Introduction
The company Louis Vuitton S.A is famously known as LVMH and is based in France. The company is a multinational luxury goods manufacturer and distributor, and has its headquarters in Paris, France. The company was formed after a successful merger between Chandon, Moet-Hennessy, and Louis Vuitton.
Later the company expanded and currently is controlling over 60 subsidiaries each managing a prestigious brand. However, the subsidiaries are independently managed. The company was formed in 1987 as a French company, but currently is the leading global luxury manufacturer. The company has over 2300 stores globally with about 77,000 employees (Funding Universe Para 2).
Its business activities are subdivided into 5 business groups explicitly fashion and leather products, jewelry and watches, cosmetics and perfumes, selective retailing, and wines and spirits. The company’s functions are span across numerous geographic locations, including Asia, the United States, and Europe.
LVMH was incorporated in 1854 as Louis Vuitton SA but later changed its trading name to Moet-Hennessy in 1771. The company is a luxury manufacturer or producer. It produces products such as wines, spirits, distilleries, women’s handbags, purses, clothes, perfumes, beauty cosmetics among other luxurious products.
The success of the company is traced back in 1743 when the company was formed by Claude Moet as a sole owned company to sell wine. In 1792, when Claude Moet died his son Jean-Remy became in charge but handed over control of the company to his son and son-in-law in 1832 and they renamed it Moet et Chandon. In 1971, Moet et Chandon merges with Jas. In 1984, Louis Vuitton goes public and merges with Moet-Hennessy in 1987 to form LVMH, which presently is world’s leading company in luxurious products manufacturer.
The company Louis Vuitton Moet-Hennessy (LVMH) presently leads in vendor of luxurious goods globally with provision of goods ranging from designer handbags, perfumes to champagne (Funding universe Para 11). LVMH is current in the cosmetics and perfume subdivision via French houses Christian Dior. The luxury products group, Christian Dior, is the principal investment company of LVMH. It owns up to 42.36 percent of the company’s shares plus 59.01 percent voting rights. The Chief Executive Officer of LVMH and chairman of the company is Bernard Arnault, who is the majority shareholder of Christian Dior.
The company LVMH is a combination of Louis Vuitton and Moet-Hennessy. Initially, Louis Vuitton was involved in the production of fabrications and leather products. On the other hand, Moet-Hennessy was involved in the production of perfumes and wines. The two companies merged in 1987 to expand their production units and produce other luxury products.
The 1987 merger was helpful to both companies due to several reasons. For instance, it saved Moet-Hennessey from takeover due to the problems they were facing at that moment and it allowed Louis Vuitton to expand their investment in luxury business. Though the company was faced with some management wrangles after the merger, they adjusted and entered an agreement, which solved the wrangles (Funding Universe Para 36).
After the merger, the company had a growth and expansion strategy, therefore; it was making use of any advantage they came across. In the late 1990s the company acquired several companies leading to the expansion of the luxury empire business. The company acquired companies such as Sephora, Arnult, DFS Group Ltd, Celine Loewe and Chateau D’Yquem. After the investments and acquisitions, the company grew and diversified but was faced with several problems between 1997 and 1998.
The company suffered from sales sagging and the Asian economic crisis. Asian region accounted for 60 percent of the company’s sales hence the economic crisis led to decline in company’s sales. Other problems that faced the company during this period were decline in profits from DFS Group by 50 percent and Sephora by 22 percent in 1998. The fragrance and cosmetics section also realized a three percent decline in sales. The company remained strong and focused despite the challenges it faced in between 1997 and 1998 (Funding Universe Para 41).
The following year, 1999, the company realized an increase in sales due to the recovery of the Asian economy. The company recorded a remarkable increase in share by 77 percent in the first half only. The sales of the divisions also rose leading to the recovery by the company and becoming the leading company in luxury business globally. In 1999, after the recovery, the company opened 127 new stores and by end year, it had 50 stores in the United States and 253 in Europe and Sephora.
It also opened website selling in Sephora the same year. The company recovered from the loss between 1997 and 1998 and increased their operation by opening several principal subsidiaries globally each managed independently, but they also have principal competitors such as the Seagram Company limited, Chanel SA, Gucci Group NV and Pinault Printemps Redoute SA (Funding Universe Para 45).
Company’s mission and vision
Due to the good management and setting of realistic strategies, the company is the leading company in luxury goods globally. This has led to the company controlling the industry and increasing its market share despite close competition from other companies in the industry. Mission and vision of a company plays an important role in the success of a company. These are usually formed during the marketing stage. The company’s mission and vision determines how an organization operates and is long-term goals and objectives. For instance, LVMH mission and vision has played a great role in the success of the company.
