Executive Summary
Marketing is an imperative attribute for improving the sales, loyalty, trust, and reliability of product sales. The sales of productions are essentially affected heavily by the strategies applied to the marketing techniques to reach the highest number of people being targeted. To understand this imperative role of marketing being handled within the business progress, this analysis evaluates the marketing strategies applied by Coca-Cola Company in its endeavors to supply its target market with quantities of the product referred to as Minute Maid in China.
The subject analysis seeks to review the implementations of budgetary and strategic management on all levels of marketing that can lay a sustainable base for the sales of Minute Maid. The techniques review such common ways of marketing as advertising and assess the tactical approaches involving product promotions through credit cards. The integrated marketing communication (IMC) plan primarily commences by laying profound arguments about the basic sub-branding of this product. This aspect refers to discussing such factors as imaging, segmentation, branding, SWOT analysis, and competition, among other fundamental aspects.
Industry Analysis
In China, the Coca-Cola Company functions within the Chinese Food and Beverage industry, depicting a substantial growth rate as exemplified by the 30% growth from 2006 to 2012. Figure 1 shows an analysis of growth from the F&B industry since 1991.
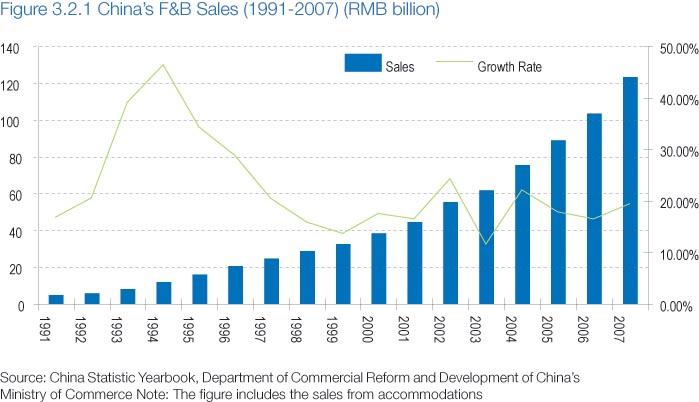
This evident advancement is precarious when many companies are taking a sizable interest in delivering similar products. Factually, competitive markets provide ardent, reliable, and sensitive managerial direction based on quality improvement and sponsor of the competitors’ strategies. This factor implies that a competitive company must invest properly in the quality of products to attain dependable loyalty. Whereas this fundamental approach has been laid within the industry, barriers of business prowess are seemingly inevitable, and their presence is beyond reproach. Twenty-three out of the 646 sub-brands of Coca-Cola distributed globally are supplied to the Chinese markets.
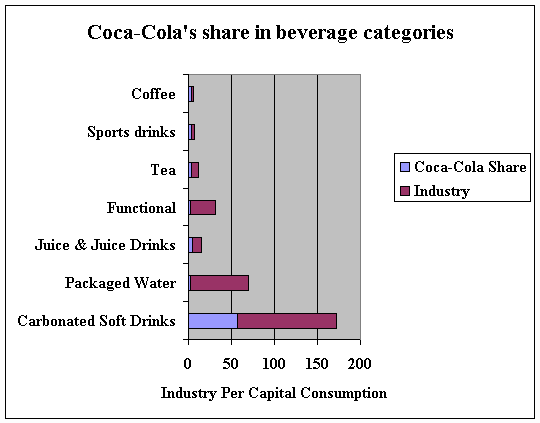
They compete with other products from such re-known companies as Pepsi, Jiangxi Runtian Beverage, and Unilever. Supplement and complement good are evident within the Chinese market, which leads to the sharing of the china beverage industry as stipulated within figure 2. It shows some of the primary products sold within the industry and the efforts of the subject company in this business. The most dominant companies pay attention to the delivery of carbonated soft drinks, canned and bottled water, tea, and coffee, among other beverages.
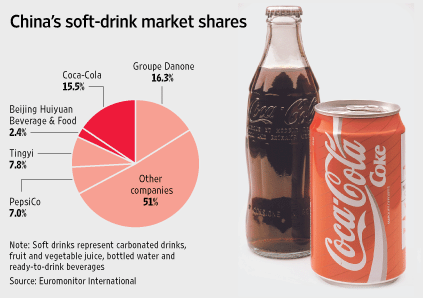
The Coca-Cola brand shares the largest market in the sales of soft drinks within china. Figure 3 shows the proportion of the market as shared among the various supplementary or complementary competitors from the beverages industry. The major threat to Coca-Cola Company is its competitor Groupe Danone. Other competing companies within the industry are Pepsi, Tingyi, and Unilever, among others. A comparison between some of these major companies is displayed in figure 3.
