Netflix is an American-based production company operating in the media and entertainment industry. The company was established by two businessmen Reed Hasting and Marc Randolph, in 1997 (Burroughs, 2019). It started its operation as a movie rental service where consumers bought motion pictures on its website, and they also received DVDs. Ever since its inception in California, the video streaming arena has developed and emerged as an exceptional online entertainment podium in the world (Jenner, 2018).
Currently, this company distributes films and has over one hundred and fifty-one million paid subscribers in at least one ninety nations globally (Lobato, 2019). In 2002, Netflix started the process of stock market flotation in the United States and began operating in the National Association of Security Dealers Automated Quotations (NASDAQ)(Jenner, 2018). Moreover, Netflix witnessed a tremendous time of growth in 2007 when it introduced its video streaming capabilities (Lobato, 2018). This paper explores the significant aspects encompassing Netflix’s strategic landscape, discusses various elements of its corporate performance, and offers recommendations for its long-term growth.
Company’s Current Situation
Video streaming has several dominant players offering exceptional and competitive services to the customers. Therefore, regardless of Netflix’s global recognition and large base of paid subscribers, the company faces stiff competition from Amazon’s streaming platform, Prime Video, which charges lower subscription fees and has around 150 million subscribers (Hastings & Meyer, 2020). However, compared to other brands such as Hulu, Disney Plus, HBO, and Prime Video, Netflix remains the leading brand with the most views in the United States as shown in Figure 1. Moreover, in 2018, this American conglomerate had eight of the leading most streamed shows in the United Kingdom (Lobato, 2018). This industry’s competition is primarily based on the subscription fees, content provided, and other additional services.
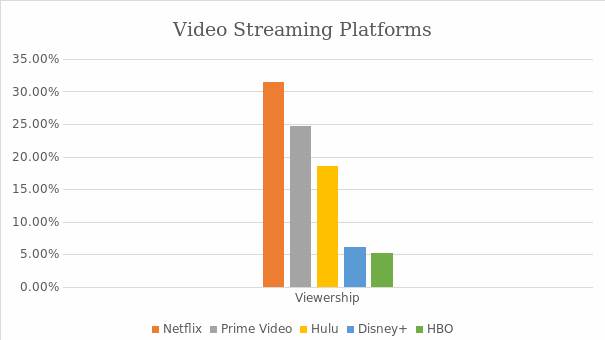
Competitive Position
Generally, Netflix has revolutionized how people watch television series and other films. The company continues to dominate every part of this industry; however, its strategic team cannot ignore the fast-growing Amazon Prime Video. Due to such trends, Netflix has continuously repositioned itself as a creator and distributor of content. This approach seems to be effective for now, but it remains questionable in the long run. Therefore, the company is in an average competitive position and needs to improves its strategies to continue dominating the fast-growing industry.
Financial Position
Netflix experienced tremendous growth, which strengthened its financial position, attributed to the coronavirus pandemic. The demand for its services increased when governments worldwide introduced several guidelines to curb the spread of the COVID-19 virus, such as curfews and other restrictions (Lobato, 2019). Therefore, households worldwide had more time to watch various films and TV series distributed by the American giant. At the end of 2019, the company had long-term debt of $14.8 billion, signifying it was in a risky financial position (Hastings & Meyer, 2020). However, a significant consideration is that it can manage its obligation, primarily due to its improving free cash flow.
In its current environment, its viewership is soaring due to many consumers staying home to contain the spread of coronavirus. While its existing customers are not paying additional to watch more, an increasing fanbase means the company is signing up more subscribers. These trends reflect a high number of new clients and considerable revenue (Lobato, 2019). Moreover, over the last ten years, Netflix has witnessed significant growth in its net income and reached its all-time high in 2020, as shown in Figure 2 below.
