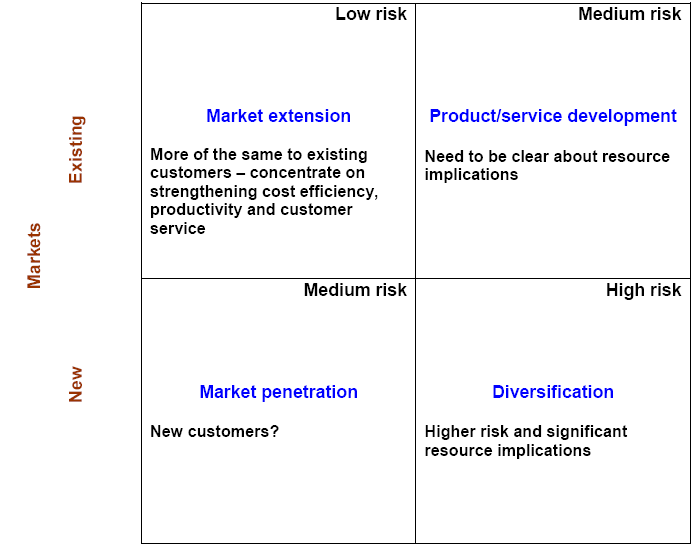
Ansoff Matrix
Ryanair already shows its success as a budget airline in the European market and it is a high-income company in Europe in the low fare market. In developing the future strategies for expansion, Ansoff Matrix can be useful:
- Market Penetration: Market penetration is the strategy to grow in the current market through current products or services. Ryanair can make substantial growth through the existing market as it has a strong position in the European market. By increasing the frequency of flights in different destinations in Europe, Ryanair can expand the current market. It also can increase the destinations in Europe by introducing flights in more European cities;
- Market Development: Market development refers to develop a new market through current products or services. Ryanair currently operates in the European market at low cost and this low cost is very important for third world countries in Asia, Africa and Some parts of Latin America and this airline can make success in that region with its current low-cost model;
- Product Development: Product development refers to develop new products in the existing market and Ryanair can offer new services. Ryanair can introduce new aircraft in the existing route in Europe, which are comfortable, and environment friendly. Besides this, Ryanair can introduce more services in the flight like food, music and another value-added service, which will contribute to the revenue of the company. It also can some long haul flight in the long destination in Europe besides the intercity carriage.
- Diversification: Diversification refers to develop new products for new markets to diversify the business. Ryanair can expand the market into the USA by offering premium services to the new market. If it introduces a long haul route in the current line, they need to enter into the new market especially in Asia where a large number of passengers visit every day. It can change its no-frill service to frill service in the long route
Expansion Method Matrix
According to the expansion method matrix, which was developed by Richard Lynch, Ryanair operates to expand its current market in the European region. Ryanair can expand its market share through its current market or enter into the new market outside the home country:
- Current Market: Ryanair can expand its business in the existing market through two different strategies, which include expanding the capacity of the company or merger, acquisition, joint venture or other modes of operation. To expand the capacity, the company can buy or hire more fleets to raise the number of travelers. The company can also use mergers or acquisitions with competitive airlines to grabs more market share to reduce the competition
- New Market: On the other hand, Ryanair can expand in outside areas like Asia, Africa, or America through establishing subsidiaries there or it can merge with the local companies. Acquisition of the local airlines is much easier than setting new operation because setting new operation, entails a large amount of investment and cultural shock is also important
Porter’s Generic Strategies
- Cost Leadership Strategy: Lundberg (2008) argued that most of the strategies of Ryanair build on the philosophy of minimizing costs to turn it into a cost leader in the industry. Ryanair is a low fare and no-frills airline, which shows a huge profit and a large number of passengers in Europe. It is possible only for the cost reduction and value addition in every step of the operation.
- Differential strategy: Differential strategy refers to the uniqueness of the product or service of a company, which gives a competitive edge (Porter, 1996). Ryanair is a service company where the business model and services given to the customer are very different from other conventional airlines in Europe. As a result, it gives Ryanair a uniqueness to build differentiation in the market and the differential strategy of the company is low fare and no-frills airlines in Europe.
