Introduction
The global soft drink industry has been dominated since the late 19th century by two companies, Coca-cola and PepsiCo. These two American companies share between themselves the majority of market share of the soft drink industry of almost all countries in the world. Though Coca-cola has dominated Pepsi globally in terms of revenues, market share and profitability (Brooker, 2006); Pepsi has posed a formidable challenge and has kept Coca-cola on toes through development of innovative products, creative advertising campaigns and through global expansion (D’Altorio, 2010).
In terms of market share, Pepsi has followed Coke closely for almost 108 years. According to the Beverage Digest report of 2009, Coke led the market with 42% market share, followed by Pepsi with 30.8% of US market share (Beveragedigest.com, 2010).
However a recent market survey released by the Beverage Digest indicates that this year, Pepsi slipped from its long term second spot to a third position and has been replaced by Diet Coke (Rosman, 2011). This is seen as a major victory to Coca cola in its century old war with Pepsi. PepsiCo urgently requires a critical analysis of its marketing strategy in order to identify what needs to be done for it to recapture its position and if possible challenge Coke for the number one position.
Company Profile
Pepsi is a carbonated soft drink that is produced and marketed by PepsiCo. It was first produced in 1895 and is the flagship brand of PepsiCo; it is a Fortune 500 company that is headquartered in Purchase, New York.
The Company employs over 285,000 employees all over the world and its annual revenues in 2009 exceeded the $60 Billion mark out of which $4Billion is from the sale of Pepsi brand alone (Pepsi.com, 2011).
The company’s CEO is Ms Indra Krishnamurthy Nooyi since 2006 who has focused on retaining the company’s leadership in convenient foods, snacks, and beverage industry since she took over (Pepsi.com, 2011). The company is at the forefront of manufacturing healthy snacks and beverages using environmental friendly and sustainable techniques and this is captured in the company’s philosophy; “Performance with Purpose” (Pepsi.com, 2011).
The Company’s Marketing Mix
The company’s marketing mix consists of 4 elements that we shall discuss using Kotler’s guide to evaluate it (Kotler, 1997).
Products
The company manufactures and markets a wide range of carbonated and non-carbonated beverages as well as salty, sweet and grain based snacks and foods (Pepsi.com, 2011). The other brands manufactured by the company include bottled waters such as Aquafina, Propel and Lifewater brands, carbonated soft drinks such as Mirinda, Seven-up, Diet Pepsi and energy drinks such as Amp, Amp Sugar Free and No Fear, ready to drink teas such as SoBe, Brisk, Tazo, Lipton amongst others (Pepsi.com, 2011).
The company also produces and markets in partnership with Starbucks a variety of pre-packed ready to drink coffees such as Starbucks Frappuchino and Doubleshots Coffees (Pepsi.com, 2011). Finally, Pepsico also manufactures an assortment of healthy snacks such as Frito Lays and Quakers Oats; some of the successful food and snack products include Lays, Ruffles, Dorritos, Tostitos, Cheetos, Fritos, Rold Gold, Sunchips amongst others (Pepsi.com, 2011).
Distribution
Pepsi products are widely available in many parts of the world mainly distributed through shops, restaurants, bars, schools and automated vending machines amongst others.
Promotion
PepsiCo has successfully used celebrity endorsement to promote its product. The company also employs viral marketing strategies which target the youth segment. It also extensively sponsors arts, sport and musical events which have served to increase its visibility (Till, Priluck and Stanley, 2008). Currently it is running a programme which involves giving part of its revenue to charity.
Price
Because of its successful product and promotional strategies, little mention is made on its price. The price of Pepsi closely matches that of Coca-Cola and Dr Pepper on segment to segment basis; this has been attributed to the oligopolistic nature of the market. Rival companies however maintain flexible pricing policies for example during the recession period, Pepsi created special products that would retail at lower prices
Situational Analysis – Product Level: Pepsi Cola
Situational analysis involves the evaluation of a company’s 5C’s which includes the company, the consumers, competitors, collaborators, and climate (Kotler and Armstrong, 2010).