The company has a mission of representing refined qualities of the western region globally. This has enabled the company to stay synonymous with creativity and elegance. The vision and mission of the company has enabled it to diversify their products by blending innovation and tradition and kindling fantasy and dream. Furthermore, the company values innovation and creativity, they are acting as entrepreneurs, they yearn for product excellence, bolster their brand image with passionate determination and striving to emerge the best in all their undertakings.
LVMH is currently the leading company in luxury products but it has several operators who are also competing stiffly with it. In an industry, all companies believe to be the most efficient whether incurring losses or not. Investors form businesses with an aim of maximizing profit but are uncertain about the survival of the business due to several reasons and factors prevailing in the business environment.
Therefore, companies need to evaluate all business factors so as to remain relevant and continue operating in the market. Considering LVMH, the company was well versed with the market trends hence adequately responded to them and strategized on how to curb the various changes that could threaten their operation.
Corporate structure
LVMH is located within the eighth arrondissement in 30 Avenue Hoche in Paris, France. The company, which is a part of CAC 40 index, is among those listed on Euronext Paris exchange. By 2010, the group registered revenues worth 20.3 billion Euros with a net revenue of more than 3 billion Euros. With more than 77,000 employees, 30 percent of these employees operate within France. In this context, LVMH has ensured that the Louis Vuitton goods are put on the market only via Louis Vuitton boutiques found in up market localities within affluent cities, or in dispensations with auxiliary luxury products shops.
Strategic analysis of LVMH’s operations and businesses
Louis Vuitton is not solely one of the renowned fashion boutiques within the globe with an incredibly rich history, but is as well among the most well-known fashion houses within the continent. The company embraces superior craftsmanship given that it is among the few brands leading the avant-garde fashion with no compromise of customary craftsmanship. In this context, LVMH produces handcrafted products using exquisite materials and paying attention to excellent detail.
Equally, the company embraces the policies of instant disposal of any defective products and no promotions or discounts. Owing to its superior quality on its products as well as the high degree of inimitability and paucity on the goods, LVMH commands high prices on its products, thus placing the company on a highly profitable edge. LVMH maintains a strong image and brand identity within the global leading financial hubs, such as Hong Kong, China, and Japan. These localities are known to have the utmost concentration of high net worth persons and loyal consumers.
Nevertheless, like most luxury brands within the top luxury group, LVMH has a limitation of having limited customers, comprising principally of the super elite and the rich who aspire to be distinctive from the populace. Besides, LVMH has registered a rise in indebtedness. The increased debt obligations could deem it hard for the company to acquire more loans to fund its functions and liability requirements, thus limiting its ability to counter the altering business dynamics.
However, LVMH is endowed with immense opportunities given that the fashion industry is dynamic, changing swiftly over the seasons. The company possesses the ability to refurbish its image on a timely basis to meet the present-day styles, preferences, and tastes of its consumers. LVMH enjoys continual innovation and support to various environmental, societal, managerial, and humanitarian concerns.
Hence, the company can benefit from increased customer loyalty, which will provide them with a better competitive advantage over their rival brands. Besides, with the surfacing of novel wealthy markets such as South America, India, and China, the universal luxury products market is prospected to attain strong growth. Strong growth within these countries is likely to result in great absorption of high net worth individuals, thus enhancing LVMH’s market size and probable profits.
The chief threats facing LVMH include explosion of counterfeiting. Owing to its status symbol, LVMH is among the most counterfeited brands within the fashion industry. Hence, the company faces the threat of loss of revenue as well as plummeting brand reputation as the expertise employed in counterfeiting the products augments and the distinction between genuine LVMH and counterfeit goods decreases. The intense competition within the fashion industry remains a threat to LVMH.
The fashion industry is highly vibrant and competitive, and LVMH is not immune to this threat. In every region of its worldwide market, LVMH encounters significant competition from strong brands such as Hermes and Gucci. This high extent of competition poses a threat to the company’s market share.
Porter’s five forces analysis
The company effectively evaluated the market and its affairs via the porter’s five forces analysis. For instance, the industry was attracting several investors. This led to several companies changing or opting to enter the luxury products industry. This led to entry of close competitors; however, the company dealt with the challenge and maintained operation.
The company established customer loyalty leading to closure of new entrants or acquiring the new entrants who were closing operations. The industry also has high costs leading to only companies with strong economic base to enter the industry. Since the company speculated entry of new competitors, it merged with companies that had interest in operating in the industry hence limiting the number of competitors in the industry while expanding and gaining competitive advantage while increasing their market share.
