Introduction
In 1939, Sara Lee started its journey with a glorious background of acquisition of C.D. Kenny Company by Nathan Cummings while Cummings was just an undersized wholesale and distribution channel of sugar, coffee, and tea in city of Baltimore of Maryland, the US state. The company turned into to Sprague Warner-Kenny Corporation and shifted in California due to the change of ownership in 1942. The company became a listed company in NYSE (New York Stock Exchange) and due to its uniqueness and diversification of the food industry, its share price raised three times above in 1946, later on, it had named Consolidated Foods Corporation. The company derived in to the food retailing market by purchasing Sara Lee’s Kitchens along with 34 Piggly Wiggly outlets all over USA in 1956.
Strategic Situation
Sara Lee Corporation kept its continuous efforts acquisition that evidenced in 1962 by purchasing Dutch canned food processing company Jonker Fris. In 1966, it purchased Oxford Chemical Corporation and E. Kahn’s Sons Company while the first one is nonfood and the second one is meat-processing company, it also purchased Bryan Foods, Inc, Gant, and Canadelle in 1968. Other acquisitions are Aris Gloves in 1969, Hillshire Farm and Rudy’s Farm in 1971, Chef Pierre in 1978, Douwe Egberts in 1980, Playtex Apparel, Inc and Rinbros in 1990, Mexico Underwear in 1991, Aoste, Italiana SP. and France SA in 1994 while all these had turned Sara Lee Corporation as a multination company.
At the beginning of this millennium, Sara Lee concentrated its business focus on foods and soft drinks, apparel and undergarments, packaged households, bakery, France, games and diversified so on. The company purchased US second largest bakery Earthgrains Company in 2001, and in 2002, it purchased Douwe Egberts, the 250 years old Coffee concentrate of Netherlands. In 2005, the company introduced highly nutritious whole grain white bread while Steven McMillan was the chairperson of this unit and in the subsequent year, it integrated European branded apparels and acquired Hanesbrands Inc a publicly traded company.
However, in 2005, the CEO of Sara Lee Brenda Barens had decided to implement divestiture strategy to build up brand image and improve financial position with smaller number of business units. In order to do so, Brenda Barens started to find out the weak sectors of Sara Lee and identified five segments those failed to generate positive profit margins and classified two other frail sectors those never succeed to reach expected level. However, it had generated total $8.2 billion from selling weak brand among them $85 million earned from US retail coffee sector, $9 million from Meat Snacks, $450 million came from business that sold cosmetics, skin care and household products (Direct selling).
External Analysis
Technology
Sara Lee had integrated most up to date technology in its production and marketing as well as complete customer relationship management (CRM) that provided the company the cost effective production, boosted sales and increased profitability. For CRM solution Sara Lee Corporation applied its complete resolution Microsoft Dynamics that has produced effective customer relation, effectual feedback and deliberated sales force to enhance its continuous development. Moreover, Sara Lee has flexible and responsive outlook to choice and adopt it technologies those have closely incorporated with supplementary technologies that are in existing use at its operation with the corporation’s higher acceptance at user level. The sales force of Sara Lee has shaped themselves with available technology and enough efficient to take probable actions directly changes it existing sales process due to the corporation’s user friendly technology adoption and contemporary features of the technical solution and the most important benefits of the technological solution is an unique outcomes than the competitors.
General Economic Conditions
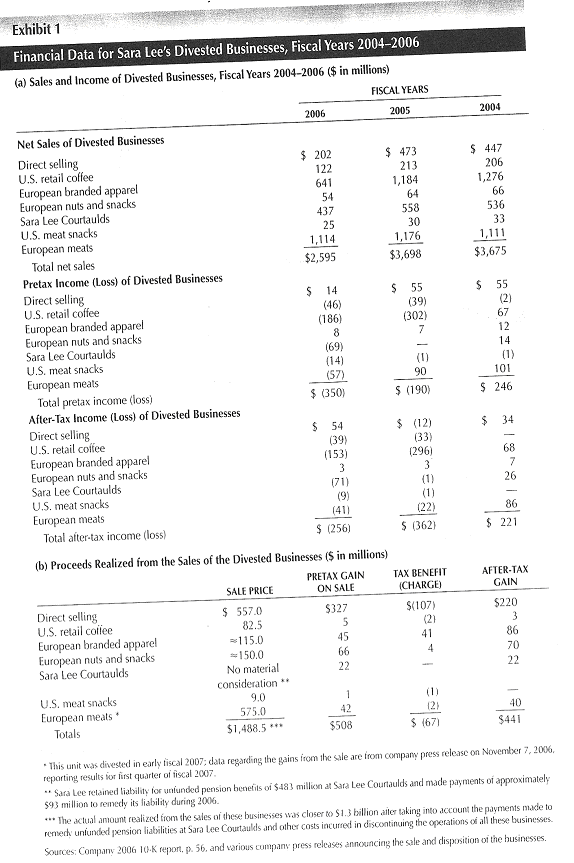
By 1998, its sales reached $20 billion from food sector whereas its net sales were about $24 million in 1939 and $5 billion in 1980. According to the case, it had $450 million from direct selling, $213 million from US Retail Coffee, $33 million from US Meat Snacks, $1.1 billion from European Meats, and $4.5 billion from Sara Lee Branded Apparel. However, exhibit 1 demonstrates that in 2004, its seven business units generated profits, for example, total net profit from these seven sectors was $221 million among these units direct selling, European Meats and Branded Apparel sectors had generated more profit than its other business sectors. Exhibit 1 also shows that the economic position in these sectors had decreased dramatically and only two sectors were profitable in 2006. However, the management team decided to sell these units in order to recover its financial condition of the company though it had chance to change the strategy to improve the position of weak business units.