Company Analysis
A review of the history of PepsiCo reveals a strong and resilient company that survived bankruptcy severally and emerged strong (Pepsi.com, 2011). This fighting spirit portrays a company that is able to bounce back from any setback successfully. The company has extensive product lines in foods, healthy snacks and beverages. The company brand which is widely recognized is associated with youthfulness, entertainment and fun. The image of the company globally can be described to project hope and vitality and has overall been considered more innovative than Coca-cola especially because it releases more new products and uses creative and innovative marketing strategies.
In addition, PepsiCo uses advanced technology since its workers are highly educated and trained. The organization has a strong culture that is focused on ethics, sustainability, and social responsibility amongst others. The company’s vision, mission, objectives and goals are designed to ensure growth and profitability into the future.
Collaborators are partners and sponsors that a company works with to deliver value to customers (Armstrong and Kotler, 2010). In this case they include suppliers, physical distribution firms, marketing services agencies, financial intermediaries, co-producers and resellers. PepsiCo’s partners are able, reliable and committed to the organization’s long term growth plans
Customers’ evaluation refers to the market size and future prospects, the attractiveness and profitability of the consumer segments that the company operates in. and the behavior of consumers (Armstrong and Kotler, 2010).
Soft drinks are virtually ritual purchases since most consumers will buy soft drinks on a daily basis unless there are health issues to prevent someone from doing so.
Coca Cola and Dr. Schweppes are the most important competitors for Pepsi. Coke is the most competitive has more resources and experience to produce new and market innovative products such as Diet Coke besides being the owner of the world’s most popular soft drink; the coca-cola.
The climate consists of the wide environmental factors that define the environment the company operates in and includes political, economical, social, technological, environmental and legal factors (Armstrong and Kotler, 2010). The global economic environmental is improving thus increasing the purchasing power of consumers. Politically, PepsiCo enjoys favorable relationships with governments and their agencies in most regions where it have branches. Technologically, Pepsi uses some of the most modern methods and techniques in processing, packaging, distribution and marketing which are both efficient and environmental friendly. Pepsi is accepted in many cultures because its non alcoholic in nature, but there are concerns about its effects on health.
SWOT Analysis
Strengths
The brand name and logo are well recognized in the market. The company brand atmosphere is associated with youth, fun and entertainment and is a mature brand which enjoys fierce customer loyalty. The company has a wide range of products to meet diverse market needs and unlike its rivals it has healthier products on its portfolio. Generally business is lucrative as the cost of inputs is low and returns are high.
The Company has over 60 years now achieved a steady annual growth in revenues and profits; in 2010 for instance, revenues grew by 34% compared to the previous period (Pepsi.com, 2011). Pepsi is respected for its strong ethical values because it has self regulation principles and takes highest responsibility of the welfare of its staff, environment, and the society as a whole. The company has a strong sophisticated and highly developed global supply chain and has a higher inventory turnover rate which shows its warehousing costs are low.
Weaknesses
The soft drinks industry is saturated; the company has a long portfolio of products that can be confusing to customers. In addition it has global presence that is limited since it does not operate in all markets of the world.
Opportunities
Soft drinks is described as ritual purchases in America, thus the company is assured of steady demand. Besides this, there exist expansion opportunities in the international markets which include China, and other fast growing Asian economies. The company can also expand through mergers and acquisitions strategies that currently exist in the industry. Due to high costs of operations, barriers to entry are high thus limiting new entrants into the industry.
Threats
The most critical threat to the company is the concern by people about health impact of consuming sugary carbonated drinks (Rosman, 2011). Overall sales in the industry continue to slide as consumers switch to healthier drinks such as fruit juices, teas and coffees (D’Altorio, 2010).