The expansion strategy of the company by merging with any company that opted to operate in the industry led to the company merging with companies such as DFS Group Ltd and acquiring others for example Sephora among others. This led to the establishment of strong financial base by the company hence controlling the global market by manufacturing quality and diversified products. Though other companies entered the industry, they could not outdo the company since they had established brand loyalty due to the production of several brands but maintained quality.
Secondly, to curb threat of substitutes in the industry, the company produced several brands. The company established several principal subsidiaries each independently managed. This led to the company producing several brands in the industry competing among each other but all profits accruing to one principal company LVMH.
The different subsidiaries produced differentiated products hindering availability of substitute by competitors. Instead, the subsidiaries of the company produced substitutes to their products in the market hindering production of substitutes by the competitors or other companies in the industry. This gave the company competitive advantage over other firms in the market. New substitutes could not be produced in the market because the company had produced substitutes to the products it was selling in the marketing through its subsidiaries.
Bargaining power of customers. Due to the position and strategies of the company, they controlled the customers’ bargaining power. The company established several subsidiaries each managed independently with several stores globally. This led to the domination of the company’s products in the market because they produced several luxury products each targeting a different group of consumers with a substituting product also in the market.
The several stores availed controlled the degree of dependency of the consumers on the existing channels of distribution. The company control over the industry and customers’ preference is effective due to the analysis of consumers via the Recency Frequency Monetary Value (RFM) analysis. The company used the analysis to analyze behavior of consumers and for market segment definition leading to the company establishing several subsidiaries producing different luxury products each satisfying or addressing the changing needs of the consumers and the market. This led to the company producing variety of luxury products.
This analysis enabled the company to determine how often consumers purchase, the amount they spend, and how recently the consumers have purchased. This enabled the company to determine the most demanded products and the amount demanded for each product hence producing and pricing as per the consumers preference (Raymond 136).
Bargaining power of suppliers, the power of suppliers is controlled by availability of substitutes. Fewer the substitutes higher the prices or charges of suppliers and vice-versa. Since the company has several subsidiaries and each independently managed, this has led to the control of the bargaining power of suppliers.
This is because the company has several suppliers who they rely on for raw materials. The subsidiaries are globally located leading to the company accessing different suppliers from different regions hence controlling their bargaining power since the company can contract another supplier in case the other is not available or charges high prices.
The company also produces large quantities, therefore; they demand same quantities of raw materials from suppliers leading to competition among suppliers to supply the company which has greatly reduced the prices of suppliers since there are several suppliers in the market (Hitt and Hoskisson 115).
On the other hand, the company has successfully dealt with intensity of competition in the industry. Since the company has been incorporating innovation in its production process, it has led to the company setting up several subsidiaries in the same industry each producing different products and managed independently. Since the company is innovative, this has enabled it to gain and maintain competitive advantage in the industry.
The company also has a strong marketing strategy. This is because the company uses all forms of advertising, for instance, the company was the first in the industry to open up website selling hence boosting the sales of its products. The strategy of the company is also giving it competitive advantage and ability to control the industry and contain competition. The company produces several brands leading to barrier of entry in the industry and production of substitutes. Through acquisition of companies willing to operate in the industry, the company successful controlled competitive rivalry.
The company also applies balanced vertical integration hence controlling all components in the industry from raw materials to the final delivery of its products. The company has strong celebrity following hence frequently uses celebrities to advertise its products. For instance, the company has been using Jenifer Lopez and Angelina Jolie whom most people identify with hence boosting sales of the company.
Rappers such as Juicy J and Kanye West have also named the products of the company in their songs. Since most people listen to songs and identify with celebrities, by copying their styles the company has recorded an increase in profits due to associating its products with celebrities or using them to advertise (Porter 63).
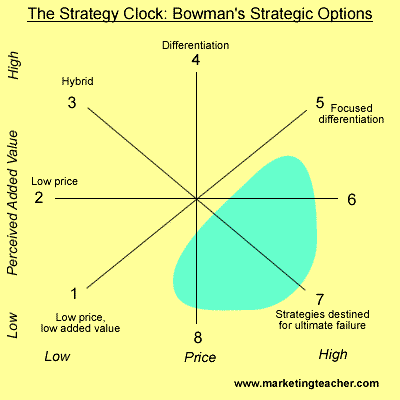
Using the strategic clock developed by Bowman, the situations and development of LVMH may be adequately analyzed. The clock provides eight options depending on the market situation. For instance low price/low added value, hybrid, low price, differentiation, increased price/standard, focused differentiation, and low values/increased price and standard price/low value. The options address differentiation or cost advantage in the market by a firm in the respective industry.