Legislation and regulation
According to the case of Sara Lee, it has business operation in many countries in Asian and European market, so it has to follow the rules and regulations of the relevant countries. Moreover, it has to consider national laws and companies own constitution in order to avoid the risk of litigation and unnecessary harassment. However, Sara Lee bound to pursue the competition law of European Union, as Sara Lee’s apparel business unit was popular in UK, Italy, Spain, and Garman market and its Meats products unit was highly accepted in France, Poland, and Romania etc. Here it is important to mention that European commission regulates Competition law and all EU countries have own set of regulation, so Sara Lee is subject to both these laws for its operation in foreign countries. In addition, Sara Lee has to follow the rules and regulation in order to enter a new market, mitigate legal problems, contract with any parties, advertise it products, success with the growth plans, control the corporate governance system, ensure equality in work place, and so on.
Population demographics
Sara Lee international brands considered the population factors to expand its business in outside of US market and fixed up its target customers accordingly. It has established thirty new factories in outside of US market in order to manufacture more products for international market. Its insecticide brands had endeavored to capture Asian market as India, Malaysia, Indonesia, and other countries were high-populated area in this region. As Sara Lee was a customer-oriented company, it had designed its strategy by considering demographics of these countries.
Societal values and Life styles
The socio-cultural factors played a vital role to implement strategy of its business units because Sara Lee has different range of customer in most of the countries of the world. In 2006, Sara Lee had more than 109,000 employees who came from different place of the world. Initially, there was no cultural problem, as the company ensured equal rights but international employees of Sara Lee worked with tension due to job losses of co-workers. Sara Lee regularly cut the job of employees though these employees were efficient in their own sectors, for example, it had more than 4500 skilled employees in European meats segments, but it decided to cut the jobs of 1300 International employees to reduce operating costs and invest in new sector. Negative growth rate of employees demonstrated the weak financial position of the company though the CEO of Sara Lee tried to establish this process as a part of retrenchment strategy.
Industry Analysis
Driving Forces of Sara Lee
The values of diversity and variety of enclosures of different level business and holding up all these concepts in an aggregated manner with supporting cultural is the major driving force that turned Sara Lee Corporation as a billion dollar company. The core issue of its driving force is to operating a number of separate entities with the company’s own board of directors who are committed to the growth of the company and humanizing the communities where it works with different cultural initiatives those are crucial to nurturing the healthy communities that support present and feature the perspective of the company. Sara Lee’s grant making drives deliberately addressed on the nexus of food insecurities, nutrition measures, and awareness of healthy lifestyles, women’s intimates, and diversity that definitely grounded with cultural initiatives.
Sara Lee always has taken the strategic impression of one-step forward than the present stands of providing ready to use packaged branded consumer products in the market rather than foods, beverages, and bakery products ensuring the prime quality. Sara Lee maintains not only the tale and quality of the of the products are the driving force for the company to attract millions of customers worldwide but the maintenance of previous brand heritage with new resource has contributed the company to touch a skyscraping success. Sara Lee considered that product line is a significant issue but not any longer single driving force to induce customers to depend on the brand, the company is too skillful to appreciate the dynamics of customers including the resources of supply chain management, marketing strategies as well as the most recent consumer trends.