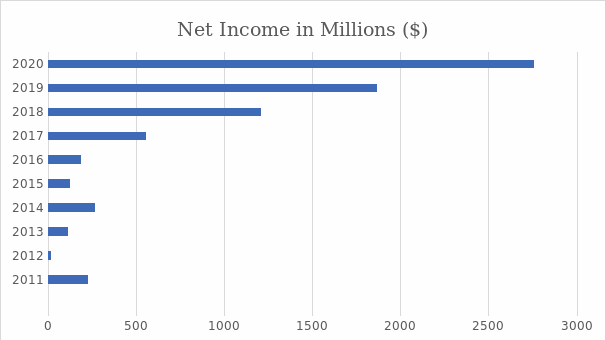
Problems to be Addressed
Several problems are likely to affect the profitability of the American giant in the future. For example, content fragmentation is a significant challenge facing this company. Chief Executive Officer Reed Hastings has deemed the traditional category of television as its biggest competition. Moreover, Netflix has been unable to precisely know what its viewers are watching, which remains a threat in the future. Its management team should therefore find an alternative to addressing this situation early enough.
Proactive or Reactive Strategies
A proactive approach is a tactic adopted by organizations to prevent a problem from occurring. In essence, this strategy is incorporated before any challenging situation emerges to minimize the severity of a risk. Netflix’s methods are primarily proactive, especially in managing its video streaming platform. The former is often vulnerable to some technical issues, which may render it unusable for the customers. The American giant recognized this flaw and took proactive strategies to satisfy their clients. Whenever such a problem arises, the company releases a statement informing the outage customers (Jenner, 2018). Its management also apologizes by giving the viewers credit on their accounts.
Implications of Proactive Strategy for Netflix
While proactive approaches may come with several benefits, they are limited to some extent. For example, Netflix finds it hard to use this strategy because it encompasses several steps connected to others. Therefore, it is a model of interdependence which must be constantly adjusted whenever a new factor emerges. As a result, the entire strategic planning process is affected due to its complexity and heavy commitment to objectives.
Company’s Mission, Vision, and Strategic Objectives
Netflix’s mission and vision statements are remarkably fine-tuned to improve its performance in the entertainment industry. Its strategic team utilizes these elements to inform corporate development direction and performance achievement. These tactical tools help push for organizational effectiveness in the international business market. Therefore, Netflix’s mission statement is “To entertain the world,” and it has some aspects; entertainment and global reach (Hastings & Meyer, 2020). The first component highlights its operations’ nature, primarily based on show business, including stage plays, films, series, and performance art. The second component of its mission is to reach global heights. Currently, Netflix has used its online services to reach diverse viewers from around international markets.
The American media company’s vision statement is “To continue being one of the leading firms of the internet entertainment era.” In particular, this tool emphasizes the American syndicate’s need to remain the leading corporation, considering dominant players like Amazon, Hulu, and Disney Plus (Hastings & Meyer, 2020). The first component of its vision reinforces the goal of continuing industry leadership, while the second element, the “Internet,” denotes online media as a significant factor in its operations. Also, Netflix’s characteristics as an entertaining platform are included in its vision, emphasizing its business and operations.
Netflix has several strategic objectives driving its growth in the long-run. For example, its primary goal is to develop its streaming membership enterprise. This objective is supported by both its vision and mission statements as described above. Moreover, it suggests that the company constantly improves its online streaming business to effectively reach its goals and objectives (Wayne, 2018). Currently, the American enterprise has managed to uphold both its vision and mission aspirations.
Opportunities and Threats
Netflix operates in the video streaming and entertainment sector, which several opportunities and threats. Therefore, a PESTEL analytical framework can be adopted to explore market gaps and challenges present in its external business landscape. Moreover, Porter’s industry is also incorporated to examine its competitive environment for possible market openings and shortcomings. Lastly, a strategic group map is applied to analyze Netflix’s position in the industry to identify areas that can improve its profitability.
Macro-Environmental Factors and Their Implications
Political forces are drivers that companies do not overlook. Since Netflix is regarded as a technology organization, it is subjected to government inspection similar to other firms. Regimes around the world have intensified their grip on such enterprises, especially in regard to data collection. Therefore, the American giant has to tailor its services according to various countries’ government requirements (Lobato, 2019). For example, Netflix does not allow viewership of various programs for all countries in the world. The company shows different films in numerous nations as some motion pictures are excluded from specific regions.