Apart from the analysis of competitors and the strategic situation within the company as described above, intercompany analysis of industry competitions can be realized in figure 4.
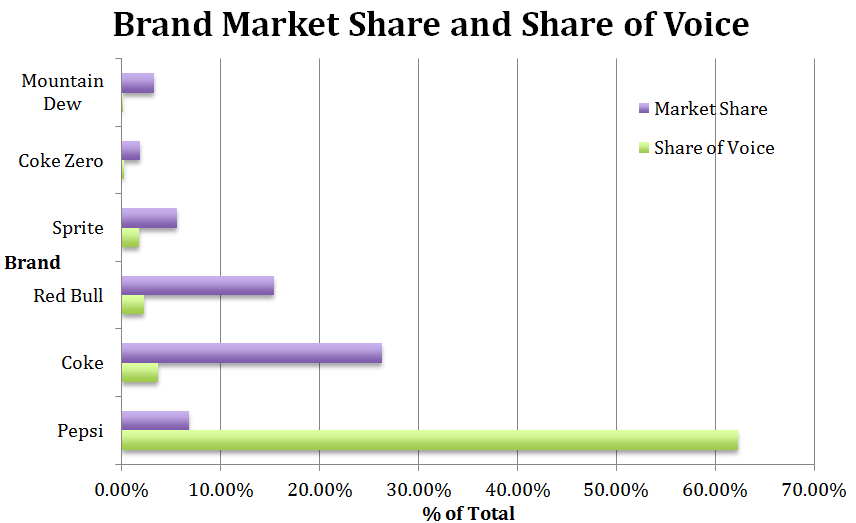
Competitive Analysis
Figure 2 shows how the market and loyalty of customers have been shared between Coca-Cola and other companies within the industry in China. The Coca-Cola Company is releasing its new credit card to capitalize on the increased number of sales. These cards are attained either by applying at the local bank or through the online bank website. The cards are emblazoned with the company’s logo giving the eligible bank clients an opportunity to choose the establishments they would like to link with their card.
Whereas this factor boosts the competitive and loyal nature of customers, other strategies involve promotion, quality improvement, and decrement in the prices of products (Crespo-Almendros & Del Barrio-García 2014). However, the cards enable the company to avail of special discounts after purchasing beverages from the Coca-Cola brand.
Corporate Imaging and Brand Positioning
Coca-Cola has a well-established brand name with loyal customers across China. The brand has been patented for beverages and the sale of other related drinking products. The popularity of the brand is cultivated by the delivery of a quality product. The establishment of the brand arose at a time when few companies were offering the same products. Therefore, most people had managed to familiarize themselves with Coca-Cola.
When the sole domination is conjoined with quality, people were able to trust the producer and use the commodity. The overall perceived image after mentioning the term Coca-Cola is the perception of soft beverages. This perception has been developed through progressive marketing and advertisements and the involvement of the public in credit card launching. The involvement of the public in such events as credit scores is vital (Lowe & Barnes 2012).
Segmentation and Targeting
The segmentation of Coca-Cola Company to provide substantive access to customers is evident. In this regard, the broadest segmentation apparent in connection to the industry involves the region where Coca-Cola operates in china. However, there are further consumer market segmentations that are regional in nature. For instance, the factories producing the beverages within China have profound and majorly independent management to produce and supply the products in the various states within China.
The nation is densely populated while compared to other states allowing access to many people and the requirement of large factories to meet the customers’ demand. Essentially, the consumer segmentation has been met through the resonance of adequate and tactical strategies involving urban and rural regions. This segmentation allows the company to orient its products in regard to their destination since urban areas have many people demanding higher quantities of the Minute Maid.
Since China is the most populated country within the globe, there are adequate reasons to implement such population-based segmentation. The other segmentation base involves demographic factors such as age, where young people are targeted as the majority customers. Even though other ages beyond the age of 30 are considered within this aspect, the main customers are between the ages of 10 to 30 (Lowe & Barnes, 2012).