This could explain Diet Pepsi’s increasing popularity. The rivalry between Pepsi and its competitors Coke and Dr Pepper remains intense and this risks overexposure of the brand which threatens its image of exclusivity. The global financial crisis affected its core customers’ base in Europe and North America reducing its profitability during that period. The Company’s plan of extensive diversification into foodstuff and snacks is affecting its brand image negatively.
There is also risk of rise in global input prices such as energy, sugar, and metal used for making cans amongst others. In addition, the company claims of ethics and its philosophy ‘Performance with Purpose’ were severely challenged when traces of pesticide were found in its products in India (Pepsi.com, 2011).. Finally, there are legal limitations placed by foreign governments in countries that PepsiCo seeks to operate.
Summary of the SWOT
A review of the SWOT generally indicates that the firm’s strengths exceed its weaknesses. This shows that the company’s position in the industry is strong; however the threats the company faces are numerous and critical in nature. The company therefore needs to urgently review its strategy with a view of mitigating the threats it faces and its effects. The company also needs to use its strengths to exploit the opportunities present in overseas markets; a shift into healthy drinks and products has been identified as a key success factor both in the long run and in the short run. The company has a strong portfolio of healthy products and snacks such as diet Pepsi, fresh juices, teas, coffees, amongst others and the marketing budget for these products should be augmented.
Critical Evaluation of Marketing Strategies
The evaluation of the strategies used by any company involves the assessment of the industries key success values, the company’s source of competitive advantage, the attractiveness of the industry and the firms corporate, business and marketing strategies (Grant, 2008).
Identification of Key Success Factors in the soft drink Industry
A strong, positive brand image and continuous innovation has been identified as one of the key success factors in the industry (Murphy, 1990). Companies must regularly develop new products, new efficient business processes as well as marketing strategies because the industry is highly dynamic and the competition and rivalry is intense. The concern about the impact on health is also a critical factor that must be addressed.
Various publics and interest groups have sustained a campaign to label soft drinks as health hazards. Because of this the general sales in the industry has been declining (D’altorio, 2010). Industry members are responding to this challenge by developing new products that contain less sugar, caffeine or non carbonated drinks. It is because of this reason that Diet Coke has gradually increased its sales over time and it recently leapfrogged Pepsi to occupy the second position after Coke.
Source of Competitive advantage
According to Michael Porter, competitive advantage arises out of the value a Company is able to create for its consumers at for a price that is higher than the cost of creating it (Porter, 1985). “Value is what buyers are willing to pay, and superior value stems from offering lower prices than competitors for equivalent benefits or providing unique benefits that more than offset a higher price” (Porter, 1985). Porter identified two basic types of competitive advantage, cost leadership and differentiation (1985).
As a challenger to a much stronger market leader, Pepsi has used differentiation to its advantage. It has established a strong brand identity using clear advertising messages and a unique communication strategy using celebrities to build the brand image. Since the ‘Pepsi Challenge’ of the 1960’s the brand fostered an image of a unique product that is much sweeter, better than its ubiquitous and much stronger competitor Coca Cola. This image is seen in its logo, branding, packaging, distribution and advertising. Its identification with successful sports, acting and musical celebrities links the product to success, youthfulness and fun; this strong fun-full image has endeared it to the youth market.
The company has continuously invested in new products development and that has resulted in wide range of successful and unique products. There is minimal mention of price which indicates that the company competes on the basis of product leadership, operational excellence and customers’ intimacy as opposed to cost. Michael Porter also identified the determinant of a competitive position of a firm in an industry as the interaction between its generic strategy and its competitive scope (Porter 1985).
Competitive scope is the choice to target broad market segment or to narrow on specific or limited segment. Pepsi has defined its market clearly but also broadly. Pepsi is designed to be accepted by the mass market. Its variant brands such as diet Pepsi, Pepsi Max and other brands are targeted to the special groups in the market. This is how the company has maintained its place in the soft drinks industry.
Pepsi strategy is differentiation using a broad market target scope.