Economic forces are continuously shaping how businesses operate in the international market. With increased economic activity, consumers with disposable incomes are more likely to spend on non-essential services. In the last decade, the global economy’s financial performance has been remarkable, leading to people spending more on Netflix’s services (Shattuc, 2020). In particular, since the coronavirus’s advent, the American giant has experienced a substantial rise in its subscriptions (Hastings & Meyer, 2020). However, low economic activity for prolonged periods can have detrimental effects on the operations of Netflix.
Sociocultural factors are vital in the operations of global businesses. Since the worldwide market accesses Netflix’s services, the company needs to understand customers’ various tastes and preferences from different cultures (Shattuc, 2020). As a result, the American corporation has a collection of content well-matched with other viewers worldwide. A significant social factor promoting the growth of Netflix is the rising group of millennials who prefer to watch their favorite films on digital platforms rather than the obsolete television sets (Hastings & Meyer, 2020). Moreover, a survey indicates that this group of people are more likely to subscribe to Netflix’s services than the older population, as shown in Figure 3. Generally, sociocultural trends have favored the growth of this company since the advent of the Internet.
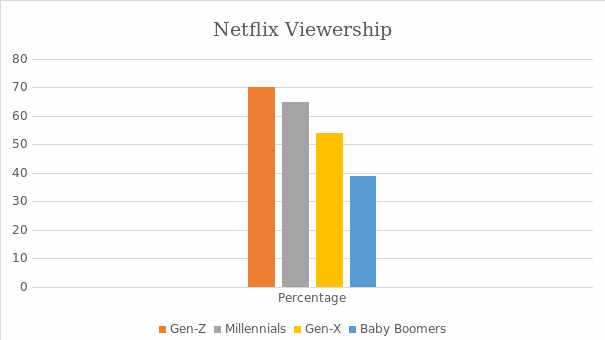
Technological factors are essential in international businesses since companies are constantly revamping their research and development approaches. The growth of Netflix is attributed to its improvement of customer experience by revamping its user interface (Hastings & Meyer, 2020).
As such, technology is the primary source of competitive advantage for the American giant. It utilizes algorithms and machine learning to suggest films worth watching to its viewers. While these resources improve the company’s competitiveness, it also increases competition since other streaming platforms such as Amazon Prime Video and Hulu have advanced technological assets.
Environmental forces are shaping every company regardless of their industries. While Netflix’s core operations are Internet-based, it has to invest in social responsibility. For example, its reliance on online services leads to high consumption of electricity. The company used approximately ninety-four-megawatt hours of energy which originates from non-renewable sources, making it hard to reduce its ecological impact (Lobato, 2019). However, it supports various projects aimed at harnessing renewable sources across the United States and other countries.
Legal factors are also essential in the digital media industry since various regimes continuously develop laws to regulate it. However, apart from user protection, consumer privacy is one of the most significant concerns for Netflix. Since the advent of technology, legal compliance has become compulsory for firms since non-conformity may result in substantial financial losses and damage to business reputation (Jenner, 2018). In essence, the American giant ensures its operations adhere to the required legal framework.
Porter’s Five Forces and Their Implications
The possibility of new entrants in the video streaming sector is considered a threat to Netflix. Major companies such as HBO, Disney, and Apple are either introducing or have unveiled their new streaming platforms. Therefore, the threat of new players penetrating the industry remains high for organizations with enough capital, supplier contracts, and technological resources (Lobato, 2019). However, new businesses are limited by entry barriers such as high investments for producing content or obtaining them from established brands.
The suppliers of Netflix can be deemed as holding a high degree of influence. It is attributed to the few numbers of institutions producing content. Moreover, acquiring a license to distribute motion pictures involves negotiating pricing, where the merchants have an advantage. Netflix had to minimize its profits to maintain agreement with the suppliers to strengthen its customer base, signifying its vendors’ high power (Burroughs, 2019). Therefore, this industry element remains vital because it helps the company understand the forces shaping its supplier-relationship.
The influence of the customers is vital for Netflix, especially in determining its pricing strategies. The entertainment sector dynamics enable the buyers to have an increased power of bargaining over a service platform as Netflix. Moreover, the business’s sales and proceeds are reliant on the subscribers who are located in various nations across the world (Burroughs, 2019). In addition, low switching costs allow viewers to consider other brands, especially since Netflix can cancel a subscription. Therefore, the customers will continue to have substantial power over the company.