On another dimension, the company modified the Minute Maid to meet the demands of the consumer in China. This aspect was facilitated by the suggestions and interests retrieved from the consumer behaviors. In this regard, there have been various differentiations where Minute Maid juices are prepared as orange, pineapple, strawberry, and blackcurrant.
Similarly, the market segmentation has been perceived depending on the seasonal variations. The company has found that the sales of Minute Maid increase during summer and reduce during winter. Also, it is argued that the beverages are used heavily in areas around educational institutions where many young people are found.
Customer analysis and profiles
Specific behavioral factors that should be present include:
- High and occasional purchases of meals with Coca-Cola products.
- Little variation in purchasing location (i.e., Continuous patronage of the same restaurants).
- High amounts of purchases of soft drinks.
- Little or no delinquency in paying for purchases made.
SWOT Analysis
Strengths
The use of credit cards in the sales of products such as Minute Maid restricts the customer from buying other beverages. It boosts the involvement of customers in marketing that suits them. Furthermore, brand loyalty has accumulated heavily, allowing the consumers to ignore other brands in the market. It is also apparent that the company has a dependable market, which prevents other companies from entering the market. This aspect implies that the entry into the market has been made tougher.
Weaknesses
There are many compliment brands and products available in the market, which compromises the effective prowess of the new product. Minute Maid is not able to achieve a good market share because other competing companies, as well as other products from Coca-Cola, have divided the possible sales. In this case, the emerging products are not able to survive in this oligopolistic environment due to unlimited resources. The products did not manage to reach the target sale and profits.
Opportunities
Young people have the tendency to try new products and measure their level of satisfaction. In this light, the sales of Minute Maid through the use of credit cards may have baseline customers. Such companies have made the customers the core of the organizational culture across all departments and functions to improve the motivation of customers. They have also ensured that a healthy relationship between the customers and the employees are hosted, and they have achieved the full profit potential from each and every consumer.
Threats
The growth of the F&B industry has attracted many companies to provide similar products. This aspect may reduce the target achievement of the Coca-Cola Company in regard to Minute Maid. They may introduce competition and cause adequate loss through advertisements for achieving competitiveness. These include finances used while funding promotions and advertisements to boost the product.
Setting Objectives
IMC Objectives
The marketing objectives for this endeavor are to;
- Increase the amount of Coca-Cola customers within China by 30% within one year
- Achieve a product penetration rate of 60% within the market of Beijing, Shang Hai, and Guangzhou after one year
- Increase consumer awareness of the Coca-Cola brand by at least 30% within one year in China
- Achieve an initial subscription rate of 20% of targeted market demographics within the first year of release, after which subsequent rate in consumer subscriptions should increase by 10 to 15 percent per year.
IMC budget
The IMC budget for this promotion will start at $1,000,000 for the initial promotion yet will increase to $10,000,000 on weekly prizes that will be given away in conjunction with the Coca-Cola credit card promotion.
Agency selection
Agencies are not needed since the entirety of the promotion campaign is handled within the company and banks that are part of the promotional activities.