Key Success Factors
Sara lee always emphasis on customer and customer-driven innovation and concentrate on continuous development:
- It had created new paths for even greater success in the future;
- Seven key strategies, retrenchment strategy, managing its procurement activities, strengthening, technology were the main success factors;
- Other factors are lower costs, improve effectiveness, simplify, expand in high-growth, developing markets, outstanding performance in North America;
- New product development, fresh and quality products,
- Increase rate of repeated customers for unique facilities;
- The concept of working together with business partners one of the important success factors;
- In addition, Sara Lee had tried to create lower-cost global supply chain.
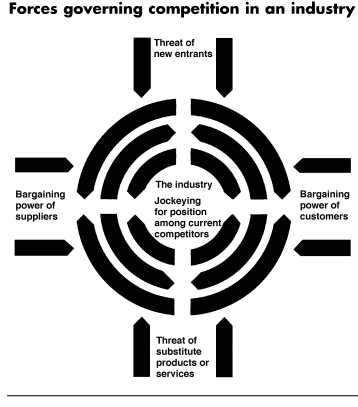
Porter’s 5 Forces Analysis
Purpose: The purpose to use this model is to discuss the competitive situation that Sara Lee faced from the local and international competitors
Addressing the Forces:
Threats from new entrants
For Sara Lee, the threats of new entrants are moderately low because –
It was difficult for the Sara Lee to sustain in the market by increasing profit though it was a large multinational company, so it would be difficult to become successful for a new entrant;
- In addition, new companies would require large investment but investors were show less interest to give large amount of bank loan;
- New companies would not have brand image, as a result they are not threat for Sara Lee;
- However, the new entrants only become threat for Sara Lee if the companies enter in the market as the franchise of other existing branded company or joint venture company by using any entry mode strategies.
Bargaining power of the suppliers
As there were available suppliers to supply the raw materials, the bargaining power of supplier is low and there were few other reasons which influence the relationship:
- Sara lee has maintained long term relationship with the suppliers as the are the essential parts of the business;
- It also worked closely with suppliers for continuous development and innovation projects;
- According to the view of CEO of Sara Lee, its procurement department implemented supplier management strategies in order to gain purchased commodities and services at more predictable, stable and competitive stages;
- Moreover, this power also depends on foreign suppliers as Sara Lee had to purchase raw materials from foreign suppliers;
Bargaining power of the buyers
The Bargaining power buyers were comparatively high as –
- The major customers of Sara Lee were retail customer and it had to contract with other companies to purchase its product, so there exists a moderate level of buyer- seller understanding;
- In addition, unique brand item or food items influence the purchaser;
- According to the case, these retail buyers share their promotional tools with Sara Lee to increase sales of the products;
- The bargaining power of buyer has automatically reduced as Sara Lee offered low price or discount price;
Threats of substitute products
Sara lee mainly operates seven business units and most of the sectors were too common, therefore the risk of substitute products are comparatively high –
- It has some direct and some indirect substitutes for its products;
- However, threats depends on the quality of products as it has no direct substitutes Ball Park franks or fresh bakery breads;
- On the other hand, the threat of indirect substitute products was high as there were many other companies, which offer competitive price.
Rivalry among existing competitors
All the business units of Sara Lee were extremely competitive, so, rivalry relationship exists among most of the competitors in the US market, for instance –
- Hostess Brands, Inc., Kraft Foods Inc., Tyson Foods Inc. and other processed & packaged goods industries were the major competitors of Sara Lee;
- The competition is high, as other similar companies also offer similar facilities, for example, its food and Beverage of North American retail business competed in three of the largest grocery categories;
- However, Sara Lee had many indirect competitors in meat packaged, food industry, retail, and apparel segments.
Company Situation
Financial Analysis: Profitability, liquidity, leverage and activity
Sara Lee Corporation sold out its seven business wings in 2006 with the objectives to save the corporation from continuous losses and to generate more cash flow and marvelous resources for the wings those are more profitable. At this stage, the corporation has set up its goal to enhance its sales volume at a minimum 2% that would result an enlargement of its profit margin around 12% within 2010 through raising the competitive advantages in rest of its lingering business wings that would progress its net profits in years.
The corporation applied the strategy that facilitated to boost its corporate profitability and retrenching most of its loosing business concerns and the seven sold out business wings has involved U.S. retail coffee in European Market, European apparel, European snacks, and European meats both in European Market and in US. In 2006, among them five business wings has demonstrated negative profitability with depressing operating margins where four of them evidenced more than 10% loose per annum and historically most of those wings accounted very steady earning otherwise recorded serious declines of profitability since 2004.