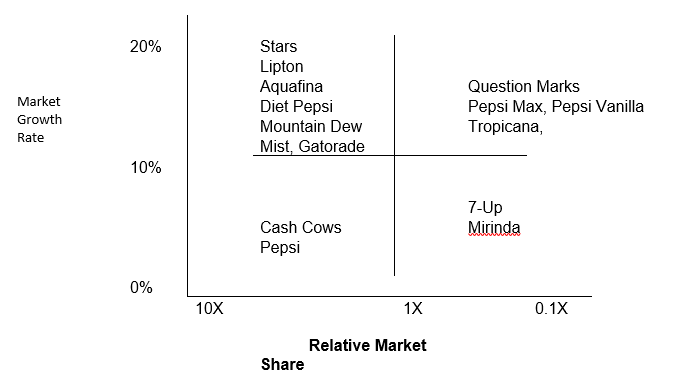
Fig 2. BCG Market Share Growth Matrix for Pepsi (cited from Bcg.com, 2011).
The BCG Matrix serves as a useful tool to guide investment in products in a portfolio. The principle of the BCG Matrix is euphemized as “Invest in the stars, get rid of the dogs and maximize in the cash cows” (Bcg.com, 2011). The matrix shows the strategic importance of a product in a company through the analysis of two important factors that is market growth rate and market share (Bcg.com, 2011).
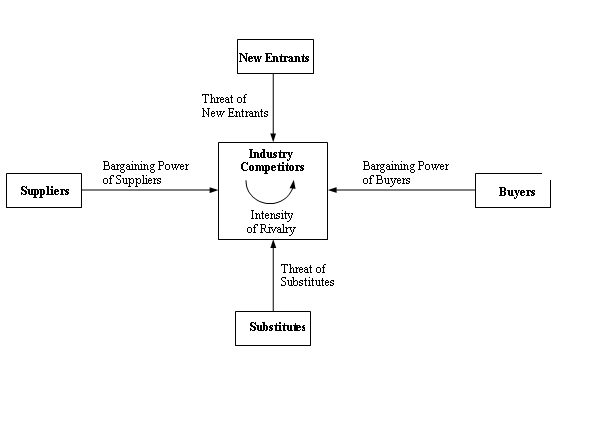
Porter’s Five Forces Model of Industry Attractiveness
According to Michael Porter, the structure of the industry and the product positioning within the industry forms the basis of any strategy (Porter, 1980). The structure of the industry is defined by the interaction of five dynamic forces. These forces determine the nature and intensity of competition within an industry, its profitability and reflect the attractiveness or lack of it within an industry (Porter, 1980). Therefore it is prudent for these forces to be considered carefully when a company is designing a strategy to compete effectively in that industry.
Using Porter’s model in the Soft Drinks Industry
Level of Rivalry
Rivalry in the soft drink industry is intense, the general slow decrease of the total market size caused by health concerns and economic stagnation in the western hemisphere have increased the level of competition as companies fight for the shrinking market share. Strong brand identities and brand related activities such as advertisements, sponsorships, endorsements, global presence also increase the level of competition. For instance, Coke one of the brands in the industry is the most recognized and most valuable brand in the world with a brand value of $70.45 Billion in 2010 (Interbrand.com, 2011).
Most of the products are intrinsically not very different as they are served chilled or warm and in servings that are closely related in volumes. Prices also closely match and are often not a source of competitive advantage. Fixed costs of production and marketing are prohibitive thus limiting speculative companies from entering the industry and rivalry is not limited to local market, but extends to the whole world.
The bargaining Power of Buyers
The ability of consumers to organize themselves and agitate for better terms is important to any Company. This is because it is likely to determine what they want, when and at what price. The bargaining power of soft drink buyers is also limited since most consumers see themselves as individual rather than group users of the products. The volumes they buy are low and the price difference insignificant, thus these purchases are convenient low involvement activities. Whereas there are numerous substitute products in the industry, branding and promotion activities have made customers to identify with particular brand as regular and loyal customers. Finally, consumers are more informed than previously and are demanding healthier products and ethical business practices.