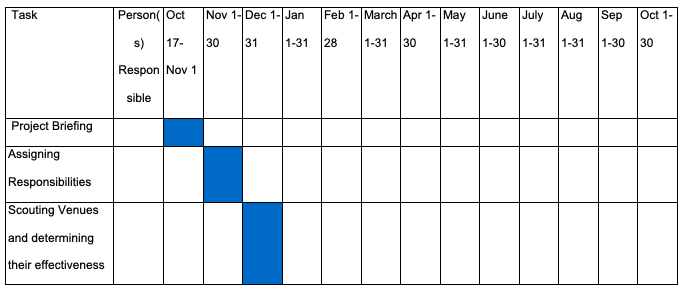
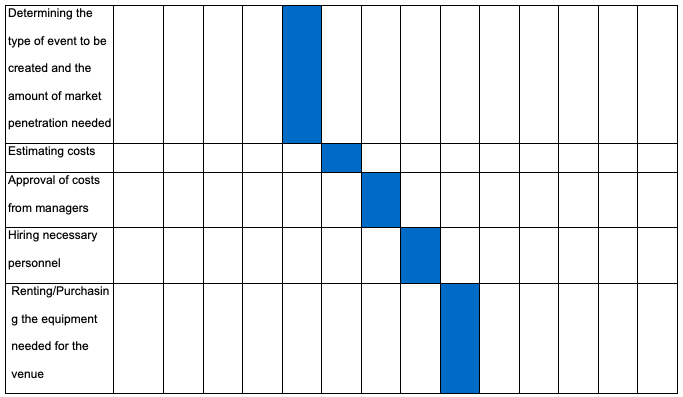
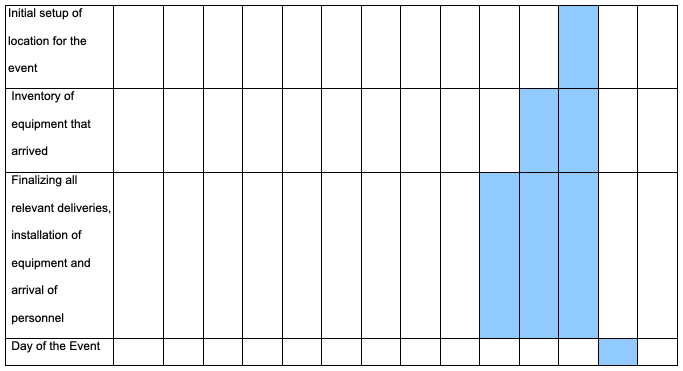
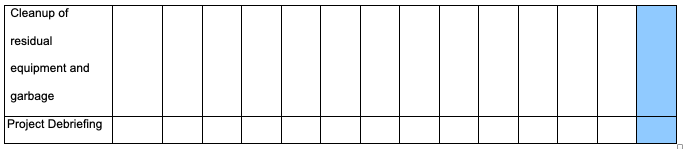
Timing: Gantt chart
The Gantt chart is located in the Appendix section of this paper.
Developing Corporate Strategies
Media distribution and planning
The media distribution and planning strategy for this advertising campaign focus on the Coca-Cola giveaway and concerts as a means of drawing media attention towards the Coca-Cola credit card. Furthermore, banks will send flyers to their customers in the envelopes containing their monthly credit card bills advertising the Coca-Cola card as well.
Evaluation metrics/ KPIs
In order to determine how well Coca-Cola was able to meet its market objectives, sufficient market research could be conducted. First, it will be necessary to examine whether the company was able to increase the coke consumption of its target clients after six months period. This examination may be done by assessing the credit histories associated with the card and evaluating the amount of Coca-Cola products purchased as meals (Liu, Cheng & Ni 2011). Thereafter, an evaluation should be conducted to determine how many current subscribers are present in the Coca-Cola credit card program versus the number of estimated users within the launching regions. Therefore, the degree of market penetration, usage, and Coca-Cola’s ability to meet its market objectives would be possible after combining both data sets.
Promotional Tools
Sponsorship Programs
For this venture, no sponsorship programs are imperative. The entire process should be handled by the company itself.
Consumer promotions
The consumer promotion for the product is done primarily through the event and via the bank.
Personal selling
There is no personal selling conducted. The promotion focuses on the giveaway, concert, and Coca-Cola card primarily.
Direct Marketing
Advertising and promoting the Coca-Cola credit card will involve three specific strategies: direct consumer invitation, targeted commercials, and press releases for the public. In the first strategy, the Coca-Cola Company will copy the current credit card promotion method utilized by various banks by sending specific invitations to select customers via mail. These invitations will include a summary of the benefits the card would give to the consumer, how much it would cost them per year to maintain, and the selection of stores to link to the card. Several email addresses will be placed on the invitation that the customer can use to directly contact the affiliated bank and facilitate the transaction at a later date.
Internet
The application of the internet to the marketing of Minute Maid is prevalent. Essentially, these sales have been facilitated by advertisements on social media and other online websites or search engines (Crespo-Almendros & Del Barrio-García, 2014). The sites used mainly while making online advertisements include Facebook, Twitter, Google Plus, Google, Yahoo, and Coca-Cola website among others. The ads are done through the use of digital media, including pictures and video, to inform the public.