The threat of substitutes poses a moderate level of risk in the video streaming industry. Traditional medial avenues are regarded as a significant threat to the profitability of Netflix, regardless of the shifting trend towards online viewing (Jenner, 2018). Moreover, consumers can also consider other sources of leisure, which threaten the American giant’s services. Therefore, Netflix manages these challenges by continuously updating its content library by adding films and TV series, which are highly demanded by its customer segment.
The level of competitive rivalry in this industry is intense due to pressure from dominant players. Netflix faces aggressive competition from rival players such as Amazon Prime Video, Hulu, Disney Plus, and many more. In addition, the company also competes against traditional avenues selling videotapes. Its primary competitor is Amazon because it also provides rented DVDs, thereby competing for the same target market (Shattuc, 2020). With this intense rivalry, Netflix has to constantly revamp its strategies to remain the leading brand.
Strategic Group Map
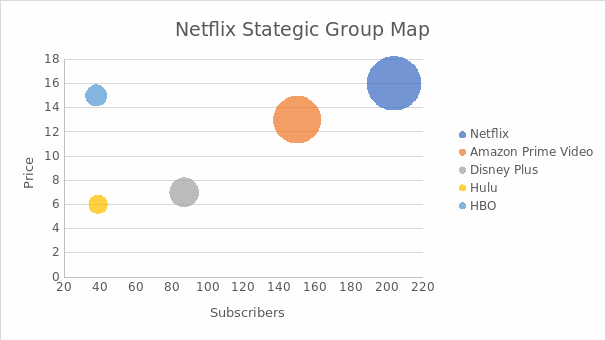
Value Chain Analysis
Table 1. VRIO Analysis of Netflix.
Several parts of the value, rarity, imitability, organization and non-substitution (VRIO/VRIN) analysis explain Netflix’s sustained competitive advantage. For example, its brand equity represents its global recognition, and it supports its long-term competitive edge. Moreover, other players will find it difficult to imitate the company’s online platform, making it a core competency. Another valuable capability of Netflix is its access to original content creation (Hastings & Meyer, 2020).
While numerous companies may offer content to consumers, they cannot do so at the scale, and frequency Netflix does. However, the company is limited due to its over-reliance on third-party content creators. Although its value chain finds its original films and shows, the enterprise also distributes content from other parties on the platform (Lobato, 2018). Therefore, this component makes Netflix susceptible to strategic transformations and other firms such as Disney.
Generic Competitive Strategies
Generic strategies refer to firms’ approaches to effectively compete in the industry by making decisions based on market depth and economic reasons. Netflix primarily uses differentiation and cost leadership as its generic strategies (Wayne, 2018). Cost leadership allows the American giant to lower its selling prices to remain competitive in the market (Hastings & Meyer, 2020). In essence, this approach enables Netflix to reduce costs and the resultant ability to sell at affordable prices. In contrast, differentiation allows the company to develop its online operations and its offerings in ways that distinguish them from market products and services (Lobato, 2018). For example, the American online platform improves its competitive advantage by producing unique content, apart from streaming other parties’ content.
Advantages and Disadvantages
The cost leadership approach comes with several pros and cons. For example, it has enabled Netflix to gain a significant portion of the market share, reflecting its strategic intent of becoming a global leader in entertainment (Wayne, 2018). It also helps the company in minimizing its cost of operations. Moreover, this approach has also enabled the American syndicate to create more capital which can be used for further growth and investment. However, this approach comes with several disadvantages to Netflix. For example, other firms can easily follow it to remain competitive in the market (Wayne, 2018). Also, cost leadership may encourage the production of low-quality products in the market. Therefore, a company as Netflix should balance its generic strategies to maintain its industry leadership.
Differentiation is an approach that may come with some pros and cons. For example, it enables Netflix to attract and retain viewers, thereby strengthening its intensive strategies to develop its online business further. Moreover, it also bolsters consumer brand loyalty which ultimately boosts profit margin while eradicating perceived substitute products (Lobato, 2019). However, the only disadvantage of this approach is that revenue increases are not guaranteed since the consumers may not find value in the services provided.