From the strategic clock considering LVMH, the company basically majored on differentiation mostly. The company established several subsidiaries producing different brands in the market. During the economic crisis in Asia in the late 1990s, the company had to apply option one by lowering prices and not adding value to its products in the divisions that were experiencing losses so as to control losses in the respective divisions.
However, considering the industry has close competitors such as the Gucci among others, option seven is not applicable since competitors are available and are working towards gaining competitive advantage in the industry hence produce high quality goods at high prices (Khosrow-Pour 361).
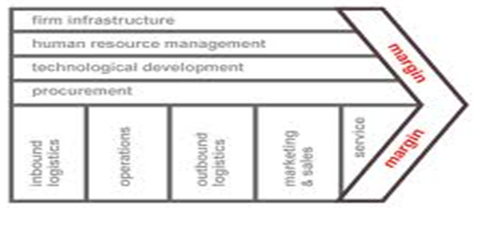
The company LVMH has gained competitive advantage in the luxury goods industry. To effectively understand the advantages of the company and how it gained the competitive advantages, the generic value chain developed by porter may adequately analyze the strategies of the company. The chain is comprised of both support and primary activities.
The primary activities consists of sales and marketing, service, inbound logistics, outbound logistics and operations which are supported by company’s infrastructure, technological development, human resource management and procurement. The profit margin of an individual company depends on the effectiveness of perform these activities efficiently. Profit may arise if the customers are willing to pay more than the cost the company incurs in the production of the products or delivering a service.
From analysis of LVMH, the company has some core competencies from cost advantage and differentiation. The company establishes a cost advantage in the industry through many ways. The company had several stores in different locations globally. This enabled the company to avail its products at different stores in respective countries where they operated.
The company also had several principal subsidiaries each producing a different product and managed independently. The company also fully utilized its big size by going global in operation and locating several stores. The company had a strategy of expanding and becoming an international company hence it strategically entered markets through acquisition or mergers with companies that were attracted to the industry.
Though it had several principal subsidiaries managed independently, they were coordinated and effectively served the interest of the whole company hence working in line with the mission of the company. The company also incorporated a balanced vertical integration enabling it to control raw materials and final distribution of its products to stores. The company consistently reconfigures the value chain by adoption of new marketing methods, introducing new distribution channels, changing their production process by adopting new technologies that improve quality of production.
The company has also gained differentiation advantage over other relevant companies in the industry. For instance, the company has established several principal subsidiaries producing different products hence satisfying the changing needs of different consumers in the market. Though the subsidiaries are managed independently and produce different products, they are interrelated. The company also has its stores in several areas increasing supply and reach by consumers.
The company is also big hence providing better services to the consumers. The creativity of the company is also a major contributor to its differentiation advantage. LVMH is one of the companies globally that are adaptive to technological changes in the market. Technology generally changes operations of a company in all aspects. Due to technological changes by the company, it has changed several aspects of its operations, which have positively impacted the company.
For instance, technological change has led to the company adopting online marketing and developing a website. Production process of the company has also changed with introduction of new production methods and techniques. This has led to LVMH changing its quality and branding of products and communication with customers and employees.
The company is currently holding online conferences due to the introduction of second life technology as opposed to before when it used to hold face-to-face meetings. It has also established an online customer care service which operates on a 24/7 basis which has enhanced its service to the customers.
The company was formed in 1987 after merger between Louis Vuitton and Moet-Hennessy. Though the two companies came together, they were experienced with a series of challenges ranging from management to operations. The most remarkable is the period between 1997 and 1998 when the company incurred losses but later recovered.
These challenges positioned the company at a stronger position compared to other firms in the industry. The company also has a financial advantage over other firms in the industry. This is due to the several acquisitions and mergers that the company has been engaged in. the companies LVMH was acquiring, later turned into potential profit generating avenues which furthered their financial status in the industry, this is coupled with the returns levels of the company (Funding universe 2011).
Another competitive advantage that the company has over other companies in the industry is value creation. The company changes its production methods due to technological change leading to quality production. This is easily adopted by the company due to its financial status in the industry. Furthermore, the company has several principal subsidiaries producing different products in the market leading to the company hindering production of substitutes to its products by other competing companies in market.
Setting up of several stores in the market especially in areas where it operates has enabled the company to avail its products globally. This led to creation of brand loyalty since consumers can easily access their products from any region in the global market. The consumers have also relied on the company for luxury goods due to the production of diversified and different products. The company produces different kinds of luxury products ranging from wines and spirits, fashion and leather goods, selective retailing, watches and jewelry to perfume and cosmetics.