Event marketing
Marketing the event will be straightforward since the company will set up various posters and use local television advertisements to broadcast the free concerts and giveaways at a certain location. During the event, the various attending pop stars and idols will promote Coca-Cola as a product and give their recommendations regarding the new Coca-Cola credit card that consumers can avail. Both methods of marketing should lead to a considerable level of public interest, especially when considering that the prizes will range from free Coca-Cola products to iPads, iPhones, cars, and fully paid international vacations. These promotions will entice the consumers more and lead to more inquiries about the card.
Implementation Process
Promotional tools should be instilled properly according to the real organizational plans. The process commences with the distribution of products throughout the state, where promotional techniques are incorporated. The order of promotion strategies may be gifts under the lids, giveaways, concerts, digital marketing, and events.
Promotional Materials
Ads series and Digital Marketing
The advantage of digital marketing trends over their traditional counterparts is their capacity to provide instantaneous consumer data regarding their effectiveness, which enables companies to change the marketing techniques based on consumer’s reactions. This aspect can be possible due to the current use of advertising analytic data, which takes the form of page views, the number of clicks on an advertisement, the user demographic (i.e., IP address) of where it is primarily being viewed from as well as the rate by which it is viewed. By utilizing such data, companies can immediately determine how effective a particular campaign is and make an immediate change via the advertising provider’s console interface (ex: Google Ads). Such data is not available in traditional advertising campaigns, which makes digital marketing campaigns much more appealing when taking this into consideration.
Direct mail
Social media allows calling, texting, and emailing as the most dominant methods of communication where millions of people utilize their networks, such as Weebo in China, in order to reach other people and communicate globally. It has resulted in a more interconnected society where Coca-Cola can instantaneously reach out and communicate to hundreds or thousands of people within a few seconds.
Online Ads
Online advertisements are fundamental where add-ins are used to inform people who are browsing about the sales of Coca-Cola products. The ads are connected to the people browsing the internet in China. They are connected to websites addressing connected ideas.
Preparing Whole Plan
Budget and ROI
The total budget for the project is estimated at $11,000,000, with a return on investment of at least 100% due to the increase in the amount of coke consumed within a year.
Cost Approach
The cost of the project was based on an examination of budgets outlined on various online websites regarding event management and expanded to fit the needs of the company. In this case, the cost approach takes into consideration the percentage of sales needed to recoup the amount paid per million people and the estimated amount of sales needed on a daily basis.
The following was the formula applied:

This is equivalent to 0.0025 x 10,000,000 = $25,000 per city per day. With five cities being scheduled for the initial trial period, the consumption sums up to $125,000 a day. The amount spent on the promotion will be recouped within five months.
The daily advertisement expenses may amount to100 dollars. If conducted on a daily basis through the mass media, the total cost for the five months would be $5000. Finally, the estimated cost of credit card production and distribution can sum up to $1000000 as envisaged in a similar cost for the USA.
Campaign Timeline
The start of the campaign is October 17, and it will end by the middle of the next year after the various other promotional events that the company will create.
References
Ailawadi, K, Harlam, B, César, J, & Trounce, D. 2006. ‘Promotion Profitability for a Retailer: The Role of Promotion, Brand, Category, and Store Characteristics’. Journal Of Marketing Research (JMR), vol. 43, no. 4, pp. 518-535. Web.
Crespo-Almendros, E, & Del Barrio-García, S. 2014. ‘The Quality of Internet-User Recall: A Comparative Analysis by Online Sales-Promotion Types‘. Journal Of Advertising Research, vol. 54, no. 1, pp. 56-70. Web.
Liu, T, Cheng, T, & Ni, F. 2011. ‘How Consumers Respond to the Behavior of Missing a Free Gift Promotion: Inaction Inertia Effect on Products Offered as Free Gifts‘. Journal Of Social Psychology, vol. 151, no. 3, pp. 361-381. Web.
Lowe, B, & Barnes, B. 2012. ‘Consumer perceptions of monetary and non-monetary introductory promotions for new products’. Journal Of Marketing Management, vol. 28, no. 5/6, pp. 629-651. Web.
Parre-Selva, J, Mas-Ruiz, F, & Ruiz-Conde, E. 2014. ‘Price promotions effects of virtue and vice products‘. European Journal Of Marketing, vol. 48, no. 7/8, pp. 1296-1314. Web.
Appendix
Gantt Chart for Coca-Cola China Promotion