Generally, Netflix’s differentiation strategy is primarily based on its sources of sustained competitive advantage in the VRIN framework. For example, this approach reflects its core competency of having its original content production to create value for the customers. Moreover, its cost leadership strategy is also based on its brand equity, signifying its significant market share in the industry (Lobato, 2019). Netflix’s cost leadership has played a vital role in neutralizing threats in its environment. For example, one of its challenges is the increased competition which can be addressed by offering reasonable prices to attract and retain customers.
Netflix’s rival companies also use several competitive strategies. For example, Amazon adopts the cost leadership approach to manage its Prime Video business. It utilizes advanced computing and networking technologies to improve its operational efficiency while cutting costs. Disney applies differentiation to enhance its competitive advantage over other companies. The firm offers its entertainment services and focuses explicitly on family-oriented programming.
Action Plan
Table 2. Action Plan for Netflix.
Multi-domestic/Global Competition/Transnational Strategy
Netflix adopts various marketing strategies to approach different areas in the global industry. For example, its multi-domestic approaches enable it to customize its offerings to multiple states in the US. However, with its ownership of original programming, the American company can distribute its entertainment services across borders. The company primarily utilizes global strategies to reach its international consumers (Hastings & Meyer, 2020). Its global content is a vital part of its transnational strategy. Shows and motion pictures that appeal to numerous regions enable the streaming giant to capture viewers in at least one ninety countries (Jenner, 2018). Since this approach often works for the company, it remains one of its cost-effective tactics.
The primary strategy Netflix has used to establish its presence in the global market is licensing. The latter is a contract between two companies from different nations, with the proprietor receiving the rights and resources to use the licenser’s patents, copyrights, and technological resources (Lobato, 2018). This approach has been effective for the streaming giant as it enabled it to sell its online services and original content to new markets. Apart from its home country, the US, Netflix also competes in Canada and Europe.
Nine-Cell Industry Attractiveness-Competitive Strength Matrix
Table 3. GE 9-Cell Matrix for Netflix.
Table 4. GE/McKinsey Matrix for Netflix.
The diversification strategy of Netflix is related to its business unit strengths, as indicated in table 4 above. This approach has several advantages and disadvantages for the firm’s strategic landscape. For example, it allows the company to attract and retain consumers, thereby reinforcing its intensive growth strategies to develop its streaming business. However, it is limited because it is vulnerable to not creating value for its viewers. In particular, the matrix used above comes with several implications; for example, it is expensive to conduct while it also requires an expert to evaluate the industry attractiveness and business segment strength as precisely as possible.
Netflix can consider divesting its sale of rented DVDs as indicated in the table 3. This business segment is gradually becoming obsolete as more consumers are shifting towards an online-based experience, thereby eliminating the need for these compact discs (Hastings & Meyer, 2020). However, the company should continue investing in its online streaming services and generate new approaches such as improving their content and maybe minimize their prices. In essence, its streaming business segment has significantly created value for stakeholders.
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
Netflix’s CSR enables it to adhere to business standards and ethics required in enterprise management. For example, it allows the streaming giant to work with integrity and civilization involving handling conflicts of interests. Moreover, the approach also facilitates compliance with applicable guidelines, legal laws, and regulations. Lastly, it establishes a favorable environment to implement change in management (Jenner, 2018). In essence, Netflix’s CSR approach is associated with giving its employees unlimited paid parental leave. The American giant can improve its social responsibility methods by minimizing its energy consumption while also promoting the use of renewable sources of power (Hastings & Meyer, 2020). It can also consider participating and improving philanthropic initiatives to help low-income families in underdeveloped nations.