- Focus Strategy (Cost): Focus strategy on cost refers to concentrate on a narrower market segment through achieving cost advantages. Ryanair can enter into the narrower segment of the market that may be the customer segment on price. When executing business in the European market, some customers are traveling for enjoyment purposes and they are price sensitive.
- Focus Strategy (Differentiation): Focus Strategy on differentiation refers to concentrate on narrower market segments through introducing variations in services. At this time, Ryanair does not focus on this strategy.
Evaluation of the options identified under
Above using suitable tests or evaluation methods
- Consistency: Consistency refers to matching the strategies with the objectives and goals of the organization. An Ansoff Matrix, market penetration and market development strategies are most useful for Ryanair as it is already branded as a low fare and no-frills airline in the industry. On the other hand, in the market expansion matrix, market development in the home country and outside country through merger or acquisition or other modes of the alliance will be effective for Ryanair, as it requires no additional cost of setting up the new operations. In generic strategies, the cost leadership strategy best fitted with Ryanair’s current objectives and strategies (Rumelt, 1980).
- Consonance: Consonance is the positive response from the external environment due to the adapting strategy. When Ryanair adopts a strategy to develop a new market like Asia, Africa where the income level of the general people is low, it will work well and low fare can be a competitive advantage, which is difficult to imitate. Another advantage in such a market is the entry barrier is a low and the external force of the industry will positively interact with Ryanair.
- Advantage: The main target of all strategies is to create or sustain the competitive edges of Ryanair. At present, the competitive advantage of Ryanair is its cost leadership in the industry and the suggested strategies aimed at maintaining and developing this advantage including other advantages in the existing market to the new markets. Ryanair penetrates and develops new markets purely on basis of these advantages and adopting all of the mentioned strategies will trigger to maintain current advantages as well as create new benefits well.
- Feasibility: The strategies like entering into a new market through merger or reliance, using it in the current market, and establish Ryanair as a cost leader in the new markets, all are feasible in terms of financial viability and capabilities of the company.
Strategic Decisions and Recommended Strategy
Description of the Recommended Strategy for the company
Ryanair should take the following steps to implement the above-discussed strategies:
- Market Expansion: Ryanair currently operates in Europe where most of the passengers visit the airline, so it should consider the market expansion strategy addresses both in the domestic and international markets. When expanding in the domestic market, it requires enhancing its operation or merging with other company and in case of international expansion, it requires setting new operations in regions like Asia, Africa, etc.
- Growth Strategies: Growth implies both in revenue or market share where revenue generates through increasing the price and market share increasing the customers or passengers. Ryanair needs to concentrate on both market share and revenues as the following figure shows that after 2007 it is not in a stable position.
- Addition revenue: Additional revenue generates from doing some activities, which are not directly, involve with the main operation. Ryanair can manage some additional revenue by introducing some value-added services in the flight and outside the flight though it is the first position in terms of customer services.
- Competitive Advantages: Through more flight, new operation and minimizing costs and prices, Ryanair can achieve additional competitive advantages with the current ones and it will help to compete more strongly in the market.
Key strategic decisions and actions needed
- Ryanair should try to increases the frequency of the route by running more flights than the present and it will help to amplify the current market share;
- It should expand the destination outside Europe like Asia, Africa, and Latin America, etc. and to extend the existing market through market penetration, Ryanair must increase the destination in Europe where trafficking is high;
- It should continue the negotiation with Boeing to purchase new aircraft from them, which will require for expanding its operation.
- It should try more to increase the additional income like currently, it signs a contract with B2B Companies for branding the aircraft;
- Ryanair should decrease the fare of the flight further to attract more passengers to visit its flights;
- It should introduce some long haul service for passengers and it will increase the market shares of the company.
- It should invest more money to buy new aircraft to increase the flights;
- It should make a contract with airports to increase the destination;
- It should more concentrate on reducing the cost further.