In the operation of a company, it has to consider both the internal and external factors. The internal factors may be regulated by the company whereas the external factors are normally regulated either by law or the respective industry where a company operates and others. The external factors, which affects operations of companies include; social, political, economical, legal, technological, and environmental factors. Each affects an organization in different ways and they may threaten existence of a company.
For instance, political factors have to some extent affected operations of LVMH in several ways, which has cost the company profits. In most countries, there are regulations, which control drinking of alcoholic products and importation of luxury products. Countries faced with economic crisis insists on limiting importation of luxury products which has led to the company decreasing their exports to such countries hence decreasing incomes in such areas.
In most countries, people below eighteen years of age are not permitted to take alcoholic drinks, which have led to decrease in the number of consumers. Some countries also impose high taxes on luxurious goods leading to rise in prices of the products hence decreasing demand.
Economically, the sale of the company has been affected due to factors such as inflation and undervaluation of some currencies leading to high prices of the products in such countries. Countries with slow or weak economies have also not opted for importation of luxurious products. Socially, low income dominated countries record low sales due to low demand for the products. This has limited exportation of the products of the company.
Changes in technology have also led to changes in demand patterns and preferences, which have to the company changing products value and operational methods. The company has also selectively exported some of their products depending on the environmental conditions. For example, the company exports heavy leather products in cold areas but not hot and desert areas due to low demands. Environmental conservation has also led to the company changing production methods to protect the environment.
To ensure ethical practices in the business world, industries and governments impose several laws. For instance, there are health and safety legislations, consumer laws, employment laws and competition laws. The competition laws have hindered LVMH from monopolizing the industry though they could considering the mergers and acquisition plans they had.
The company had an emergent strategy hence merged with several companies while acquiring others this increased the market share of the company and its financial base and strength. Due to the several subsidiaries, the company had both primary and secondary shareholders but the management had full control over the company. The shareholders were ranging from investors to the individual companies that it merged with or acquired.
Burberry, on the other hand, has adopted a different approach.
There is no secret that over the past few years, Burberry has been undergoing serious changes; it has re-constructed its famous logo (Burberry Logo), reconsidering the font under the picture; its staff members have been replaced by new professionals, and even the chair of the company’s CEO was finally taken by Angela Ahrendts.
However, by far the most challenging an tricky issue was re-shaping the company’s financial policies. By evaluating the company’s financial assets and specifying the differences between the firm and industry, one can possibly figure out if Blueberry still remains a competitive company and whether it can possibly achieve bigger success.
Financial Ratio Analysis
Liquidity
According to the existing evidence, Burberry’s liquidity rates have been raised to 1.41 (Current asset/current liabilities) (Burberry Current Ratio).
Capital structure and solvency
As the recent researches on the issue say, Burberry’s optimum capital structure can be described in the following way:
Reports say that Burberry’s solvency is currently at 28.0 (Current and archived solvency of Burberry (Suisse) SA), which meets the standard. However, it seems that Burberry could have upgraded its solvency rates by updating its financial policies.
Return on investment
Burberry’s current return on investment is 24.26%, which might be viewed as a letdown compared to the results achieved in 2013 (Burberry Group PLC). A minor nitpick, it still shows that Burberry’s financial policy has its obvious flaws.
Therefore, it can be concluded that Burbery is on the right track. Although there are some minor issues that still need to be tackled, the company has definitely set its priorities straight. However, Burberry seems to have issues with solvency. While the current ratio seems adequate, it still feels that Burberry is unwilling to take risks to achieve even more and increase its revenues.
Conclusion
Therefore, due to the realistic strategies by the company, it gained and maintained competitive advantage over other firms in the industry and emerged as the leading firm in luxury goods business.
Works Cited
Analysis of Burberry. n. d. Web.
Burberry Current Ratio. n. d. Web.
Burberry Group PLC. n. d. Web.
Burberry Logo. n.d. Web.
Current and archived solvency of Burberry (Suisse) SA). n. d. Web.
Funding Universe. “LVMH Moet Hennessy Louis Vuitton SA”. Fundinguniverse. 2011. Web.
Hitt, Maurice, and Robert Hoskisson. Strategic Management: Competitiveness Globalization and Concepts. Ireland: Cengage Learning, 2010. Print.
Khosrow-Pour, Mehdi. Issues and Trends of Information Technology Management in Contemporary Organizations. United States: Idea Group Publishing, 2002. Print.
Porter, Michael. Competitive Advantage: Creating and Sustaining Superior Performance. Unites States: Simon & Schuster, Inc, 1985. Print.
Raymond, Papp. Strategic Information Technology: Opportunities for Competitive Advantage. United States: Idea Group Publishing, 2001. Print.