Netflix’s Key Stakeholders
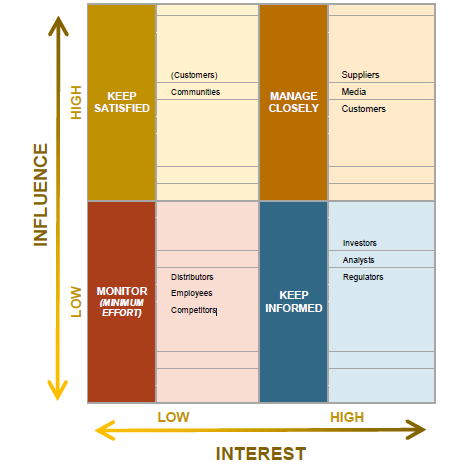
The most significant stakeholders of Netflix are its customers, suppliers, employees, investors, and communities. The company’s primary source of income is attributed to its clients’ viewership; therefore, the streaming giant engages them by giving the differentiated and original contents (Wayne, 2018). Netflix also ensures its employees’ wellbeing by monitoring their performance to continue releasing engaging content for the consumers. Reflecting its mission and vision statements, the company promises its customer segment stellar services, its suppliers a good relationship, its investors the possibility of sustained lucrative growth, and its employees the allure of significant impact.
Decision-making Process
The decision-making process of Netflix is fine-tuned to react to consumer needs from various markets specifically. Therefore, its organizational structure primarily exhibits decentralized control, considering that a firm which adopts centralization slowly responds to the dynamics of the entertainment industry (Shattuc, 2020). In particular, Netflix’s corporate configuration is a unitary arrangement that incorporates hierarchy for supporting managerial control and direction throughout the firm. However, its organizational structure has few elements of mechanistic departmentalization, signifying a flat configuration.
Netflix’s corporate configuration primarily consists of functional groups, geographical divisions, and departments for different product categories. Its functional segment manages its online and non-online operations and consists of the following parts; CEO, talent, finance, product, content and communications, and legal teams (Hastings & Meyer, 2020). Its geographic departments are in-charge of handling both local and international streaming. In essence, Netflix’s centralized structure is consistent with its competitive and diversification approaches in some ways. For example, its organizational design allows it to react to dynamics of the online streaming business effectively. Moreover, it is vital in helping the American giant manage its aggressive competition from companies such as Disney, Amazon, and HBO.
Recommendations
It is recommended that Netflix should consider acquiring a potential brand to improve its distribution of content and further expand its business model. For example, the streaming giant can consider obtaining Roku, an American firm specializing in hardware digital media players. Since a significant percentage of Netflix viewing happens on televisions, purchasing Roku will help it gain access to more clients while retaining other consumers in its platform. The streaming giant can also consider continuing its product improvements. The goal of this approach will be to increase user engagement and sustain product lead.
In addition, introducing new subscription offers, especially including advertisement-supported and yearly plans can improve the company’s financial position and competitive edge. Regarding Netflix’s corporate social performance, the firm performs poorly among its rivals for its carbon emissions. Therefore, it should consider incorporating energy efficiency procedures, green measures, and investing in renewable energy sources. Moreover, Netflix’s performance on corporate governance is poor when compared to its core competitors. As such, the company should consider improving its accounting systems, executive pay, and ownership structure.
Conclusion
This paper has majorly explored the significant aspects of Netflix’s strategic landscape. The company operates in a highly competitive sector consisting of dominant brands such as Amazon Prime Video, Hulu, HBO, and Disney Plus. However, irrespective of this rivalry, the American streaming giant has remained at the peak of the competition except for some limitations. As recommended, the streaming platform can consider a potential acquisition and other approaches to utilize its core competencies in neutralizing threats in its macro-environment. Therefore, purchasing Roku, introducing new subscription offers, and continuous improvement of its services will enhance its financial performance in the long-run.
References
Burroughs, B. (2019). House of Netflix: Streaming media and digital lore. Popular Communication, 17(1), 1–17. Web.
Hastings, R., & Meyer, E. (2020). No rules efficiency procedures: Netflix and the culture of reinvention. Penguin Press New York, NY.
Jenner, M. (2018). Netflix and the Re-invention of Television. Springer.
Lobato, R. (2018). Rethinking international TV flows research in the age of Netflix. Television & New Media, 19(3), 241–256. Web.
Lobato, R. (2019). Netflix nations: The geography of digital distribution. NYU Press.
Shattuc, J. (2020). Netflix, Inc. And Online Television. A Companion to Television, 145–164. Web.
Wayne, M. L. (2018). Netflix, Amazon, and branded television content in subscription video-on-demand portals. Media, Culture & Society, 40(5), 725–741. Web.