The direct selling business wings and the European snack divisions are the concern those proved their profitability but evidenced decreasing operating margins and dilapidated revenues. Selling out the snack business may argued as smart decision as they have generated net profits of US$ 3 million only that don’t keep any contribution to the business to enhance shareholders’ value while the corporation has gained US$ 70 million after-tax and it is 22 times above than the concurrent net profitability. Retrenching the direct sales units is not a smart decision as they illustrated 27% profitability that amounted US$ 54 million simultaneously household and body care units evidenced positive contribution and after retrenching the seven generated US$ 440 million profit that overcoming US$ 260 million net loss and the actual gaining of 2006 figured US$ 700 million.
The sold out of Hanes brands proved doubtful as the revenue, gross profit margin, and operating profit have smooth growth of US$ 100 million net income in 2005 but accounted 5% decrease of return on investment (ROI) and return on equity trapped at least 50% relation to 2004. Meanwhile within this period the Debt-to-equity figured almost at 5 that demonstrates the capabilities to maintaining its debts lower weighted against the sum of equity that is on hand, thus this business wings acquired noteworthy debt in array to continue as an impartial business and able to accelerate other businesses of Sara Lee.
The Sara Lee Corporation has introduced numerous brands in US market as well as in global market by ensuring strong operating profits among some of its brands and its global operation has also demonstrated sky-scraping operating profit that recorded about 13% though it was 15.7% in 2005 and caused from 3% declines in beverage, body-care, and household sectors. The bakery-oriented business pointed a decrease of 1% caused form the turn down of packaged food demand in the European market while Sara Lee’s coffee outlasts captured up to 10% of the existing market and it has facilitated Sara Lee the opportunity of further expansion by increasing US$ 2.4 billion sales revenue.
The foodservice wings surprisingly displayed the decreasing operating margins in 2005 although sales volume has jumped greater than before $100 million but margins have decreased 2% in that year and the sales of bakery products have turn down in the outlets while beverages sector contributed about 30% of total sales by addressing the US customer’s eating trend out of home. Within the period, the meat lines sold in US groceries have enlarged around US$ 100 million and contributed the boost of profit margins up 2% growth by integrating promotions and more innovative product line while revenues of bakery sector hang about stagnant with a tiny margin of 0.5%.
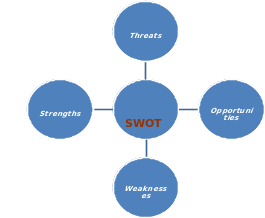
SWOT Analysis of Sara Lee
Strengths
Sara Lee has excellent brand awareness and quality image, which facilitate the company to boost its profit day by day, it has diversified product line, for example, it operated seven different business units in 2005 those demonstrated its strong administrative control on the company with skilled human resources to successfully handle any business at any extend. According to the given case, its income from sales has increased, such as, in 2006, its sales income was 4,472.832 million whereas it was 4683,683 million in 2005, while the fixed assets, financial capabilities, cash inflows, and strong brands help the company to follow growth expansion strategy simultaneously in different business units. Sara Lee has turned itself as the market leader of few sectors like Coffee, meat and bakery, it worked as a team with integrity, used imagination, and had passion to excel its loyal customers, potential strategic decision-making process, direct selling, and merger with renowned companies were key strengths of the company.
Weakness
According to the given case, some products of Sara Lee were not enough popular to the customers, such as home desserts and coffee pods experienced little growth while distributors channel for the products were not well designed as many of the products were not easily available to the customers end at retail outlets consequently it affects on the sales revenue. It is most imperative to mention that net profit margin has decreased though the sales revenue has increased for high operating costs created hindrance to generate large profit, moreover the scoring of Sara B+ for huge debt as Hansbrands borrowed about $2.6 million, and sales revenue could adversely affected due to reduced advertisement costs in order to decrease operating costs.
Opportunities
The food service industry offered Sara Lee a considerable growth opportunity as US customers continued to eat a higher percentage of meals out of home and It offered five times better services and products, as a result, sales of Sara Lee’s whole-grain white bread has increased two times above than its competitors. The Asian markets were prospective for its cosmetic or body care products and European market was potential for insecticide products while international expansion helped the company to build up strong brand image in global market; moreover according to the case study, new product introductions, new marketing programs, increased in-store promotions, and developed placement were expected to drive sales increases.
Threats
The most remarkable threat for Sara Lee is that, it has already integrated retrenchment strategy but many sectors failed to reach its goal, such as five business units had negative net profit margins and negative operating margins in 2006 while as a large diversified company, Sara has different pressure for different segments, like customer choice. The quickly changing fashion trends are a big challenge for apparel segment, offering special menu is a threat for food segment while competitors carried out foremost threat for Sara Lee and its income has decreased due to high income tax rate and increased the interest expense.