Resource commitment, investment, and timing implications
In 2009, most of the companies in the airline industry had suffered losses due to the economic downturn and Ryanair also faced this problem but currently, it shows higher profitability, as result, the company is now in a position to invest to grow in the market. Yahoo finance and news media reported that the world economy is in a position to recover from the downturn and success in investment is very high. Currently, Ryanair plans to earn more revenue to distribute more profit to the shareholders. However, it will be fruitful in the short-run and to sustain the revenue in the long run there is no alternative to expanding the market as Ryanair made a huge profit for the expansion of Stansted Airport. As it terminates the contract with Boeing, Ryanair should negotiate with them or find new suppliers to purchase new aircraft or follow its old strategy to hire aircraft from outside suppliers. Ryanair has the available resources to support the investment and manage the growth.
Conclusion
As one of the budget airlines in Europe, Ryanair holds its market by offering low fares to passengers from 1990. It operates in an environment where many competitors in the market but all of them are not offering low fare and in fact, Easy Jet is the main competitor of Ryanair. In the air industry, the bargaining power of the suppliers and buyer is very high and it is difficult for the new entrants to succeed. The environment of the industry is very sound but the government of each country prefers to give advantages to the flag air. The customers of the industry are very price-sensitive, which is an added advantage for Ryanair but the fluctuation in fuel price presents the real challenge. The pollution of the environment and air is a real concern for the airline company and Ryanair is not an exception. The main competitive advantage of Ryanair is its cost-effective strategies, which enable the company to charge low fares to the passengers. Its current strategies mainly focus on reducing the costs of operation and decreasing the price of the services.
To grow and expand the market, Ryanair must concentrate on certain issues like increasing the number of flights, increase more destinations and finally operates flights outside Europe. Recently, the company terminate its purchasing contract with Boeing, which negatively affect the growth of the company. However, this decision is taken to reduce the cost of the company because Boeing charged a higher price for their aircraft; and Ryanair wanted to give dividends to the shareholders rather than investing in this issue. Ryanair must expand its operations in Asian and African regions in order to earn more profits, as people of these areas are more concerned about the costs because of their low-income levels. To enter into these areas, Ryanair requires introducing a long haul route with frill and additional services. If Ryanair is able to provide high-quality flights with low costs, it will be able to get benefits over its competitors.
Reference
Allé, M. M. & Schmitz M. A. (2004) Séminaire d’elaboration d’un Business Plan. Web.
Butler, C. (2006) Comprehensive strategic analysis, BSC Multimedia Technology. Web.
Itami, H. & Noto, L. (2007). Analyzing Resources and Capabilities. Web.
Johnson, G., Scholes, K., & Whittington, R., (2008) Exploring Corporate Strategy: Text and cases. 8th ed. Pearson Education Limited.
Lundberg, J. (2008) Are Porter’s generic strategies enough to guide operations strategy. Web.
Lynch, R. (2007) Corporate Strategy: Expansion Matrix, Pearson Education. Web.
M&C News. (2009) Ryanair ends talks on post-2012 Boeing orders in new strategy. Web.
Mun, J. (2008) Analysis of Ryanair’s Competitive Advantages. Web.
Porter, E. M. (1996) What is Strategy? Harvard Business Review. Web.
Porter, E. M. (2004) A Model for Industry Analysis. Web.
Rumelt, R. (1980) The evaluation of business strategy. Web.
Ryanair. (2008) Strategy. Web.
Ryanair. Annual Report 2008 of Ryanair. Web.
Ryanair. Annual Report 2009 of Ryanair. Web.
Ryanair. (2010) History of Ryanair. Web.
Smith, I. (1994) Meeting Customer Needs: SMALE Consulting Ltd. Web.
Snell, J. D., (2007) Ryanair Holdings PLC (RYAAY). Web.
Yahoo Finance (2010) Basic Chart of Ryanair Holdings (RY4B.IR).Web.
Appendix