Bargaining Power of Suppliers
The ability of suppliers to determine availability of inputs, quality, volumes and costs is significant because it can impact on the effectiveness of the organization’s strategy. In the soft drink industry, the bargaining power of suppliers exists although it is not critical. Due to global commodities price increases, the cost of most inputs has increased. This exerts pressure on the company to increase its prices which is unlikely due to intense competition from its rivals Coke and Schweppes.
There is also fear of disruption of supply of raw materials and long term availability of clean water is a sustainability issue in the company. This is why the company advocates for careful use of resources.
Threat of Substitute Products
The industry faces threats from substitute products in the beverage industry. This includes bottled water, fresh juices, healthy teas, and diary based beverages. The advantage of these beverages is their perceived health benefit over sugar based carbonated drinks. Some entrants at the lower end of the market are cheaper than Pepsi. Again due to no costs involved in switching brands, the substitution process is easy.
Barriers of Entry
This refers to the ease of new companies entering into the industry and exploiting its opportunities as well as increasing pressure on the existing operators. The barriers of entry in the soft drink industry are significant. The brand name is one of the key factors in effective competition and it is not easy to build one over a short period of time. High initial capital outlay is required to establish production, distribution and sourcing systems.
Recommended Growth Opportunities for Pepsi
Fig 4: Igor Ansoff Growth Strategies for Pepsi (Adapted from Igor Ansoff, 2007).
Conclusion
The global soft drink industry has been dominated by two major players; Coca-cola and PepsiCo. These two companies have combined continuous product innovation and innovative marketing strategies to achieve phenomenal revenue and profit growth year on year for over a century. However, recent concerns over the health risks posed by sugar based carbonated drinks as well as global recession has seen the growth in the industry gradually slide to a halt (D’Altorio, 2010). Consumers who are now more informed and discerning are demanding for healthier products.
It is because of this that Pepsi has lost its long held position in the US soft drink market to newcomer Diet Coke. This is a huge marketing coup for its arch rival Coke as well as a strong indicator of future long term trend of sugar based soft drinks. This paper aimed at analyzing Pepsi’s marketing strategy and to identify how it can be used to re create value through which it can reverse recent events. The paper identified continuous innovation and strong brand image as key success factors for Pepsi. Pepsi is a strong innovator and it has a well respected and favorable image; unlike Coke, it has a wide range of healthy products other than soft drinks. The company should therefore invest more in marketing its healthy drinks Diet Pepsi and Pepsi Max to healthy conscious consumers amongst others.
References
Bcg. 2011. BCG Matrix. Web.
Beverage-digest. 2010. 2009 Top Ten Data. Web.
Brooker, K. 2006. How Pepsi Outgunned Coke. Web.
D’Altorio, T. 2010. Coke vs. Pepsi… Are the Cola Wars Finally Over? Web.
Grant, R.M. 2008. Contemporary Strategy Analysis. Malden, MA: Blackwell.
Igor. Ansoff, H. 2007. Corporate Strategy. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Interbrand. 2011. Best Global Brands 2010. Web.
Kotler, Philip. 1997. Marketing Management: Analysis, Planning, Implementation, and Control. New York: Prentice Hall.
Kotler, P. & Armstrong, G. 2010. Principles of Marketing. New Jersey: Pearson Education.
Murphy, J. 1990. Assessing The Value of the Brand: Long Range Planning. Journal of Consumer Psychology, 23(3): 23-29.
Pepsi. 2011. 2010 Annual Reports. Web.
Porter, Michael. 1985. Competitive Advantage. NY: The Free Press.
Porter, M.E. 1980. Competitive Strategy. New York: Free Press.
Rosman, Katherine. 2011. Why Diet Coke Beat Out Pepsi. Web.
Till, B.D., Priluck, R. & Stanley, S. M. 2008. Classical Conditioning and Celebrity Endorsers, Journal of Psychology and Marketing, 25(2) 179-196.