Recommendation
Strategic Problem
This scenario raised the question, to what extent this divestiture strategy was profitable for Sara Lee as most of the business units were potential for the company.
Strategic Recommendations
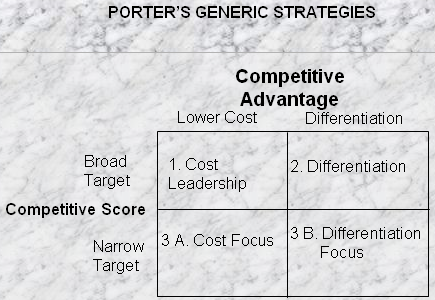
Generic Strategy
Cost Leadership: Sara Lee should offer low price for its products in order to maximize its profits and sustain in the market in adverse economic condition, as the food market is too competitive. However, it was possible for Sara Lee to increase sales revenue and save its other business units by minimizing the price of the products whereas the CEO of the company mainly focused divestiture strategy, diversification, and retrenchment strategy to recover its financial position.
Focus: According to the case, Sara Lee wanted to concentrate on its core business for further expansion but this strategic decision created some barrier for further development. However, it had chance to reallocate all business units besides operating core units to lessen the market risks but it lost this opportunity by taking some unreasonable decisions and selling seven major units. For example, Sara Lee generated more than $213 million profit from US Retail Coffee but Sara got only $85 million by selling this segment.
Differentiation strategy: From the beginning of its operation, Sara Lee followed very High-Levels of diversification strategy by extended product line with high quality as it earned less than 50% from single sectors and it did not share the raw materials.
Grand Strategy
From the very beginning, Sara Lee had maintained porter’s diversification strategy but from 2005, it had decided to follow divestiture strategy to highlight more on core business units.
Divestiture: The decision of Brenda to sell Direct Selling Business and European Meats of Sara Lee with lower price was not a correct decision and there were no reason to sale a profitable segment, for instance, it had generated $1.1 billion from European Meats units but Smithfield purchased this unit with $150 million. In addition, the sale price was disproportionate with the total net assets and reputation of the company because the sale price of US Retail coffee was $82.5 million (after tax gain only $70 million), the sale price of direct selling was $557 (after tax gain only $220 million) and sale price of European branded apparel was $115 million (Exhibit 1).
According to the case, Sara Lee’s decision to spin-off Hanesbrands was questionable due to several reasons like this segment was totally isolated from other food related North American Business segment, which made huge profit from international market. In addition, the products of this unit had generated a solid base of revenues for Sara Lee, for example, in 2004, it sales revenue was $2.25 billion and total income was $221 million though its sales revenue slightly decreased from 2005. However, it is clear from the case that Sara Lee had the opportunity to utilize its net income for the development of other sector, which could accelerate the profit margin of that segment. Moreover, Sara Lee could pay off the debt of this unit by changing business strategies or pay off from its net profits but the administration showed less interest to continue or expand the operation of this unit in international market. In this perspective, Sara Lee should have retained this business unit because it was potential sector not only for other segments but also for the entire company.
Objectives
Its ultimate aim was to concentrate on core business and increase profit by decreasing operating costs, eliminating major risks, applying divestiture strategy and restructuring its core business units. In addition, it wanted to establish the company as a market leader in US and international market with innovative ideas, extraordinary customer care, constant development, and diversified product line.
Strategic Justification
Before selling its major sectors, Sara Lee should have considered the overall debt position, net losses, and strategic problems to assess major risks of the company.
The fact of the case demonstrates that its aggregate financial situation was quite stable from 1939 to 2004 but it failed to sustain this position from 2005. It had financial capabilities, innovative ideas, supply chain, reputation, business structure, and human resources to diversify its product range but implementation of divestiture strategy stopped its further expansion though the case mentioned that it gained $8.2 billion revenues. Sara had no justification to sell profitable business units but it was justified to sell dessert items, as a result, it should invest more for weak units to protect further divesture and in should concentrate on air freshener, insecticides, household and body care brands.
Implementation, functional and operational plans
Sara Lee should encourage the profitable business units and arrange adequate funds for these units in order to adopt organizational change approach like it should implement business level or corporate level strategies. However, Sara Lee reported that from the production to marketing of goods, it had maintained high quality, as a result, it offered high price and it was not possible for the company to lead in the market through cost leadership. Therefore, it should reduce the price of the products though Sara Lee offered discount but it was not sufficient to increase net sales. In addition, the company should increase budget for promotion but according to the case, it decreased advertising costs, which adversely affected the company.
Appendix